Biology Part 1 Grade 10
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Hans and Zacharias Janssen
Created the first compound microscope in early 1600s
Robert Hooke
He observed cork and called remnants of living plant cell walls cells in 1665.
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
First to observe single-celled living organisms (from gunk on his teeth) and called them animalcules. Also observed blood cells from frogs, birds, and humans in 1674.
Light Microscope
The curved lenses bend the light making the image larger. When light crosses the image appears upside down.
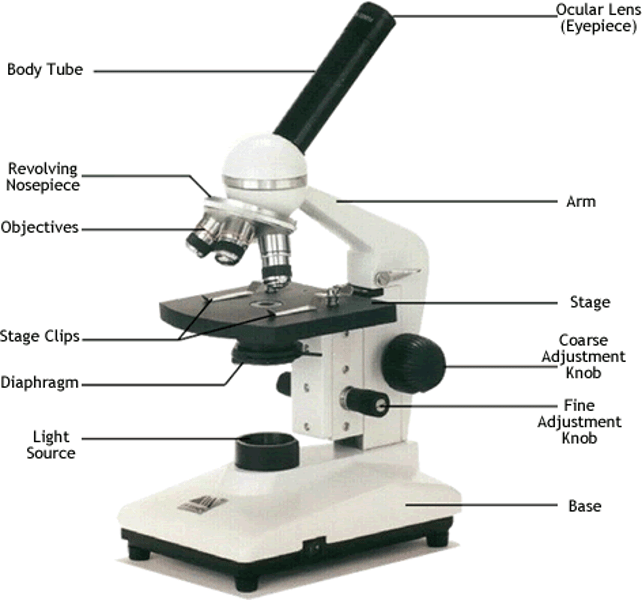
Simple and Compound Microscope
Simple: one lens.
Compound: two or more lenses
Confocal Microscope
Uses a laser to concentrate light onto a specimen. The reflection passes through a pinhole and into a sensor which creates an image.
Every image is a thin section, when combined creates 3D image.
Fluorescence Microscopy
Can be used with confocal microscope and are fluorescent substances that are attached to molecules in the tissues for detailed imaging.
Electron Microscope
Electrons are used to illuminate the image. They are absorbed or scattered by the materials they pass through.
Smaller wavelength = higher resolution
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Electrons pass through very thin section of a stained tissue fixed in plastic. Usually used to observe organelles in cell.
Scanning Electron Microscope
Allows vision of the surface of a specimen which is covered in an electron-dense material (like gold). The electrons bounce off the surface.
Magnification
How much larger the image is than the actual specimen.
Contrast
Amount of light absorbed by the object compared to surroundings.
Resolution
Smallest measurement that you can separate/ distinguish between objects that are very close together.
Field of View
The area visible through the microscope eyepiece.
FOV is measured by the diameter of the circle you can see (usually measured with clear ruler).
Aristotle
Believed that life could be created on its own due to a "life force" (Spontaneous Generation).
Evidence: meat out = maggots formed and left sweaty underwear = mice.
Miasma Theory
An obsolete medical theory that held diseases- cholera, chlamydia, and plague- were caused by miasma (bad air).
Francisco Redi
He took the first steps to DISPROVE SG. His experiment involved meat in jars with or without lids. He discovered that the maggots formed in the jar with no lid.
First evidence refuting SG in 1668.
John Needham
He wanted to prove that living things could be produced from non-living matter. His experiment was to boil broth in a jar with no lid. Bacteria appeared and he concluded that there was a "life force" in 1745.
Lazaro Spallanzani
He believed that micro-organisms in the air were responsible for the growth → repeated Needham's experiment except kept lid on jar. He concluded that air was responsible for growth in 1768.
Louis Pasteur
He disproved SG and found sterilization technique. His experiment involved three different flasks. The third jar prevented falling particles from landing in broth but had air flow.
Cell Theory
1. All living things are made up of one or more cells (Schwann)
2. Cells are the smallest unit of life (Schleiden)
3. Cells are produced from pre-existing cells through cell division (Virchow)
Cell Theory History
1. Aristotle: classification system of animals based on observation
2. Redi (1668): maggot experiment → challenged SG
3. Spallanzani (1745): broth experiment → challenged SG
4. Robert Brown (1833): nucleus
5. Pasteur (1864): disproved SG
6. Schleiden (1838): nucleus was responsible for control. Schwann (1838): plant/ animal cells are similar
7. Virchow (1859): cells are from from pre-existing cells
What Living Things Do
1. Intake nutrients
2. Move
3. Grow
4. Respond to stimuli
5. Exchange gases
6. Remove waste
7. Reproduce
Prokaryote Cells
A cell that does not have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles (but has ribosomes). The DNA in this cell is free floating in the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotic Cells
A cell that has a true nucleus and membrane bound organelles (nucleus, ER, Golgi apparatus) surrounded by a thin membrane.
