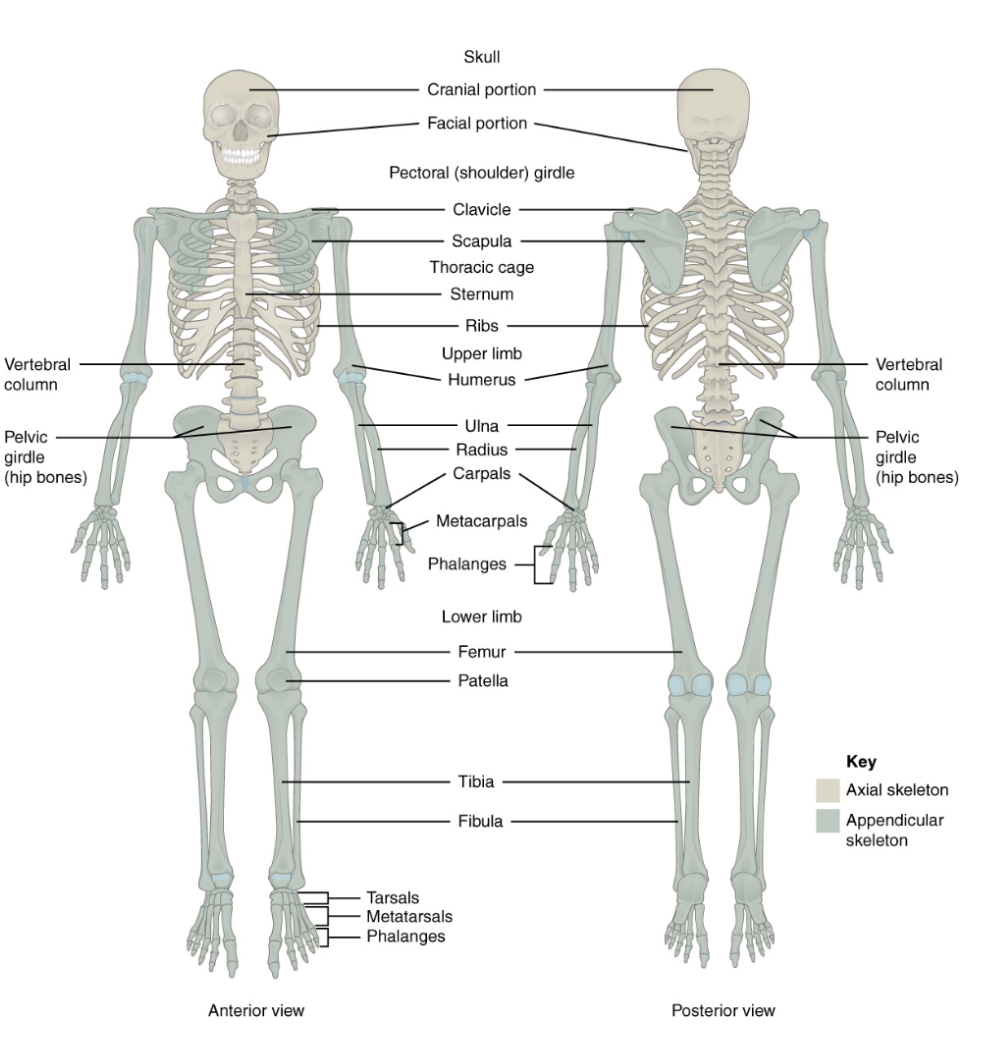
Axial Skeleton
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Axial Skeleton
80 Bones
Provides framework that supports & protects the organs
Skull
Vertebral column
Thoracic cage
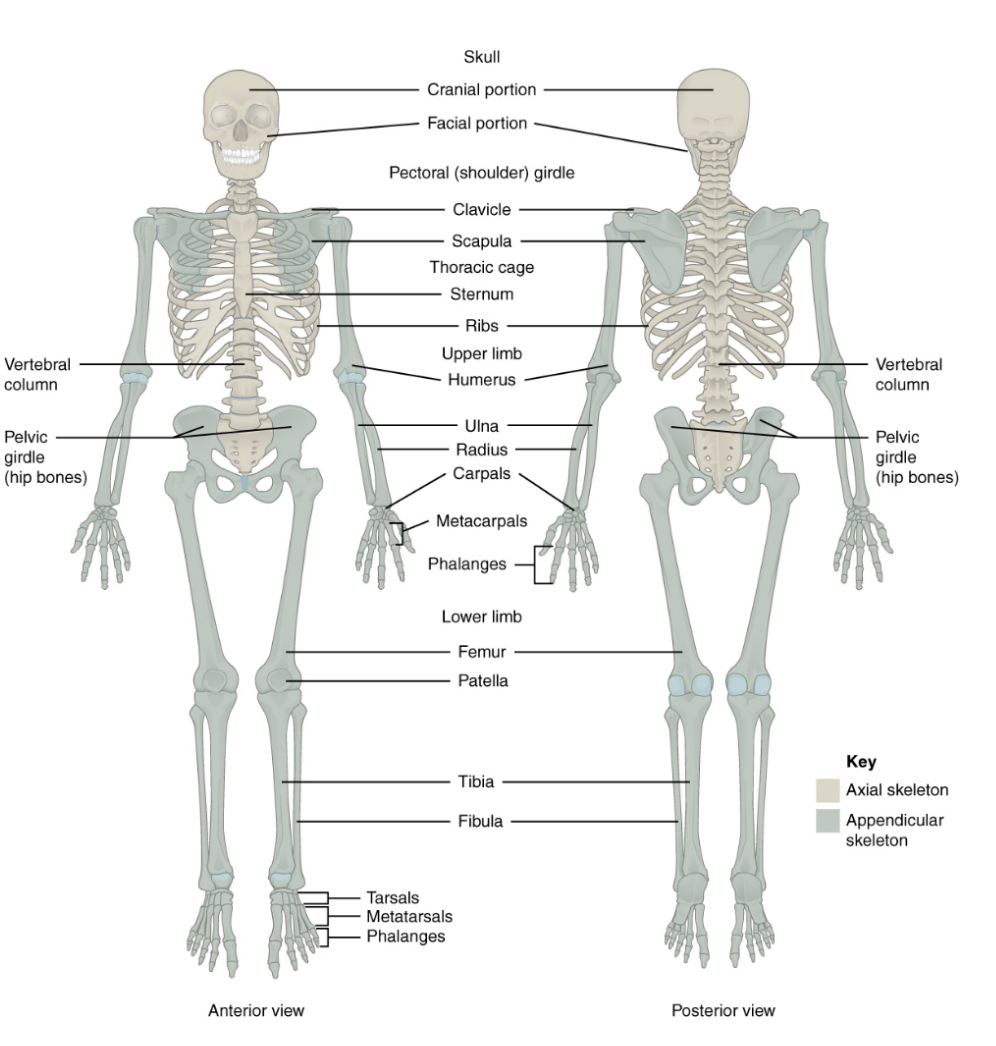
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper & lower extremities, associated pectoral & pelvic girdles
126 bones
Projection
The point where muscles, tendons & ligaments attach
Depression/Groove/Opening
Blood vessels & nerves travel
Foramen
Meatus
Sinus
Fossa
Smooth Region
Place where bones articulate (meet and move together)
Foramen
A type of opening
Opening in bone through which nerves & vessels pass
Ex: vertebral ____

Meatus
A type of depression
passageway through a bone
Ex: external auditory ____

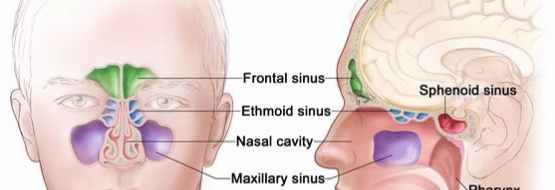
Sinus
A type of opening
Hollow space within a bone
Fossa
A type of depression
site of muscle attachment
Ex: supraspinous ____

Cranial Bones
8 bones
Protect brain & form cranial cavity
Frontal bone (1)
