
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
What is bioethics?
Field of study that deals with the ethical implications of biological and medical practice, research, and technology
What is medical ethics?
NOT the same as bioethics, falls within it, specfically looking at how doctors and patients interact
What is the Hippocratic Oath?
Early example of code of ethics for medicine, focused on the patient-physician relationship and maintaining privacy
What is Cicero’s pronouncement?
“let the safety and welfare of the people be supreme law”
What makes up bioethics?
Biological knowledge and human values, both of which adapt over time
What were the doctors’ trials in Nuremberg?
First of the follow-up trials from International Military Tribunal after WWII, for war crimes against humanity committed by Nazi doctors
What is the Nuremberg Code? (DONT MEMORIZE)
Ten aspects:
The voluntary consent of the human subject is essential: legal capacity to give consent, free power of choice (no coercion), sufficient knowledge of subject matter, duty to ensure quality informed consent rests with experimenter
Experiment should be necessary and fruitful for good of society
Based on animal experimentation and prior knowledge
Should avoid unnecessary suffering/injury
No experiments where a priori risk of death/injury occurring (unless helps subject)
No risk which outweighs importance of problem being solved.
Adequate facilities
Qualified researchers ONLY, need skill and care throughout
Subject can stop at any time
the researcher must be prepared to terminate the experiment if necessary.
Why did Nuremberg Code not work?
Not accepted as law or official ethics guidelines by any nation, seen as an obvious response to brutal experimentations (no nuance)
What was the Declaration of Helsinki?
A wide breadth of ethical regulations made by the World Medical Association (includes protection of vulnerable groups, scientific protocols, research ethics, privacy, placebo, research registration/publication)
Why did the Declaration of Helsinki not work?
Controversies, arguments, people couldn’t decide what to accept, Beecher raised 22 examples of questionable science (Beecher’s fails)
What is the Belmont Report?
Response to Tuskegee syphilis study from the National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioural Research, prioritizes respect for persons, beneficence, justice (THIS ONE WORKED)
How did bioethics rise?
Conflicts between technology and human values
Simulating intellectual and moral challenges (people weren’t using religion to guide anymore)
Openness to multidisciplinary work
What are some example theories in bioethics?
Utilitarianism, deontology, descriptive natural law, justice, virtue ethics, ethics of care, principlism
Differentiate the ethics of neuroscience from the neuroscience of ethics
Ethics of neuroscience → ethical, legal and social impact of neuroscience research and the manipulation of the human brain
Neuroscience of ethics → neural underpinnings of morality, free will
What are the 4 pillars of neuroethics?
Brain science and the self, brain science and policy, ethics and practice of brain science, brain science and public discourse
Examples of neuroenhancement drugs?
Purines and methyxanthine derivatives (caffeine, theophylline, theobromine)
Phenylethylamine derivatives (stimulant, relevant to ADHD treatment)
Modafinil (narcolepsy treatment)
What is cognitive neuroenhancement?
“improving the capacities of, or producing new capacities for, healthy individuals by means provided by neuroscience”
What are the issues with this definition of health? “Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity” - WHO (1946)
Unchanged to this day
Issues
Subjective
What does complete mean?
How are these terms defined?
Underlying conditions?
Vague
Creates a binary of healthy/unhealthy rather than a continuum
Other dimensions not included (spiritual wellbeing)
Ableist
Define health vs. disease

What are motivations for pharmacological neuroenhancement?
Responses to increasing demands of society (work, school, private life)
Individual - increased cognition, sleep reduction, mood enhancement, improved executive functions, job market advantages
Society - Increased productivity and efficiency, competition, reduced resting periods
How can pharmacological enhancements be accessed?
Diversion (stealing from friends, peers, family members, someone with prescription)
“Independent suppliers” (dealers)
Pharmacy (prescription OR over the counter medicines)
E-commerce (sold online, rogue pharmacies)
Explain the debate between bioconservatives and technoprogressive optimists
Bioconservatives favour heavy-handed prohibition for pharmaceutical users who have no deficits (ex. okay to use drugs if you have ADHD but not if you’re neurotypical)
Technoprogressive optimists believe in widespread availability of all enhancement drugs, even for those who don’t need them/are neurotypical
What are ethical concerns involved in cognitive enhancement?
Authenticity
Become a different person? Is there a “real/true” self?
