Lab Practical Study Guide
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/433
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
434 Terms
1
New cards
What level of BSL precaution do we follow?
BSL-2
2
New cards
why do we wear lab coat, closed toed shoes, and have hair tied back
prevent contaminating the working space and for our own protection
3
New cards
when should we not wear gloves?
around a flame; they could melt and injure the hands
4
New cards
when is eye protection worn?
staining and using chemical reagents
5
New cards
where do used test tubes, media, and other contaminated glass re-useable (slides, flasks) go?
red autoclave cart

6
New cards
where do contaminated disposables (gloves, paper towels) and ALL agar plates go
into a biohazard bin
7
New cards
where do uncontaminated gloves and paper towels go
into regular trash cans
8
New cards
where do contaminated sharps (broken wet-mount slides, broken tubes with culture) go
in the biohazard sharps bin after dousing with 70% EtOH

9
New cards
where do clean uncontaminated sharps (razor blades, broken glass) go
into regular sharps bin
10
New cards
what should always be on a label
GREEN
Lab section (S2)
Date you inoculated (month/day)
Incubation temperature (in Celsius)
Culture source
Species if known (never write out full genus name; B. subtilis)
Genus if known, but species not known (ex. Staphylococcus sp. )
If neither species or genus is unknown (name of environmental source)
SOMETIMES include:
First name ONLY
Experimental conditions (streak #, controls)
Lab section (S2)
Date you inoculated (month/day)
Incubation temperature (in Celsius)
Culture source
Species if known (never write out full genus name; B. subtilis)
Genus if known, but species not known (ex. Staphylococcus sp. )
If neither species or genus is unknown (name of environmental source)
SOMETIMES include:
First name ONLY
Experimental conditions (streak #, controls)
11
New cards
what should be on the label for microscope slides
source, stain type, date
12
New cards
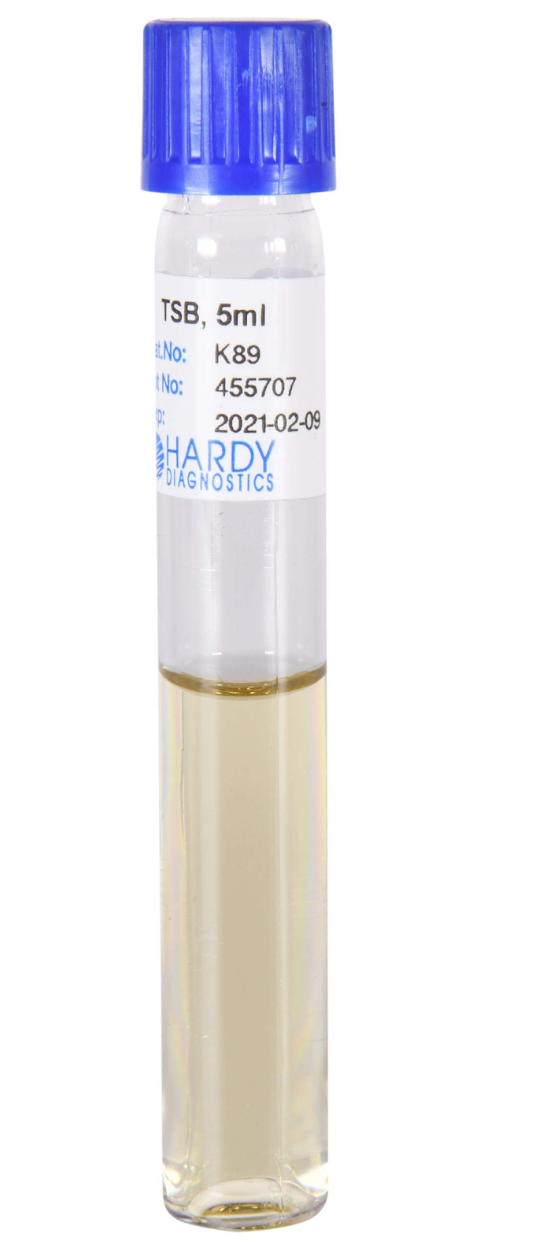

What is it and what are the pros and cons
TSA broth
Pros: Grows bacteria in large quantities, quickly, under uniform conditions
Cons: Easily contaminated
Pros: Grows bacteria in large quantities, quickly, under uniform conditions
Cons: Easily contaminated
13
New cards
what are the different types of solid media
slant, deep, and plate
14
New cards
what is the function of agar