Parietal bones (2)
Temporal bones (2)
Occipital bone (1)
Sphenoid bone (1)
Ethmoid bone (1)
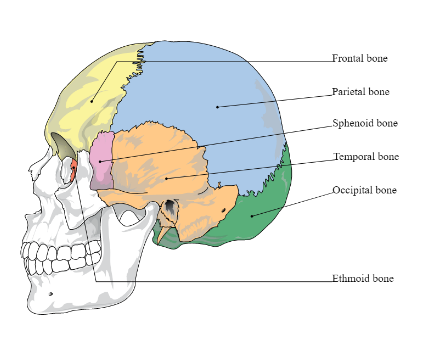
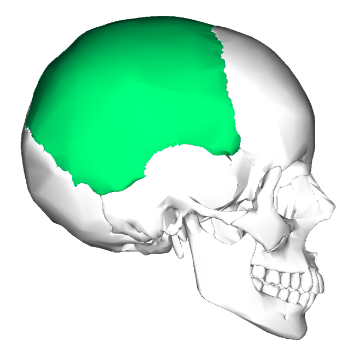
Parietal
Form sides & roof of cranial cavity
Temporal
Form inferiolateral portion of cranium
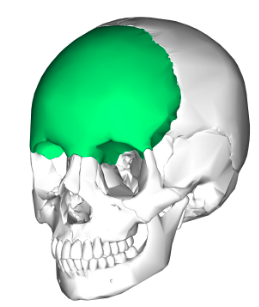
Frontal
2 separate bones at birth that fused soon after
Forms forehead & anterior part of cranial floor
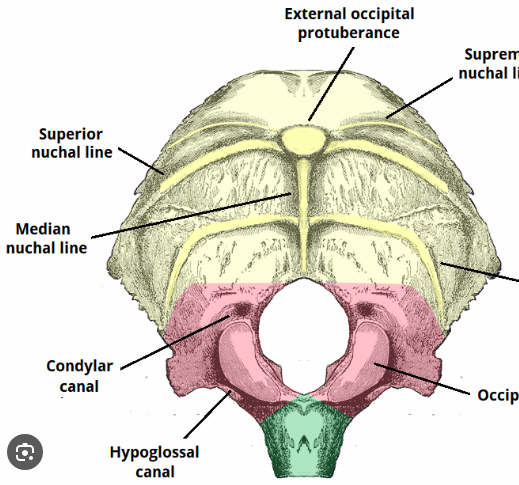
Occipital
Forms posterior & base of cranium
Contains foramen magnum where spinal cord merges with brainstem, external occipital protuberance
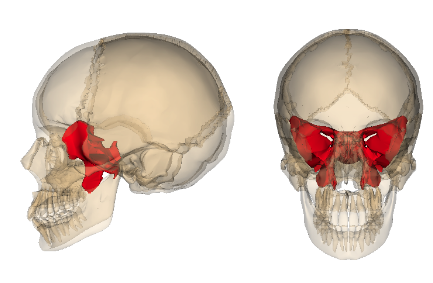
Sphenoid
Lies in middle part of base of skull
Articulates with all other cranial bones & holds them together
Lesser wing
Greater wing
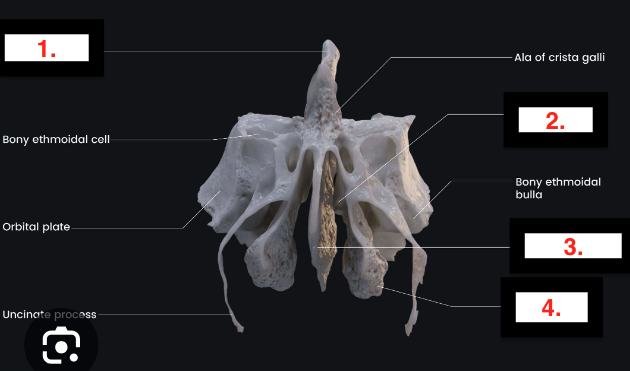
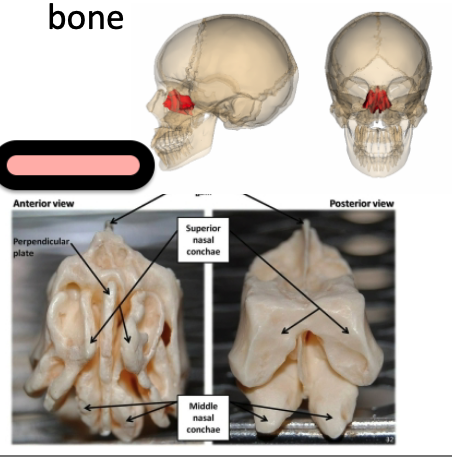
Ethmoid
Small bone sits anterior to sphenoid bone
Crystal galli
Superior nasal conchae
Perpendicular plate
Middle nasal concha
Facial Bones
14 bones
