PD E2- Newborn, Infant, Toddler
1/142
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
What is considered newborn / neonatal?
≤ 28 days
What is considered infancy / post neonatal?
29 days - 1 yr
What is considered a toddler?
1-3 yrs or 12-36 mos
What birthweight is considered extremely low?
< 1000 g (<2.2 lbs)
What birthweight is considered very low?
1000-1500 g (2.2-3.3 lbs)
What birthweight is considered low?
1500-2500 g (3.3-5.5 lbs)
What is considered a normal birthweight?
> 2500 g (> 5.5 lbs)
What gestational age (GA) is considered preterm?
< 37 wks (259 days)
What GA is considered term?
37-42 wks
What GA is considered post term?
> 42 wks
What are preterm newborns more prone to?
Resp distress, apnea, patent ductus arteriosus w/ left to right shunt, infx
What are post term infants more likely to experience?
Asphyxia, hypoglycemia, hypocalcemia
What is small for gestational age (SGA)?
< 10 %
What is appropriate for gestational age (AGA)?
10-90%
What is large for gestational age (LGA)?
> 90%
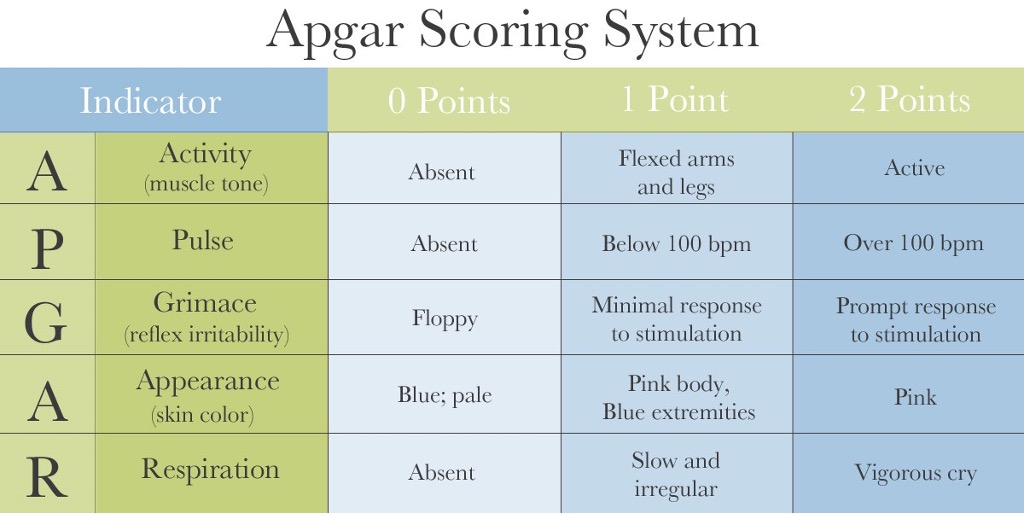
When is the APGAR score taken?
1 minute & 5 minutes after birth
What does 0-4 APGAR at 1 minute indicate?
Severe depression, require immediate resuscitation
What does APGAR score of 5-7 at 1 minute indicate?
some nervous system depression
What does an APGAR score of 8-10 at 1 minute indicate?
normal
What does an APGAR score of 0-7 at 5 minutes indicate?
High risk for subsequent CNS and other organ system dysfunction; repeat score every 5 minutes until reaches 7
What does an APGAR score of 8-10 at 5 minutes indicate?