Agar: the gelling agent used in most solid media
Cheap, sustainable, no nutritive value (few bacteria can digest it)
Cheap, sustainable, no nutritive value (few bacteria can digest it)
15
New cards
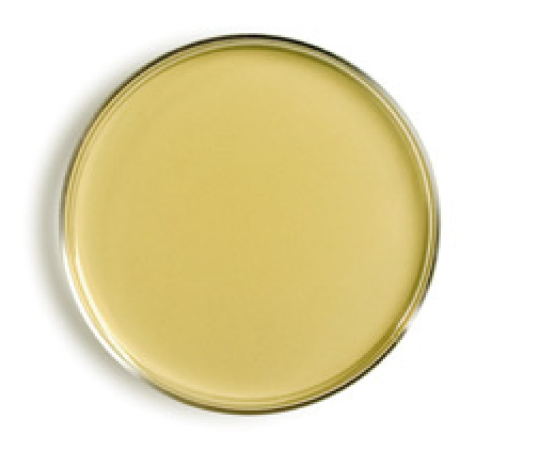

what is it and what is it used for
solid Petri dish media for isolation of pure cultures and various tests
16
New cards
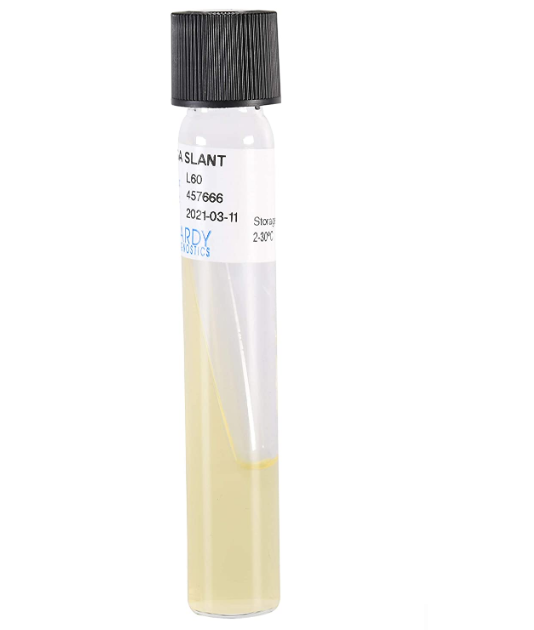

What is it and what are the pros and cons
TSA slant: solid test tube media for long-term storage of pure cultures and biochemical tests
Pro over broth: easy to catch contamination; look for unexpected growth off the S-path
Pro over plates: smaller surface for air exchange, so less likely to be contaminated and do not dry out as quickly
Con: not enough room to isolate pure culture; only used when pure culture has been isolated
Pro over broth: easy to catch contamination; look for unexpected growth off the S-path
Pro over plates: smaller surface for air exchange, so less likely to be contaminated and do not dry out as quickly
Con: not enough room to isolate pure culture; only used when pure culture has been isolated
17
New cards
What is it and what is it used for
TSA deeps: solid test tube media for long-term storage of pure anaerobic cultures and oxygen requirement tests (stabs)
18
New cards
what is defined/minimal/synthetic media
media that contains nutrient in pure chemical form and does not contain any plant or animal tissue; the exact chemical composition of the media is known
19
New cards
what is complex/undefined media
complex/undefined media: media that contains nutrients from plants or animal extracts; the exact chemical formula is not unknown
20
New cards
what are non-fastidious microorganisms
microorganisms that grow on general purpose media like TSA (our lab stuff)
21
New cards
Fastidious microorganisms
microorganisms that require specific nutrients or growth factors that are not found in general purpose growth media (pathogenic)
22
New cards
Autoclave
a machine that uses pressurized steam at high temperatures for a defined period of time; 121 degrees Celsius with steam pressure of 15 psi for 15 minutes
23
New cards
do long autoclave times increase sterilization
no, it might even burn and caramelize the sugars in the media
24
New cards
Why do we autoclave media, equipment
media ingredients/equipment are not sterile and will be contaminated with microbes from surrounding air, glassware, spatulas, and so on