Forms framework of the face, and attachment points for facial muscles
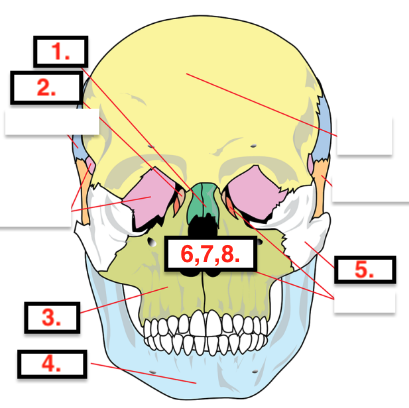
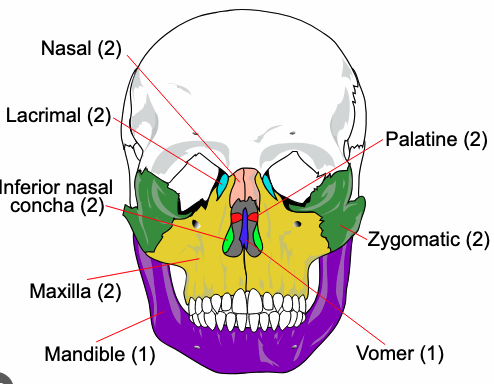
Nasal (2)
Lacrimal (2)
Maxilla (2)
Mandible (1)
Zygomatic (2)
Vomer (1)
Inferior nasal conchae(2)
Palatine (2)
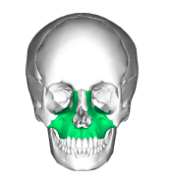
Maxilla
Upper jawbone
Articulate with every facial bone except the mandible
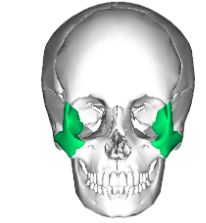
Zygomatic
Cheekbones
Lacrimal
Smallest bones of the face
Form medial wall of each orbit
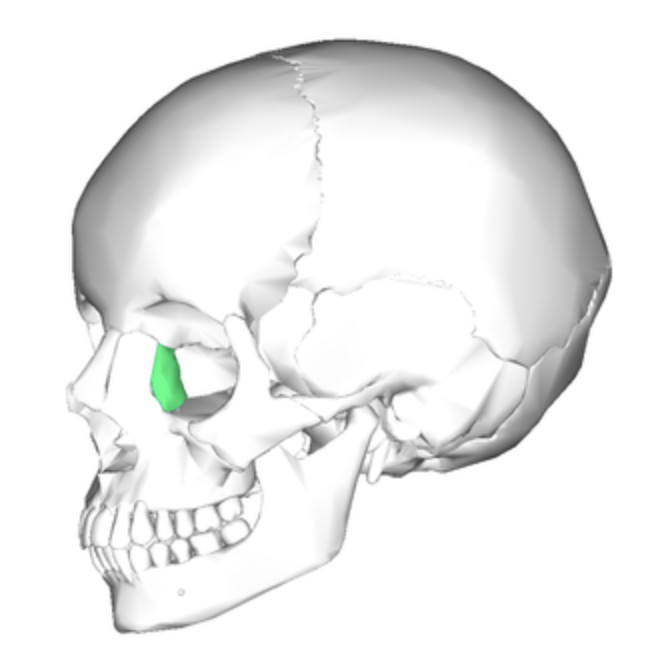
Nasal
Forms bridge of the nose
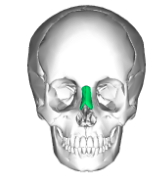
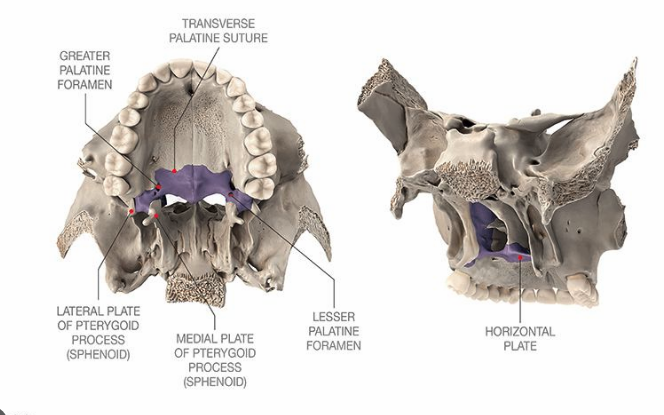
Palatine
L-shaped bones that form posterior aspect of hard palate
Horizontal plate
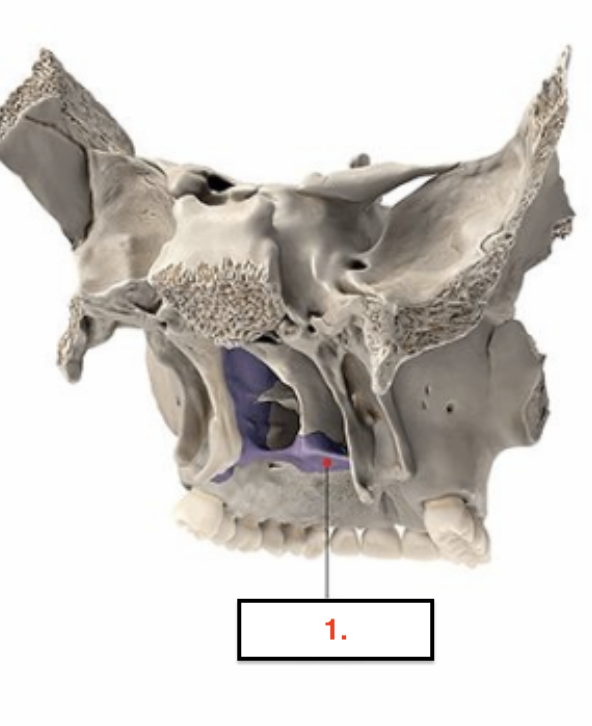
Inferior Nasal Conchae
Increase surface area of nasal cavity
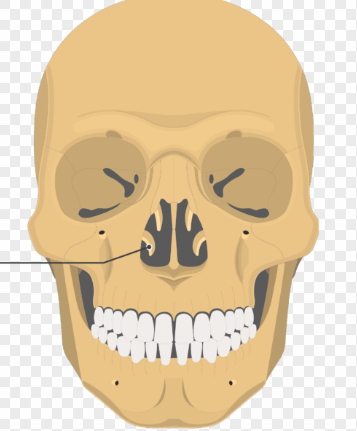
Vomer
Forms inferior portion of nasal septum
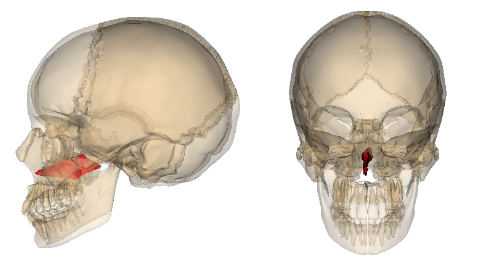
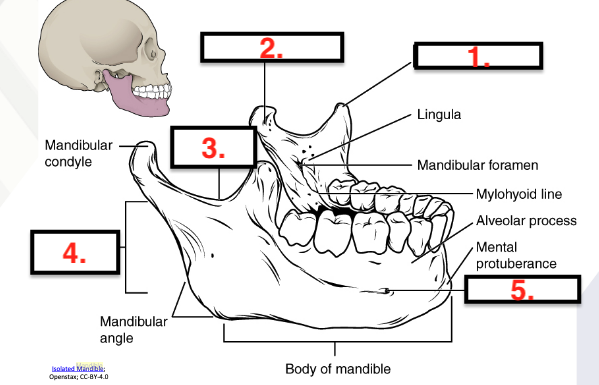
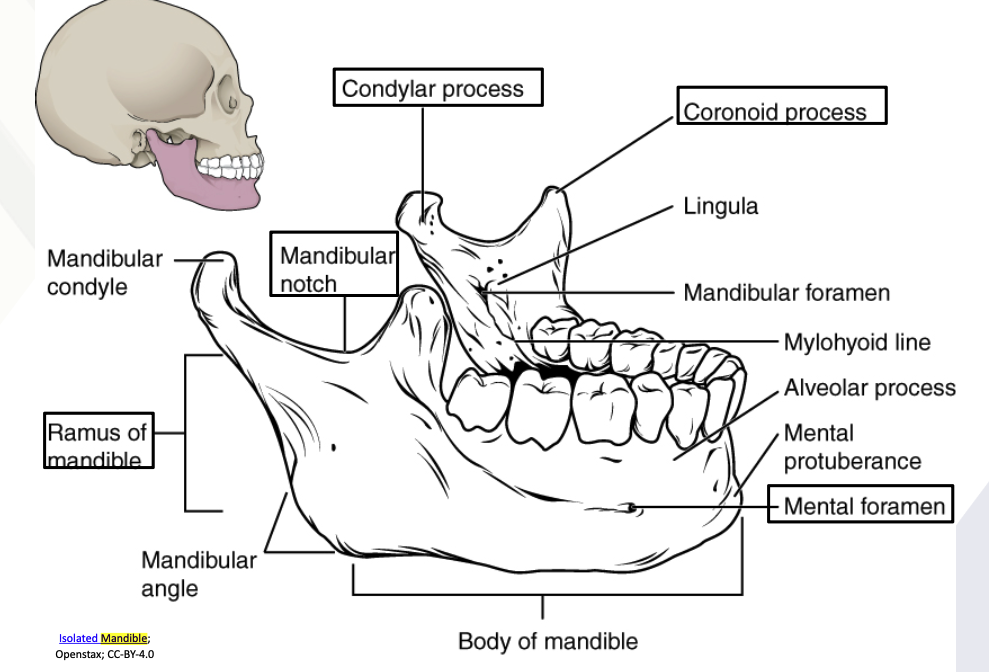
Mandible