Normal, proceed to PE
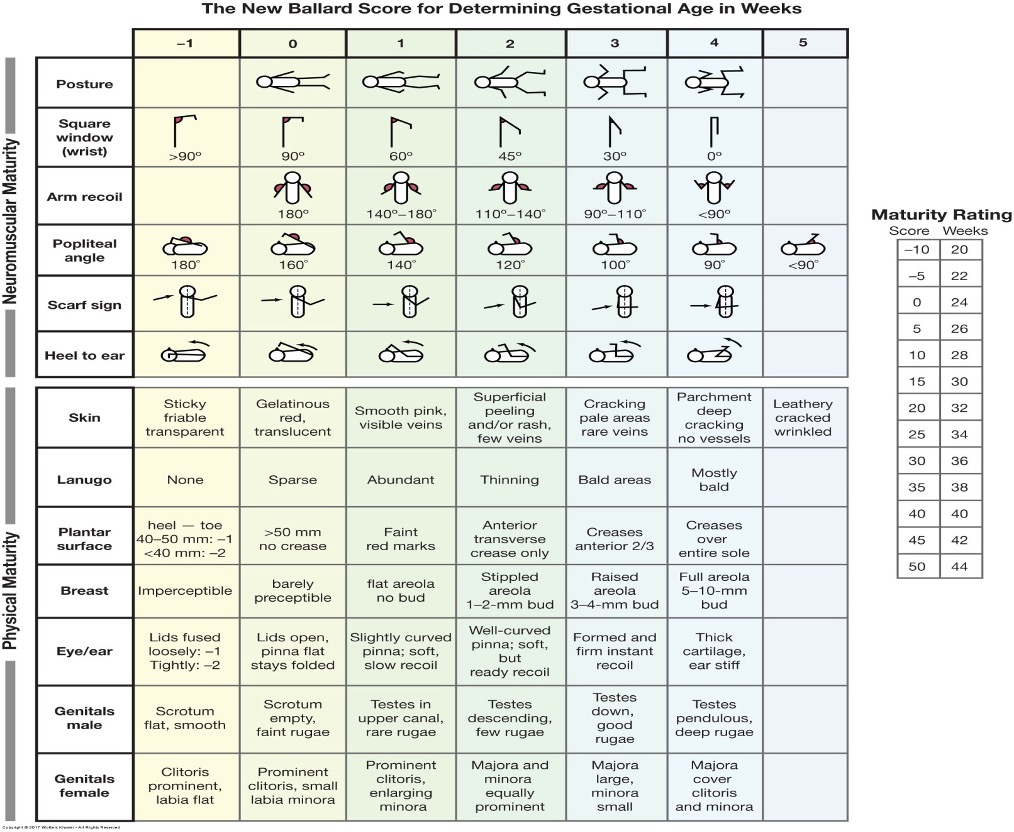
What score is used for premature infants, estimating GA w/in 2 weeks, to accurately determine level of development & tailor appropriate medical care for baby, esp when pregnancy dating is uncertain or unreliable?
Ballard scoring system
What is normal behavior for a newborn?
Turn head to look at face, sensitivity to all 5 senses, interaction & attachment w/ caregivers, state regulation, perception, habituation (gradually stop paying attention to stimulus w/ repeated exposure)
What is abnormal behavior in a newborn?
Irritability, lying in asymmetrical positions, lack of spontaneous movement, tremors at rest after 4 days post birth
What screening is used to test for delays in personal-social, fine motor-adaptive, language & gross motor skills from birth to 6 years of age, and does NOT test intelligence?
*Specific, not sensitive, false negs are common
Denver developmental test
What is somatic growth?
Height, weight, head circumference → charts separated to 0-36 mos & 2-18 yrs
What is an inaccurate method of measuring an infants height?
Measuring tape (unless infant can be still w/ hips & knees extended)
How should a newborn be weighed?
Fully unclothed w/ fresh unused diaper;
(dont weigh parent holding child & subtract parent’s wt)
How should a newborn’s head circumference be measured?
Place measuring tape over occipital, parietal & frontal prominences
Take an avg of 3 readings & use the largest
*measured for the first 2 yrs of life
What is considered macrocephaly and can be seen in conditions such as hydrocephalus, subdural hematoma, brain tumors, & inherited conditions?
> 97% or 2SD above the mean
What is considered microcephaly and can be seen in conditions such as premature closure of sutures, familial congenital infx, maternal metabolic disorders, & neurological insults?
> 2SD below the mean
What is the avg systolic BP at birth?
70 mmHg
What is the avg systolic BP at 1 month?
85 mmHg
What is the avg systolic BP at 6 months?
90 mmHg
How should BP be taken in a newborn?
