Anatomy and Physiology Lab Practical 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/235
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:30 AM on 9/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
236 Terms
1
New cards
Anatomy
study of structure
2
New cards
Gross Anatomy (Macroscopic Anatomy)
Study of structures that can be seen with the naked eye
3
New cards
Microscopic Anatomy
deals with structures that can only be seen with a microscope
4
New cards
Cytology
study of cells
5
New cards
Histology
study of tissues
6
New cards
Regional Anatomy
the study of the interrelationships of all structures in a specific body region
7
New cards
Systemic Anatomy
the study of the structures that make up a discrete body system (a group of structures that work together to performa unique body function
8
New cards
Homeostasis
the state if steady internal conditions maintained by living things
9
New cards
Cell
the smallest independently functioning living organism
10
New cards
Tissue
a group of similar cells that perform a particular function
11
New cards
Organelle
tiny functioning units within a cell
12
New cards
Organ
a group of tissues that perform one or more specific functions
13
New cards
Organ System
a group of organs that work together to to perform major functions to meet physiological needs of the body
14
New cards
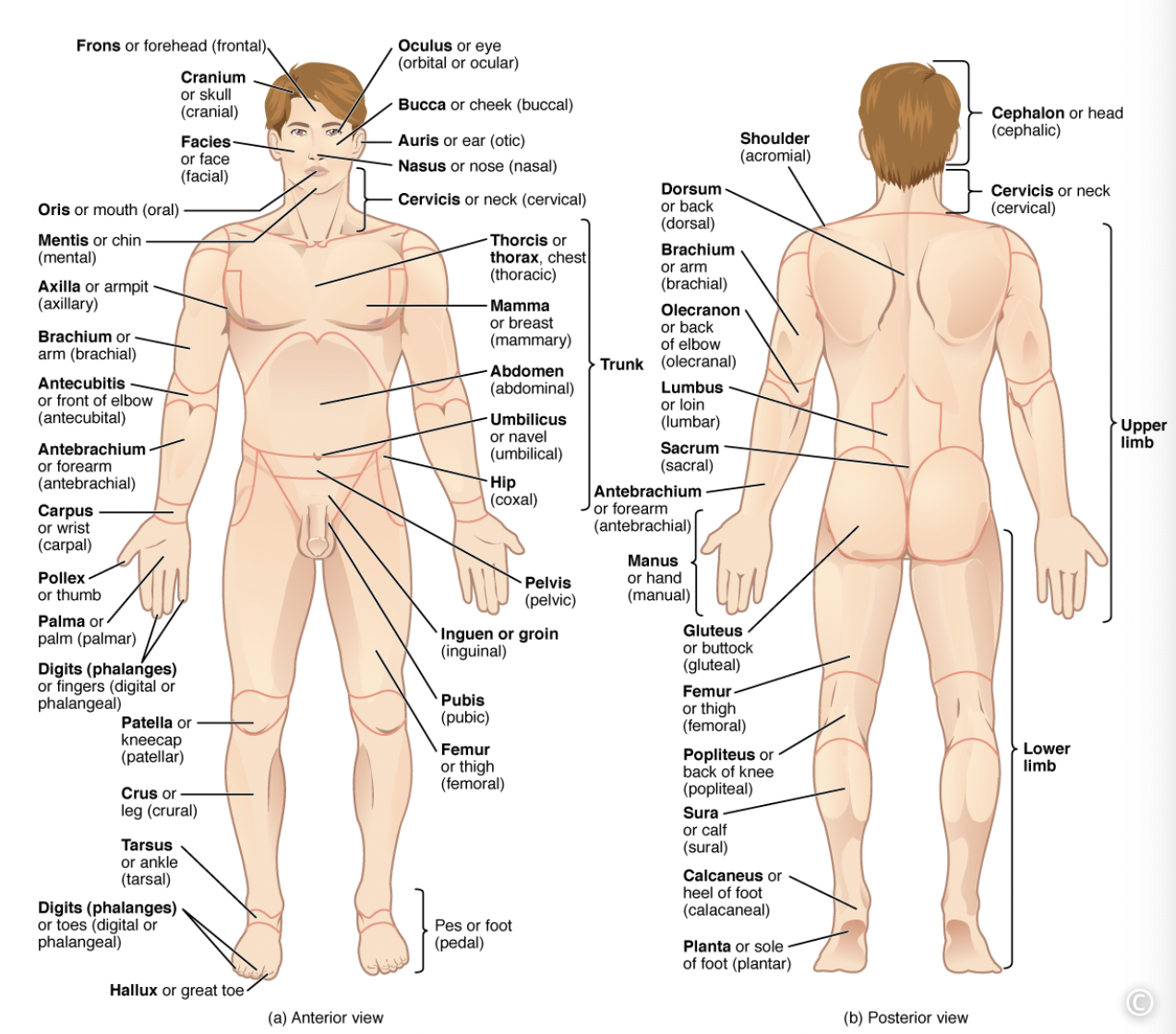
Anatomical Position
To stand erect with arms at the sides and palms of the hands turned forward
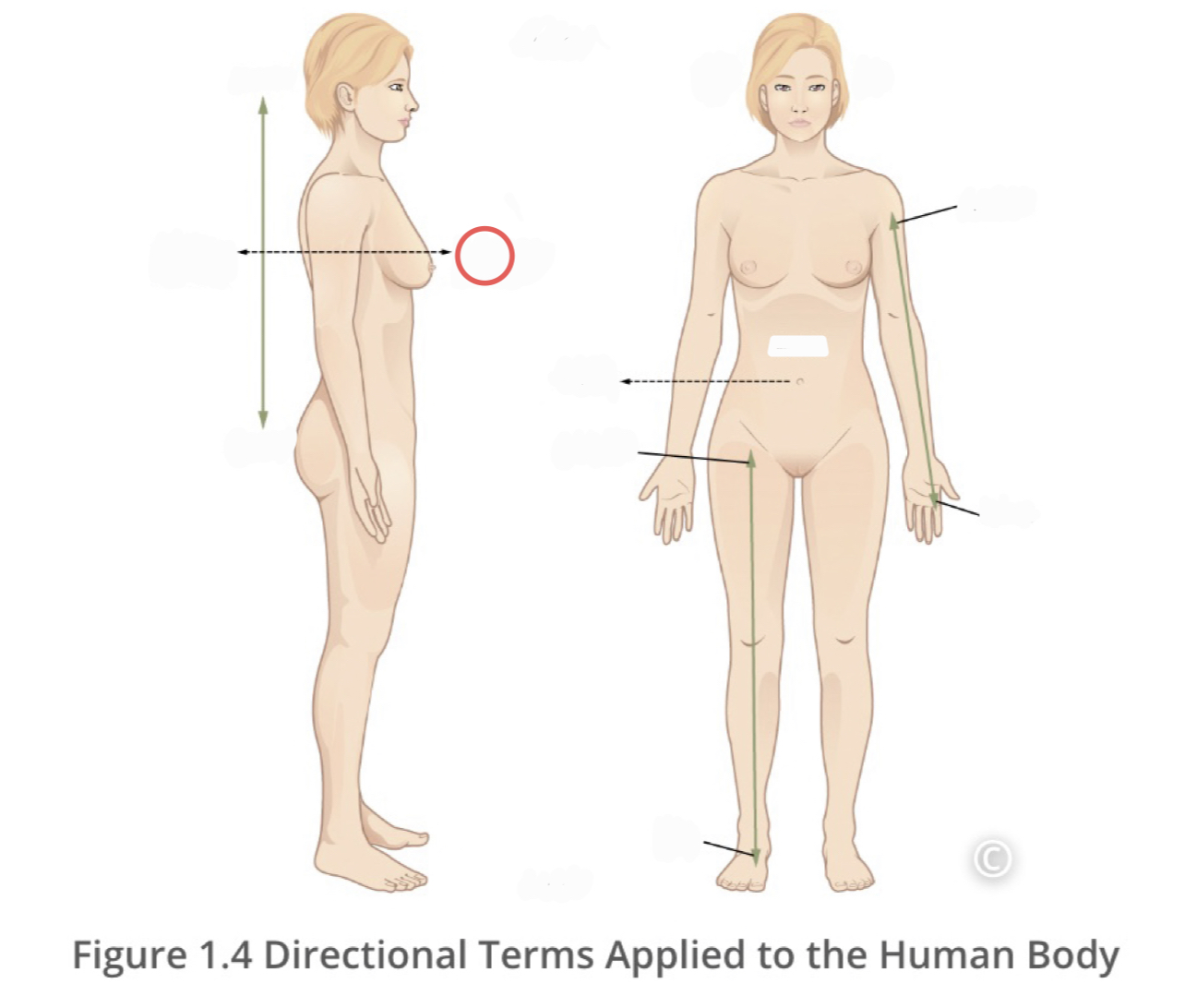
15
New cards
Anterior (ventral)
describes the front or direction toward the front of the body
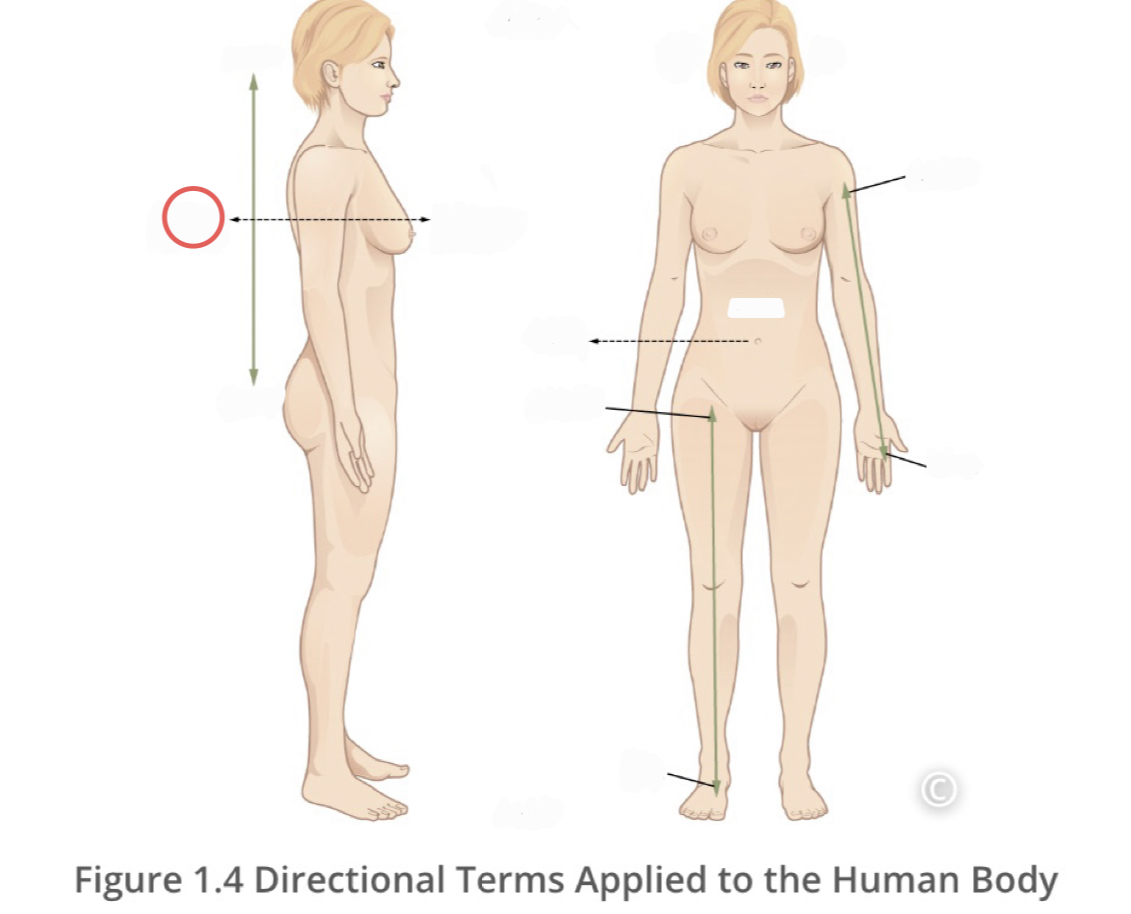
16
New cards
Posterior (dorsal)
describes the back or direction toward the back of the body
17
New cards
Superior (cranial)
a position above or higher than another part of the body
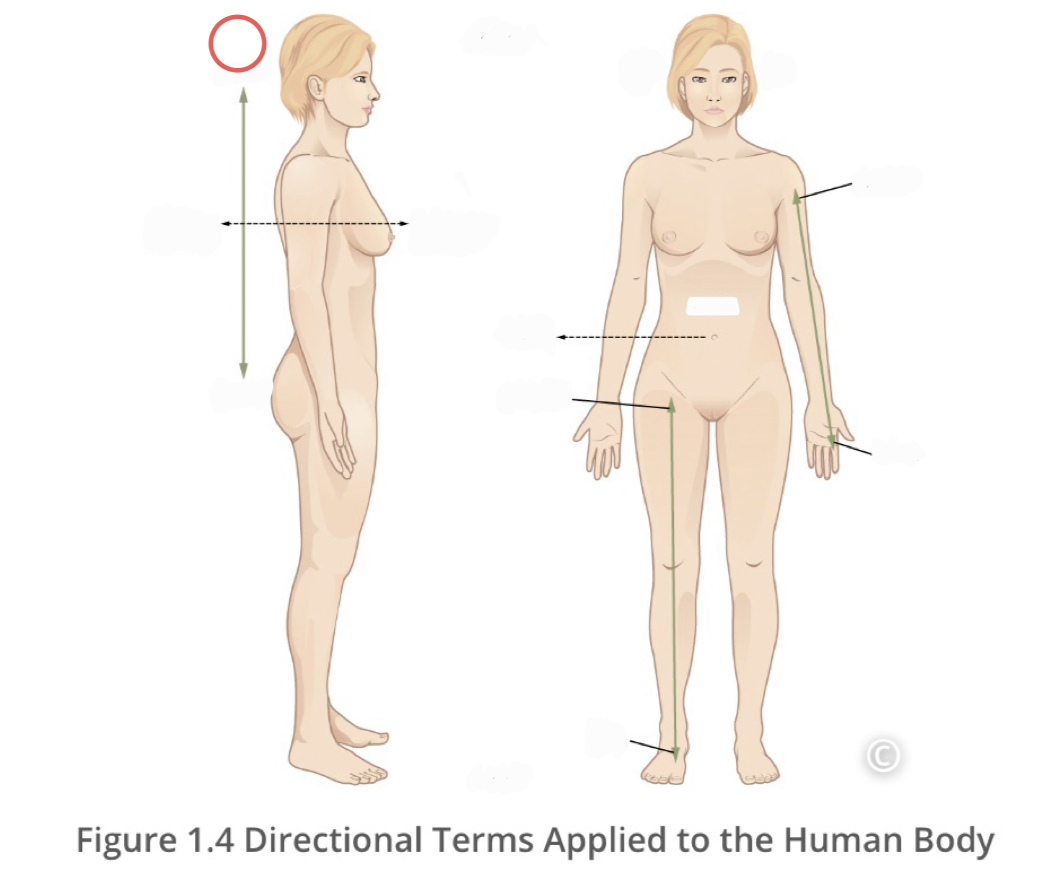
18
New cards
Inferior (caudal)
describes a position below or lower than another part of the body
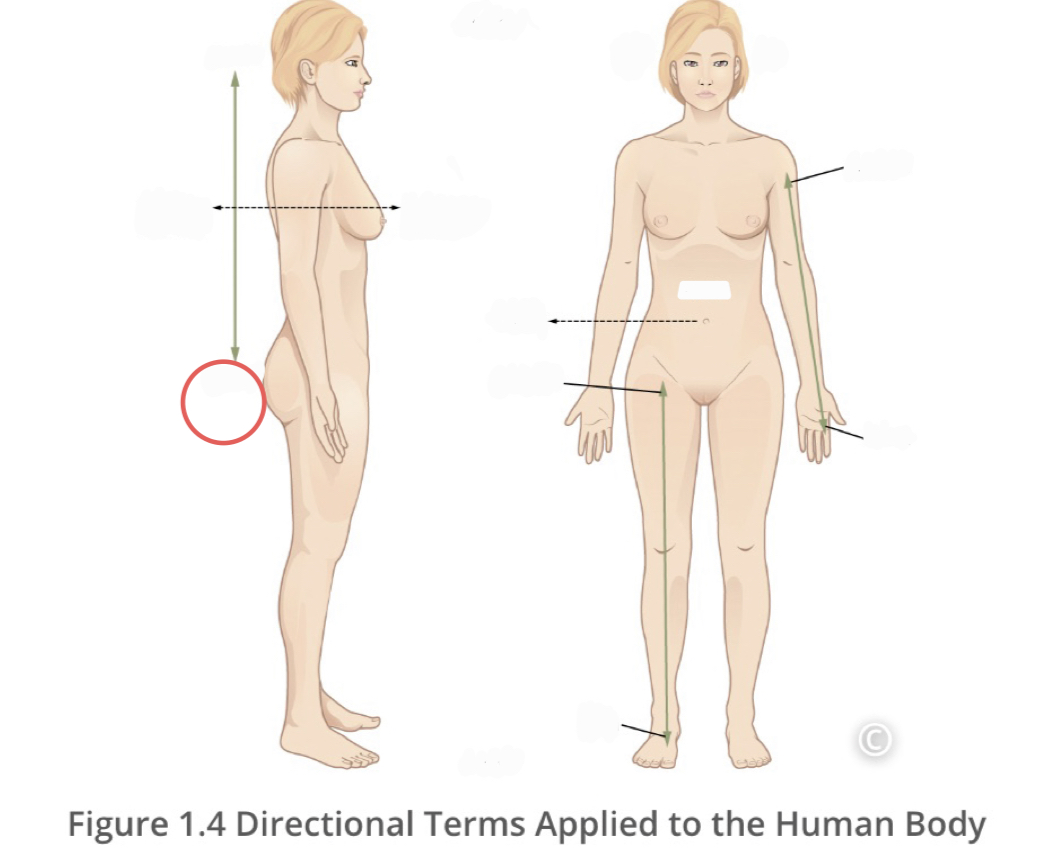
19
New cards
Lateral
describes the side or direction away from the middle of the body
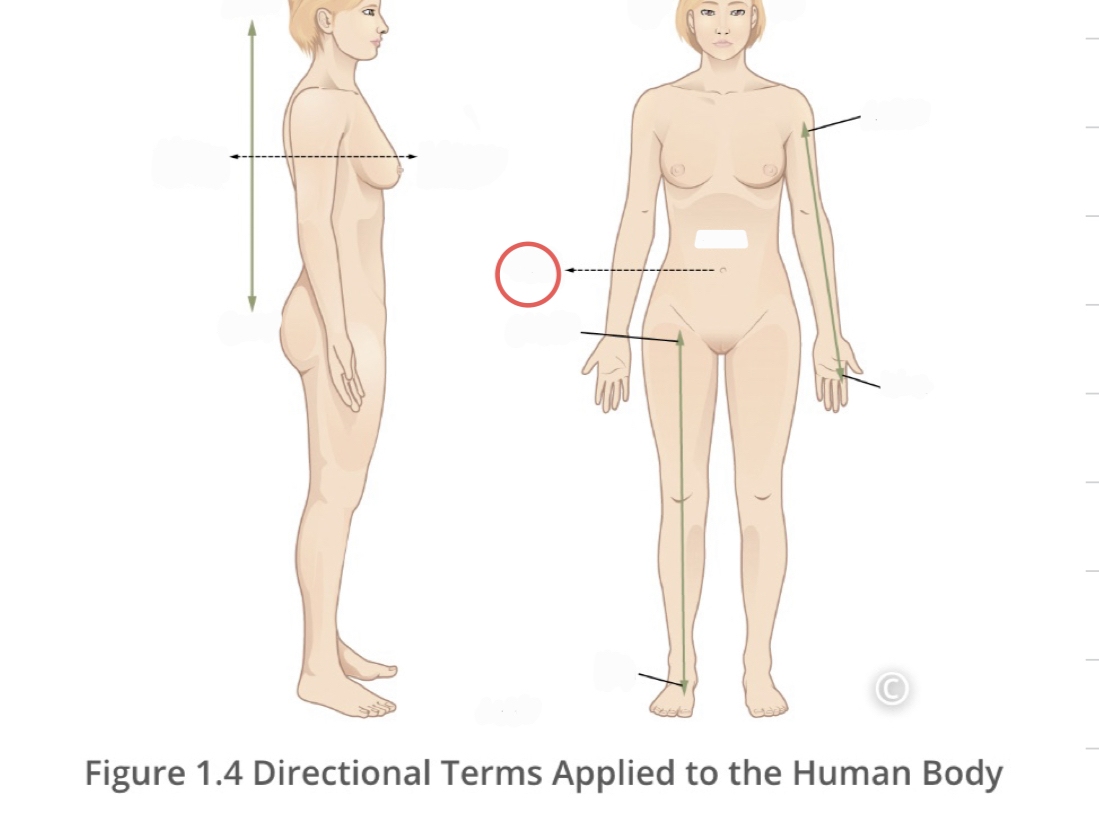
20
New cards
Medial
describes the middle or direction toward the middle of the body
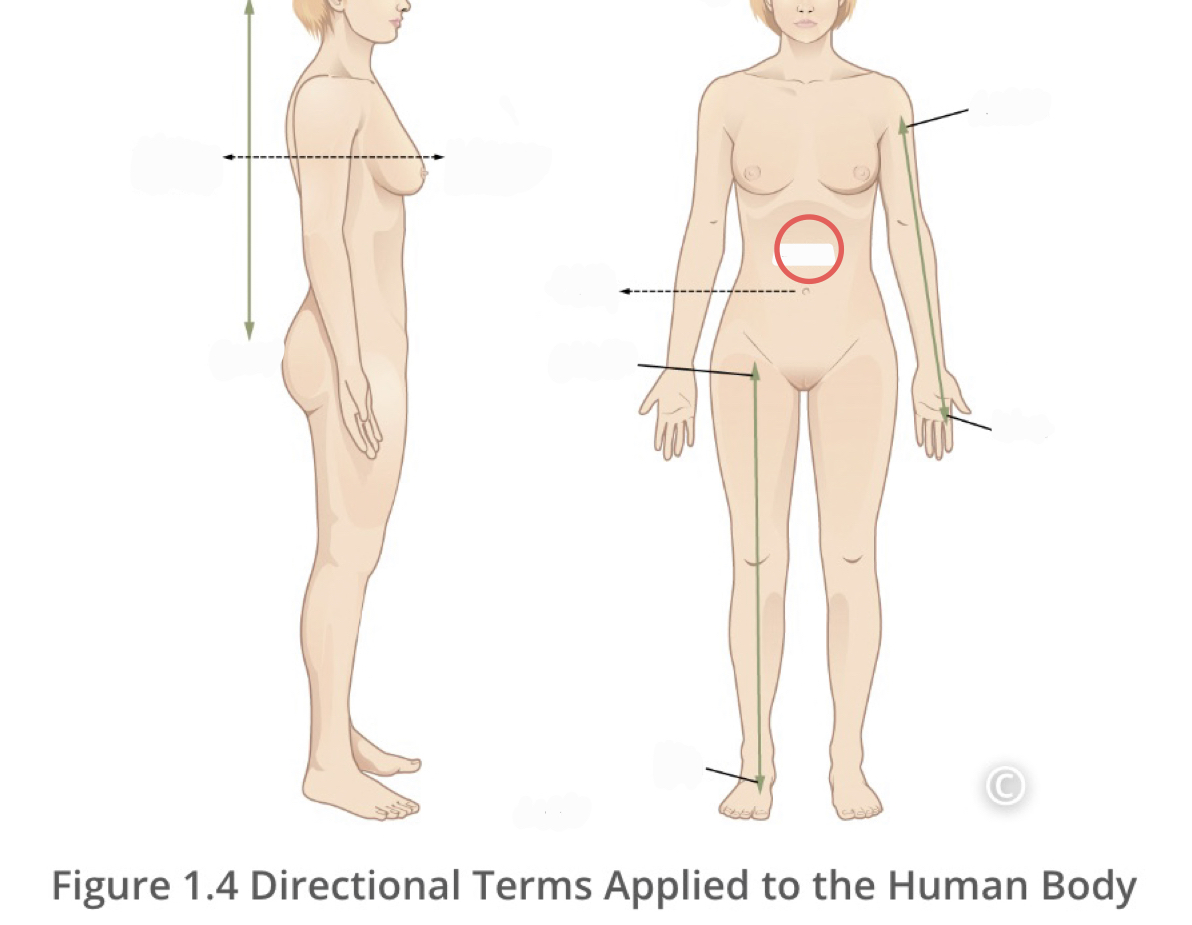
21
New cards
Proximal
describes a position in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or trunk of the body
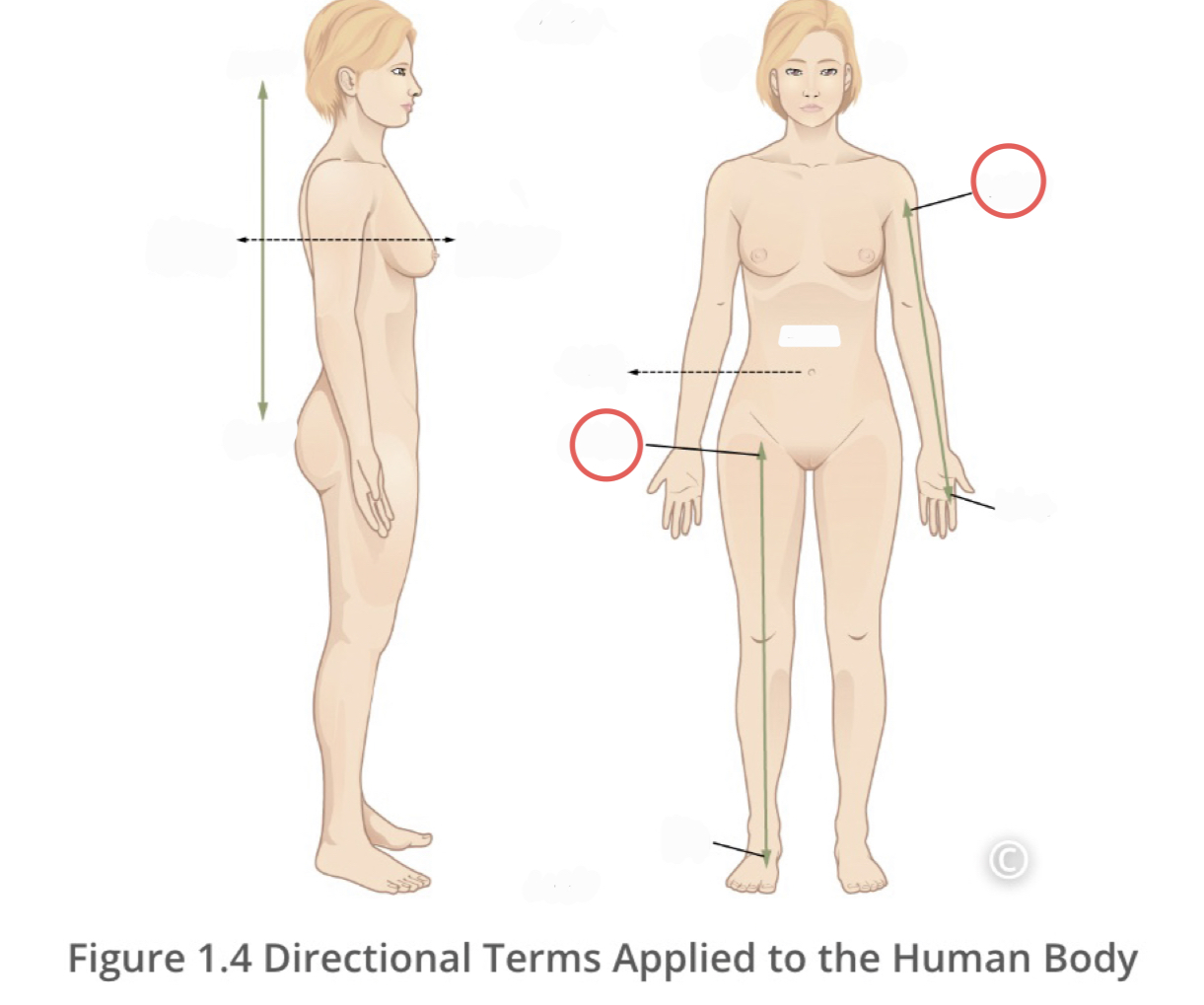
22
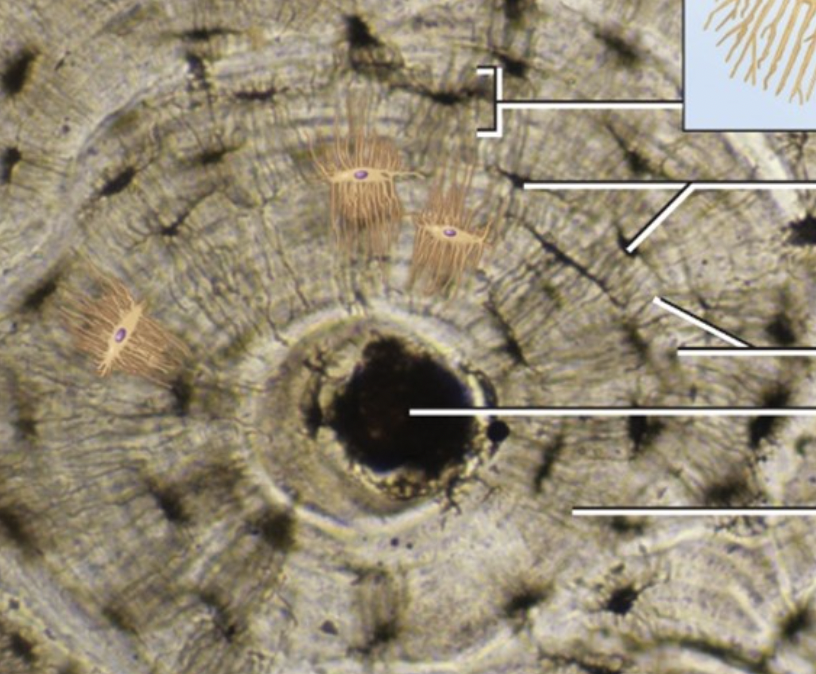
New cards
Distal
describes a position in a limb that is farther from the point of attachment to the trunk of the body
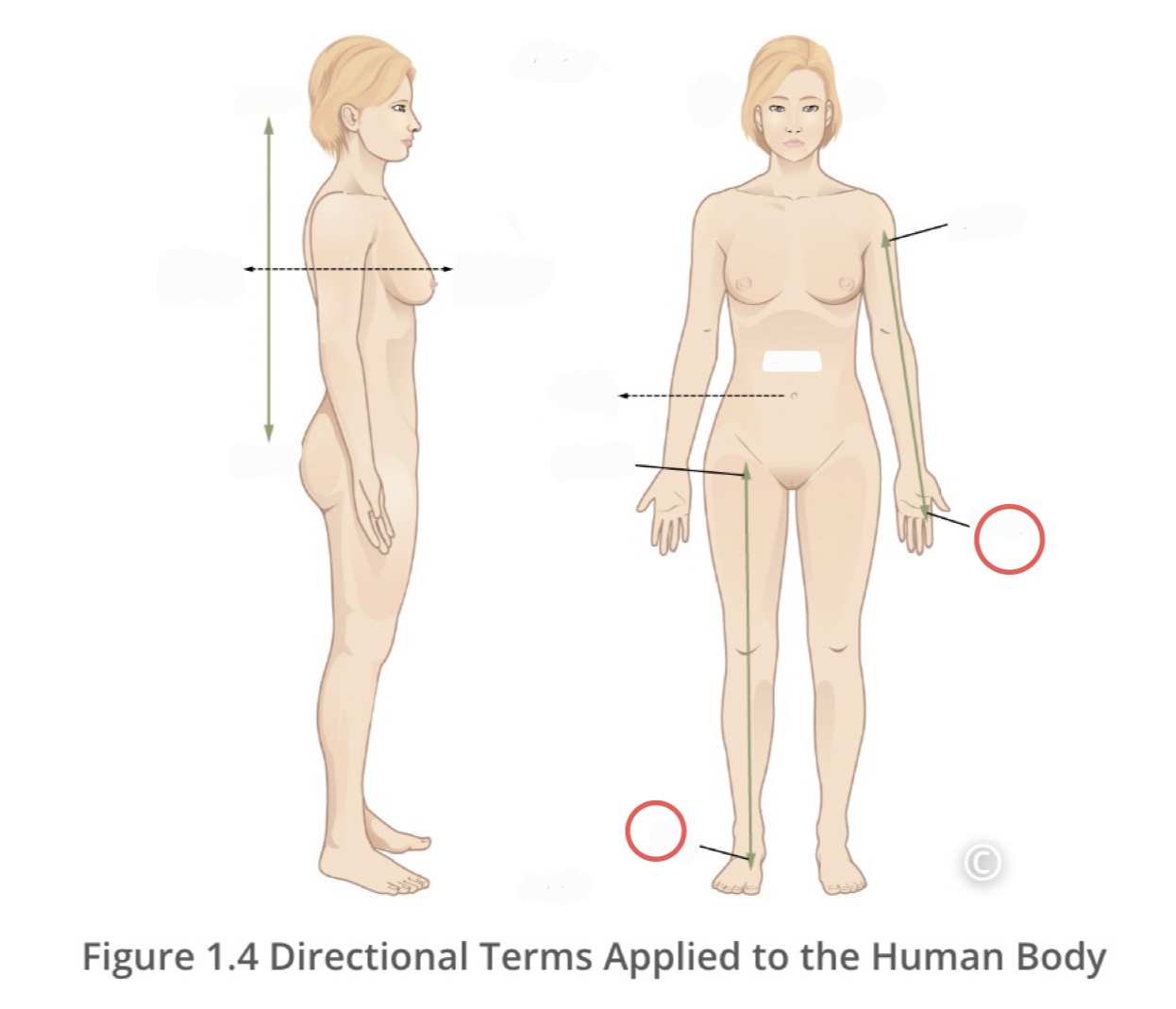
23
New cards