Only movable bone of the skull
Lower jawbone, largest & strongest facial bone
Coronoid process
Condylar process
Mandibular notch
Ramus of mandible
Mental foramen
Sutures
Immovable joint where bones fused together
Sagittal
Coronal
Lambdoid
Squamous
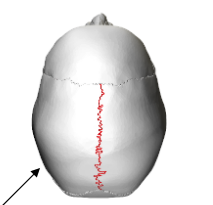
Sagittal Suture
Between 2 parietal bones
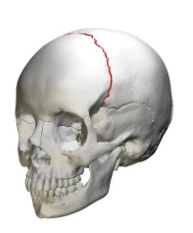
Coronal Suture
Unites frontal bone with both parietal bones
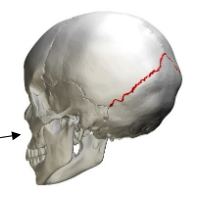
Lambdoid Suture
Unites 2 parietal bones with occipital bone
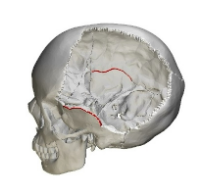
Squamous Suture
Unites parietal and temporal bones
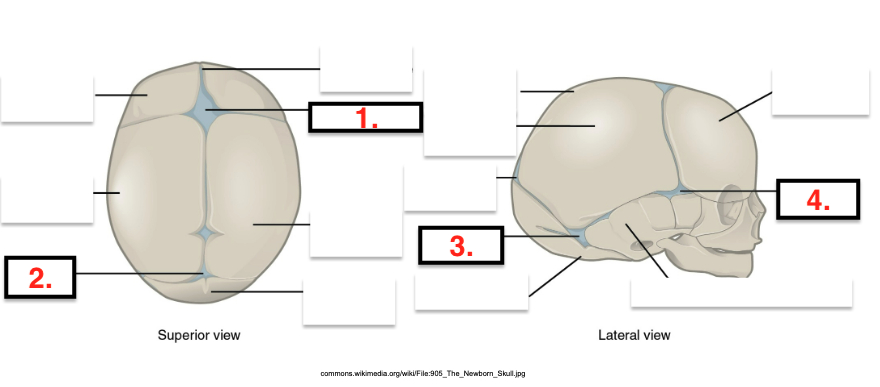
Fontanels of Fetal Skull
Enable bones to flex during birth and allow more rapidly growing brain to expand
May not fully closed until child is 18 months old
6 presents at birth
Anterior ___ (1)
Posterior ____ (1)
sphenoidal (anterolateral) ___ (2)
mastoid (posteriolateral) ___ (2)
Hyoid Bone
Does not articulate with any other bones, supports the tongue