Select correct cuff size & placement, put cuff on & leave it on, perform readings at beginning, middle & end of exam
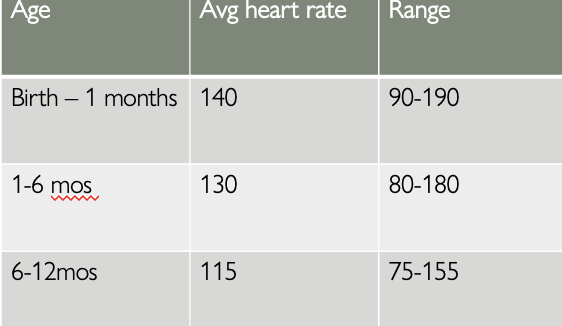
Newborn heart rates
What is considered tachypnea at 0-2 months?
> 60
What is considered tachypnea at 2-12 months?
> 50
What is considered tachypnea > 12 months?
> 40
What is the preferred way to take temperature in infants under 2 mos?
Rectal
How does skin progress in a normal newborn in the first 10 minutes of life?
Cyanosis to pink
How might lighter skinned infants appear after birth?
Erythematous flush, “boiled lobster” appearance for 8-24 hrs after birth before becoming normal pale pink color
What does cyanosis in newborn indicate?
Hypoxemia
What does pallor in newborn indicate?
Low hgb
What does plethora in newborn indicate?
polycythemia
What does jaundice in newborn indicate?
elevated bilirubin
What does slate gray color in newborn indicate?
methemoglobinemia
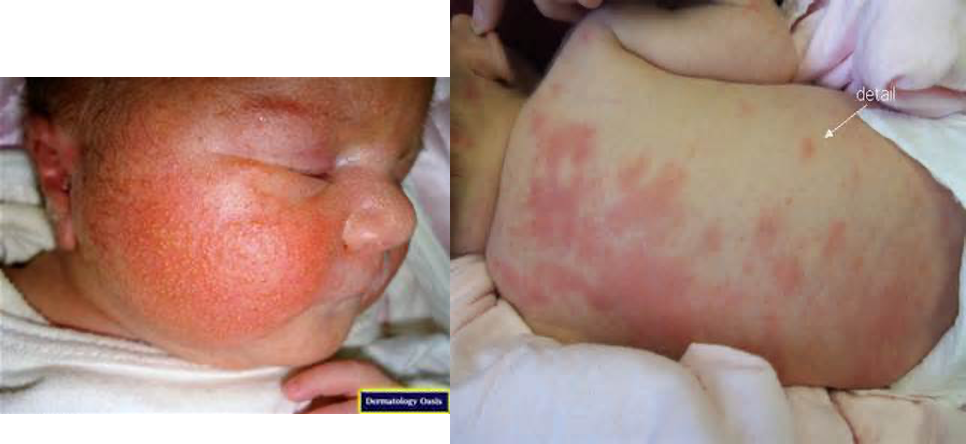
What is a benign newborn rash of variable irregular macular patches that is self limiting & lasts a few days?
Erythema toxicum
What is the dx for erythema toxicum?
Wright stain → eosinophil
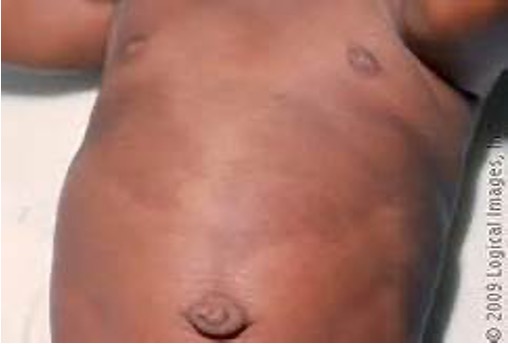
Cafe au last spots are usually benign, but ≥6 large spots are present can be associated with what condition?