Contralateral
describes structures found on different sides of the body
24
New cards
Ipsilateral
describes structures found on the same side of the body
25
New cards
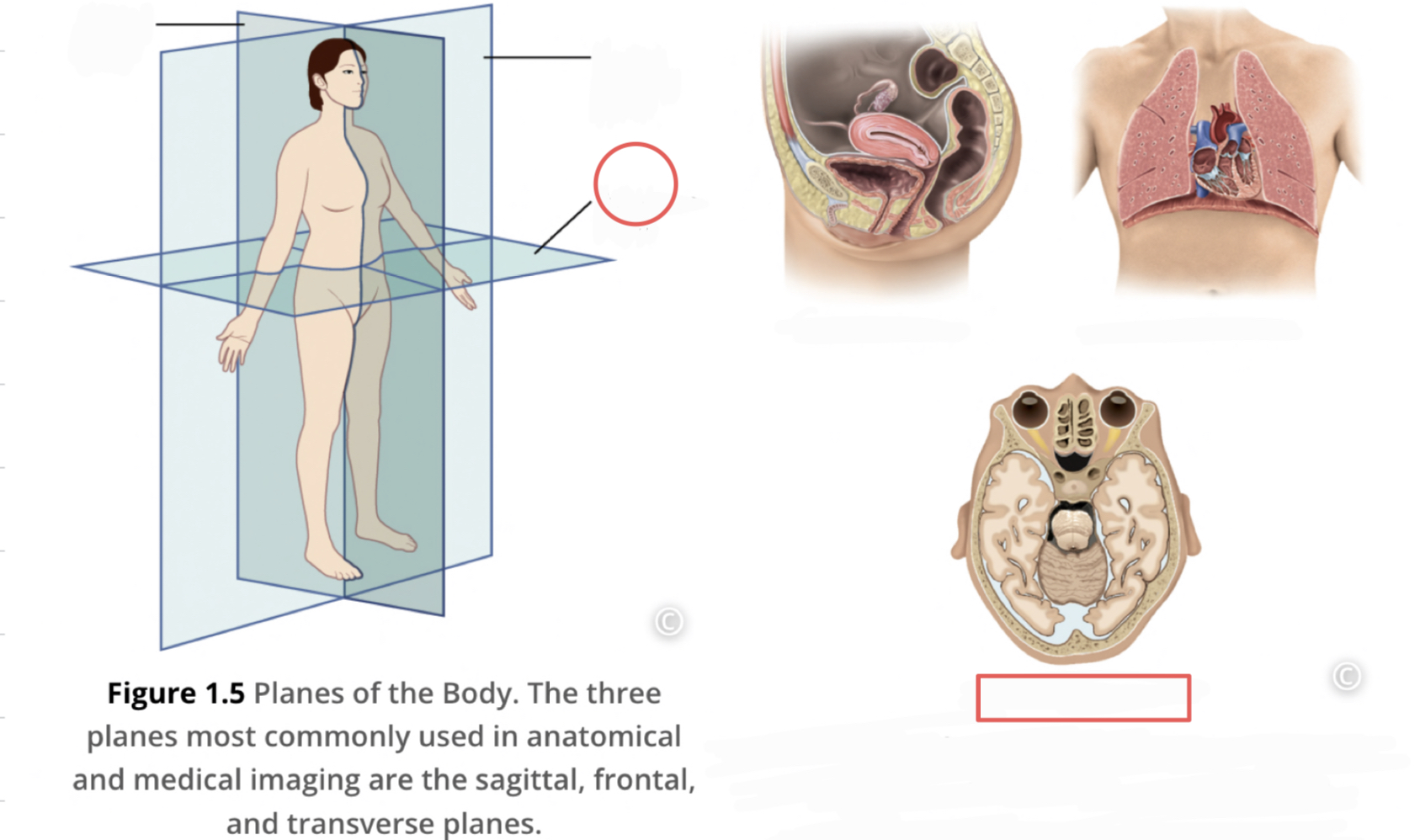
Sagittal Plane
divides the body or organ vertically into right and left sides (Midsagittal plane is a line right down the middle of the body)
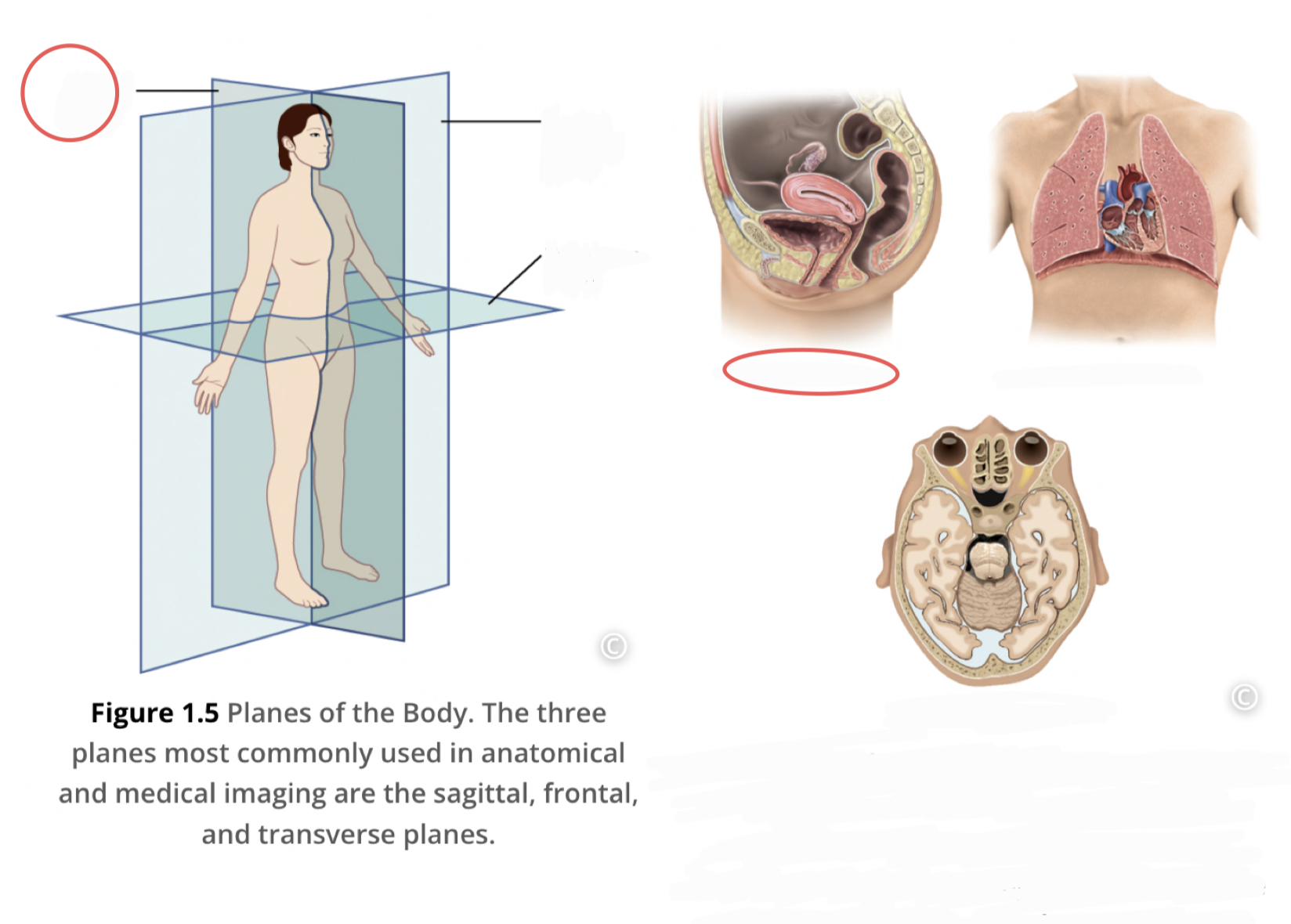
26
New cards
Frontal Plane (coronal plane)
divides the body or organ into anterior and posterior portions
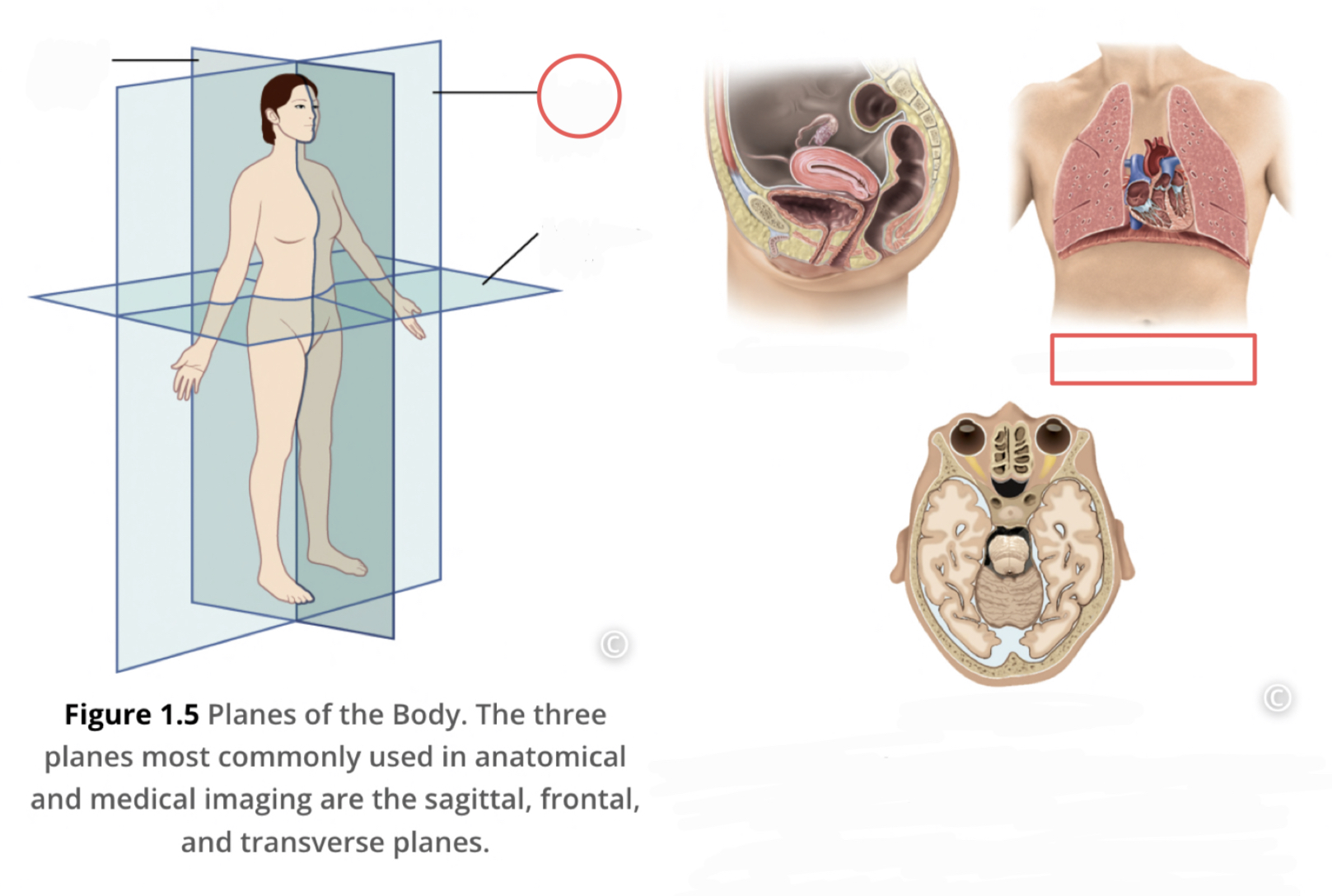
27
New cards
Transverse Plane
divides body or organ horizontally into upper and lower portions, produce cross sections
28
New cards
Oblique Plane
a diagonal cut between longitudinal and horizontal planes, produces uneven sections
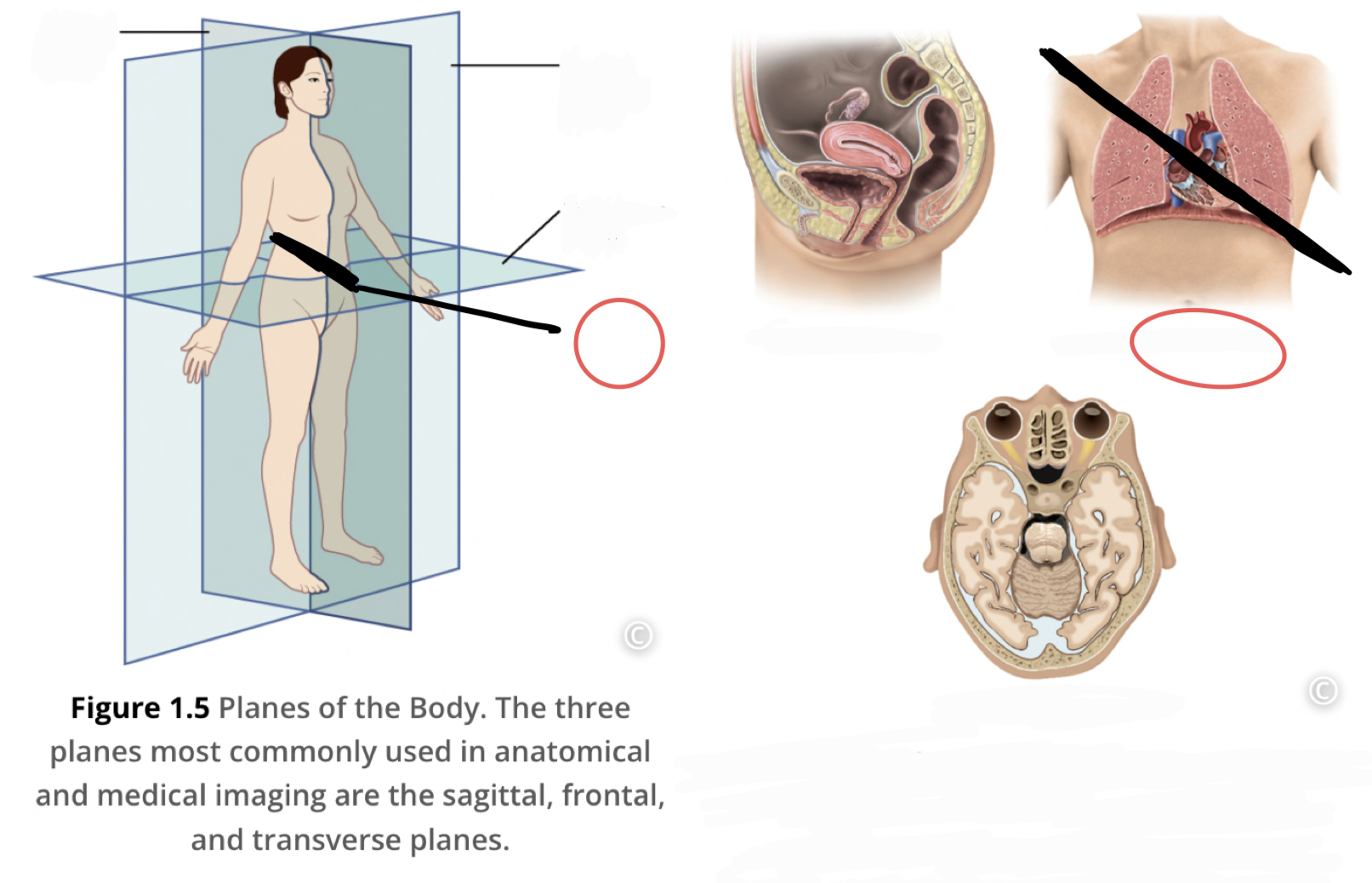
29
New cards
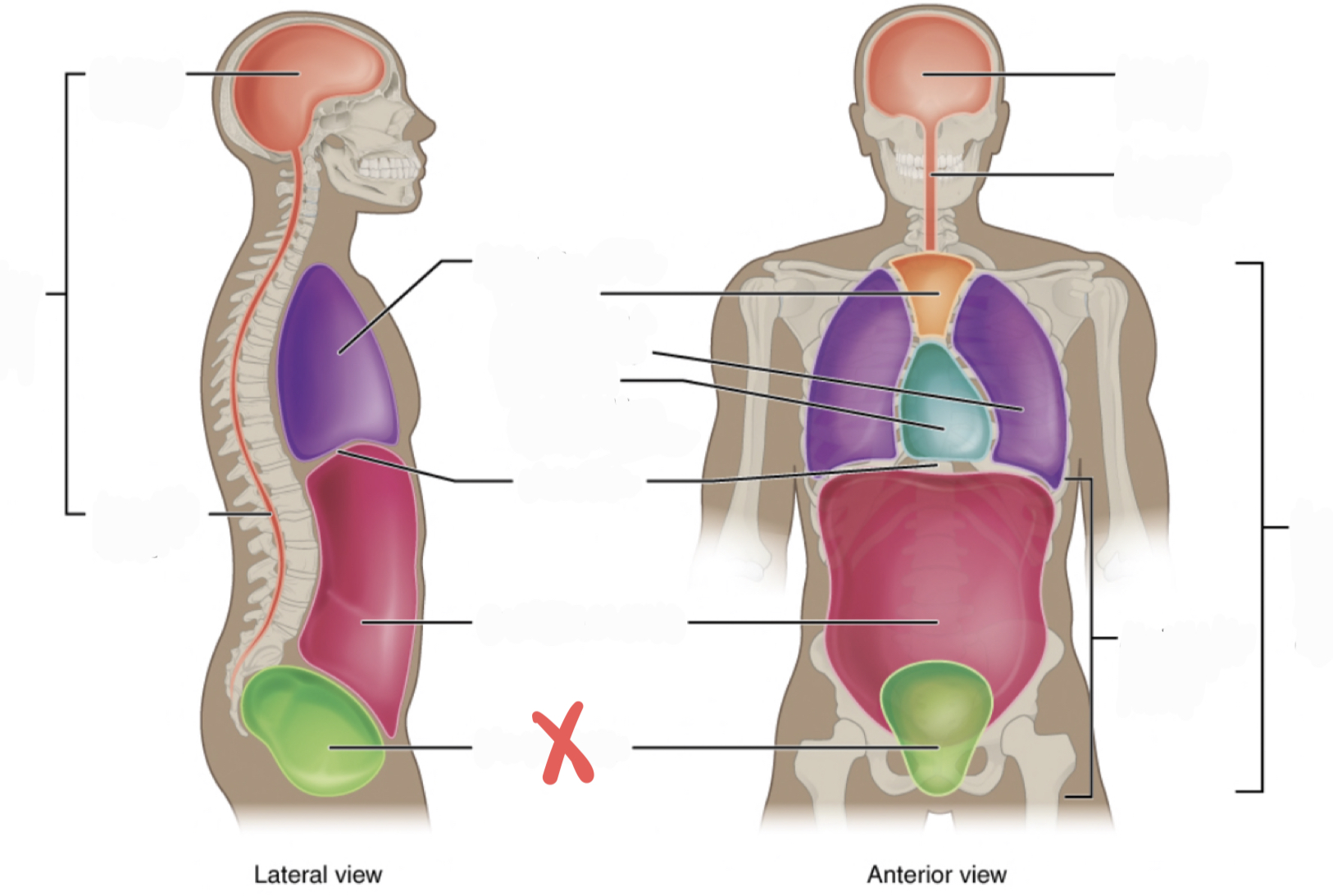
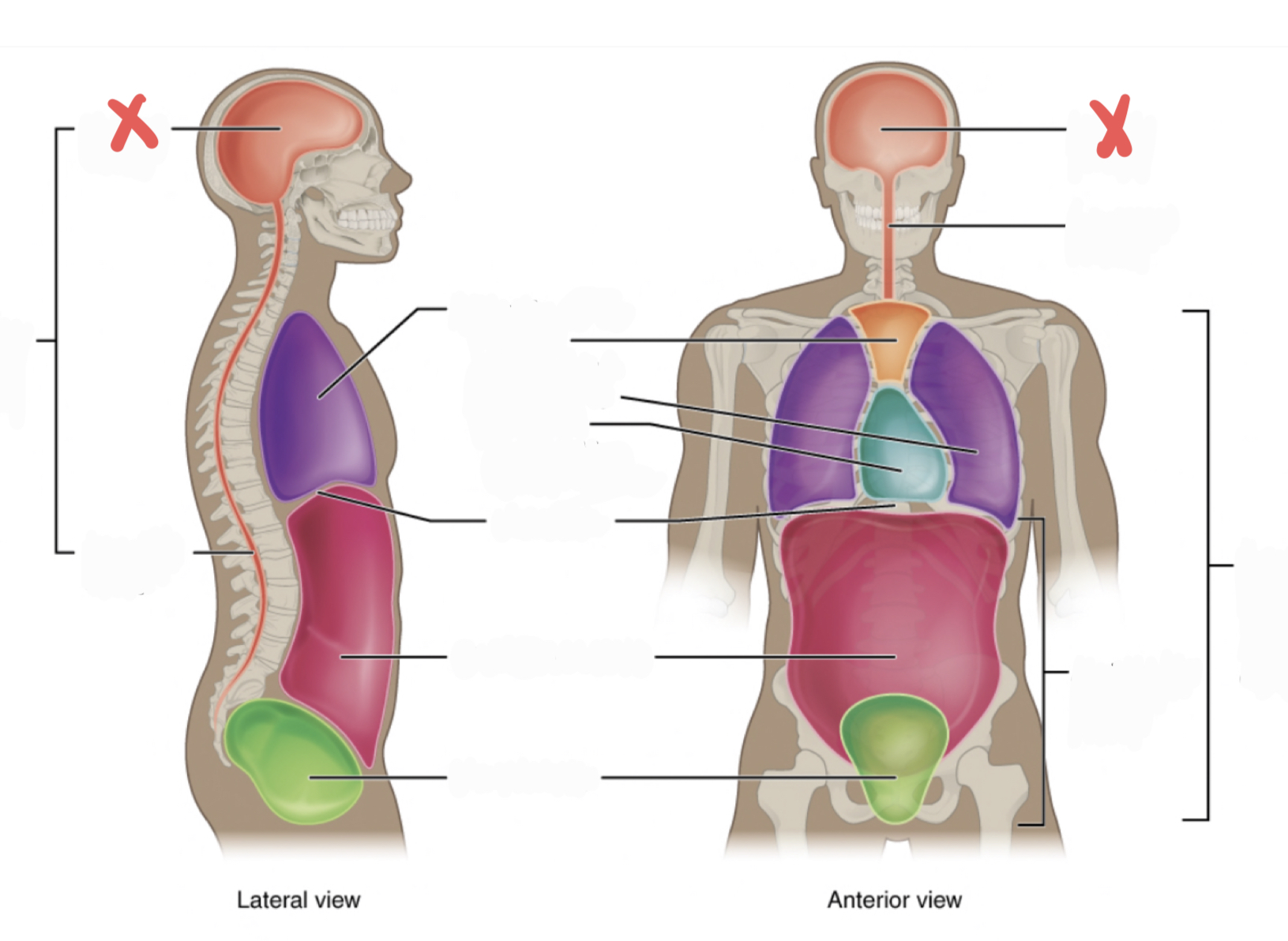
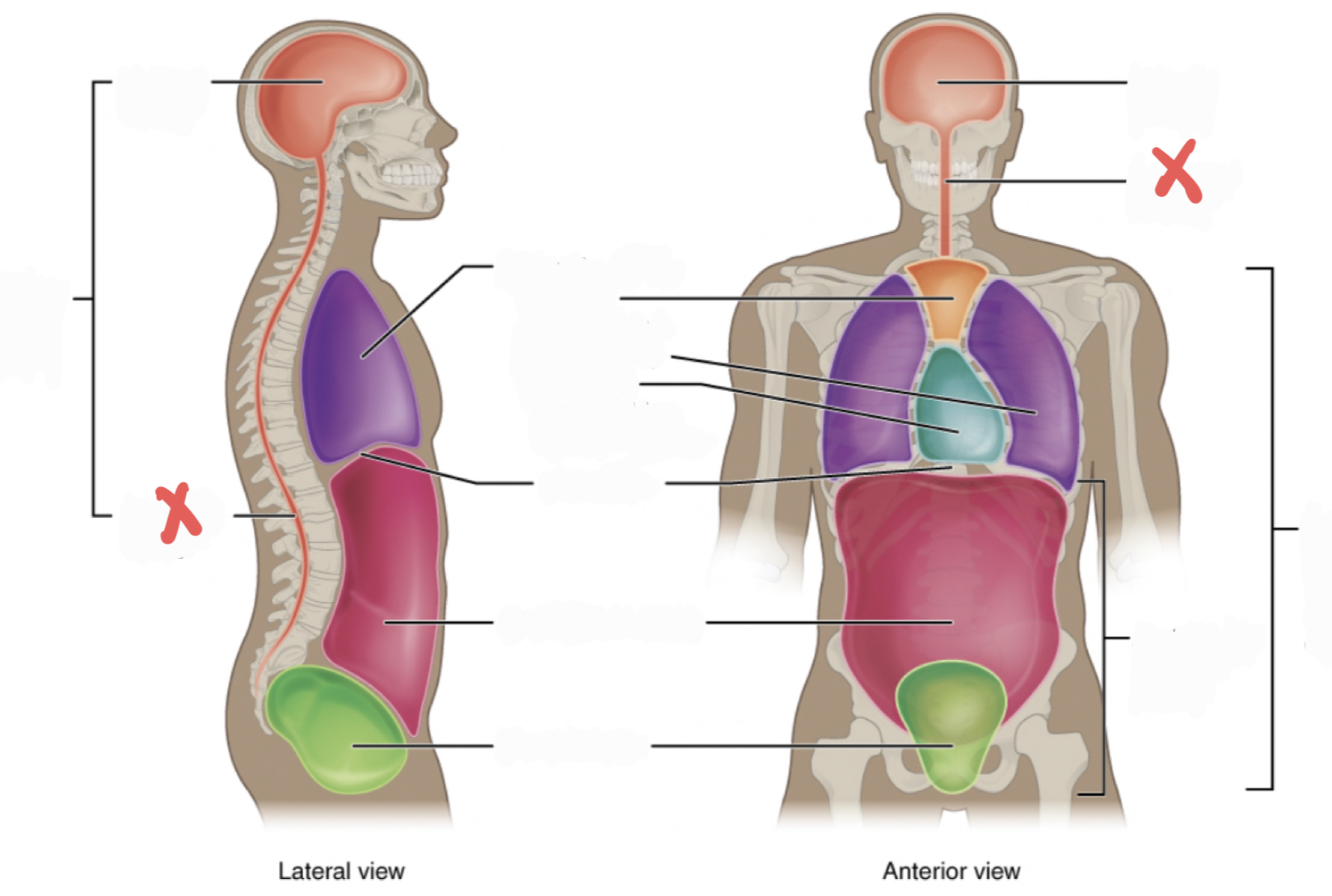
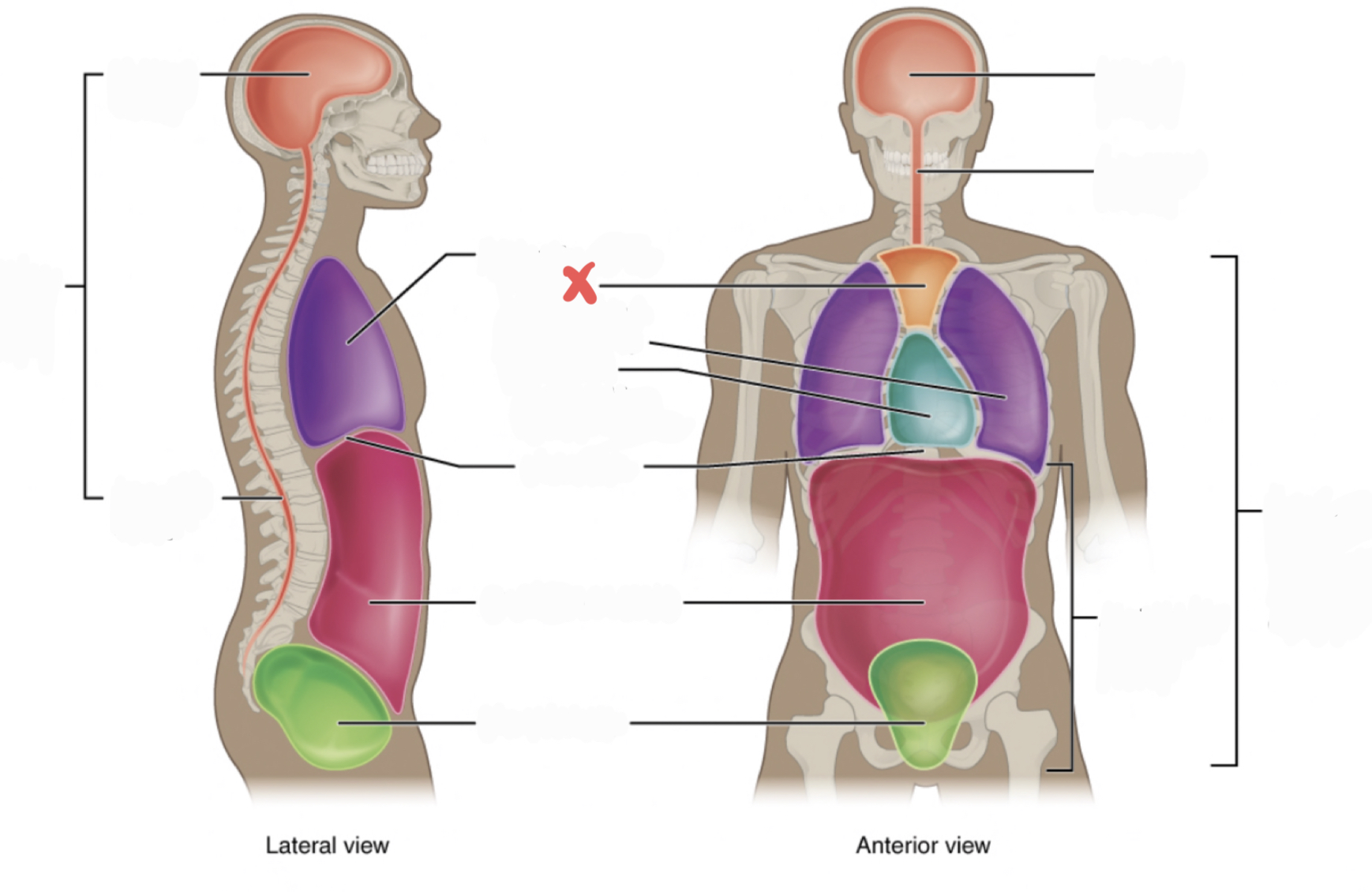
Ventral Cavity
Includes thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
30
New cards
Dorsal Cavity
includes the cranial and spinal (vertebral) cavities
31
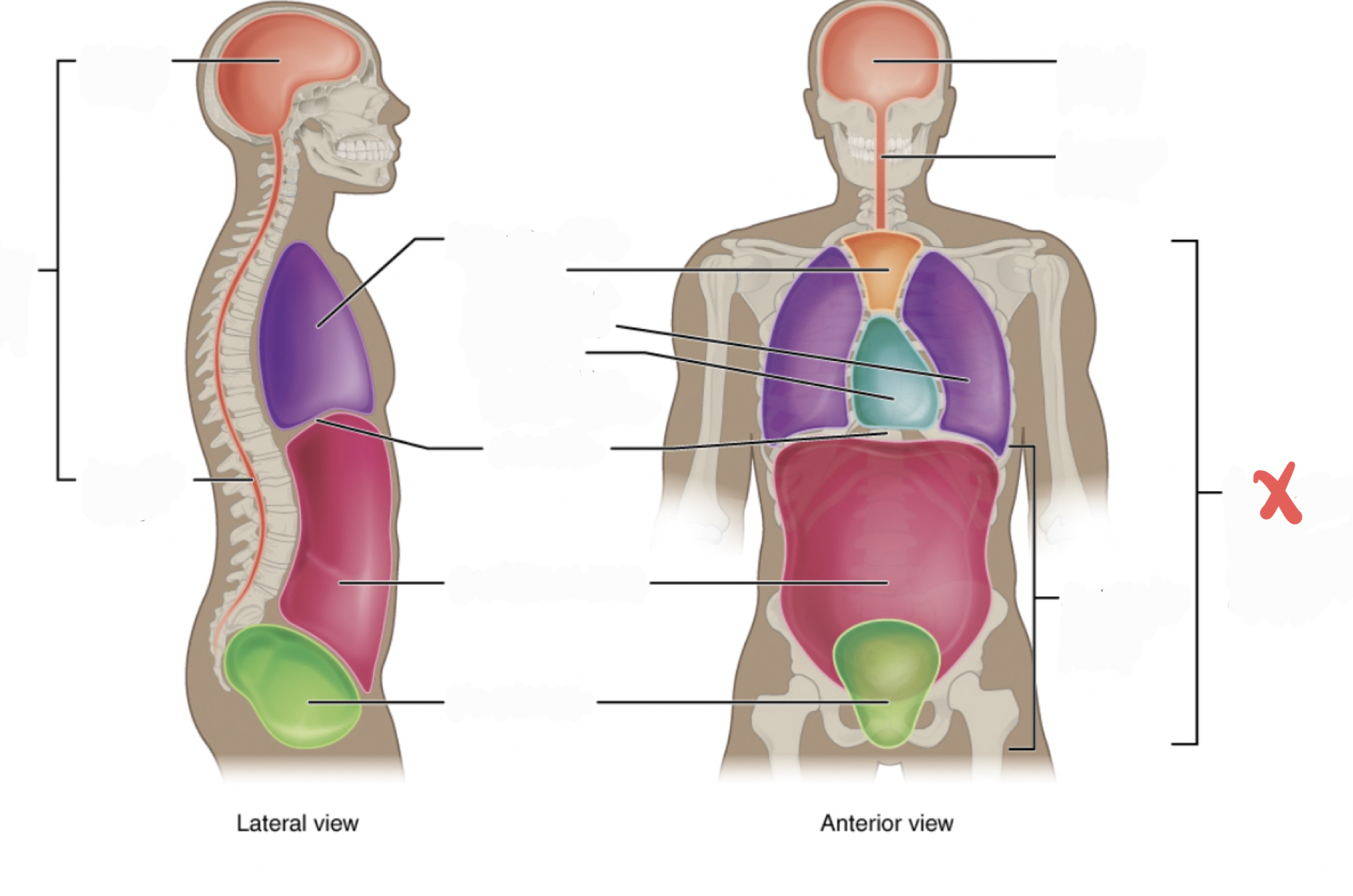
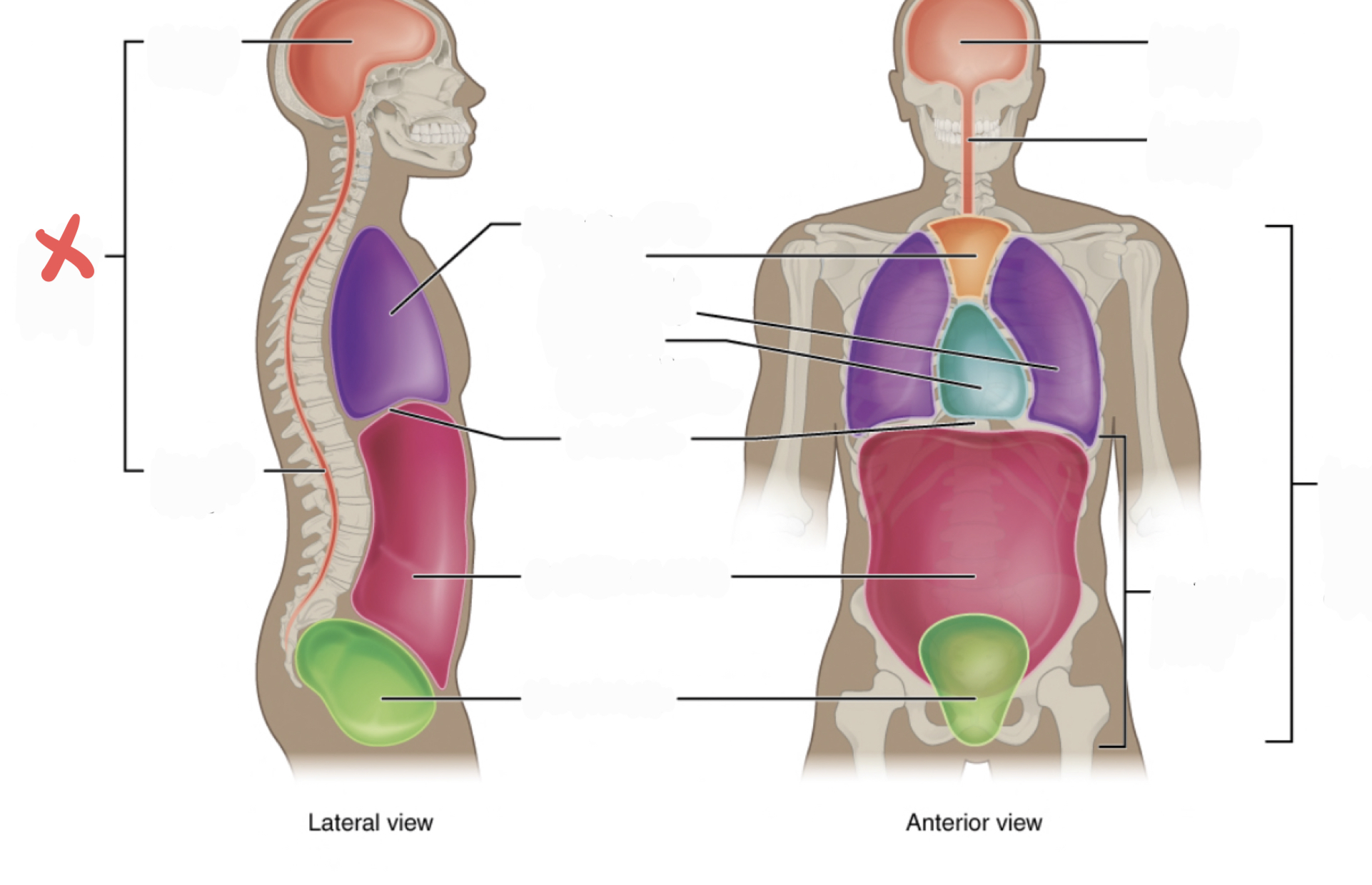
New cards
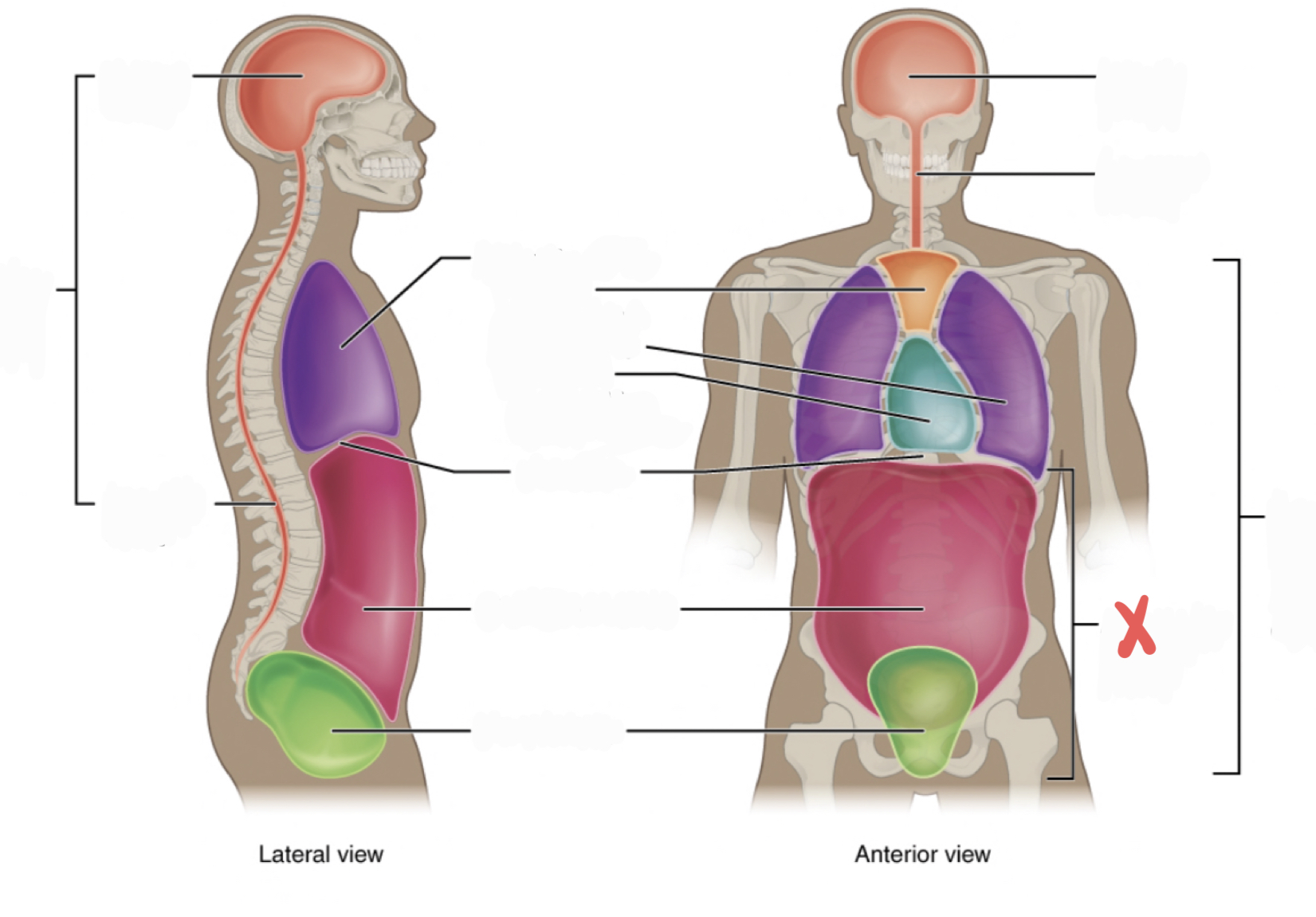
Thoracic Cavity
