Semester 1 - Review US History
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/183
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:12 PM on 11/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
184 Terms
1
New cards
What were the causes of the American Revolution?
The French & Indian War, Proclamation of 1763, Intolerable Acts, Stamp Act, taxation w/o Representation in Parliament, Boston Massacre
2
New cards
Intolerable Acts
In response to Boston Tea Party, 4 acts passed in 1774, Port of Boston closed, reduced power of assemblies in colonies, permitted royal officers to be tried elsewhere, provided for quartering of troop's in barns and empty houses.

3
New cards
john adam
A Massachusetts attorney & politician who was a strong believer in colonial independence. He helped draft and pass the Declaration of Independence. He served as the second President of the United States.

4
New cards
Samuel Adams
He had been a leader of the Sons of Liberty. He is credited with provoking the Boston Tea Party...

5
New cards
Ben Franklin
American patriot, writer, printer, and inventor. During the Revolutionary War he persuaded the French to help the colonists.

6
New cards
King George III
He was the king of England from 1760 to 1820, exercised a greater hand in the government of the American colonies than had many of his predecessors. Colonists were torn between loyalty to the king and resistance to acts carried out in his name. Was considered a tyrant king.

7
New cards
Thomas Jefferson
He was a delegate from Virginia at the Second Continental Congress and wrote the Declaration of Independence. He later served as the third President of the United States.

8
New cards
Thomas Paine
Patriot and writer whose pamphlet Common Sense, published in 1776, convinced many Americans that it was time to declare independence from Britain. He also wrote The American Crisis to urge colonists to join the fight against the British.

9
New cards
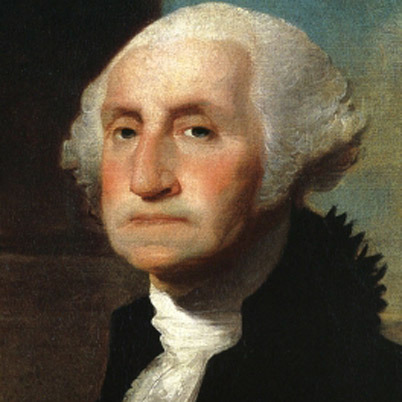
George Washington
Commander of the Continental Army. He had led troops (rather unsuccessfully) during the French and Indian War, and had surrendered Fort Necessity to the French. He was appointed commander-in-chief of the Continental Army, and was much more successful in this second command.

10
New cards
Lexington and Concord
A 1775 conflict between colonial minutemen & British soldiers attempting to take the colonists' large store of arms; began the Revolutionary War, On April 19, 1775, the first shots were fired in Lexington, starting the war. The battles resulted in a British retreat to Boston.
11
New cards
Saratoga
The battle which was the turning point of the Revolution because after the colonists won this major victory, the French decided to support the Americans with money, troops, ships, etc.
12
New cards
Yorktown
Last major battle of the Revolutionary War. Cornwallis and his troops were trapped in the Chesapeake Bay by the French fleet. He was sandwiched between the French navy and the American army. He surrendered October 19, 1781.
13
New cards
Valley Forge
Washington and troops were low on supplies, food, and clothing. Because it was a harsh winter, 1/5 of soldiers died. Name given to the 1777-1778 encampment at Valley Forge by the American military under General Washington. It was America's first real effort to field a professional military against the British.

14
New cards
Treaty of Paris of 1783
This treaty ended the Revolutionary War, recognized the independence of the American colonies, and granted the colonies the territory from the southern border of Canada to the northern border of Florida, and from the Atlantic coast to the Mississippi River.