Neurofibromatosis
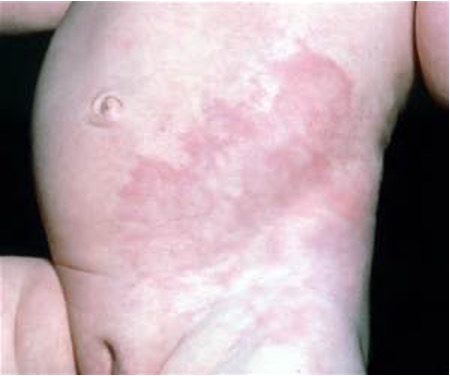
What skin condition is a vasomotor response to cooling or chronic exposure to radiant heat that appears lattice like, bluish mottled pattern on trunk, arms, & legs?
Cutis marmorata
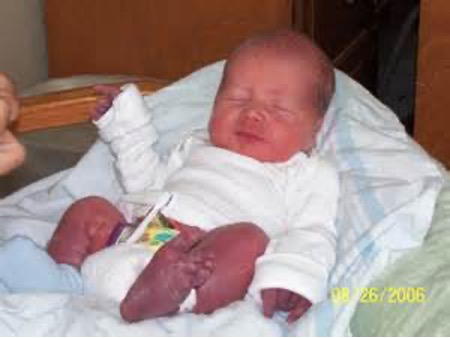
What is a blue cast to the hands and feet when exposed to cold?
Acrocyanosis
What should be expected if acrocyanosis does NOT disappear w/in 8 hours or with warming?
cyanotic congenital heart disease (TOF)
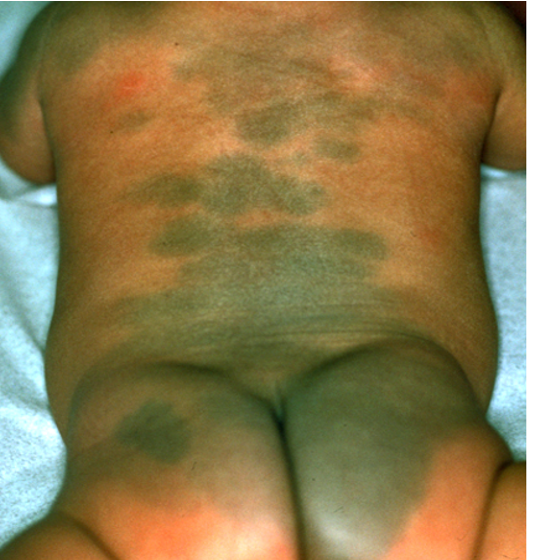
Wha tis a pigmentation in newborns to the sacral gluteal region, MC in asians & disappears by ages 6-10 y/o?
Dermal melanocytosis
What is fine downy hair on a newborn that will shed within the first few weeks?
Lanugo
What is sebum & desquamated epithelial cells that appear as a white greasy material that covers the body at birth, and must be differentiated from congenital icthyosis (harelquin icthyosis)?
Vernix caseosa
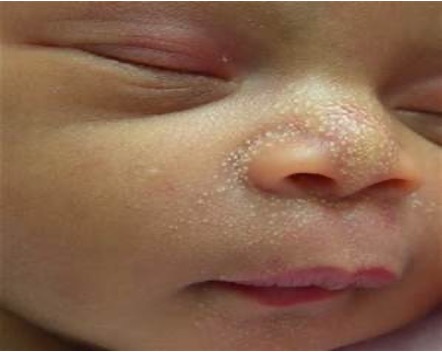
What are white papules w/o erythema to the nose, chin, & forehead that are caused by retained sebum?
Milia
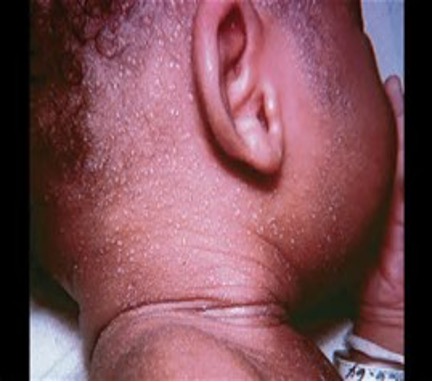
What are vesicles on an erythematous base to the face and trunk caused by sweat gland duct obstruction?