Double Membrane Bound: mitochondria and chloroplasts
Nucleus
- Controls all cell activities
- DNA
- Regulates gene expression
Nuclear Envelope
Surrounds nucleus and allows for transport of materials through pores
Centrioles
Development of spindle fibers during cell division that move copies of DNA (chromatids) to opposite ends (animal cells only).
Cytoplasm
Jelly like substance where organelles are suspended (contains nutrients required by cell).
Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Complex system of channels and sacs composed of membranes (connected to nuclear envelope)
- Internal delivery system
RER: process proteins and ships them
SER: process/ synthesize fats
Ribosomes
Composed of RNA and proteins and are responsible for synthesis of preordains from amino acids.
Golgi Apparatus
- Sorts from ER and packages them to vesicles
- Sorts, package, transports inside and outside cell
Vesicle
Membrane bound structure used for transport and storage.
Endocytosis: fuse with membranes (in)
Exocytosis: releases contents
Lysosome
- Membrane bound vesicle where digestion occurs
- Defense against bacteria
- Destroys damaged organelles
- Controls digestion of tissue
Vacuole
- Stores water, ions, sugars, amino acids, and macromolecules
- Contains enzymes to break down macromolecules and waste
Turgor Pressure
Internal pressure in a plant (with no water, pressure in vacuole is reduced).
Chloroplasts
From carbon dioxide and water (with help of light and chlorophyll) glucose and oxygen are produced.
Contains chlorophyll → photosynthetic pigment which absorbs light energy
Mitochondria
- Cellular respiration occurs (glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy)
- Converts chemical energy in sugars/ energy cell uses
Cell Wall
In plant cells and gives cell shape and structural support.
Cytoskeleton
A network/ pathway of protein fibers that extends throughout cytosol and provides structure/ shape.
Cell Membrane
Controls flow of materials in and out of cell.
Fluid Mosaic Model
- Weak attractive forces hold phospholipids together changing places many times (fluid)
- Fluid = lipids and proteins move throughout membrane
- Mosaic = different parts (macromolecules, proteins, carbohydrates)
Hydrophilic Head and Hydrophobic Tail
Hydrophilic Head: polar phosphate group (slight - and + charges)
Hydrophobic Tail: two non-polar fatty acid chains (attracted to other hydrophobic molecules)
Hydrophobic interior repels polar molecules.
Selectively Permeable Membrane
Membrane that allows some substances to pass more easily than others and blocks the passage of some substances altogether.
Passes through = determined by size, charge, soluble in lipids
Passive Transport
- Uses no energy
- Movement of ions or molecules across cell from high concentration to low.
Active Transport
- Requires energy
- Goes against conc. gradient (high to low)
Diffusion
- Passive transport
- From high concentration to low concentration until it is equal throughout
- Dynamic equilibrium reached at "end"
- In gases
Concentration Gradient
The difference in concentration between one side of a membrane and the other.
Dynamic Equilibrium
A state of balance where particles move in all directions at equal rates.
Balance inside cell allowing movement of nutrients, gases, and waste.
Polar
One end of the molecule possess more + charges whereas the opposite end has - charges = electrical pole
Rate of Diffusion
1. Molecule Size: increase size = decrease rate
2. Polarity: polar = decrease rate & non-polar = increase rate
3. Molecule/ Ion Charge: charged cannot diffuse
4. Temperature: increase temp. = increase energy = increase rate
Osmosis
- Passive transport
- In water
- Movement from high to low concentration
Tonicity
Hypotonic: lower concentration of solute than water
Hypertonic: higher concentration of solute than water
Isotonic: equal concentration of water and solute
Dialysis Tubing
Blood flows from semi-permeable membrane tubes, which are surrounded with dialysis fluid, from high to low concentration (osmosis).
Facilitated Diffusion
- Transport of ions or molecules across a membrane by means of a membrane proteins along the concentration gradient.