Coercion
Feeling unable to opt-out (what if job requires focus, are they harming people by not enhancing?)
Distributive justice
Increase or decrease societal inequality
Fairness (cheating)
Value of achievements
Hubris
Morally defective attitude, ungrateful for what they have
Cognitive liberty
Right to determine our own cognitive state
Intersectional considerations of enhancement?
Gender, racial inequity
Ableism
Holistic definitions of enhancement
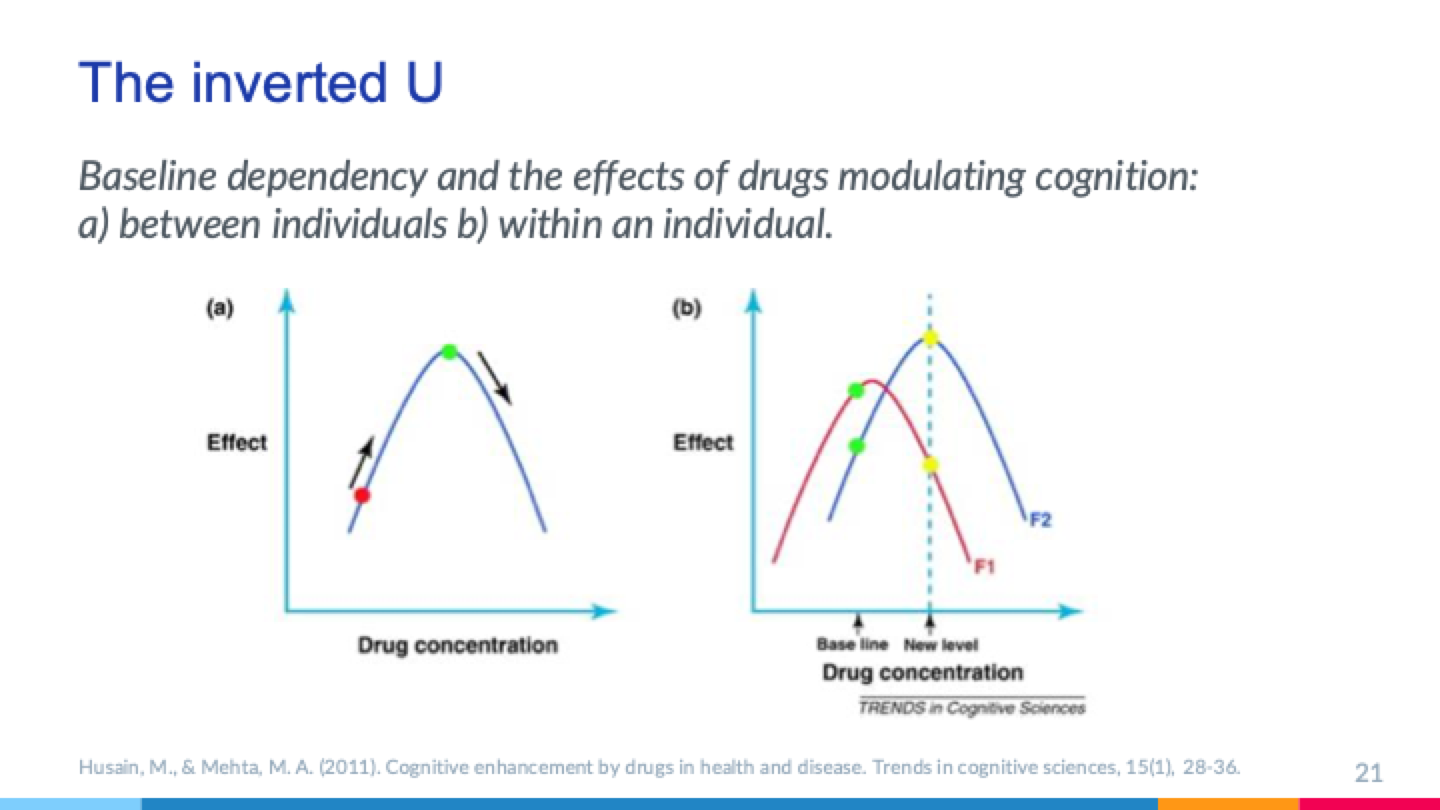
What is the inverted U?
Drugs affect different individuals in different ways (some individuals might improve while others may lose their original capabilities)
Could also cause benefits in one area (i.e. memory) while harming another (i.e. focus)
What are neurotechnologies used for neuroenhancements?