25
New cards
Why do we autoclave biohazard
to kill any remaining microbes in the bags, safer disposal
26
New cards
Why autoclave and not boil?
Autoclaving can generate higher temperatures where microbes that are boiling-resistant cannot survive
27
New cards

what shape is this
spindle
28
New cards

what shape is this
filamentous; usually fungi
29
New cards
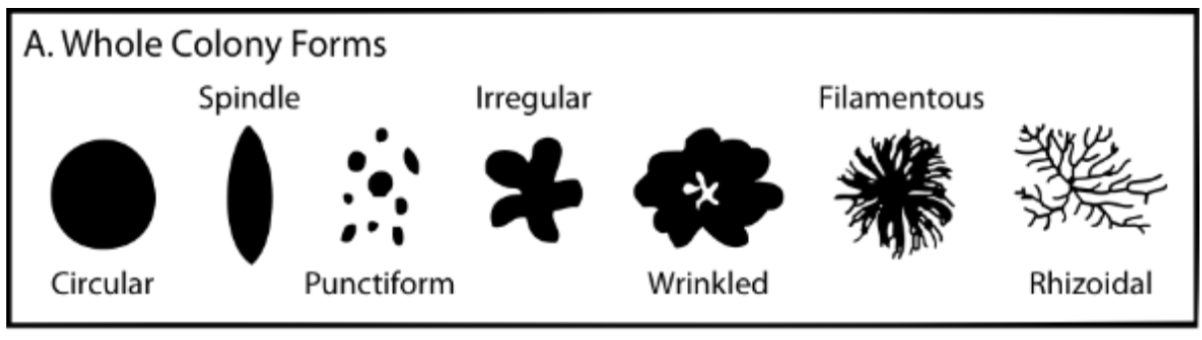
what are the different types of whole colony forms
circular, spindle, punctiform, irregular, wrinkled, filamentous, rhizoidal
30
New cards
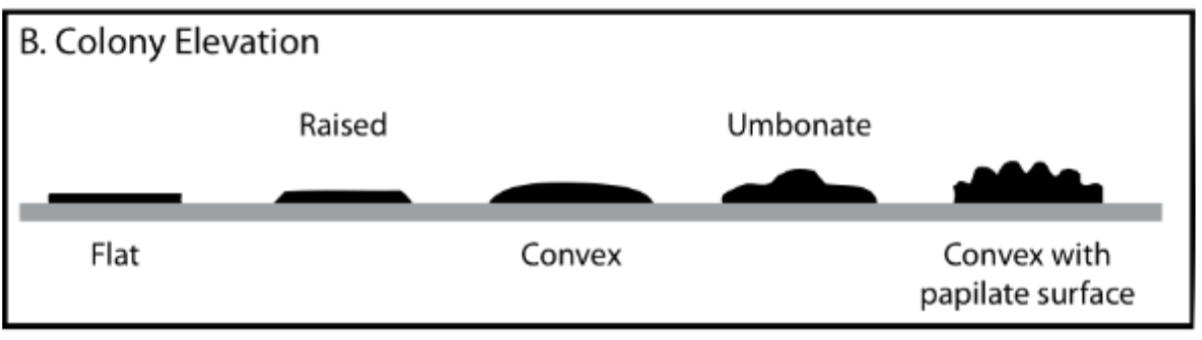
what are the different types of colony elevation
flat, raised, convex, umbonate, convex with papilate surface
31
New cards
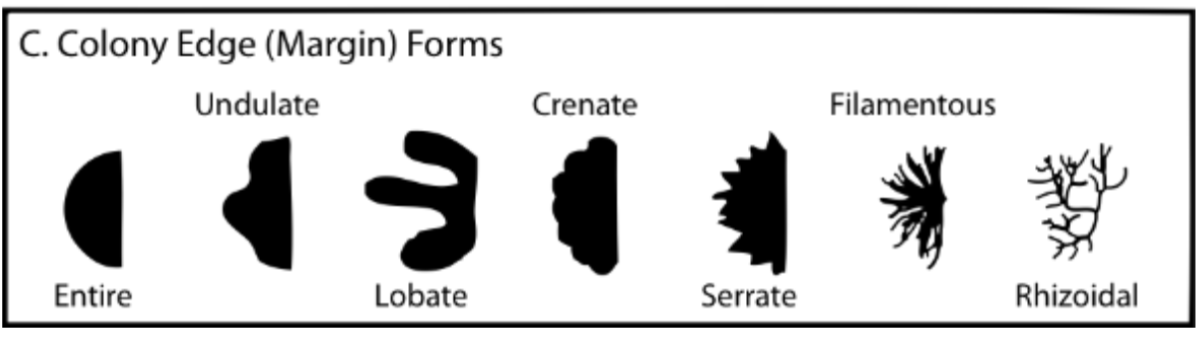
what are the different types of colony margin forms
entire, undulate, lobate, crenate, serrate, filamentous, rhizoidal
32
New cards
what kind of surfaces have high microbial load and diversity
soft, porous, natural material wha
33
New cards
what kinds of surfaces have lower microbial load and diversity
Hard, metal, non-porous, man-made surfaces
34
New cards
what are basic experimental design with control and hypothesis
Ask a scientific question
Form a hypothesis
Design an experiment to test your hypothesis
Collect results and analyze data
Draw a conclusion to support or not support your hypothesis
Form a hypothesis
Design an experiment to test your hypothesis
Collect results and analyze data
Draw a conclusion to support or not support your hypothesis
35
New cards
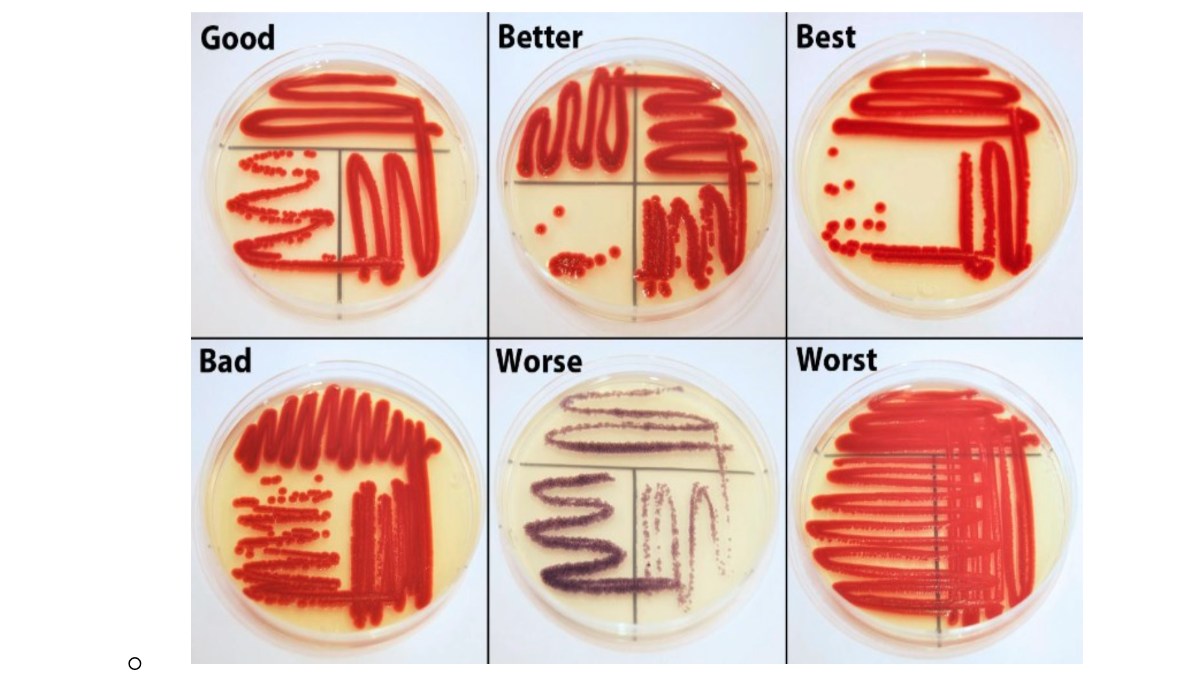
how to do a T-streak
a T-Streak as we taught it
Incinerator for 5 seconds, brand loop for 5 seconds, touch center of the colony (don’t scoop)
Streak outside to inside, incinerator for 5 seconds, turn the plate, brand loop into agar to cool, 2nd streak crosses 1st streak, incinerator for 5 seconds, brand loop into agar to cool, 3rd streak crosses 2nd streak, incinerator for 5 seconds, set sterile loop on the bench
Incinerator for 5 seconds, brand loop for 5 seconds, touch center of the colony (don’t scoop)
Streak outside to inside, incinerator for 5 seconds, turn the plate, brand loop into agar to cool, 2nd streak crosses 1st streak, incinerator for 5 seconds, brand loop into agar to cool, 3rd streak crosses 2nd streak, incinerator for 5 seconds, set sterile loop on the bench
36
New cards
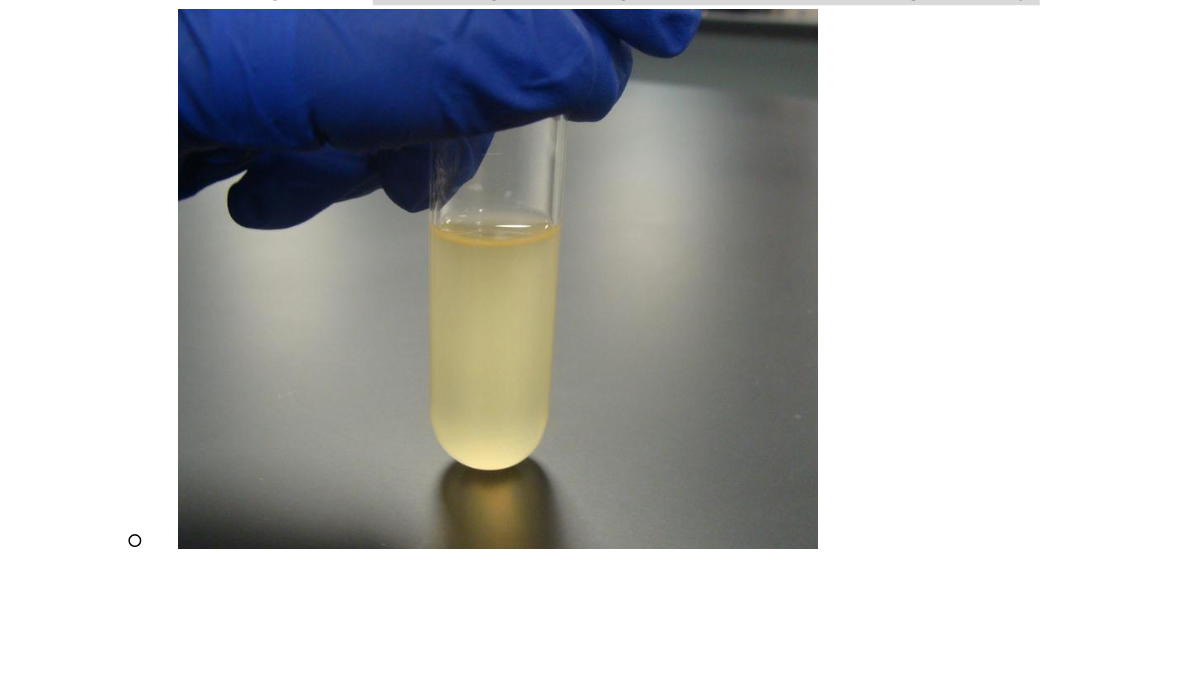

what is this