- Passive transport
- Channel proteins and carrier proteins
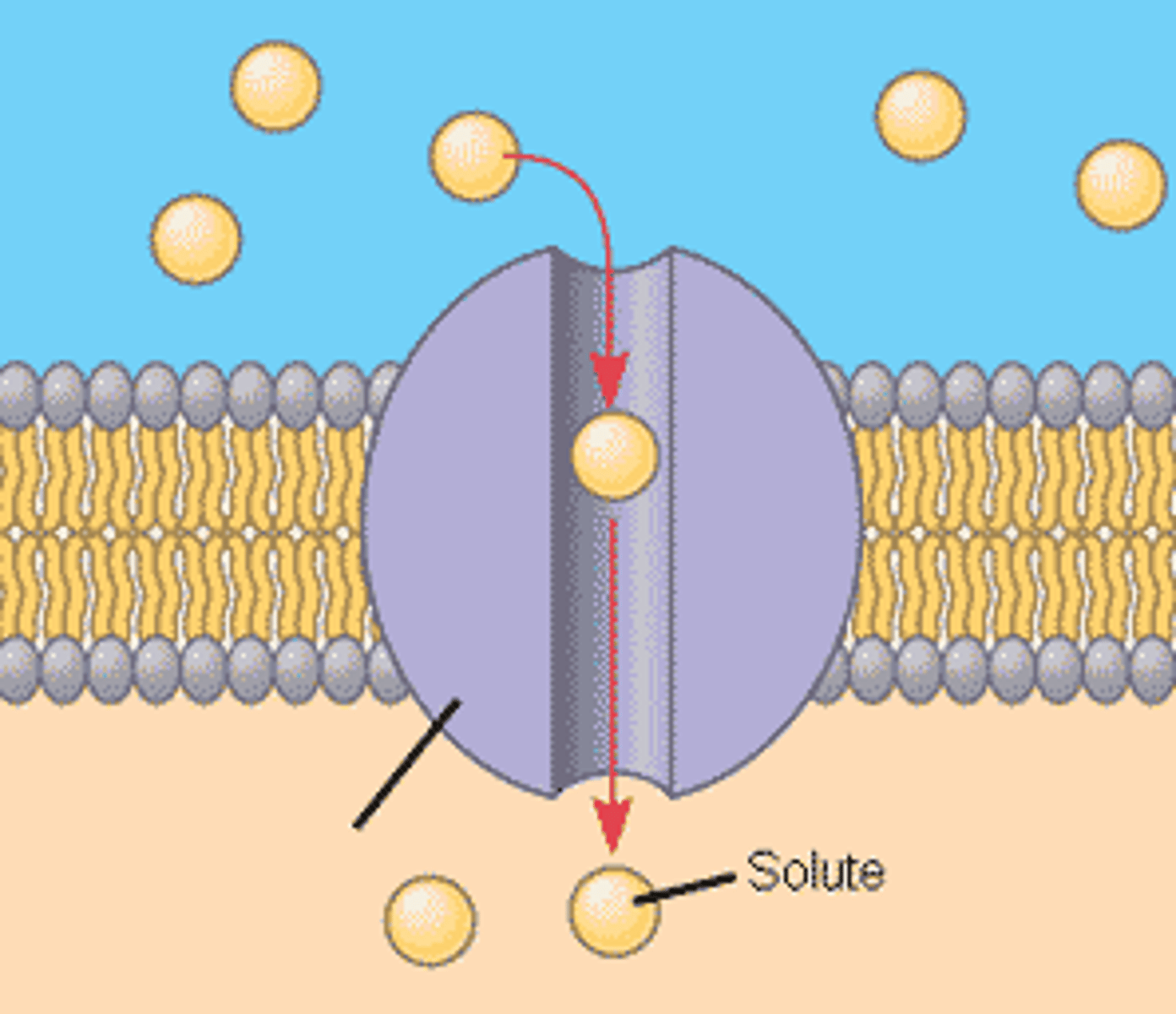
Channel Proteins
- Create channels through which small water-soluble particles are able to move.