15
New cards
Loyalist
A person who supported the British during the American Revolution

16
New cards
Propaganda
material distributed by those in favor of a specific cause and reflecting their point of view, Ideas spread to influence public opinion for or against a cause.
17
New cards
Patriot
A person who supported the colonists during the American Revolution, a colonist who wanted to break free from Britain's rule

18
New cards
First Continental Congress
September 1774, delegates from twelve colonies sent representatives to Philadelphia to discuss a response to the Intolerable Acts

19
New cards
Second Continental Congress
They organized the Continental Army, called on the colonies to send troops, selected George Washington to lead the army, and appointed the committee to draft the Declaration of Independence.
20
New cards
Continental Army
Army formed by the Second Continental Congress and led by General George Washington

21
New cards
Common Sense
A pamphlet written by Thomas Paine that claimed the colonies had a right to be an independent nation.
22
New cards
Sons of Liberty
a group of colonists who formed a secret society to oppose British policies at the time of the American Revolution.

23
New cards
Ally
a country that agrees to help another country achieve a common goal, ie. American Revolution - French were allies.
24
New cards
Boston Massacre
British soldiers fired into a crowd of colonists who were teasing and taunting them. Five colonists were killed. The colonists blamed the British and the Sons of Liberty and used this incident as an excuse to promote the Revolution.

25
New cards
Representation in Parliament
Colonists felt that the laws and taxes passed by the British were unfair because they had no____________________.
26
New cards
What were the strengths of the British?
They had a strong well-trained army and navy along with a strong central government with food, ammunition and the support of colonial loyalists and Native Americans.
27
New cards
Declaration of Independence
The document written by Thomas Jefferson and approved by representatives of the American colonies in 1776 that stated their grievances against the British monarch and declared their independence.

28
New cards
Paul Revere
American silversmith remembered for his midnight ride to warn the colonists in Lexington and Concord that British troops were coming (1735-1818)

29
New cards
Marquis de Lafayette
He was very rich and noble when he arrived in America at the age of 19 years old. He believed in the liberty that the Americans were fighting for and asked to help. He became a general on Washington's staff and fought hard. He was known as "the soldier's friend," and is buried in france but his grave is covered with earth from Bunker Hill.

30
New cards
boycott
to refuse to buy items from a particular country. The colonists upheld a __________against British goods.
31
New cards
minutemen
Member of a militia during the American Revolution who could be ready to fight in a minute.

32
New cards
natural rights stated in the Declaration of Independence
life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness
33
New cards
Quartering Act
March 24, 1765 - Required the colonials to provide food, lodging, and supplies for the British troops in the colonies.

34
New cards
Spain and France
supported the colonist's war for independence; were allies of the colonists
35
New cards
American Revolution
The spreading of ideas of Independence, brought on by the enlightenment philosophers, also helped to spark the French Revolution.

36
New cards
Parliament
body of government in Great Britain, acts as both the executive and legislative.
37
New cards
French and Indian War
due to the costly war, the king began taxing the colonists which led to a lot of tension between Britain and the colonists

38
New cards
Boston Tea Party
Colonists (mostly smugglers and the Sons of Liberty) angry over the enforcement of (lower) taxes on tea protested by throwing the tea into the harbor. They dressed up as Indians and caused millions of $$$ in damages.

39
New cards
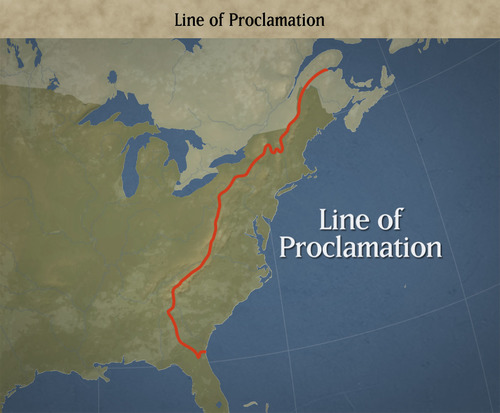
Proclamation of 1763
The British king forbade the colonists from moving into lands west of the Appalachian mountains
40
New cards
Tea Act
Tax on all British tea

41
New cards
Stamp Act
a tax on all printed materials - Really angered the colonists because it was a tax on everything.

42
New cards
Americanization
This process was designed to make immigrants more "Americanized". It included learning to dress, speak, and act like other Americans. This was done through the schools.
43
New cards
Assimilation
is the process by which a person or a group's language and/or culture come to resemble those of another group.