Miliaria rubra
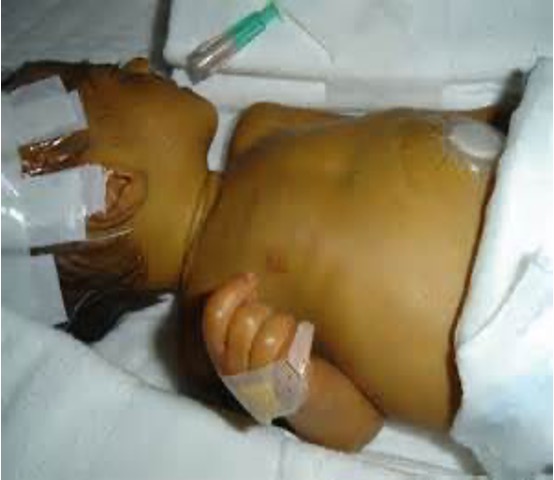
What occurs in 50% of newborns because their immature liver isn’t able to efficiently remove bilirubin?
Jaundice
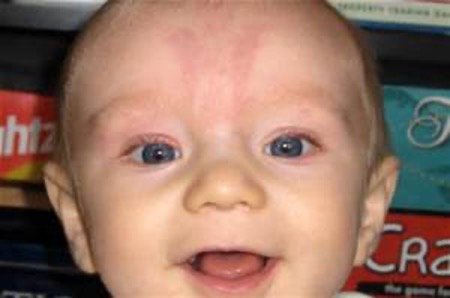
What skin condition?
Flat irregular light pink patches
often disappears by age 1
“stork bite” → nape of neck
“angel kisses” → upper lip, upper eyelids, forehead
also: “salmon patch”, telangiectatic nevus, capillary hemangioma
Nevus simplex
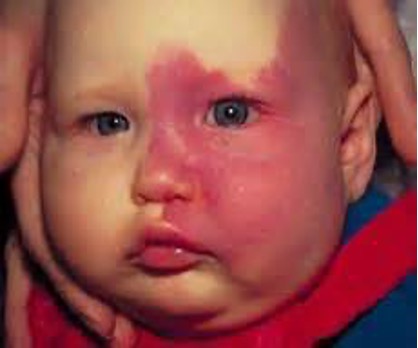
What condition is a vascular anomaly (capillary malformation of the skin) that is almost always a birth mark?
Port wine stain (Nevus flammeus)
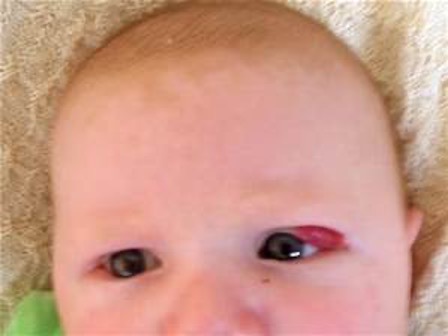
What skin condition is thought to be related to a abnormal growth of blood vessels during fetal development?
Hemangioma
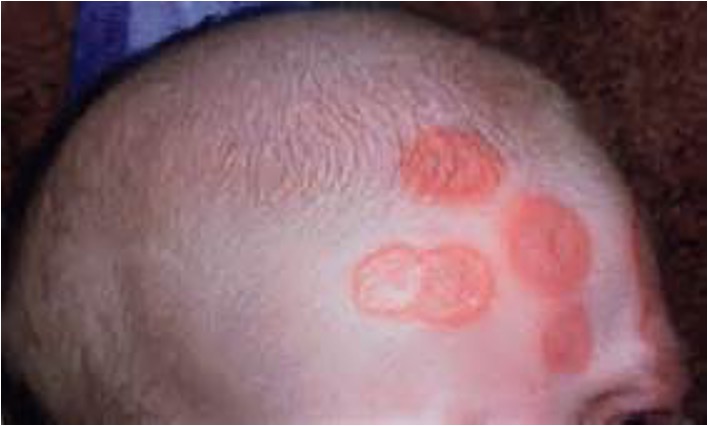
What condition is a clinical spectrum of cutaneous, cardiac, systemic abnormalities observed in newborn infants whose mothers have autoantibodies against RO/SSA and LA/SSB?