turbid liquid culture
37
New cards
what is turbidity
microbes grow throughout the medius, making it cloudy
38
New cards
WWW: if there's no growth
the initial culture was dead or you killed the inoculum with a hot loop, or the loop did not touch the inoculum
39
New cards
what is Aseptic transfer:
the prevention of contamination of the culture and the microbiologist with unwanted microorganisms from the environment or other cultures
40
New cards
what is the Purpose of aseptic methods:
maintaining stock cultures and transferring pure cultures from one vessel to another
41
New cards
what is the purpose of Broth inoculation:
impossible to tell by eye if there’s a single species, must be determined microscopically; good for growing up pure cultures or cultures quickly
42
New cards
what is the purpose of slant inoculation
inoculation of a “S” patten up the agar surface; great for pure cultures with lower risk of contamination
43
New cards
what is isolation streaking
for obtaining pure culture from mixture of the environment; used to keep pure cultures alive and pure (subculturing); necessary for pure culture but careful of contamination
44
New cards
what is the only way you can confirm pure culture
checking microscopically for the same cell morphology and gram type
45
New cards
WWW culture transfers
WWW: don’t shake loop around, don’t leave plates open, don’t go back for more inoculum
46
New cards
purpose of broth to broth
grow cultures more rapidly
47
New cards
purpose of plate to plate
pure culture isolation
48
New cards
what are the four objective lenses
4x, 10x, 40x, 100xw
49
New cards
what are the two lenses
ocular len and objective len
50
New cards
a microscope that is ready to be put away
Set the scope to 4x BEFORE removing your slide
Lower the stage
Clean all objective lenses and ocular lenses
Wrap the power cord around the base
Replace dust cover
Lower the stage
Clean all objective lenses and ocular lenses
Wrap the power cord around the base
Replace dust cover
51
New cards

what is it and what does it do
Condenser: collects light; moves up and down to focus the light on the specimen

52
New cards

what is it and what does it do
Iris diaphragm: located between the lamp and the condenser, controls the amount of light that passes through the specimen

53
New cards
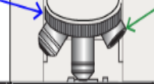
what is it
Objective lens: (4x, 10x, 40x, 100x) lenses closest to the specimen
54
New cards

what is it