contains the superior mediastinum, pleural cavity, and pericardial cavity within the mediastinum, and diaphragm
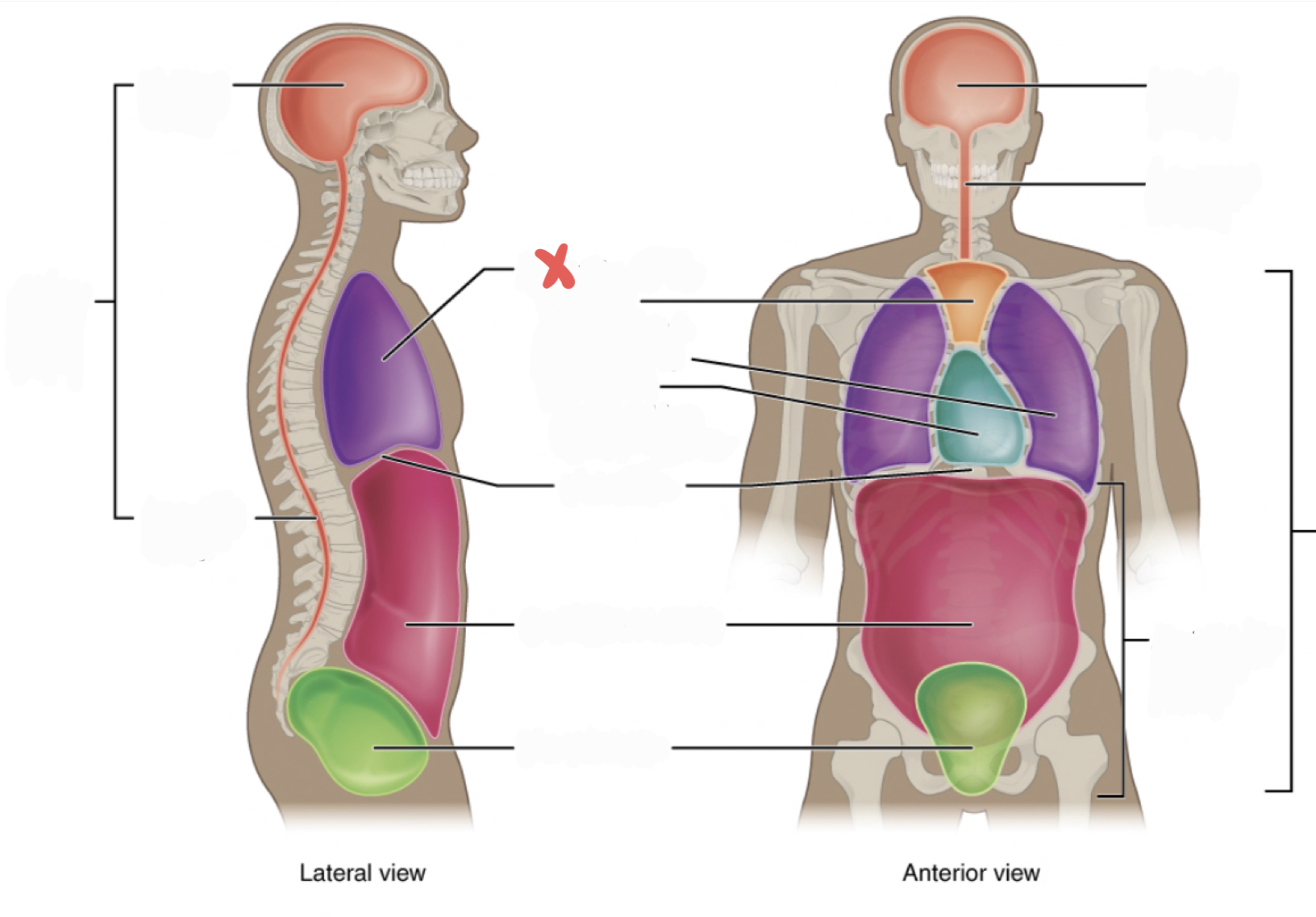
32
New cards
Abdominopelvic Cavity
contains the abdominal and pelvic cavities
33
New cards
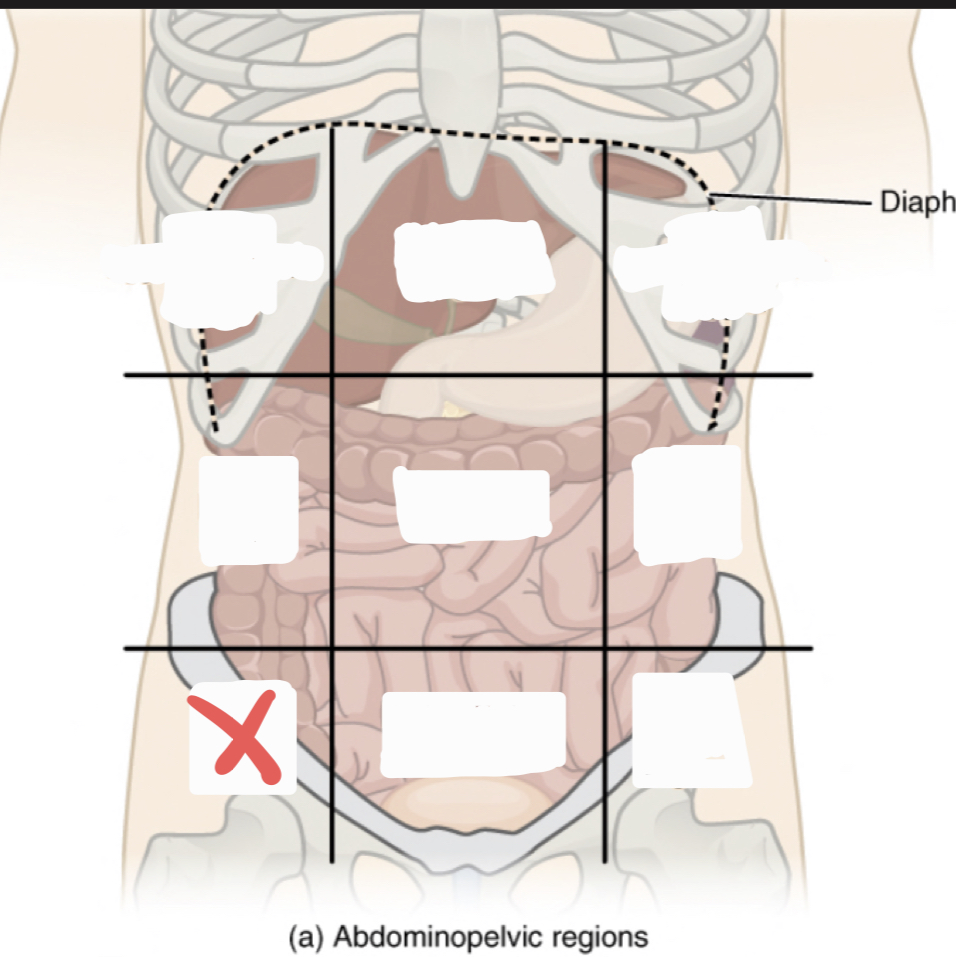
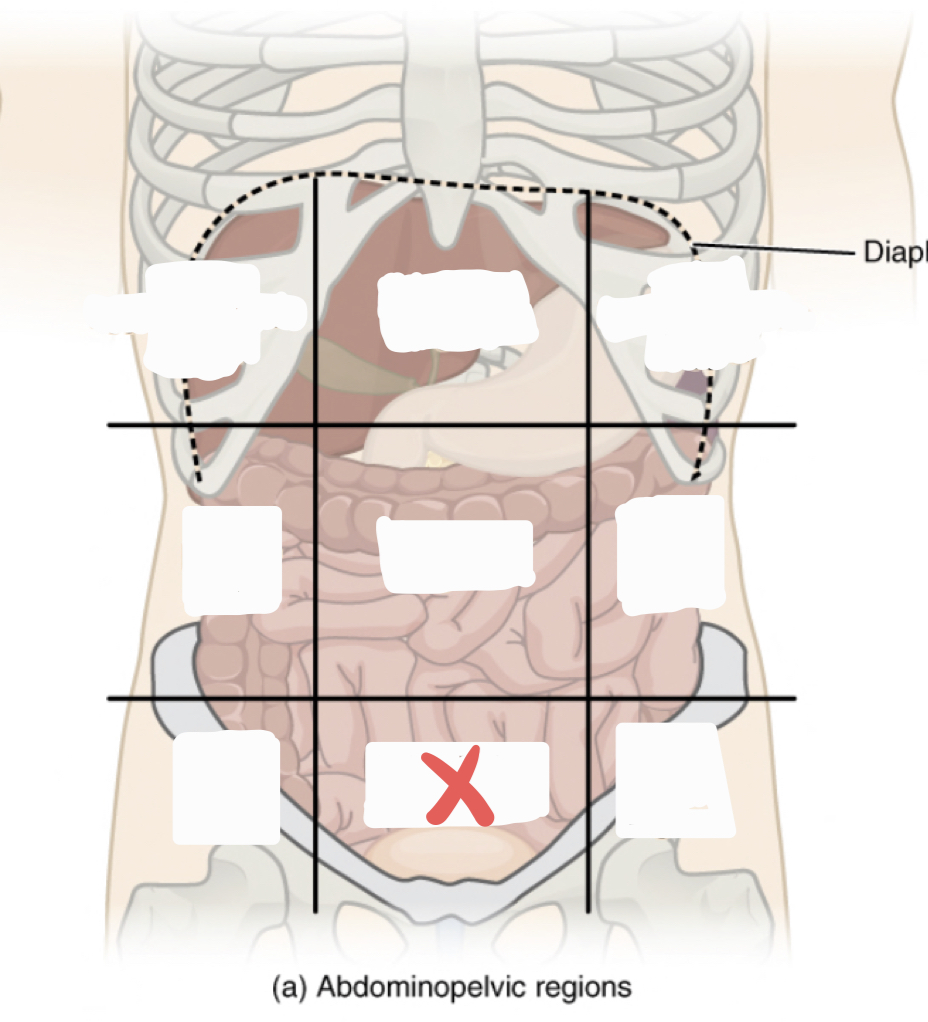
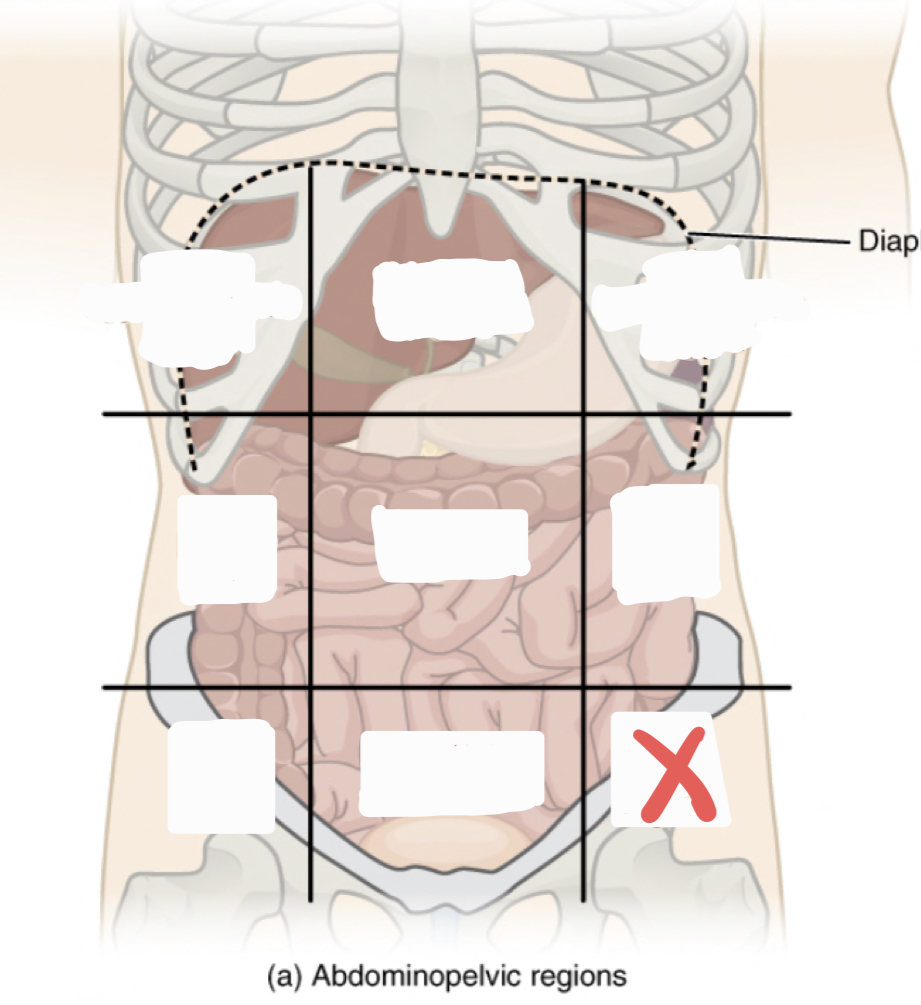
Epigastric Region
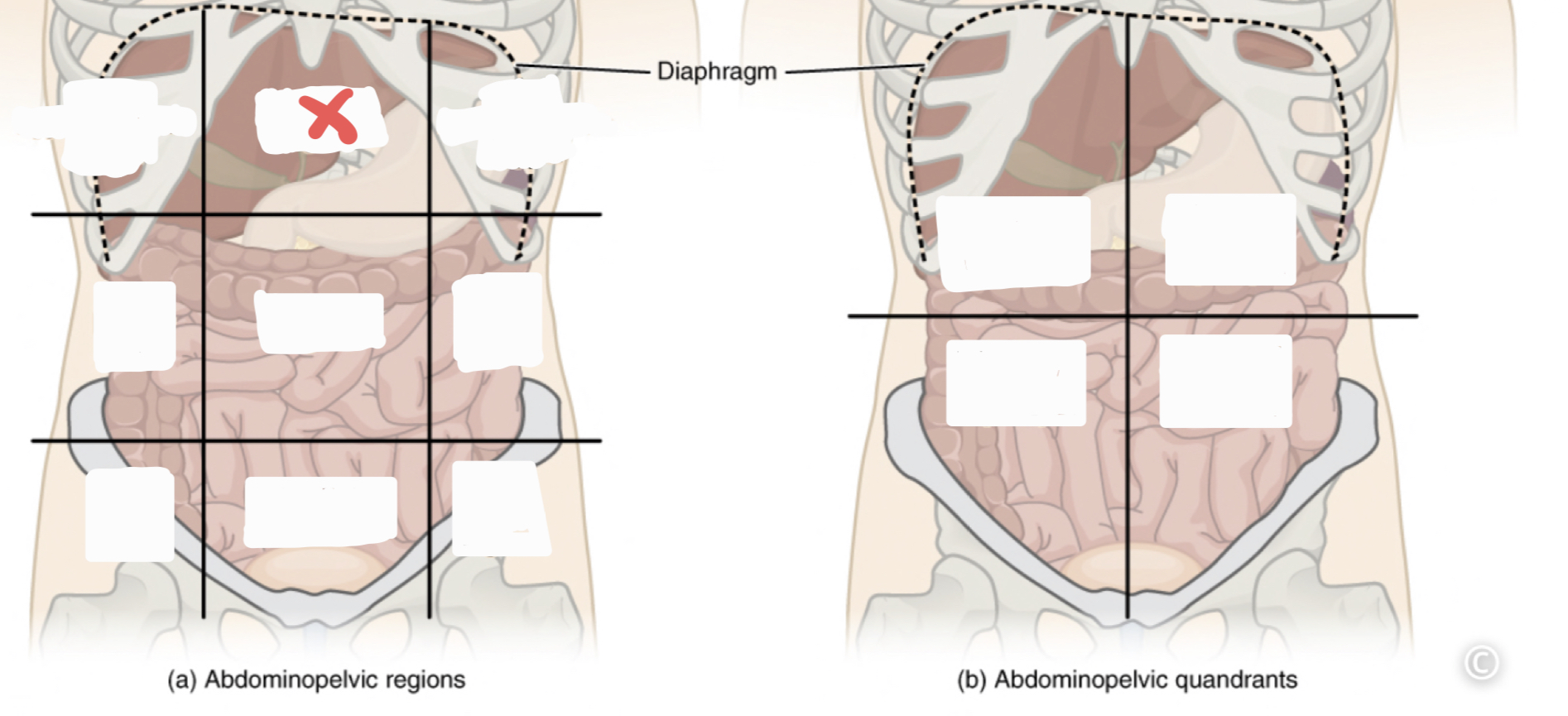
34
New cards
Right Hypochrondriac Region
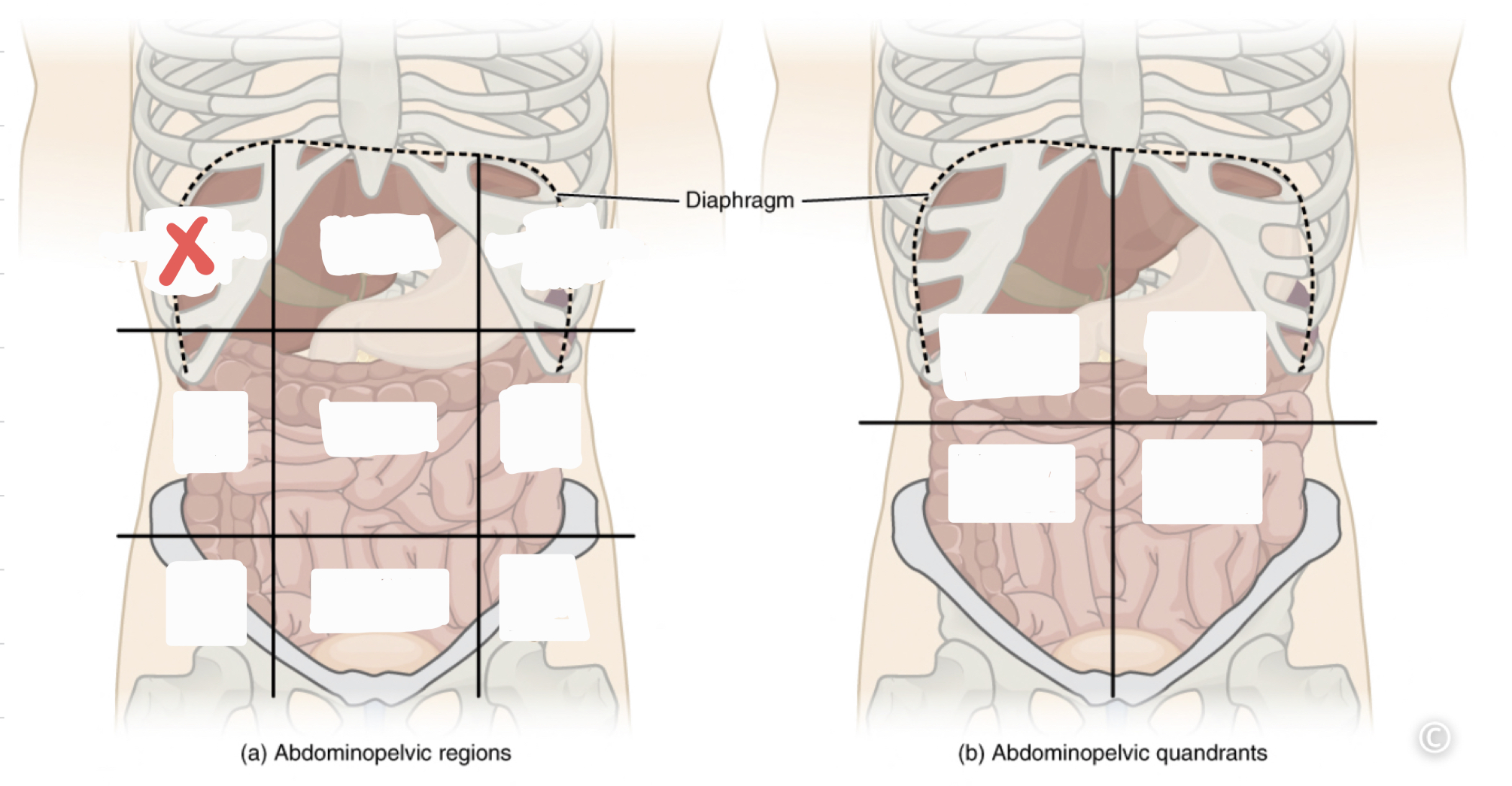
35
New cards
Left Hypochrondriac Region
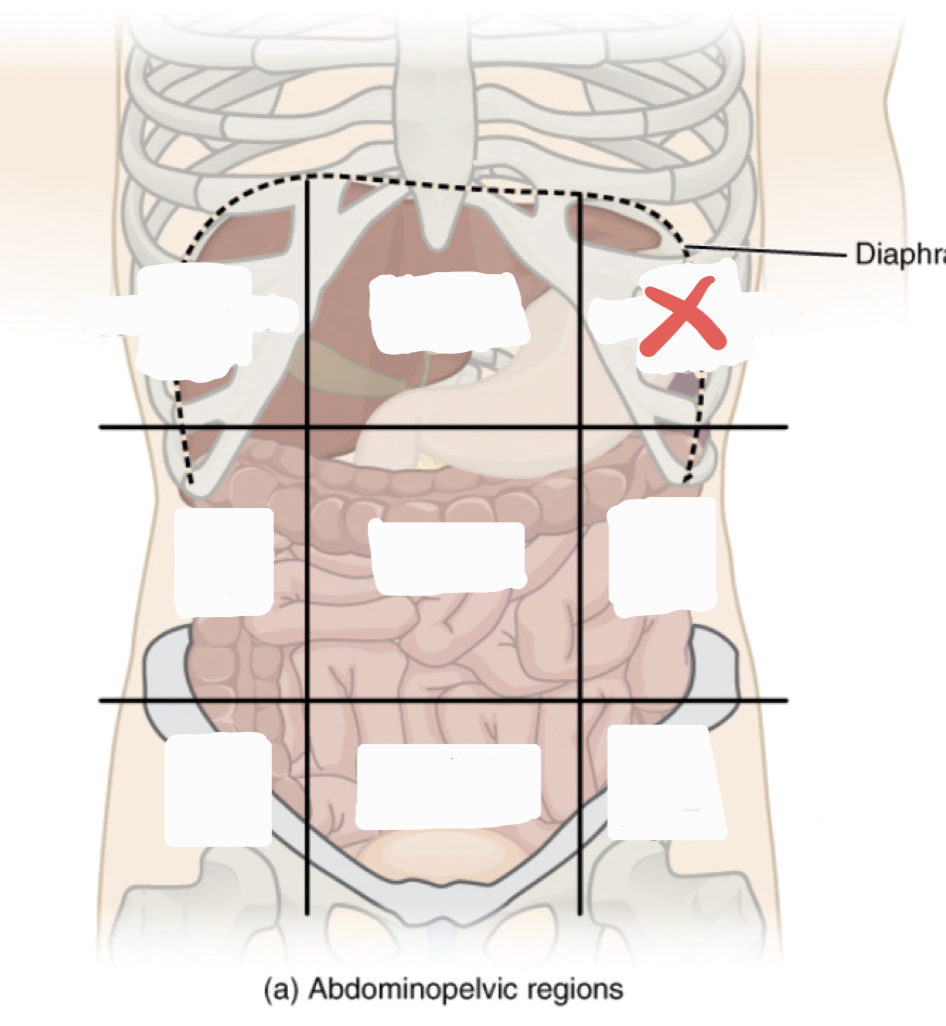
36
New cards
Right Lumbar Region
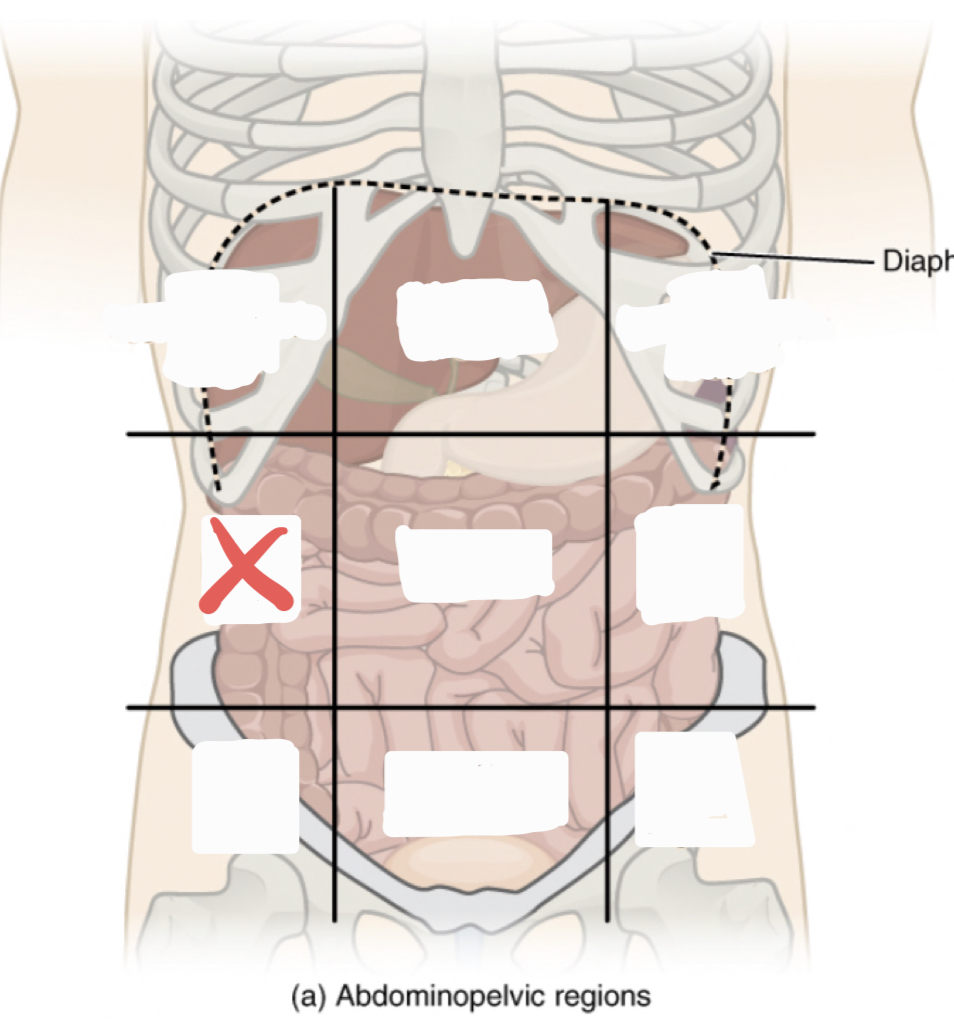
37
New cards
Umbilical Region
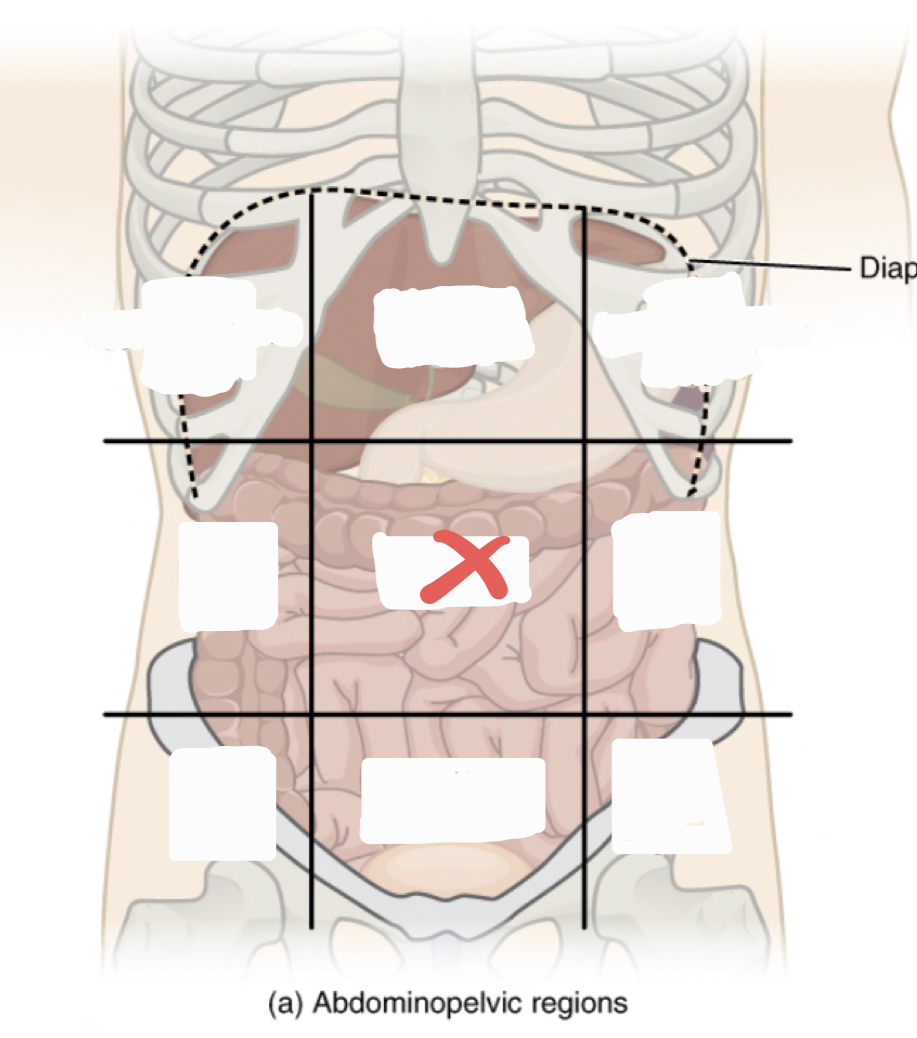
38
New cards
Left Lumbar Region
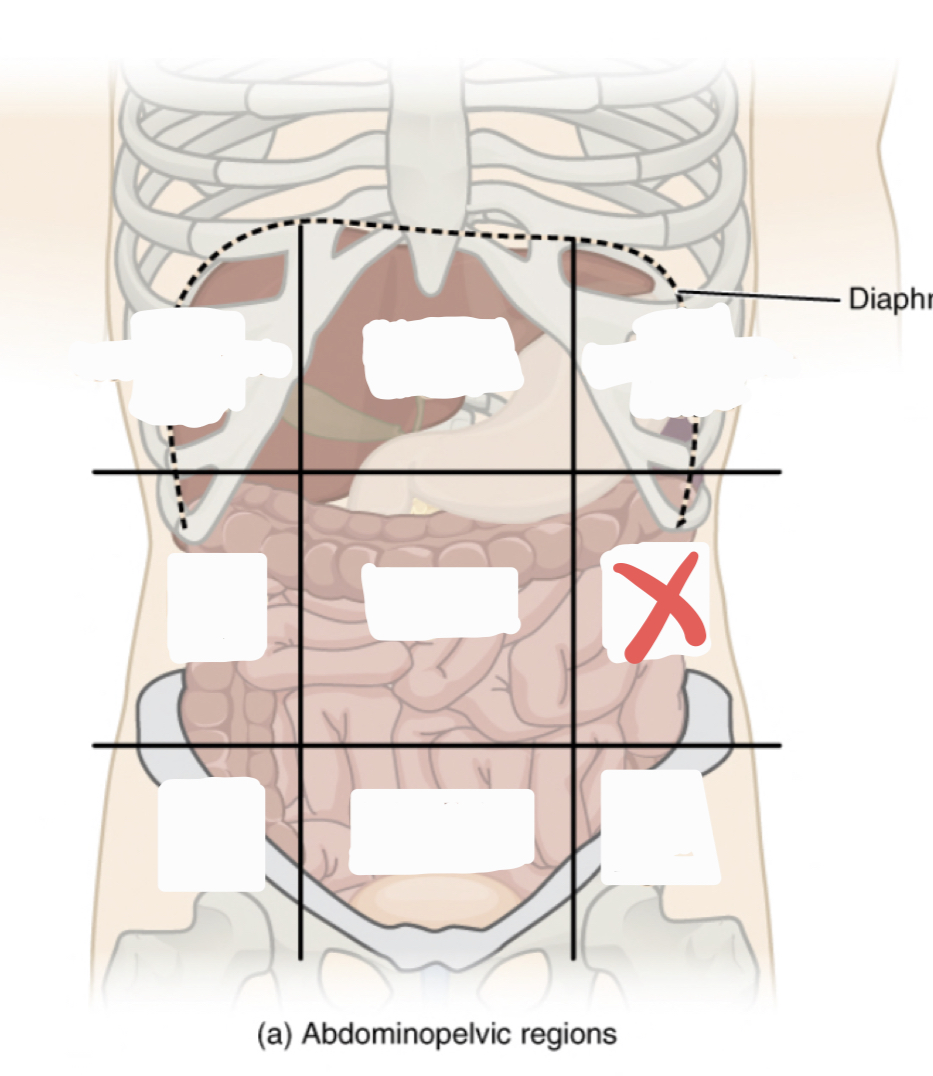
39
New cards
Right Iliac Region
40
New cards
Hypogastric Region
41
New cards
Left Iliac Region
42
New cards
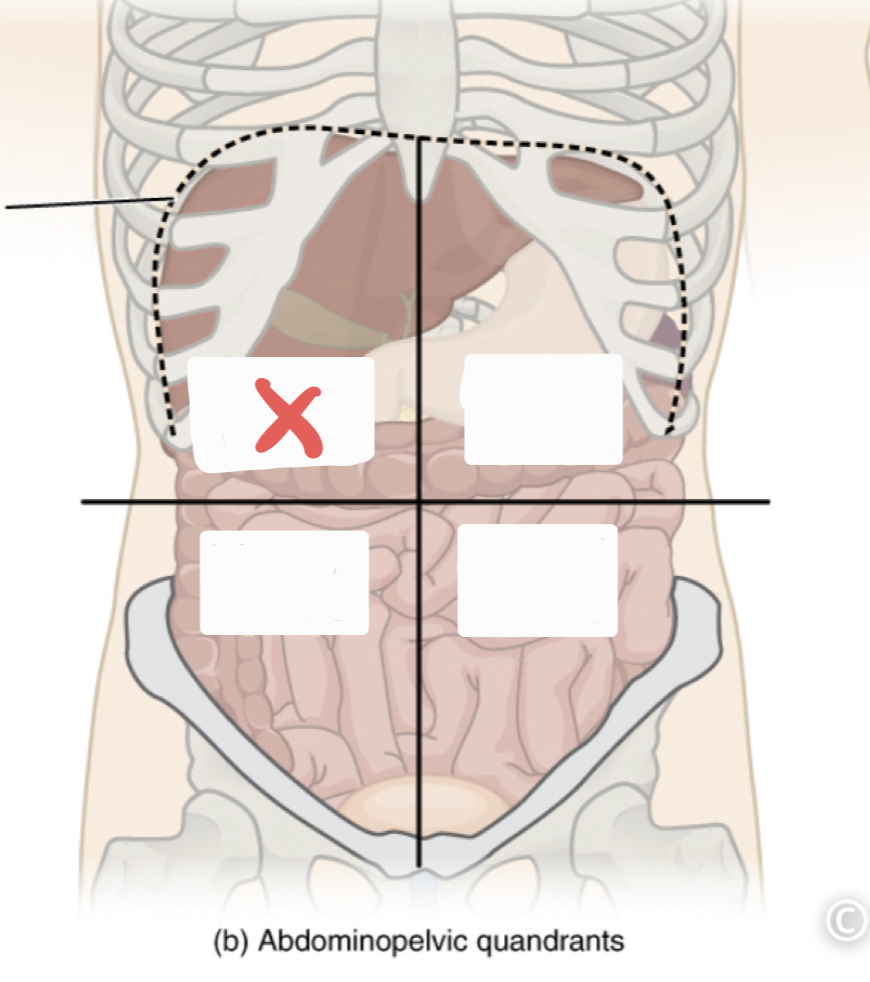
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
43
New cards
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
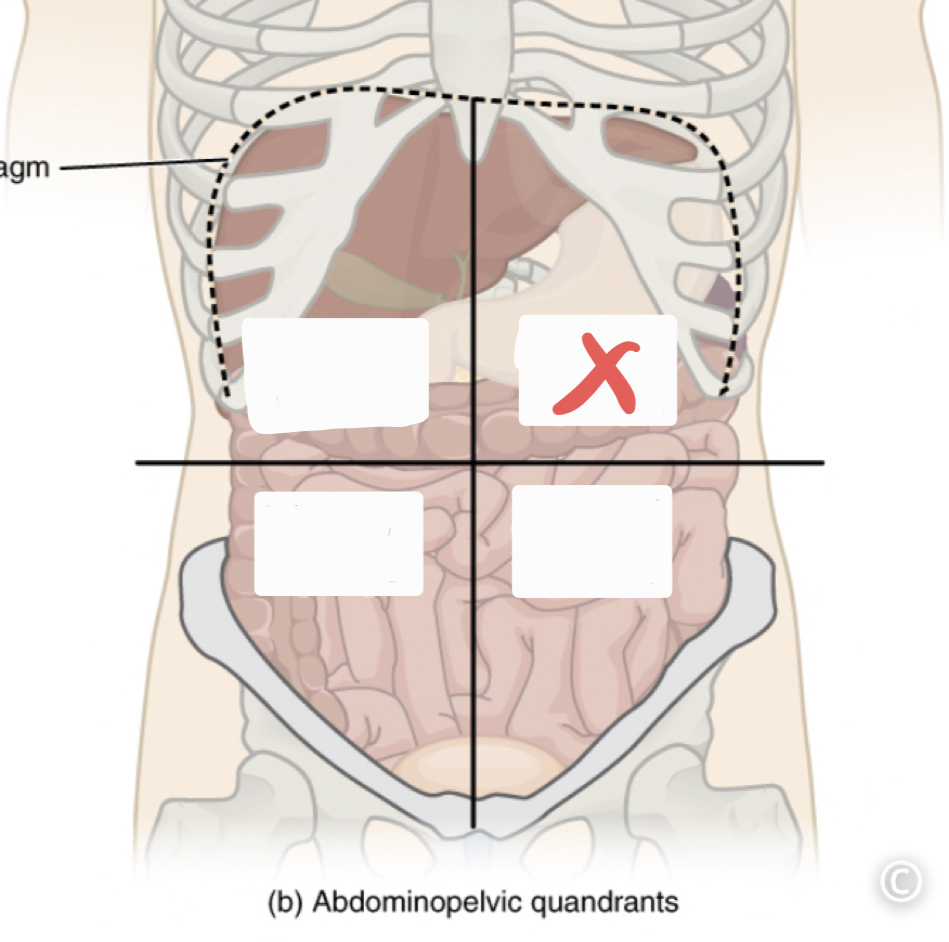
44
New cards
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
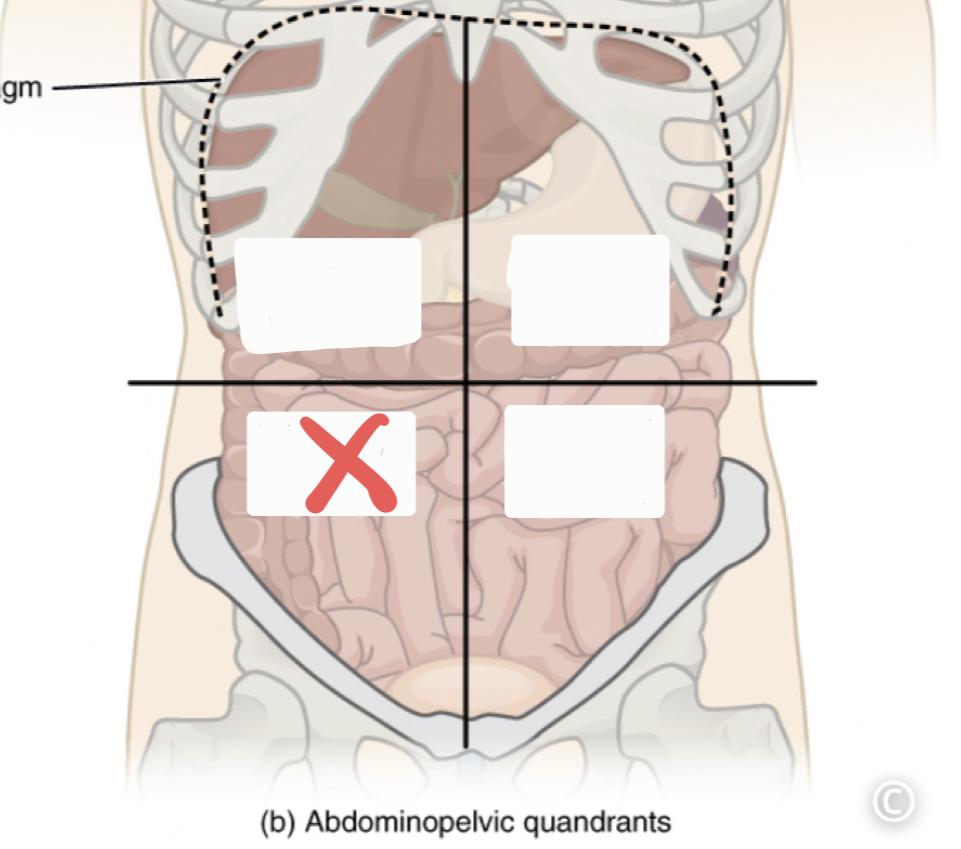
45
New cards
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
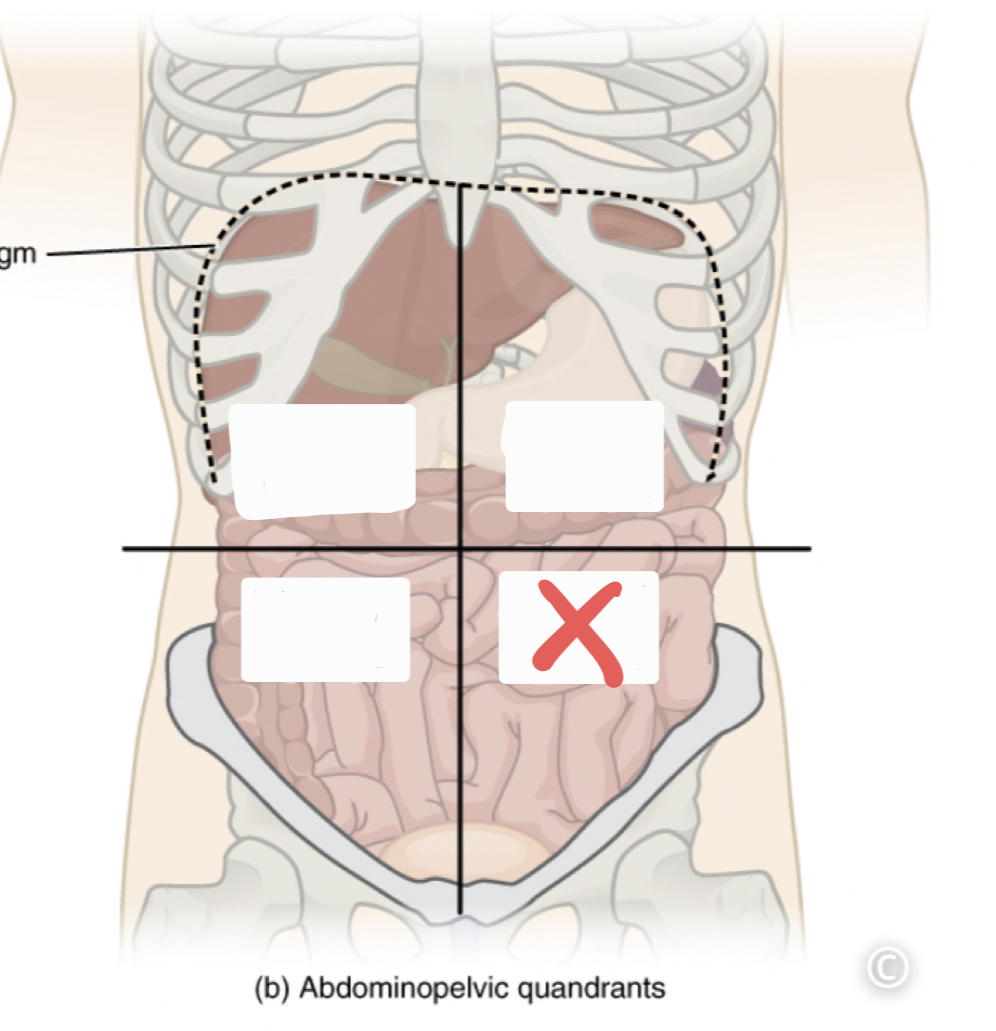
46
New cards