Inferior to skull between mandible & pharynx
Condyle
A processes that form joints
A large round projection that forms joints
Head
A processes that form joints
Rounded projection found on the end of a bone, supported by a neck

Facet
A processes that form joints
A small, smooth, flat articular surface
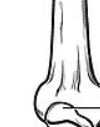
Tuberosity
A processes for connective tissue attachment
Large rounded projection usually with rough surface

Spinous Process
A processes for connective tissue attachment
Sharp, slender projection or bifid (split)
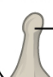
Trochanter
A processes for connective tissue attachment
Large, blunt projection found only on the femur
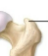
Crest
A processes for connective tissue attachment
A prominent border or ridge

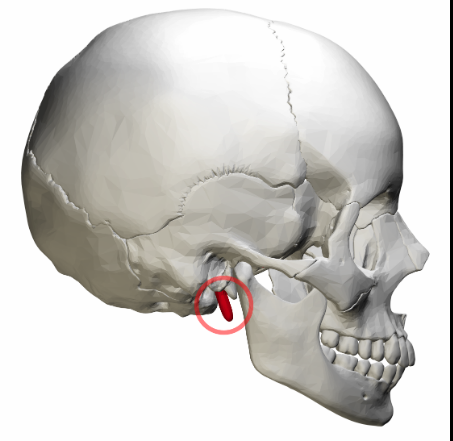
Styloid
A processes for connective tissue attachment
A pointy projection
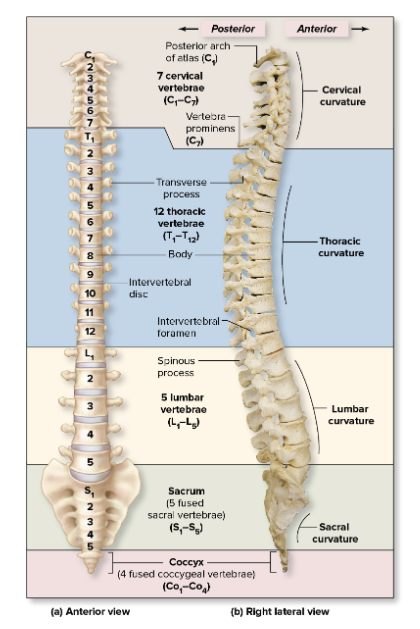
Vertebrae
Supports the head & body, protects the spinal cord.