ocular lens: eyepiece
55
New cards
how to calculate total magnification
Total magnification: 10x (ocular lens) times the objective lens
56
New cards
what mag to determine size
1000x
57
New cards
how to determine size
1 ocular unit is 10 microns (ocular units), one tick mark is 1 micron (always report in microns!!)
diameter/width and length of a cell
Might have to provide with a range for the length
diameter/width and length of a cell
Might have to provide with a range for the length
58
New cards
Why do we need immersion oil to observe bacteria?
Resolving power: ability to distinguish two adjacent points as distinct and separate
Numerical aperture (NA): the cone of light that enters the lens; short wavelength is the best
Immersion oil improves the numerical aperture and hence the resolving power of the lens; it has a refractive index similar to glass
Numerical aperture (NA): the cone of light that enters the lens; short wavelength is the best
Immersion oil improves the numerical aperture and hence the resolving power of the lens; it has a refractive index similar to glass
59
New cards
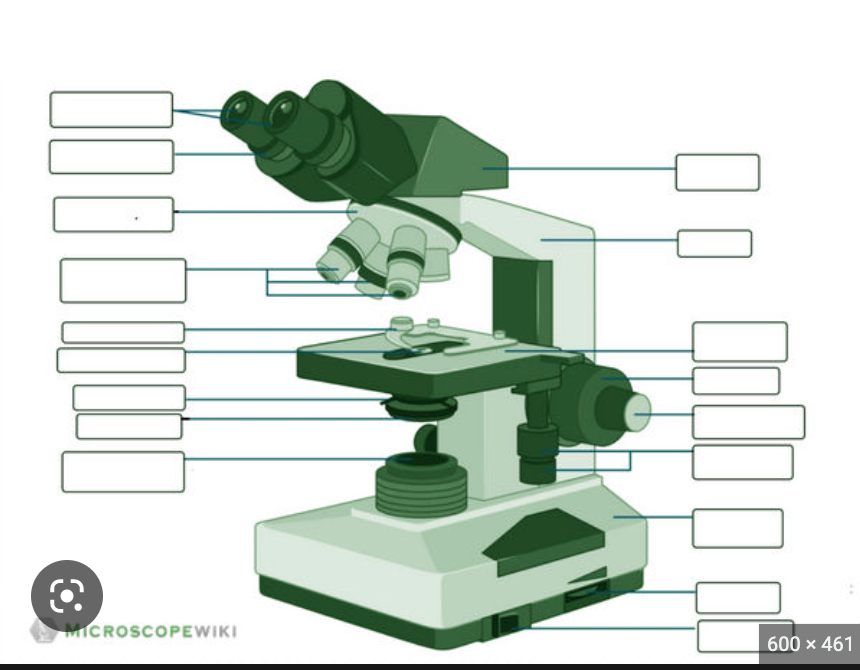
label this microscope
left
1. ocular lens
2. nosebridge
3. objective collar/wheel
4. objective lens
5. stage clips
6. stage
7. iris diaphragm
8. condenser
9. light source
right
1. NA
2. arm
3. stage
4. coarse knob
5. fine knob
6. stage control
7. base
8. light intensity dial
9. power
1. ocular lens
2. nosebridge
3. objective collar/wheel
4. objective lens
5. stage clips
6. stage
7. iris diaphragm
8. condenser
9. light source
right
1. NA
2. arm
3. stage
4. coarse knob
5. fine knob
6. stage control
7. base
8. light intensity dial
9. power
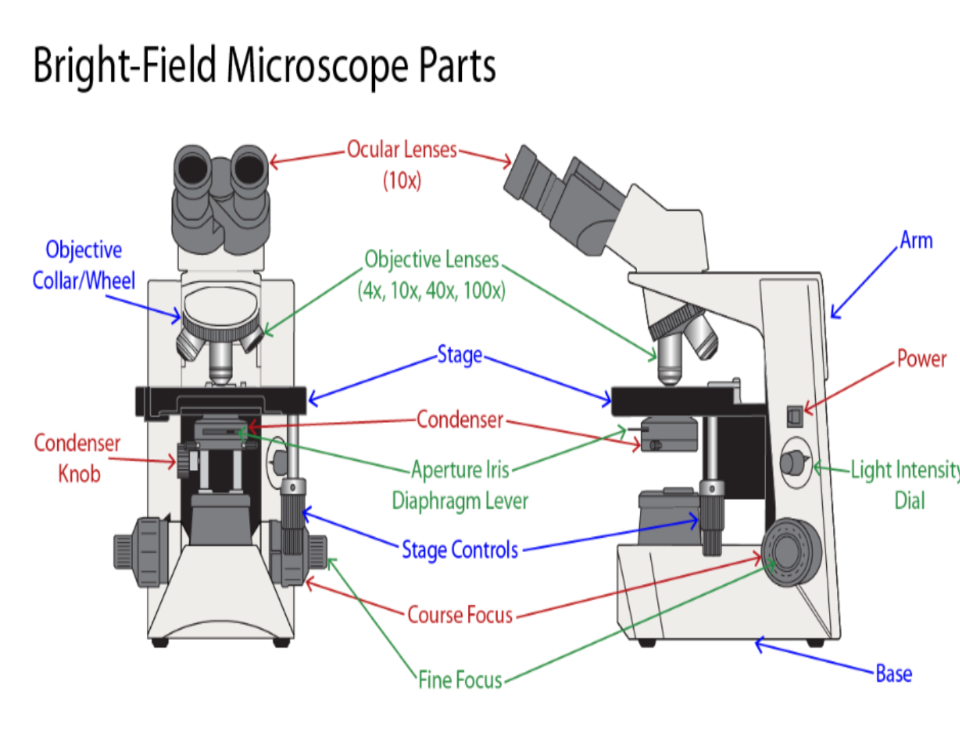
60
New cards
what stain is this
Crystal Violet: gram positive
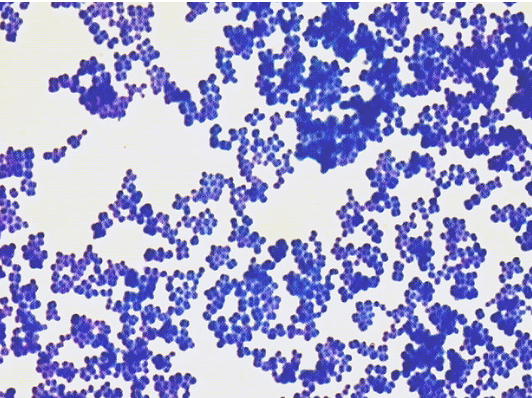
61
New cards
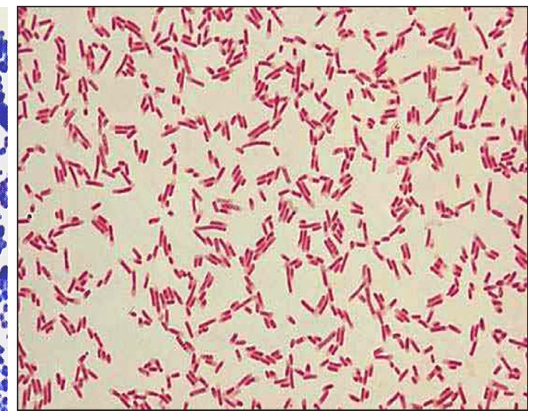
what stain is this
Safranin: gram negative
62
New cards
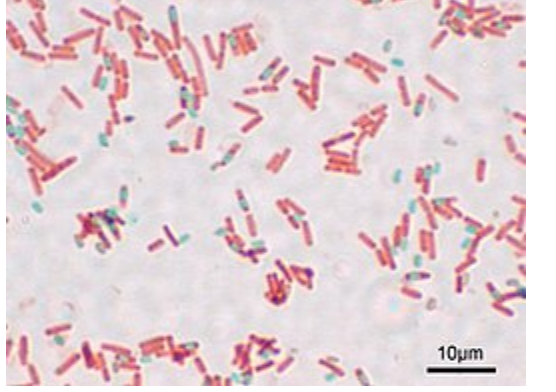
what stain is this
Malachite green: endospores
63
New cards
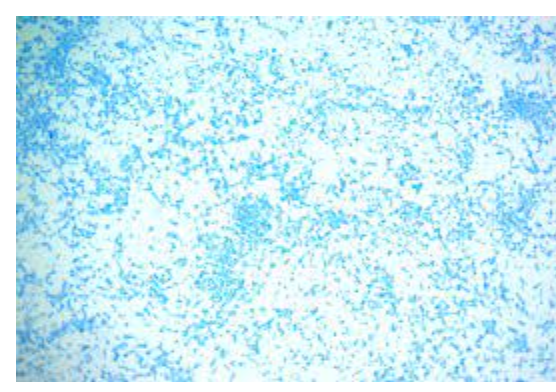
what stain is this
Methylene blue: acid-fast stain
64
New cards
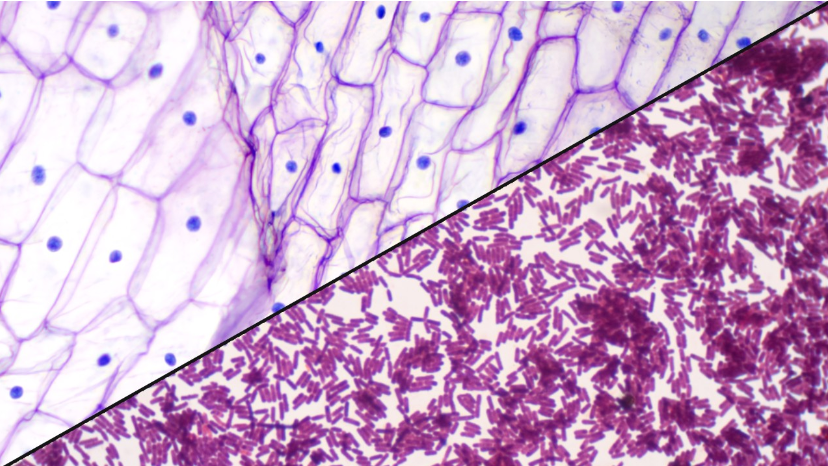
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic cells
left: eukaryotes (HUGE) right: prokaryotes (smol)
65
New cards
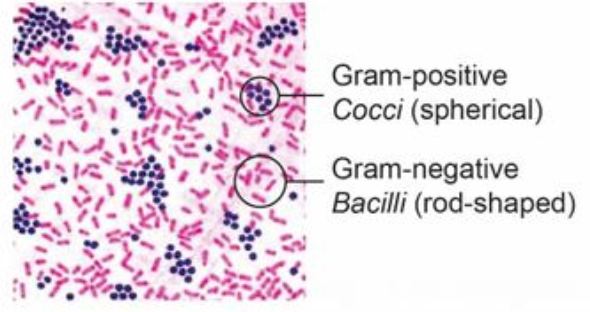
Rods vs. Cocci
NOTE: short rods can be mistaken for cocci; gram negative cocci are rare, it's probably a dehydrated rod