Abdominal Cavity
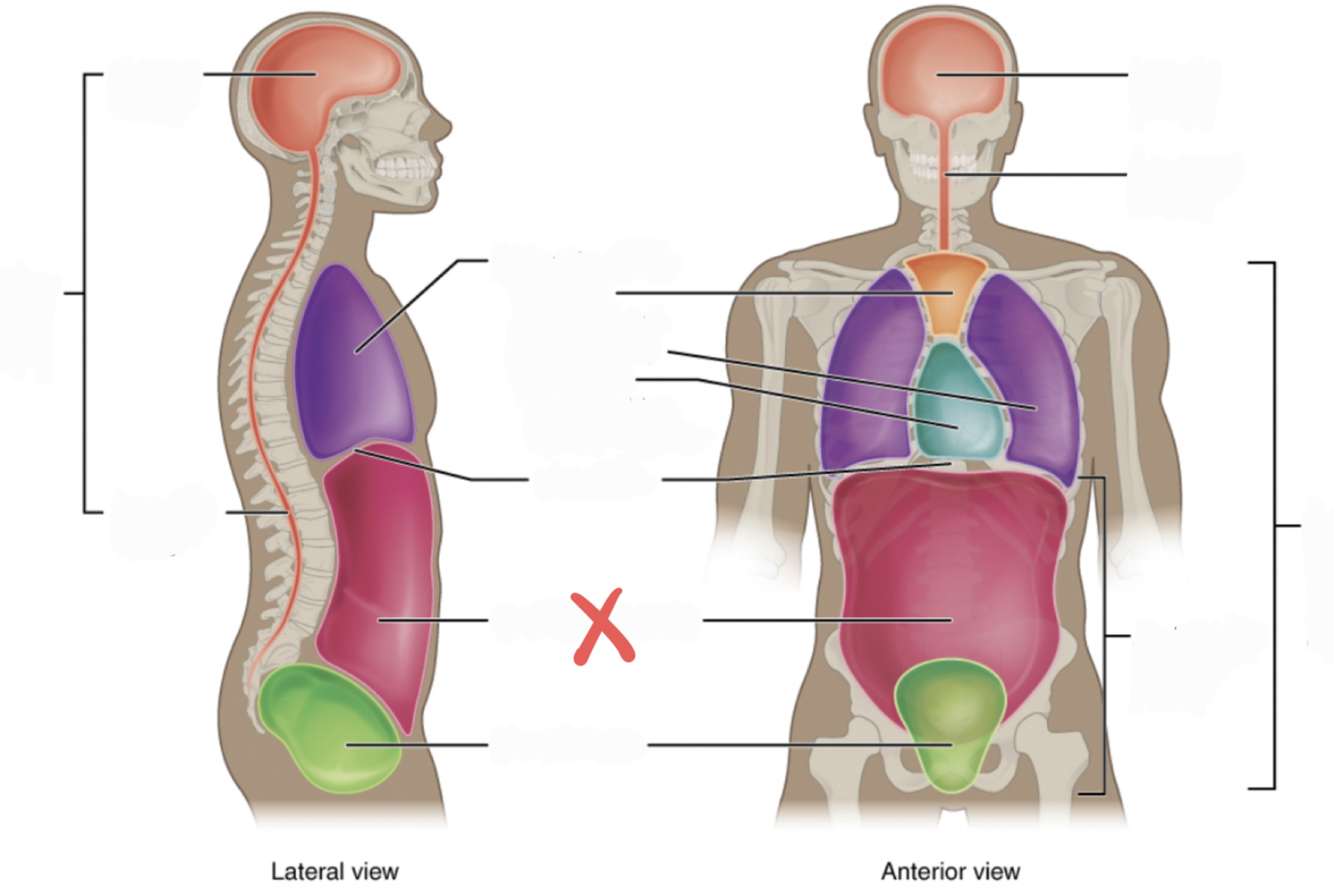
47
New cards
Pelvic Cavity
48
New cards
Cranial Cavity
49
New cards
Vertebral Cavity
50
New cards
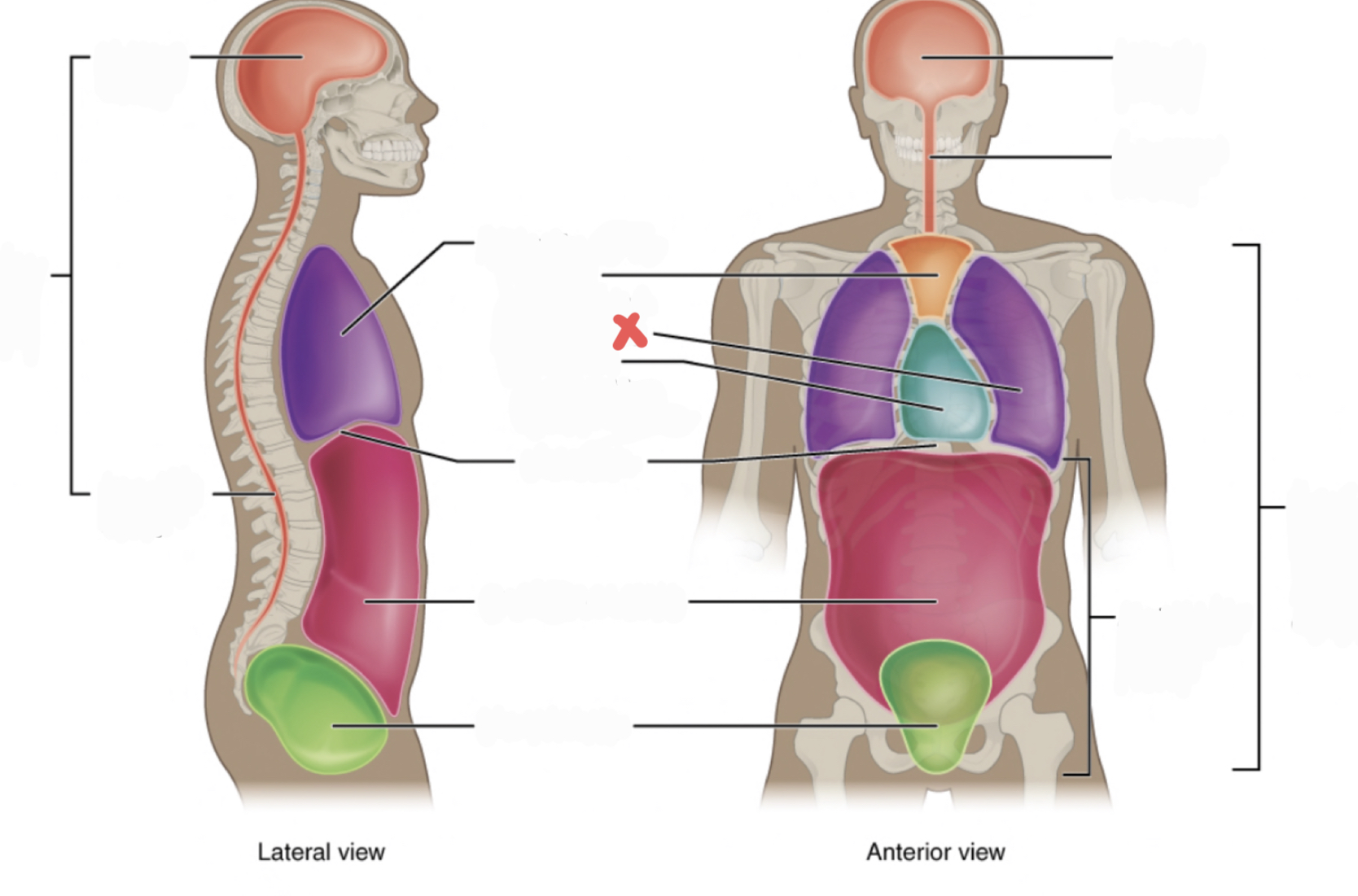
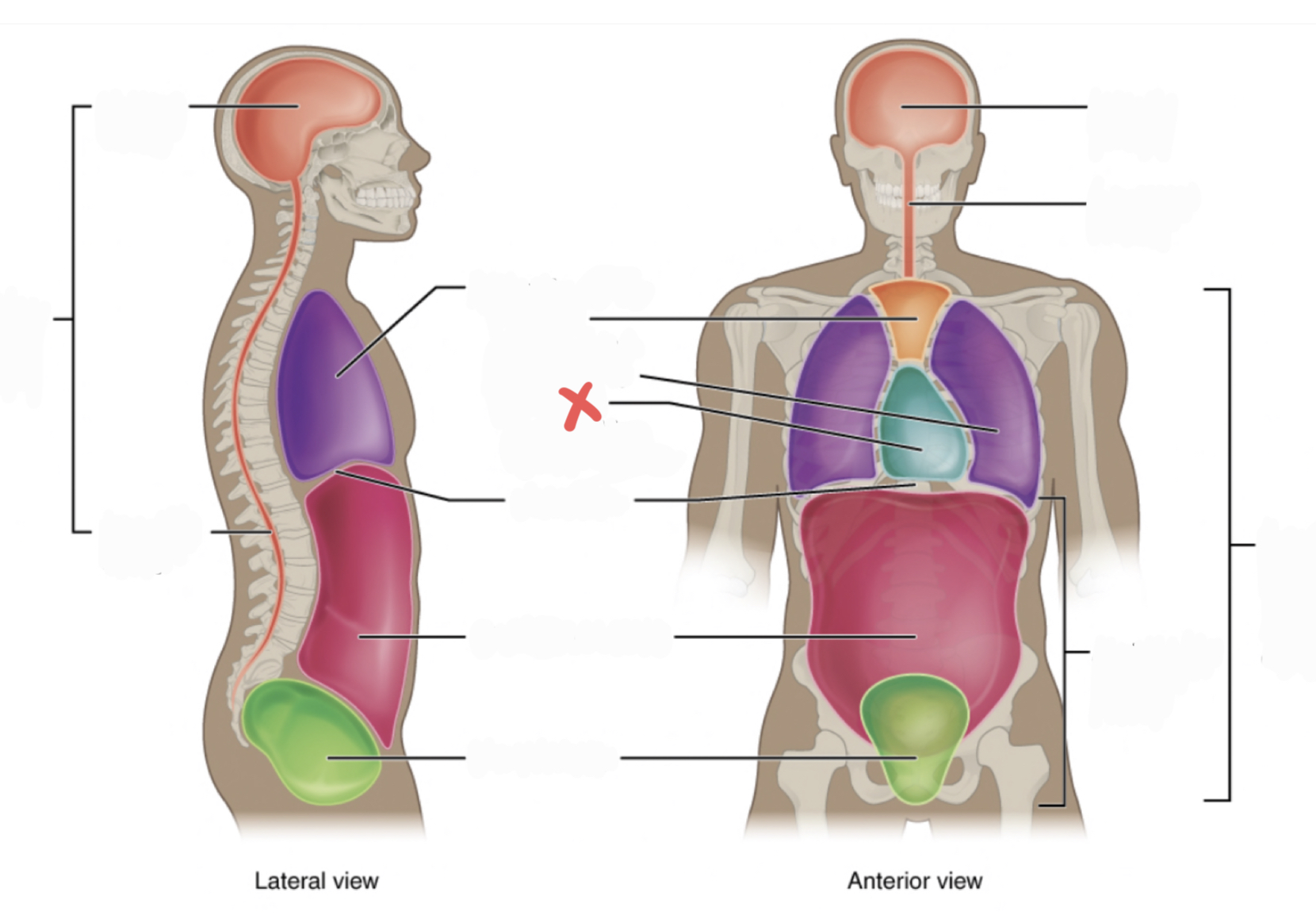
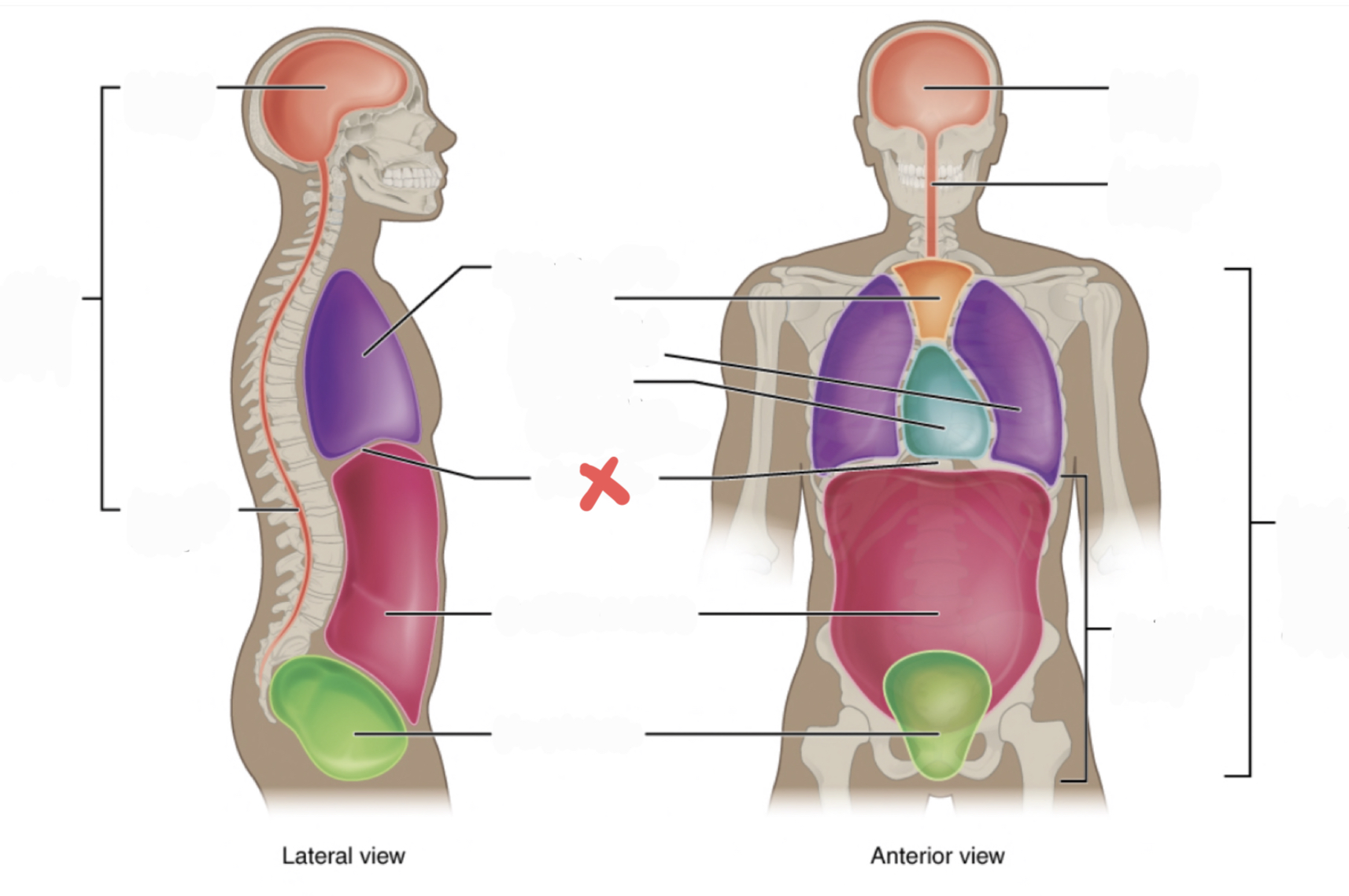
Superior Mediastinum
51
New cards
Pleural Cavity
52
New cards
Pericardial Cavity with Mediastinum
53
New cards
Diaphragm
54
New cards
Cytosol
the jelly-like fluid component of the cytoplasm that includes the components necessary for cell function
55
New cards
Cytoskeleton
a group of fibrous proteins, including microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules that help to maintain the cell’s structural integrity
56
New cards
Nucleus
contains the cell’s DNA and directs cellular functions
57
New cards
Mitochondrion
Converts energy storage molecules into the major energy molecule, ATP, to power cellular function
58
New cards
Ribosome
Protein synthesis
59
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
includes ribsomes for the synthesis and modification or proteins
60
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
lipid synthesis
61
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
sorts, modifies, and ships products from the endoplasmic reticulum
62
New cards
Lysosome
contains digestive enzymes to break down materials