Neonatal lupus erythematosus (NLE)
What is the complete or partial absence of fingernails or toenails?
Anonychia
When are techniques to assess skin the same for adults?
After the first year of life
What ages should the skull circumference be measured?
≤ 2 yrs
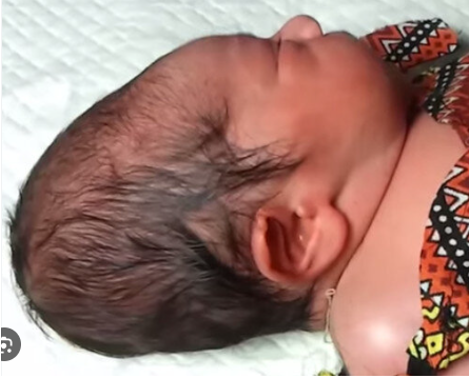
What condition is localized SC edema over the occipitoparietal region & distention of capillaries and extravasation of blood and fluid from the vacuum effect of the rupture of amniotic sac?
Caput succedaneum
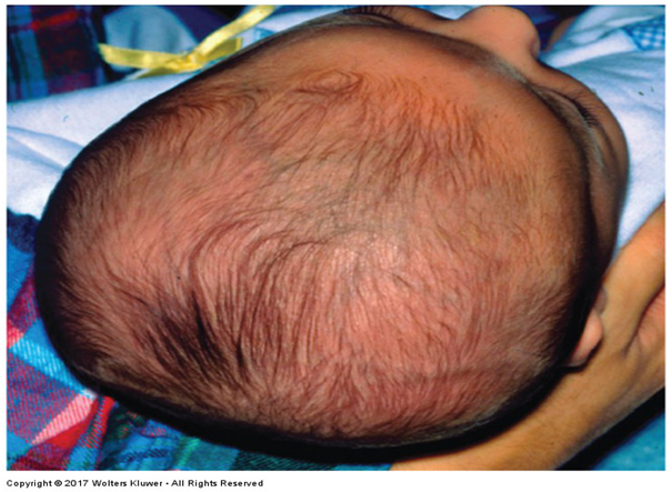
What is asymmetry of the skull caused by the child lying on one side & resolves when child becomes more active?
Plagiocephaly
How does a newborns head appear to palpation?
Bones are soft & pliable, resolves w/ age
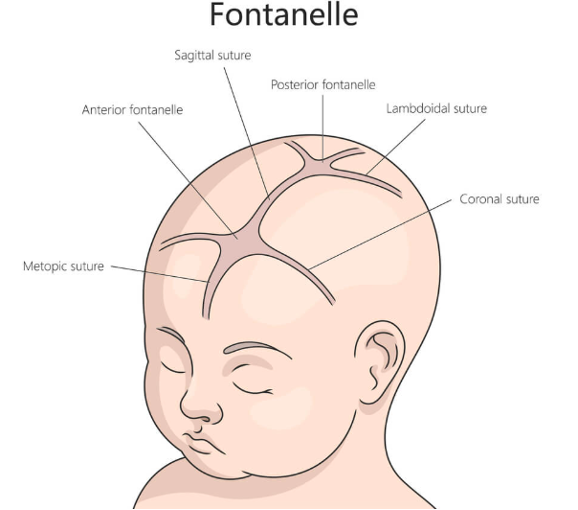
What are “soft spots” that allow for continued growth of the brain and skull?
Fontanelles
What do bulging fontanelles indicate?
Inc ICP
What do sunken fontanelles indicate?
Dehydration
How should the fontanelles should be examined?
Gently palpate anterior (9-18 mos) & posterior (2-3 mos)
What sign helps diagnose hydrocephalus and brain abscesses?
Tap the skull near the junction of frontal, temporal, & parietal bones
produces a stronger resonance sound when either are present
“cracked pot”
Macewen sign
How does a newborns head normally appear to transillumination?
2cm halo over the frontoparietal area & 1 cm of occipital area
How would hydrocephaly or reduced cerebral cortex size appear when transulliminating a newborns head?