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (variable short-term effects)
Transcranial direct current stimulation (uncertain short-term effects)
Long-term effects are unknown for both, but risks include neurohype, adverse effects, and D2C
What is moral enhancement?
“an increase in the moral value of one’s actions or character”
Moral bioenhancement is when this is achieved using “medical, pharmacological, or biotechnological means”
Can be from increases in:
Empathetic concern
Personal responsibility
Social norm compliance
Respect for societal and global fairness
Empathy and compassion for distant individuals
Moral behaviours
What are 4 principles that bioethicists frequently use?
Autonomy (informed consent)
Should have the freedom to choose
Should not nudge (let people make autonomous judges)
Beneficence (best interests of the patient, can only give positive options for their benefit)
Nonmaleficence (Do no harm)
Justice (Distribute the harms and the benefits equally)
These fall under principilism (uphold as much as possible), NOT deontology (isn’t unethical to not follow one)
What is a contrastive vignette?
Minimally contrastive versions of a master vignette (a story/situation)
Randomly assigned to participants
Participants unaware of contrastive case
Answer identical questions
Between condition measurements
What is a robot, a social robot, and a socially assistive robot?
Robot - “cyber-physical system with sensors, actuators and mobility”
Social robot - a robot that interacts with people
Socially assistive robot - robots that support in care activities like healthcare, rehabilitation or special education through socially interacting with patients (coaching, motivation etc.)
How do social robots improve mental health outcomes for older adults and children?
Older adults:
Decrease loneliness
Decrease in anxiety
Increased medication adherence
Lower need for neuropsychiatric medication in people living with advanced dementia
Improved quality of life
Children:
Improved social and communication skills of children on the autism spectrum
Relief of acute stress and anxiety
Decrease in depressive symptoms
Decrease in distress
Which robot is approved as a biofeedback medical device by the FDA?
PARO, my king <3

What are Asimov’s Laws of Robotics?
A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm
A robot must obey the orders given it by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the first law
A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the first or second law
What are some issues with Asimov’s laws of robotics?
What about harming of human property?
The use of the word “injury” is vague
How will a robot know the outcome of every action?
Difficult to instill nuanced rules into a fixed system
What are the “Principles of robotics” created by Margaret Boden?
Robots should not be designed as weapons except for national security reasons
Robots should be designed and operated to comply with existing law, including privacy
Robots are products, as with other products they should be designed to be safe and secure
Robots are manufactured artefacts: the illusion of emotions and intent should not be used to exploit vulnerable users
It should be possible to find out who is responsible for any robot
What are some issues with the “Principles of robotics” created by Margaret Boden?
Language is still not very operable
Says emotions shouldn’t be used, but this could be a reason why SARs work! (providing companionship)
What counts as a vulnerable user? Is any SAR application in healthcare ethical then?
What are some categories of ethical issues related to social robot use?
Well-being
Privacy/data control
deception
autonomy
Care
Loss of human contact
Legitimacy of the introduction of the SAR
Quality of practice
Justice
Distributive justice (is it ethical to distribute these devices knowing the ethical dilemmas?)
Politics of SAR technology
Responsibility
What are the dimensions of privacy?
Physical (personal space)
Psychological (privacy of values and thoughts)
Social (whether social conversations stay private)
Informational (user data)
What is the privacy paradox?
While many technology users report privacy concerns, not many take actions to protect said privacy.
People feel like privacy is a price we pay for free services
Lack of understanding of implications
People are resigned
How are computers social actors?
Human-computer interactions are inherently social, many human-human interaction phenomena extend to interactions with computers (i.e. treating ChatGPT nicely when talking to it)
What is the definition of privacy?
the claim of individuals, groups, or institutions to determine for themselves when, how, and to what extent information about them is communicated to others
What are 7 design solutions for increasing SAR privacy?
Proactive not reactive; preventive not remedial
Privacy as the default setting
Privacy embedded into design
Full functionality - positive-sum, not zero-sum (not sacrificing privacy for functionality or vice versa)
End-to-end security - full lifecycle protection
Visibility and transparency - keep it open
Respect for user privacy - keep it user-centric
What are some informational privacy considerations?
Capacity of social robots for data collection (including emotions, mental states, personality)
Third-party access to data
Hacking
Collecting information about third parties
Lack of user understanding
What are some psychological privacy considerations in SARs?