63
New cards
Peroxisome
contains enzymes key for lipid metabolism and chemical detoxification
64
New cards
Interphase
the period of the cell cycle during which the cell is not dividing
65
New cards
Mitosis
the division of genetic material, during which the cell nucleus breaks down and two new, fully functional nuclei are formed
66
New cards
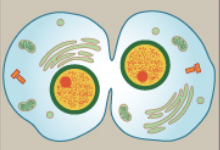
Cytokinesis
divides the cytoplasm into two distinctive cells
67
New cards
G1 Phase
when the cell grows and carries out all metabolic functions and processes
68
New cards
S Phase
the period when a cell replicated its DNA
69
New cards
G2 Phase
a second gap phase (like G1) during which the cell continues to grow and make preparations for mitosis
70
New cards
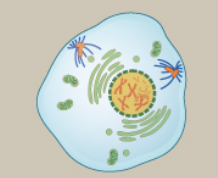
Prophase
chromosomes condense and become visible, mitotic spindle microtubules attach to kinetochores
71
New cards
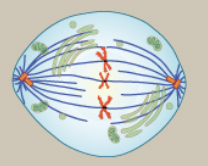
Metaphase
chromosomes line up in the middle, each sister chromatid is attached to a spindle fiber
72
New cards
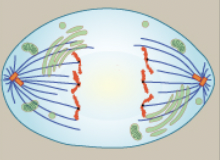
Anaphase
Centromeres split in two, sister chromatids (chromosomes) are pulled toward opposite poles
73
New cards
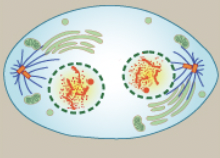
Telophase
chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to decondense, nuclear envelope material surrounds each set of chromosomes
74
New cards
Epithelial Tissue
sheets of cells that cover exterior surfaces of the body, line internal cavities and passageways, and form certain glands
75
New cards
Connective Tissue
binds the cells and organs of the body together and functions in the protection, support, and integration of all parts of the body
76
New cards
Muscle Tissue
excitable tissue that responds to stimulation and contracting to practical movement
77
New cards
Nervous Tissue
excitable tissue that allows the propagation of electrochemical signals in the form of nerve impulses that allow communication between different parts of the body
78
New cards
Apical surface
where the action happens
79
New cards
Basal surface
the side of the cell connected to the grid
80
New cards
Simple Squamous Epithelium
located in the alveoli of lungs where gases diffuse, segments of kidney tubules, and lining of capillaries, blood and lymphatic vessels. Allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration, and secretes lubricating substance
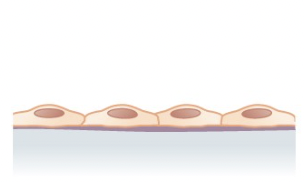
81
New cards
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
found where protection against physical and chemical wear and tear is needed; lines the esophagus, mouth, and vagina.
