science-chapter 19
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:41 PM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
what is all matter made out of?
atoms
2
New cards
what are three parts of and atom?
protons, electrons, and neutrons
3
New cards
what type of charge does a proton have?
a positive electric charge
4
New cards
what type of charge do neutrons have?
they do not have an electric charge
5
New cards
what type of charge do electrons have?
a negative electric charge
6
New cards
how much charge does an electrical charge neutral atom have?
equal numbers of positive and negative charge
7
New cards
do opposite charges attract?
yes.
8
New cards
what is Columbs law?
1. he more electric charge is present on two charged objects, the stronger the electric force between those charged objects will be. They are __directly related__.
2. The farther apart two electric charges are, the *weaker* the electric force between them will be. They are __inversely related__.
9
New cards
what is a good conductor of electricity?
a material that electrons can easily move across
10
New cards
what is not a good conductor of electricity?
a material that electrons can not easily move across
11
New cards
what is a good insulator of electricity?
a material that electrons can not easily move across
12
New cards
what happens when an object gives away electrons?
it becomes __positively charged__.
13
New cards
what happens when an object receives electrons?
it becomes negatively charged.
14
New cards
what are 3 ways to electrically charge an object?
**conduction**, **friction**, and **induction.**
15
New cards
what is conduction?
the transfer of electric charge by simple touch. Conduction happens when electric charges flow from one conductor to another (usually between metals).
16
New cards
what is friction?
charge by rubbing, one object scrapes electrons off of another object, and both become charged in the process
17
New cards
what is polarization?
when electrons concentrate, or scramble at one end of an object,
18
New cards
what is induction?
the transfer of electric charge by scrambling electrons in conducting materials. a charged object *scrambles* the electrons in two conducting materials it is brought near by repelling the electrons in the conductors so that more electrons are on the far object (see page 351 for diagram). when the conductors are separated, the charges are trapped and can’t return to where they were before
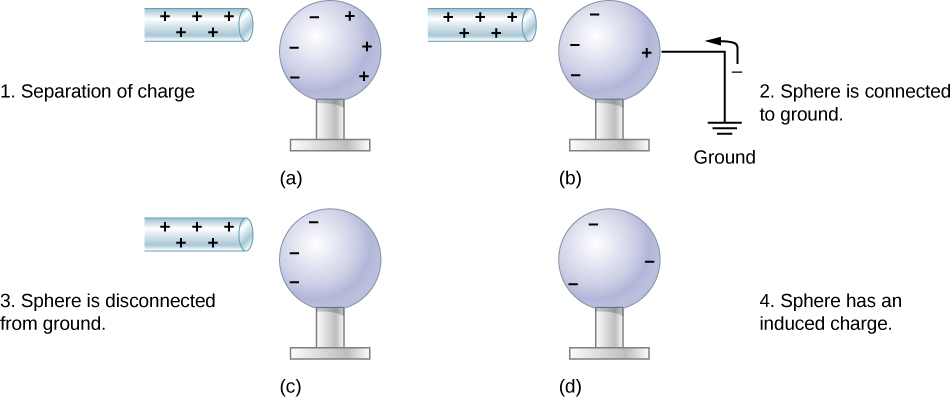
19
New cards
what is electric discharge?
when unbalanced charges become balanced
20
New cards
what is lightning?
lightning is a sudden electrostatic discharge that occurs during a thunderstorm. it is caused by the buildup and discharge of electrical energy between positively and negatively charged regions within a cloud or between a cloud and the ground.
21
New cards
what is an electric current?
the movement of electrically charged particles (electrons)
22
New cards
what is current?
the measure of how much charge is flowing through a circuit at any given moment measured in Amperes
23
New cards
what is resistance?
a measure of how difficult it is for electrons to flow through a material, measured in Ohms
24
New cards
what is voltage?
the amount of energy the source uses to move electrons through an electric circuit.
25
New cards
does a good conductor have a ___________ resistance?
__low__ resistance.
26
New cards
does a bad conductor have a ________ resistance?
__high__ resistance
27
New cards
what does **Ohms Law** tell us?
\-the relationship among current, voltage and resistance in a circuit.
\-the greater the voltage in the circuit, the greater the current will be. Voltage and Current are directly proportional.
\-the greater the resistance in the circuit, the **less** the current will be. Resistance and Current are inversely proportional.
\-the greater the voltage in the circuit, the greater the current will be. Voltage and Current are directly proportional.
\-the greater the resistance in the circuit, the **less** the current will be. Resistance and Current are inversely proportional.
28
New cards
what are the three basic parts of an electric circuit?
1. source of electric energy
2. electrical devices that transform electrical energy
3. conductors such as wires that connect everything
29
New cards
what is a **series circuit?**
there is only **one** path for the current to flow.
30
New cards
what is a **parallel circuit?**
there are **many** paths for the current to flow
31
New cards
what is a **closed circuit**?
when a **complete path** exists between a battery’s negative and positive terminals,
32
New cards
what is a **short circuit**?
any complete circuit with no resistance (i.e. it’s connected to a battery, but not to any light sources or appliances)
33
New cards
what is electric shock?
when electric current flows through your body.