- Passive transport
- Responsible for facilitated diffusion
Transports: ions and large polar molecules
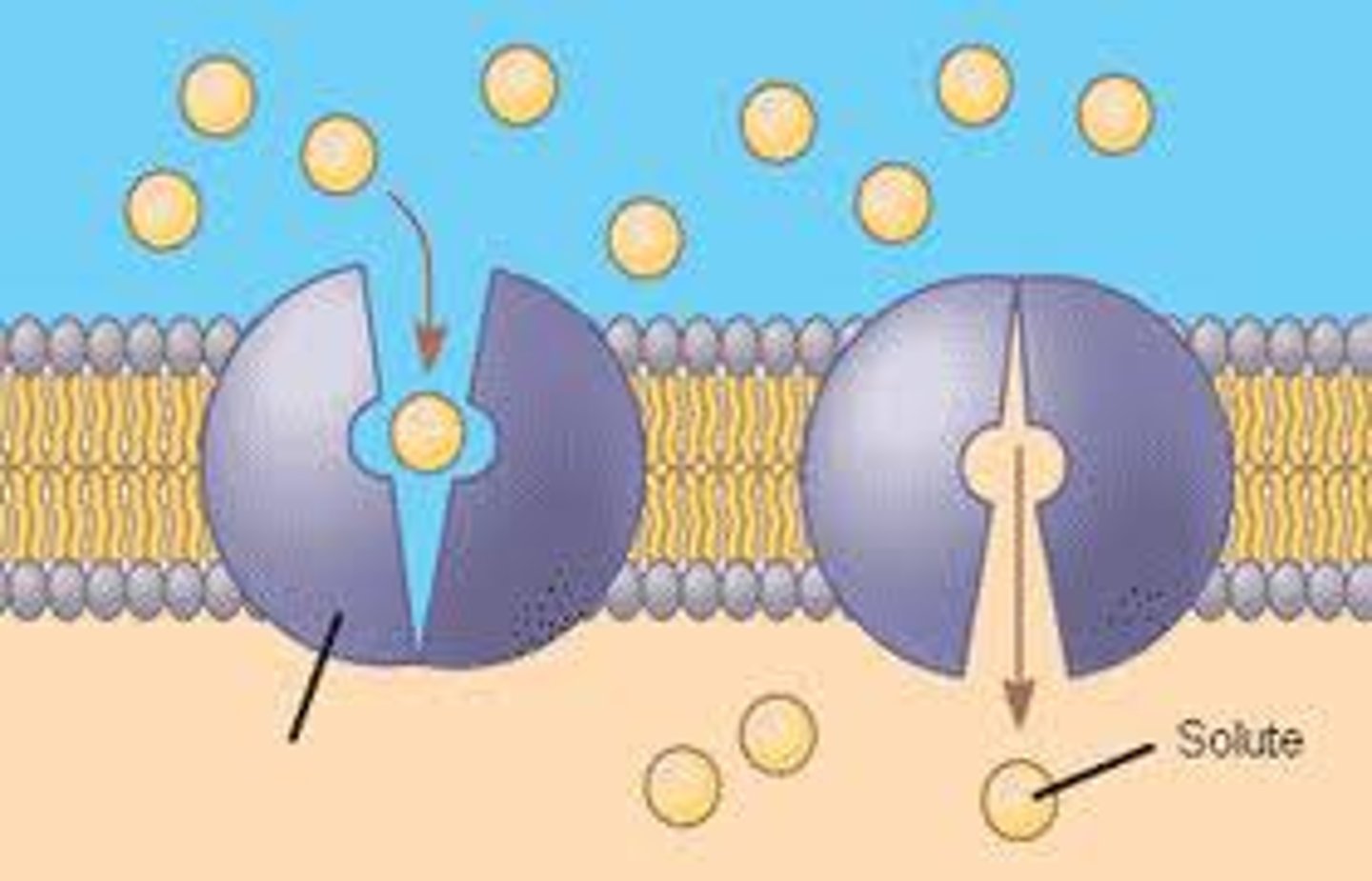
Carrier Proteins
- Membrane proteins that bind to and transport 1 > particles of a substance from one side to the other.
- Along concentration gradient
- Passive transport
- Responsible for facilitated diffusion
- Changes shape when bound to molecule
- Protein returns to OG shape after molecule is transported
Transports: larger molecules
Protein Pumps
- Active transport
- Moves materials against conc. gradient
Membrane Assisted Transport
- Active transport
- moves materials that are too large to cross the cell mem. through channel or carrier protein
-Endo. and exocytosis
Better Ratio for Cells to Interact with Environment
Higher surface area: volume ratio.
Big vs Small Cells
Big: more energy to transport more molecules, more distance
Small: fewer molecules to transport, less energy, less distance
Single Celled Giants
Stentors and Xenophyophores have many nuclei.
Caulerpa
- seaweed that have only one cell with many nuclei
- invasive (time to time)