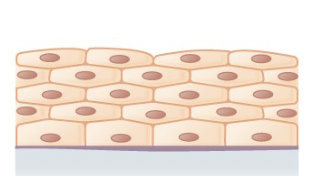
82
New cards
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
active in the secretion and absorptions of molecules, found in the lining of the kidney tubules and in the ducts of glands
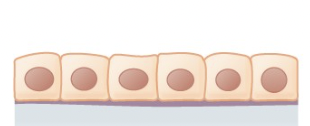
83
New cards
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
protective tissue found in sweat glands, salivary glands, and mammary glands but uncommon in human body
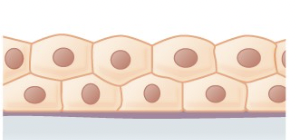
84
New cards
Simple Columnar Epithelium
active in the absorption and secretion of molecules and often has microvilli to increase SA, forms the linings of digestive tract and bladder
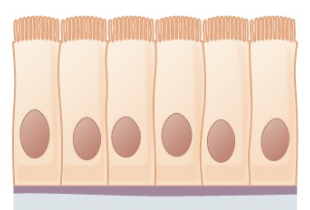
85
New cards
Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
simple columnar epithelium cells with cilia on the apical surface, found in bronchi, and the lining of the uterine tubes and uterus
86
New cards
Cilia
help to move materials along the apical surface of cells, usually found in respiratory or uterine tract
87
New cards
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
found in respiratory tract and upper trachea, ciliated tissue moves mucus
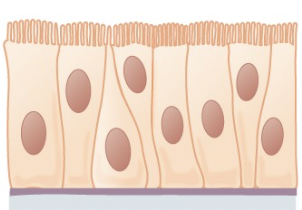
88
New cards
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
secretes and protects, found in the male urethra and the ducts of some glands
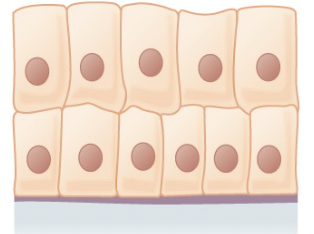
89
New cards
Keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium
ex: mammalian skin, where the top layer of skin is dead
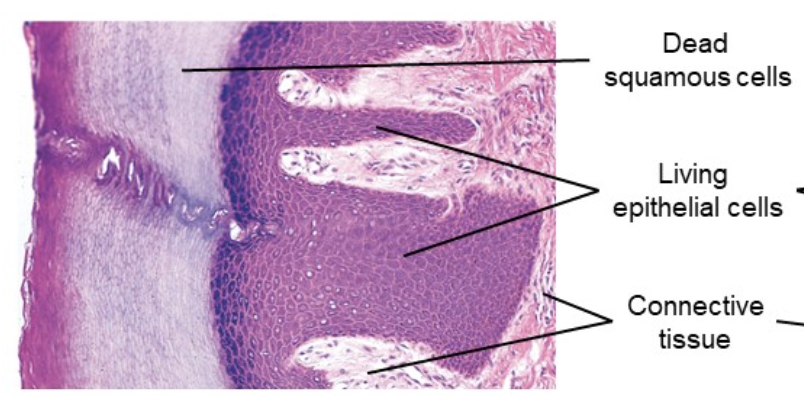
90
New cards
Transitional Epithelium
a type of stratified epithelium where the apical cells can change shape. Only found in the urinary system (bladder and ureters)
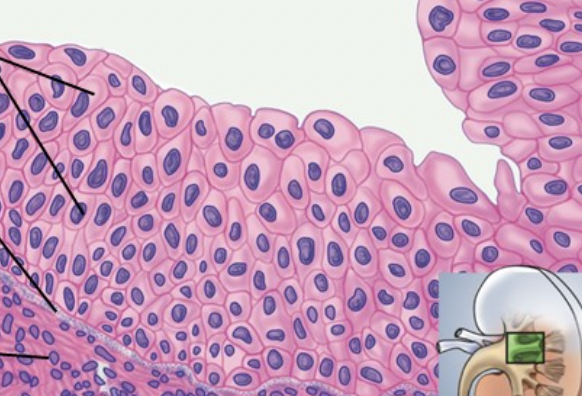
91
New cards
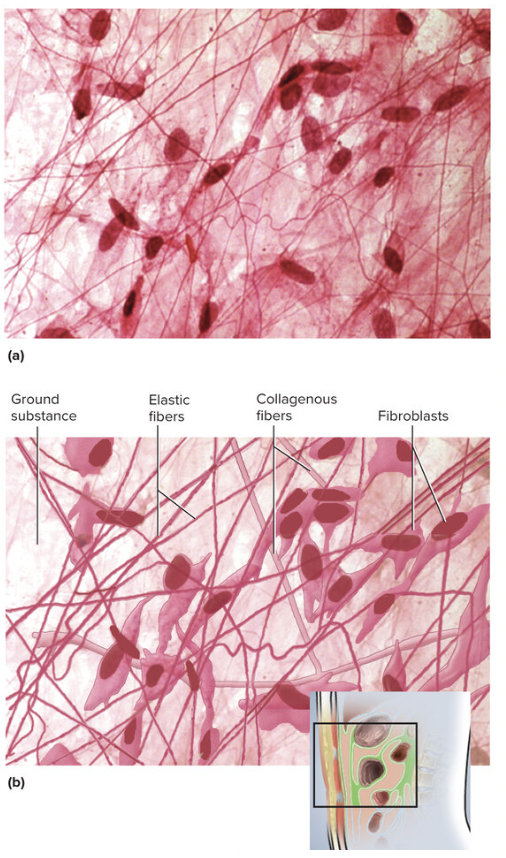
Areolar Tissue
loose connective tissue, fills spaces between muscle fibers, surrounds blood and lymph vessels, and supports organs in the abdominal cavity
92
New cards
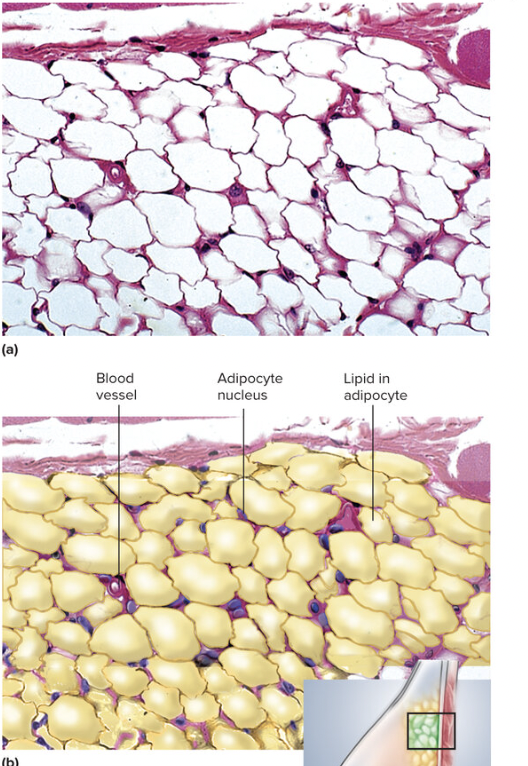
Adipose Tissue
loose connective tissue, has large capillaries that allow for rapid storage and mobilization of lipid molecules. White tissue can be found protecting the kidneys and back of the eye
93
New cards
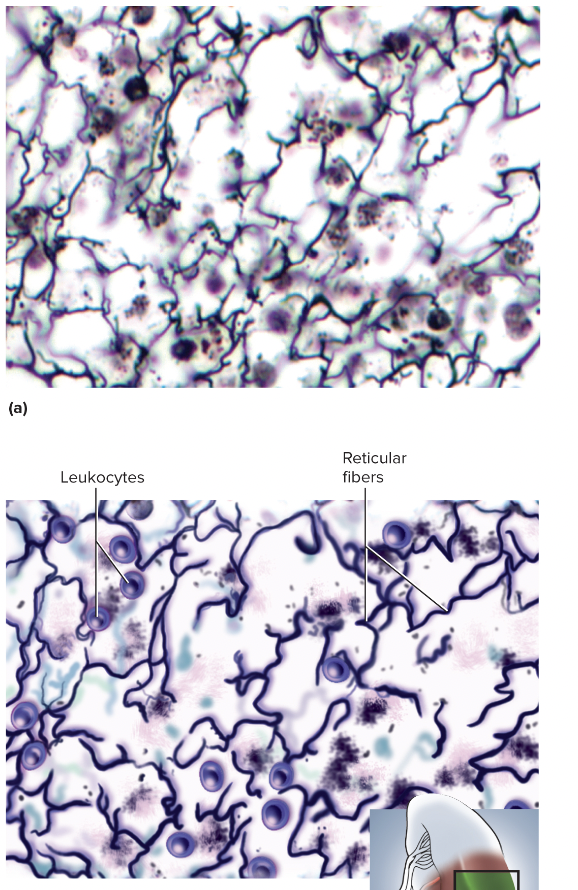
Reticular Tissue
loose connective tissue, supports soft organs like lymphatic tissue, spleen, and liver. these cells produce the fibers that form the network onto which other cells attach
94
New cards
Dense Regular Tissue
connective tissue with collagen fibers that enhance strength and resistance to stretching, used in ligaments and muscle tendons
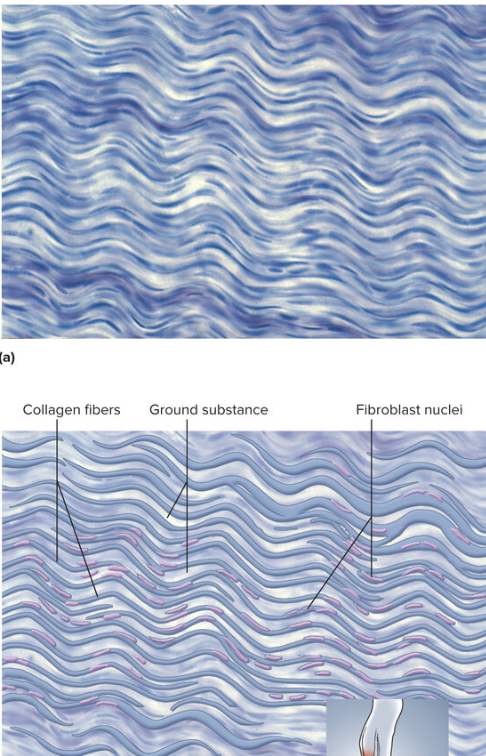
95
New cards
Dense Regular Elastic Tissue
connective tissue, found between vertebrae and vocal folds
96
New cards
Dense Irregular Tissue
connective tissue with collagen fibers arranged in different directions, found in dermis and arterial walls (provides strength and ability to regain original shape after stretching)
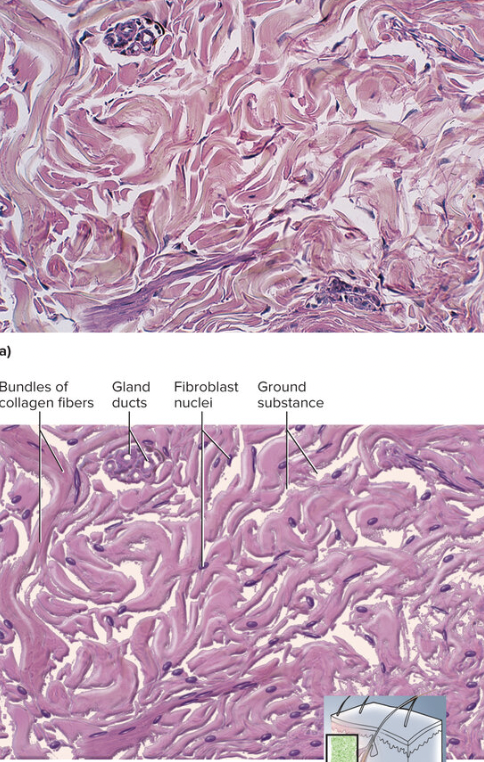
97
New cards
Hyaline Cartilage
supporting connective tissue, consists of collagen fibers and proteoglycans, found in bronchi, rib cage, nose, and covers bones where they meet to form joints
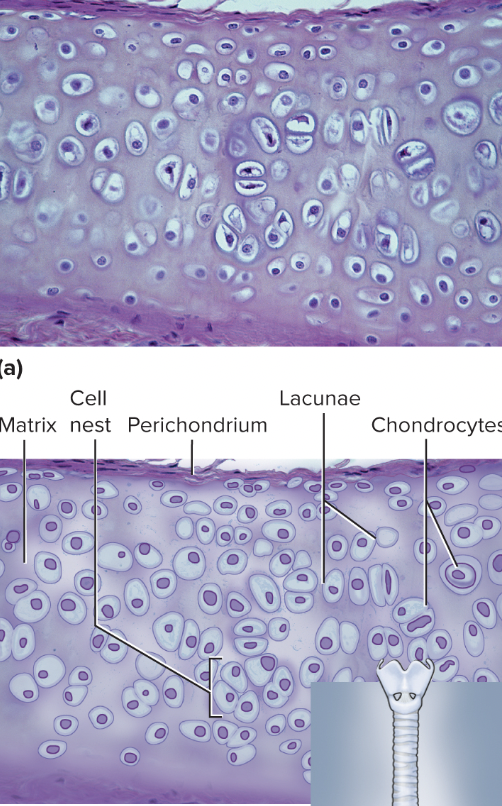
98
New cards
Fibrocartilage
supporting connective tissue, provides compressibility and absorbs pressure, has thick bundles of collagen fibers throughout its matrix, found in menisci of knee joint and intervertebral discs
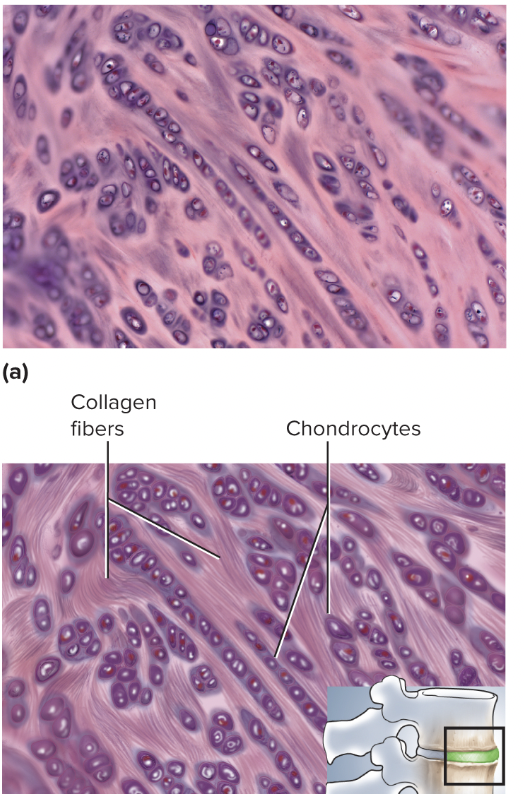
99
New cards
Elastic Cartilage
supportive connective tissue, provides firm but elastic support, contains elastic and collagen fibers, found in ear lobes
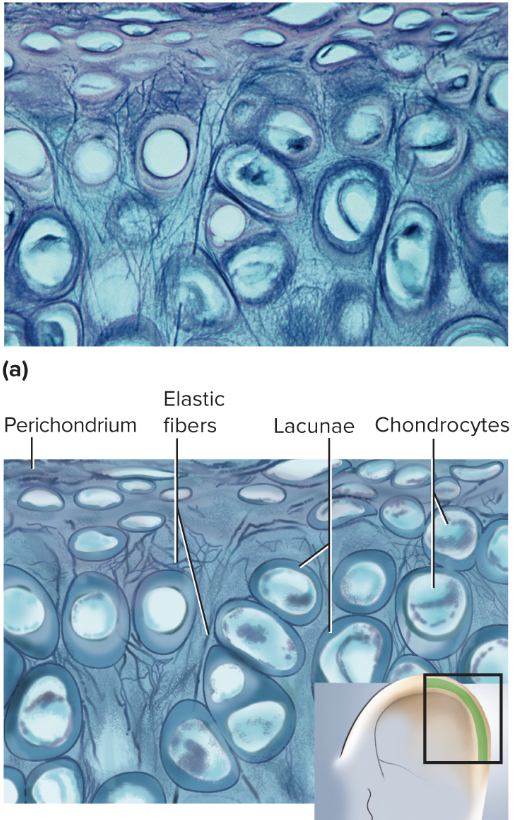
100
New cards
Bone
protects internal organs and supports the body, contain collagen fibers covered in a mineralized substance, highly vascularized