33 bones or 26 fused
4 curvatures
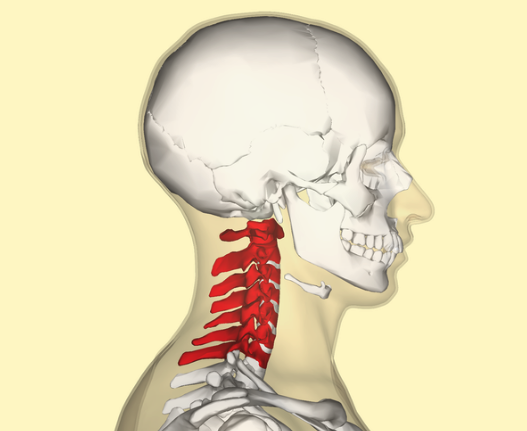
Cervical (7)
Thoracic (12) (Primary)
Lumbar (5)
Sacrum fused (5)
Coccyx fused (4) (Primary)
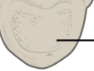
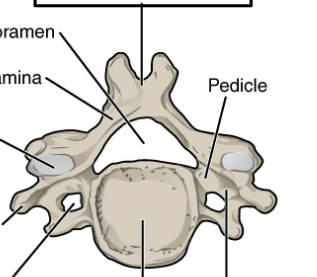
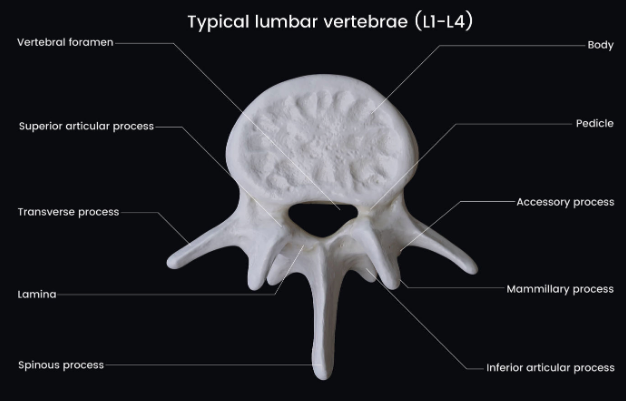
Body (Centrum)
Thick weight-bearing portion
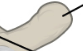
Transverse Process
Two lateral projections
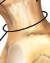
Vertebral Arch
Comprises of lamina & pedicle
Pedicle
Connect the vertebral body to the lamina
Lamina
Connect the spinous process to the pedicle
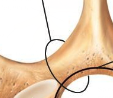
Vertebral Foramen
Opening in vertebral arch
Spinal cord passes through
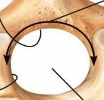
Cervical Vertebrae
7 bones
C1 is the Atlas
C2 is the Axis
C3-C6 are typical cervical vertebrae
C7 is vertebra prominens
Typical Cervical Vertebrae
C3 to C6
Bifid spinous process
Transverse foremen
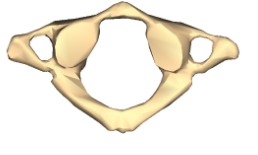
Atlas
C1
No spinous process