66
New cards
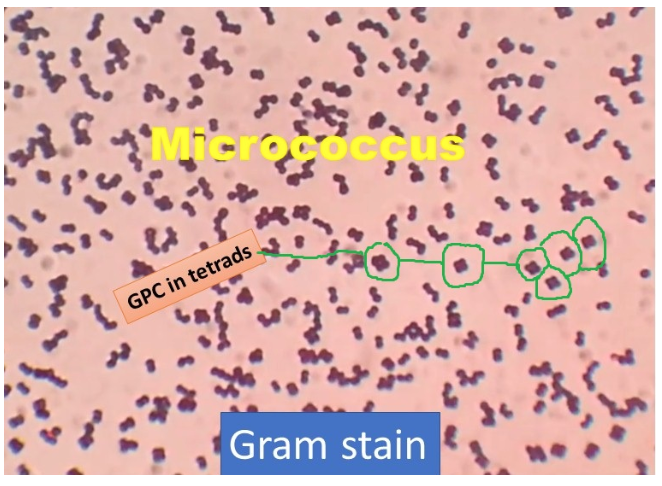
Pairs vs. Tetrads
67
New cards
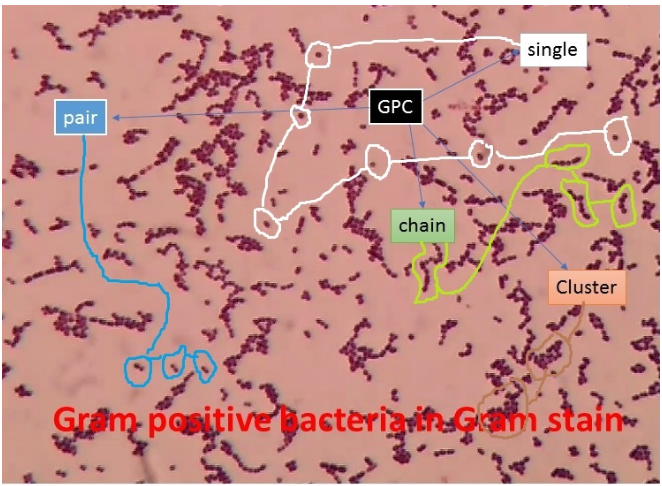
chains vs. single
68
New cards
How do you make a simple stain? What can go wrong?
smear a single-cell thick film on top of the slide (broth or water/solid), smear is air dried and heat fixed, slide is flooded with stain then rinsed with water
WWW: did not heat dry properly so cells washed off with the water, aimed the water at the cells
NOTE: timing isn’t that big of a deal with simple stains
WWW: did not heat dry properly so cells washed off with the water, aimed the water at the cells
NOTE: timing isn’t that big of a deal with simple stains
69
New cards
what is a simple stain
Simple stain: a single stain is used, all cells and structures staint he same color
70
New cards
What is a positive vs. negative stain?
Positive stain: the stain attracts to the cells
Negative stain: the stain stains the background of the slide
Negative stain: the stain stains the background of the slide
71
New cards
Cheek swab -- differentiate prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotes (10 - 100 microns) are much larger than prokaryotic cells (0.1 - 5 microns)
72
New cards
Be able to heat fix and stain a sample of bacteria
Label: source, first name, date, simple, stain abbreviation (CV, Saf, MG, MB)
Smears: solid media (drop of water, spread over slide), liquid media (one drop, spread over slide)
Set hot plate to 3 and warm for at least a minute
Stain time:
Crystal violet: 10 seconds
safranin/malachite green: 30 seconds
Methylene blue: 60 seconds or longer
Rinse with DI water, aim for the labeled part
Blot dry with bibulous paper
Smears: solid media (drop of water, spread over slide), liquid media (one drop, spread over slide)
Set hot plate to 3 and warm for at least a minute
Stain time:
Crystal violet: 10 seconds
safranin/malachite green: 30 seconds
Methylene blue: 60 seconds or longer
Rinse with DI water, aim for the labeled part
Blot dry with bibulous paper
73
New cards
crystal violet stain time
10 seconds
74
New cards
safranin/malachite green stain time
30 seconds
75
New cards
methylene blue stain time
60 seconds or longer
76
New cards
Be able to name and recognize the 4 simple stains we used
Crystal Violet, Safranin, Methylene Blue, Malachite Green
77
New cards
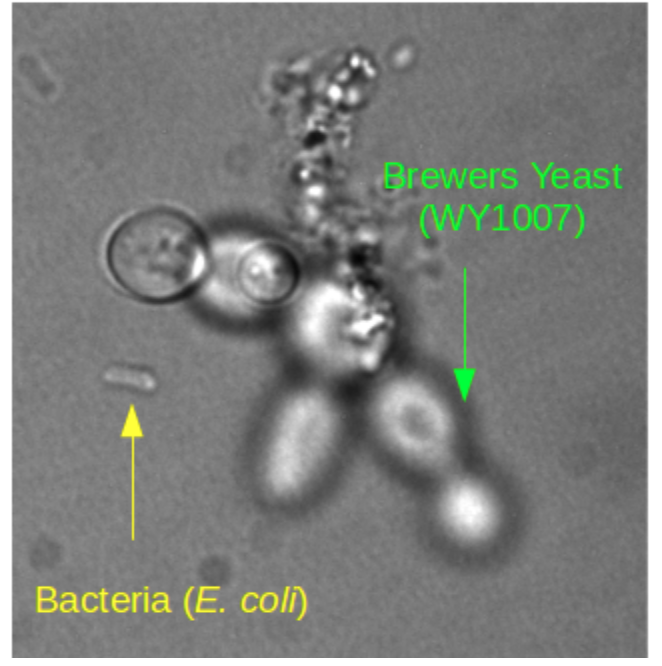
Be able to tell yeast and bacteria apart.