Entire head lights up
What can cause a chemical conjunctivitis in newborns?
Silver nitrate prophylaxis
How should the red reflex be tested for in newborns?
Hold 6-8” from eye, use +10 diopter lens, transmits a clear red color back to the observer
black dots indicate cataracts, white indicates retinoblastoma
How should an infants eyes be inspected?
Hold infant upright, support head, & rotate yourself and baby slowly in one direction → baby’s eyes will ease in direction of your turn → when rotation stops, eyes will look in opposite direction after a few nystagmoid movements
Convergent or divergent strabismus is normal until how old?
3 mos, if persists may indicate ocular weakness
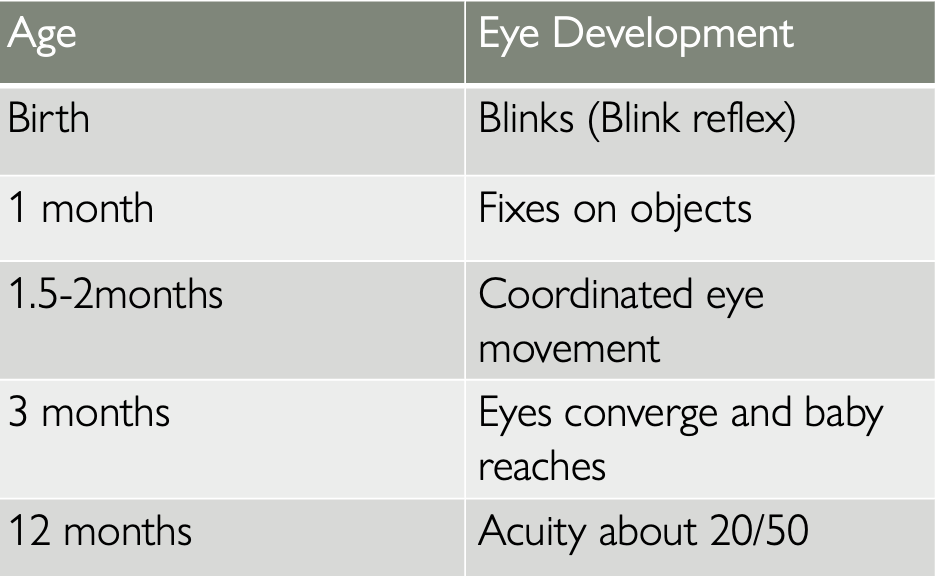
Eye development
What should you also check if there is a concern with the ears?
Kidneys
How do you perform otoscopic exam in infants/small children?
Pull DOWN on auricle
What might obscure ear canal in newborns?
Vernix caseosa
When does the light reflex become cone shaped?
Several months after birth
How do you test hearing in a newborn?
Produce a sharp sudden sound using a bell/beeper 1 foot from ear & watch for acoustic blink reflex (involuntary blinking response to auditory stimuli; difficult to elicit first 2-3 days)
What is the flaring of nostrils a sign of?
Inc respiratory effort, URI
How do you confirm patency of nostrils & detect choanal atresia in newborns?
Soft NG tube passed through each nostril
Do you need to check sinuses in newborns?
No, haven’t developed yet
What age is a little saliva normally found in infants mouth?
0-3 mos
What age is copious saliva found in infants mouth?
≥ 3 mos
What conditions is microstomia seen in?
Trisomy 18 & 21
What condition is macrosomia seen in?
Mucopolysaccharidosis
What condition is a smooth philtrum a key feature of?
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
What are small white cysts, frequently found on either side of median raphe of palate?
Epstein pearls
What is bluish/white swellings of variable size on the floor of the mouth representing benign mucous gland retention cyst?
Ranula
What conditions is macroglossia seen in?
Hypothyroidism, mucopolysaccharidoses
If a neonate has teeth (MC lower incisor) what is there a risk of if it is loosely attached?
Aspiration
What conditions is micrognathia seen in?
Pierre-robin syndrome, treacher collins syndrome, hallerman streiff syndrome
What is webbed neck seen with?
Turners & noonans syndrome