44
New cards
Andrew Carnegie
This man was the founder of the Carnegie Steel Company & promoted philanthropy among wealthy industrialists known as the Gospel of Wealth.
45
New cards
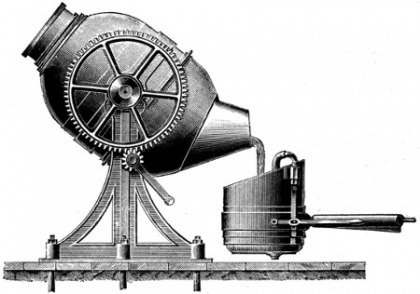
Bessemer Process
Used by Andrew Carnegie, made the production of steel more efficient, allowing for mass production.
46
New cards
Big Business
During the Gilded Age, the economy saw a rise in this, often seen as more efficient and could produce products cheaply but also as unfair competition and controlled the government

47
New cards
Chinese Exclusion Act
This was the first law (1882) to limit the immigration of a specific group.

48
New cards
Dawes Act
authorized the President of the United States to survey American Indian tribal land and divide it into allotments for individual Indians.

49
New cards
Gilded Age
Mark Twain coined this phrase to represent an era where things look good on the outside but are not really that good.

50
New cards
Homestead Act
This act motivated more Americans to settle in the west by promising 160 acres in exchange for cultivating the land for 5 years.

51
New cards
Immigrants
This group of people who came to America, were opposed by Nativists, and attributed to urbanization.
52
New cards
Labor Unions
These are formed in response to poor working conditions and low wages. (Ex: Knights of Labor, American Federation of Labor)

53
New cards
Laissez Faire
little government regulation in business. It is known as a "Hands Off Approach"; no anti-trust legislation.

54
New cards
Monopoly
total control of a type of industry by one person or one company

55
New cards
Nativist
a person who supports a policy of favoring longtime inhabitants as opposed to immigrants.

56
New cards
Robber Barons
an American capitalist who become rich by an means necessary. Seen as unethical

57
New cards
Rural
Americans move from this to the urban areas because of increased job opportunities in the cities.
58
New cards
Standard of Living
The new technological innovations in both transportation and communication saw an improvement of material comfort available to a person or community.
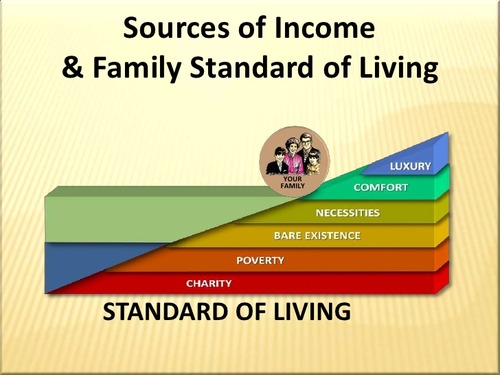
59
New cards
Urban
having to do with cities
60
New cards
Transcontinental Railroad
Accelerated communication and migration between east and west
61
New cards
Captains of Industry
Term for business leaders who created a technological revolution and gave money to charities
62
New cards
Patents
inventors get exclusive right to use or license their inventions
63
New cards
Vertical integration
controls of all steps involved in the production of a finished product.
64
New cards
Horizontal Integration
Gaining complete control of competing companies in the same industry.
65
New cards
Buffalo
This animal was used by Plains Indians for hides, meat, and bones; it was almost hunted to extinction by American hunters.
66
New cards
George Pullman
Best known for his company's production of the "sleeping car" for railroad travel, and for the 1894 labor strike surrounding it's production.
67
New cards
Gospel Of Wealth
This was the hypothesis, originally proposed by Andrew Carnegie, that wealth was the great end and aim of man, and that those with it had a responsibility to put it to good use.
68
New cards
Horatio Alger
He was an author of inspirational adventure stories for boys with the main idea that virtue and hard work overcome poverty.
69
New cards
Interstate Commerce Commission
This was a governmental agency formed in 1887 by Grover Cleveland to regulate railroads.
70
New cards
J. P. Morgan
He was a U.S. banker and financier who was a leader in corporate finance and industrial mergers in the late 1800s and early 1900s.
71
New cards
Sherman Antitrust Act
This law was passed in 1890 in order to limit the power and the formation of business monopolies.
72
New cards
Subsidy
This is financial assistance from the government to encourage the production of or the purchase of a good.
73
New cards
Cornelius Vanderbilt
American shipping and railroad industrialists who merged RR lines and offered the first rail service from New York City to Chicago.
74
New cards
Collective Bargaining
Workers negotiating as a group with employers for higher wages and better working conditions
75
New cards
American Federation of Labor
craft union made up of skilled white men. Led by Samuel Gompers
76
New cards
Pullman Strike
Pullman company lowered wages and kept rent the same which led to a strike by workers. American Railway Union joined the Pullman workers in their strike
77
New cards
Knights of Labor
Led by Terrance Powderly, Membership for ALL (skilled & unskilled) All races and ethnicity welcomed
78
New cards
Wounded Knee
This is the site in South Dakota where, in 1890, US soldiers massacred over 150 Lakota men, women, and children in response to the Battle of Little Bighorn.
79
New cards
barbed wire
invention used to close off the open range in the West. (cattle)
80
New cards
social darwinism
belief used to justify the practice of laissez faire. Survival of the fittest applied to society- Individuals should work hard for a better life.
Justified discrimination against immigrants.
Justified discrimination against immigrants.
81
New cards
Bimetallism
This monetary standard is based on the inclusion of two precious metals- usually gold and silver- and was a major issue in the Populist Movement in the United States in the late-19th Century.
82
New cards
Political Machine
This term refers to a political structure in which a powerful 'boss' commands the support of followers who receive favors in exchange for their efforts.
83
New cards
Populist
This was the movement that advocated government control of railroads and currency expansion. Supported by farmers.
84
New cards
Gospel of Wealth
Book written by Andrew Carnegie, spoke of the responsibility of the rich to share their money with the needy.