Yeast are huge!! Bacteria are tiny
78
New cards
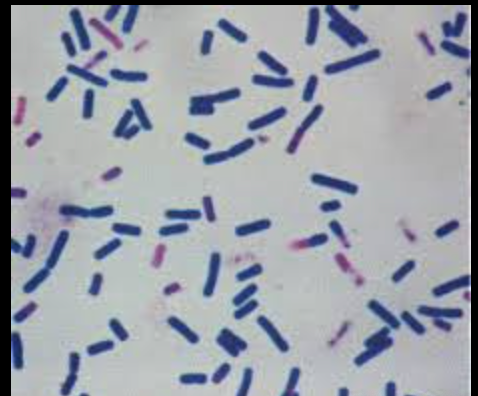
what is it
Rods: hot-dog-shaped
NOTE: gram-negative coco are rare; you probably have a short gram-negative rod
NOTE: gram-negative coco are rare; you probably have a short gram-negative rod
79
New cards
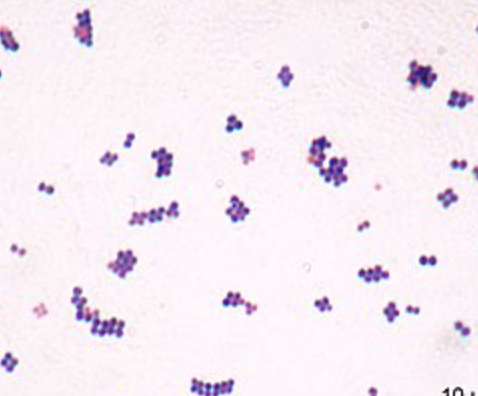
what is it
Cocci: spherical
Tetrads: groups of 4
Cuboidal: packets of 8
NOTE: can appear oval just before cell division
Tetrads: groups of 4
Cuboidal: packets of 8
NOTE: can appear oval just before cell division
80
New cards
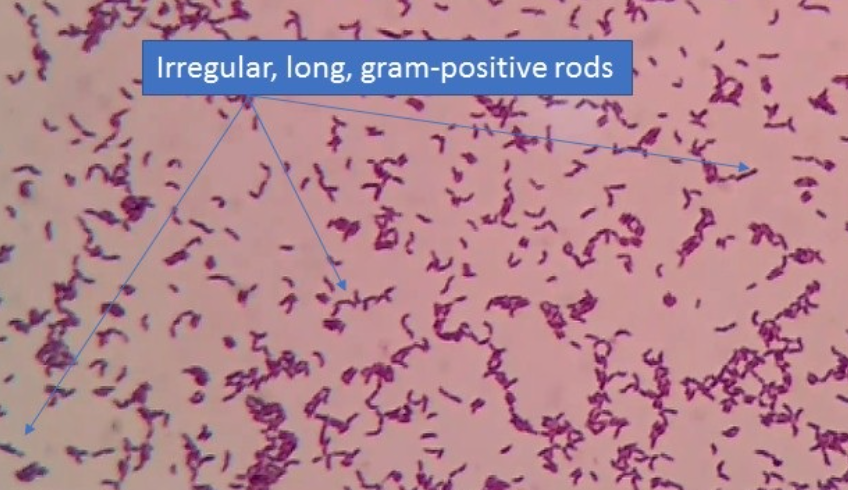
what is it
Irregular rods: dumbbell-shaped, club shaped, cells can change shape over time
81
New cards
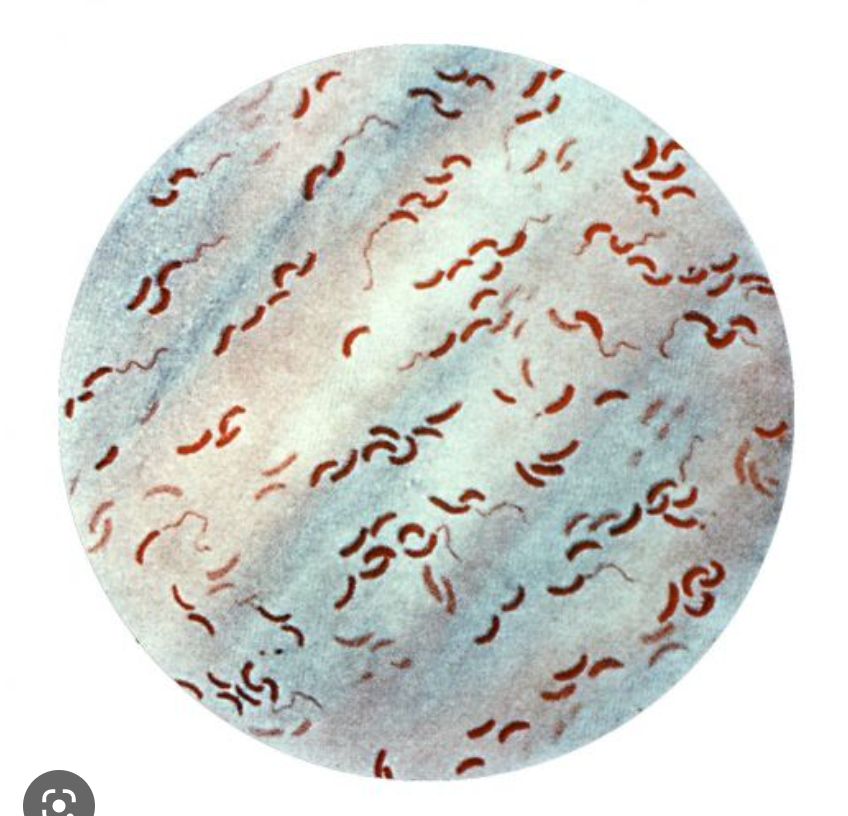
what is it
Vibrio: curve rods like a comma
82
New cards
what is it
Spiral: curly like a corkscrew
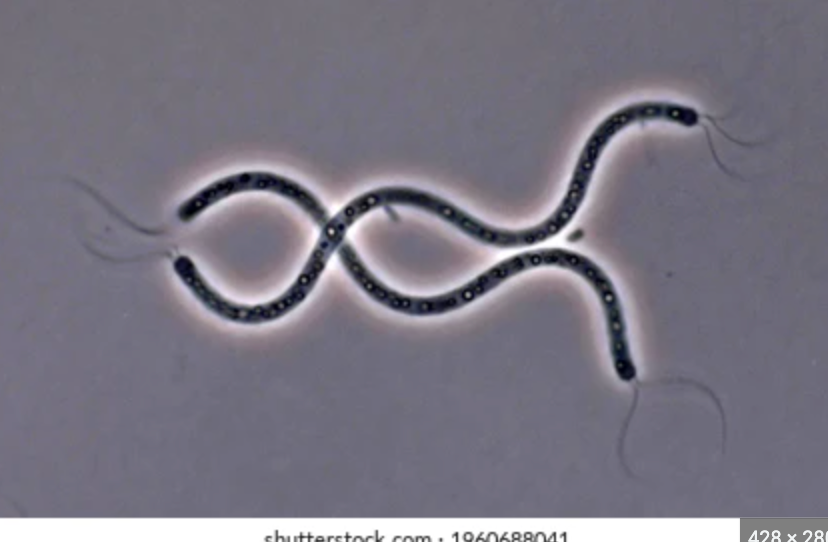
83
New cards
what is it
Spirochetes: spiral-shaped bacteria with many, many turns
84
New cards
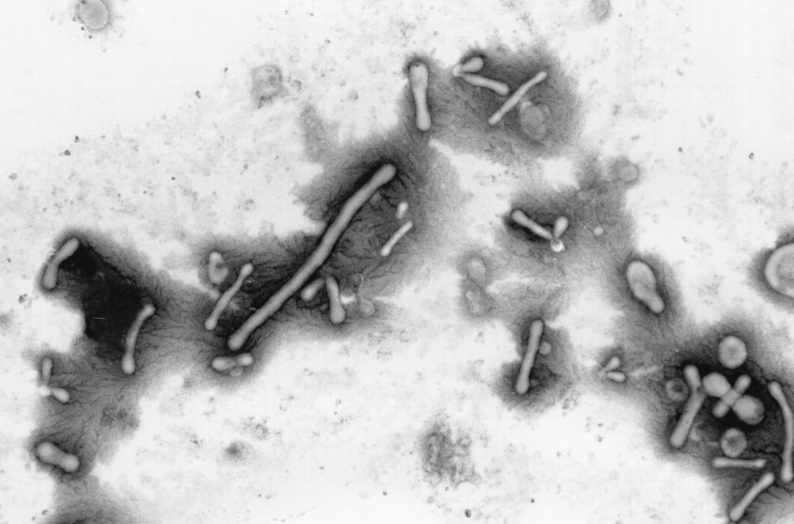
what is it
Pleomorphic: change shape over time, making X’s, Y’s and other irregular shapes
85
New cards
trust wet mount or simple stain?
trust wet mount
86
New cards
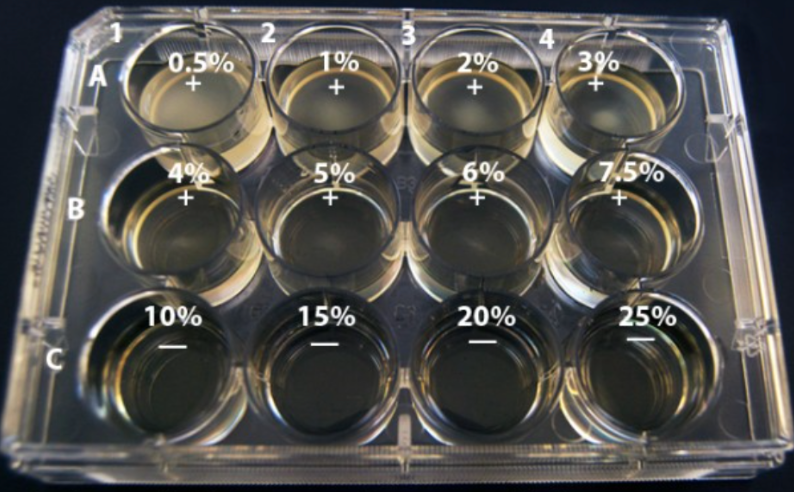
Growth on a 12-well NaCl plate
NaCl tolerance starts from the lowest concentration of NaCl with growth to the highest concentration with growth
optimum NaCl concentration: the one with the most total growth
optimum NaCl concentration: the one with the most total growth
87
New cards

what is it
TSA deep: a confirmatory test for the Gas Pak anaerobic system
88
New cards
how to interpret results for oxygen deep
Aerobic: growth on the surface of the deep and top part of the line