Articulates with occipital bone
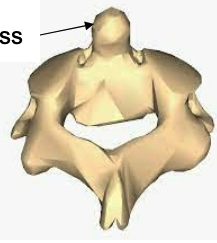
Axis
C2
contains odontoid process (dens), has transverse foramen
Vertebra Prominens
C7
Long spinous process compared to typical cervical vertebrae and not bifid (splits into two)
Transverse Foramen
A hole in each transverse process

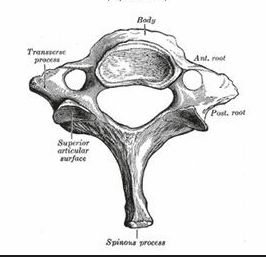
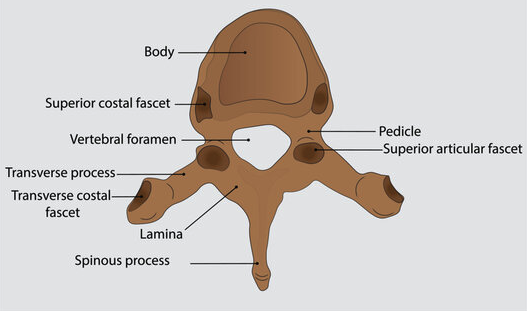
Thoracic Vertebrae
12 vertebrae
Round vertebral foramen, no transverse foramen
Support rib cage, protect thoracic organs
Superior costal fascet
Superior articular fascet
Traverse costal fascet
Transverse process
Spinous process
Lamina
Pedicle
Vertebral foramen
Body
Lumbar Vertebrae
5 vertebrae
Triangle vertebral foramen, no transverse foramen
Inferior articular process (longer)
Superior articular process (shorter)
Transverse process
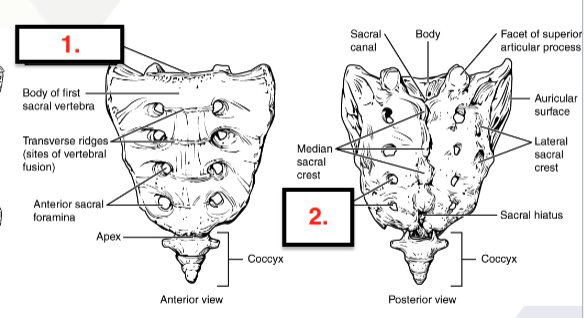
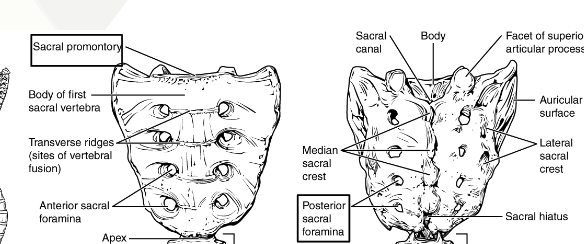
Sacrum
5 vertebrae fused into one for adults
Sacral promontory
Posterior/Anterior sacral foramina
Sacral canal
Median sacral crest