85
New cards
Tenement Housing
type of building where poor immigrants lived
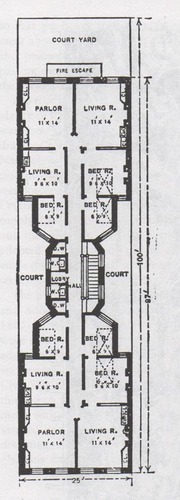
86
New cards
Philanthropy
charity; a desire or effort to promote goodness

87
New cards
JP Morgan
An influential banker and businessman who bought and reorganized companies. His US Steel company would buy Carnegie steel and become the largest business in the world in 1901

88
New cards
Agricultural
relating to farming or rural matters

89
New cards
Sweatshop
A shop or factory where workers work long hours at low wages under unhealthy conditions

90
New cards
Settlement Houses
Community centers located in the slums and near tenements that gave aid to the poor, especially immigrants

91
New cards
Assembly Line
In a factory, an arrangement where a product is moved from worker to worker, with each person performing a single task in the making of the product.
92
New cards
Consumer Goods
products and services that satisfy human wants directly

93
New cards
Mass Production
Process of making large quantities of a product quickly, cheaply by using machines and an assembly line

94
New cards
Mechanization
Using machines to do tasks that human or animal labor used to do
95
New cards
John D. Rockefeller
This man was the founder of Standard Oil & could have been considered a Robber Baron from his greed for power.

96
New cards
Thomas Edison
perfected the light-bulb & expanded electricity during the Gilded Age

97
New cards
Start of Reconstruction
1865, marked by Andrew Johnson's presidency and the creation of five military districts and the Freedman's bureau
98
New cards
End of reconstruction
Compromise of 1877 withdrew troops from the South; The North's waning resolve led to many in the North to no longer support Reconstruction.
99
New cards
Battle of Gettysburg
July 1st-3rd (1863) Union leaders defeated General Lee. A turning point battle during the Civil War
100
New cards
Appomattox
Famous as the site of the surrender of the Confederate Army under Robert E. Lee to Union commander Ulysses S. Grant