Psychological dependence on robots
Reduced self-reflection and autonomy
Vulnerable user groups
What did conceptual vs empirical scoping reviews of SARs show?
Conceptual came up with more privacy concerns, empirically, people did not care that much and focused more on benefits of SARs
What are some real-world privacy failures?
Hello Barbie
Was recording everything a child ever said (which parents coul access)
Info was used to collect marketing information for Mattel
CloudPets
Non-encrypted, information and voice recordings were leaked
What were some initial concerns of structural neuroimaging (MRI)?
Scared of nuclear explosions (was initially called nuclear magnetic resonance)
Even more wary of this during the Cold war
Cost
Economically inaccessible, a service only given to the rich
Cancer
Used to identify cancerWh
Competency
Loud, scary to be in, patients thought it would explode
Healthcare professionals were confused by machine’s output
What is an incidental finding?
Unexpected discovery unrelated to original purpose of examination (specific to imaging)
ex. unexpected masses, evidence of trauma to the brain, aneurysms bleed/stroke
What is the prevalence of different types of IFs?
Depends on IF definition, study population, methods/analysis tools used, etc.
What are some ethical considerations of incidental findings?
Team 1: Obligation to participant
Researchers must look for and disclose information about participant wellbeing
Participants should have patient autonomy
Beneficence
Team 2: Obligation to research
Responsibility of IF burdens researchers and the healthcare system
Consistency between participants
Potential for unwarranted harm to participants from disclosure
Most affected by the ambiguity of the post-disclosure period
Explain the Netherlands Epidemiology of Obesity study and its incidental findings issues?
Study investigating obesity-related diseases/pathophysiology
56 incidental findings found (including malignancy suspects, aneurysms, subdural hematoma and more)
Participants reportedly felt pain in the areas of:
Informed consent
Assumed IFs were disclosed
Unsure if info was shared with medical team
Disclosure
Took too long
Didn’t get to choose method (phone/email etc.)
Information of health info was confusing/misleading
Medical follow up
Period between disclosure and follow-up was worrying
Participants expected GP to support/follow up
Transition from participant to patient
Expected researcher (who they were “doing a favour for by participating”) to give them rapid access to medical care
Assumed all IF info was being given to medical specialist
What are some initial concerns of functional neuroimaginng (fMRI)?
Informed consent (do people know what they’re getting into?)
Incidental findings
Self-evaluation (people can make inaccurate generalized conclusions about themselves following an MRI)
Legal
Educational (could fMRIs diagnose learning disabilities? Only one point in time, inaccurate measure of intelligence)
Economic (neuromarketing, is it ok for businesses to use your brain data for marketing?)
This is just a snapshot of function/connectivity at a particular point in time, does not show full picture
What is consciousness and its relation to imaging?
Consciousness - awareness of surroundings, subjective experience of existence
fMRI can be used in disorders of consciousness, impaired consciousness, vegetative states and more.
Explain false positives and ghost fish
There is a very large sample of voxels in the fish fMRI, which amplifies random correlations, making the dead fish seem like they are still showing brain activity.
Shows that there are
large statistical challenges to keep in mind with fMRI analysis
large rate of false positives
proceed with caution and skepticism
Explain benefits and cons of the portable MRI
Portable MRI uses cloud-based imaging to create a cheap, quick, and convenient alternative to typical MRIs
PROS
Access to healthcare increases
Cheaper and quicker, more accessible in remote regions and rural areas
CONS
Can people in remote areas meaningfully consent? How to communicate in culturally appropriate ways?
What are ethical frameworks of incorporating cloud-based AI into brain scan analysis? Biased?
How will IFs be reported?
How will participants access their brain data?
What are some current privacy concerns in neuroimaging technology?
Concern that Amazon and similar health platforms will harvest consumer health data from patients
Concern about large data breaches occurring in healthcare organizations
What do surveys capture in neuroethics?
Public attitudes
Factors in decision-making
Patient experience
Why is collecting patient experience data important?
Quality improvement, accreditation, improving practices, research, actual caring
What are important questions to think about when surveying?
What is active data capture?
What is passive data capture?
What are the elements of a good vs bad survey?

Validated or custom?
Has someone done it before? (build on what exists)
Pilot
Buzzfeed (short, punchy, pictures)
Question order and wording