Lateral sacral crest
Auricular surface
Sacral hiatus
Body
Apex
Traverse ridges
Facet of superior articular process
Coccyx
4 vertebrae fused into one for adults
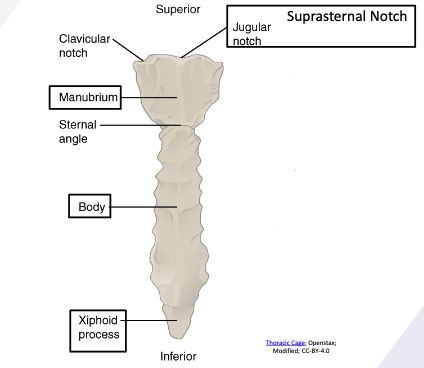
Sternum
Jugular notch
Clavicular notch
Manubrium
Sternal angle
Body
Xiphoid process
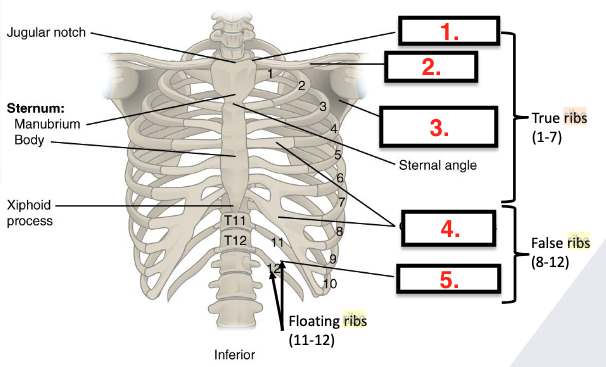
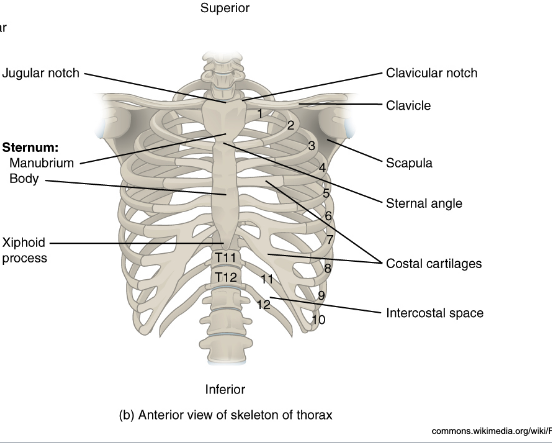
Ribs
12 vertebrae
True ribs (T1-T7)
False ribs (T8 -T12)
Floating ribs (T11-T12)
Clavicular notch
Clavicle
Scapula
Costal cartilages (connect sternum to the ribs)
Intercostal space (space between adjacent ribs)
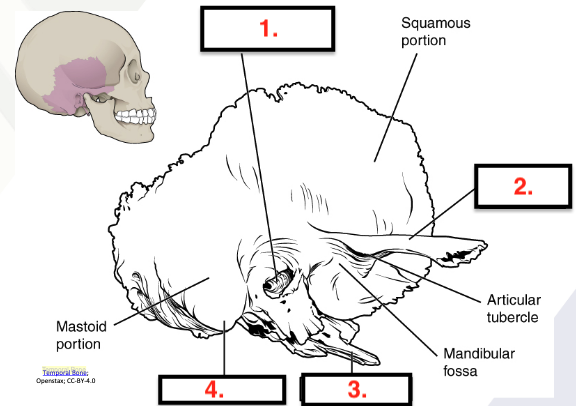
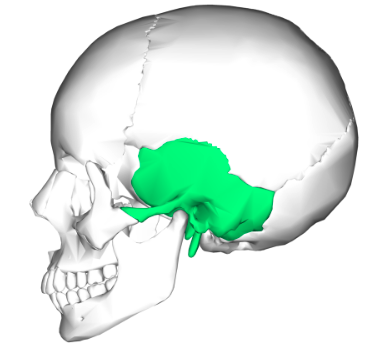
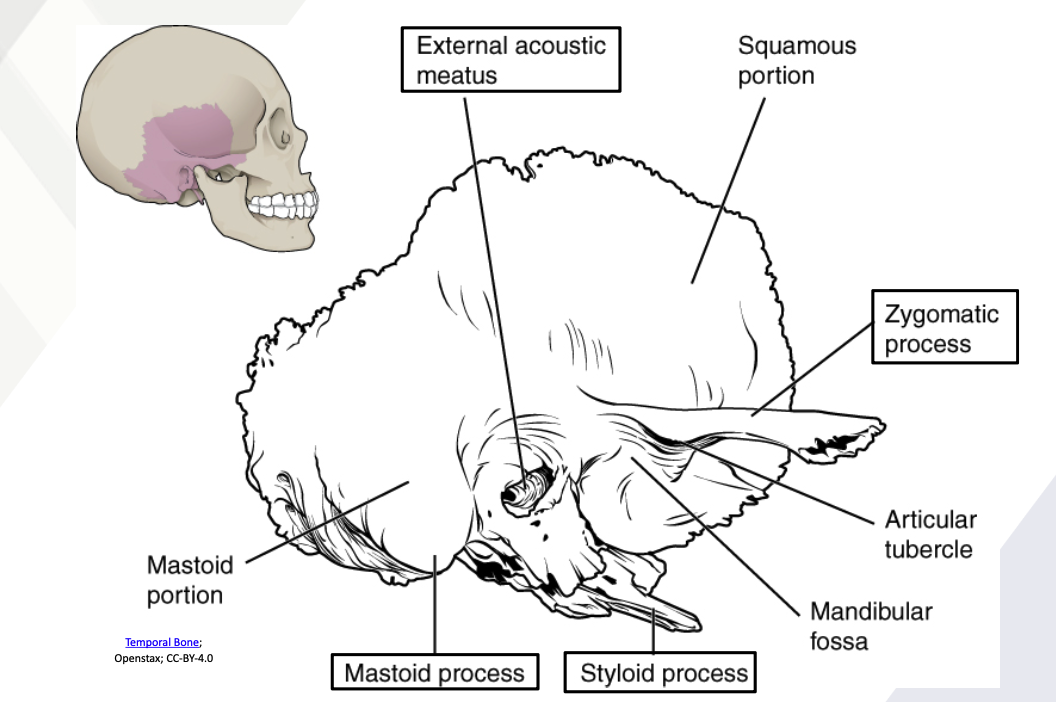
Temporal bone
External acoustic meatus
Zygomatic process
Styloid process
Mastoid process
Processes that Form Joints
Condyle
Head
Facet
Processes for Connective Tissue Attachment
Tuberosity
Spinous
Trochanter
Crest
Styloid
Function Cranial Bones
Enclose & protect the brain
Stabilize position of brain, blood & lymphatic vessels & nerves