Anaerobic: growth at the bottom of the line only
Facultative anaerobe: growth all the way down the stab line and growth on surface
Microaerophiles: no growth on top and growth in the middle (not top or bottom of line)
Anaerobic: growth at the bottom of the line only
Facultative anaerobe: growth all the way down the stab line and growth on surface
Microaerophiles: no growth on top and growth in the middle (not top or bottom of line)
89
New cards
tolerant vs philic
Tolerant: doesn’t die
Philic: grows
Philic: grows
90
New cards
what is strenotherms:
organisms that function over a narrow range of temperature
91
New cards
what is eurythermal:
microorganisms that grow over a wide range of temperatures (30 - 40 degrees)
92
New cards
what is stenothermals:
microorganisms that grow within a very narrow (
93
New cards
what is psychrophiles:
optimal growth less than 15 degrees Celsius; those that can grow below 15 but have a higher optimal temperature don’t count
94
New cards
what is mesophile:
optimal temperature between 20 to 40 degrees
95
New cards
what is thermophile:
optimal temperature between 45 and 80 degrees
96
New cards
what is hypterthermophile:
optimal temperature above 80 degrees
97
New cards
what is a halophiles:
bacteria that require high concentration of NaCl to grow
98
New cards
what is a hypertonic solution:
greater concentration of solutes than bacterium; water moves out of the bacterium into the hypertonic solution; cell shrinks and die
99
New cards
what is a hypotonic solution:
smaller concentration of solutes than bacterium; water moves into the bacterium; cell swells and bursts
100
New cards
what is a isotonic:
no water moves, bacteria can live