microbio 2125 unit 5 (part 18) - Escherichia coli O157:H7
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
etiological agent
Escherichia coli O157:H7
Distinguishing characteristics of etiological agent:
Most common aerobic, non-fastidious gut bacterium
Gram-negative bacillus
150 strains
Some have developed virulence through plasmid transfer, others are opportunists
exclusively human diseases
Virulence Factor(s):
Shiga toxin gene (acquired from Shigella)
Heat-labile exotoxin injuring nerve cells, intestine
Cell wall receptor enabling direct toxin delivery to host
Predisposing Factors:
Consumption of contaminated food (beef, produce like onions)
Contact with cattle or cattle products
Immunocompromised states
Surgical procedures, endoscopy, tracheostomy, catheterization, dialysis and immunosuppressant therapy (general E. coli risk)
Transmission:
Fecal-oral route via contaminated food/water
Low infectious dose (ID = 100 cells)
Syndrome (signs + symptoms):
Hemorrhagic colitis (intestinal hemorrhage)
Severe diarrhea (may be bloody)
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) → potential kidney damage
Traveler’s diarrhea (~70% cases)
Affected body region/system:
Gastrointestinal tract
Kidneys (in severe cases)
Treatment:
Supportive care (rehydration)
Enterotoxin inactivation where needed
Antimicrobics for non-toxin producing E. coli infections
Antibiotics generally avoided in O157:H7 due to risk of toxin release
Prevention:
Food safety measures (thorough cooking of beef, washing produce)
Hygiene after contact with cattle or farm environments
Other notes:
Frequent agent of infantile diarrhea (E. coli overall) could lead to mortality
Major cause of UTIs (50–80% of healthy individuals) by E. coli strains
High-profile outbreaks linked to contaminated food items (e.g., Taylor Farms onions)
Enterohemorrhagic
causes hemorrhagic syndrome and kidney damage, infamous strain: E. coli O157:H7
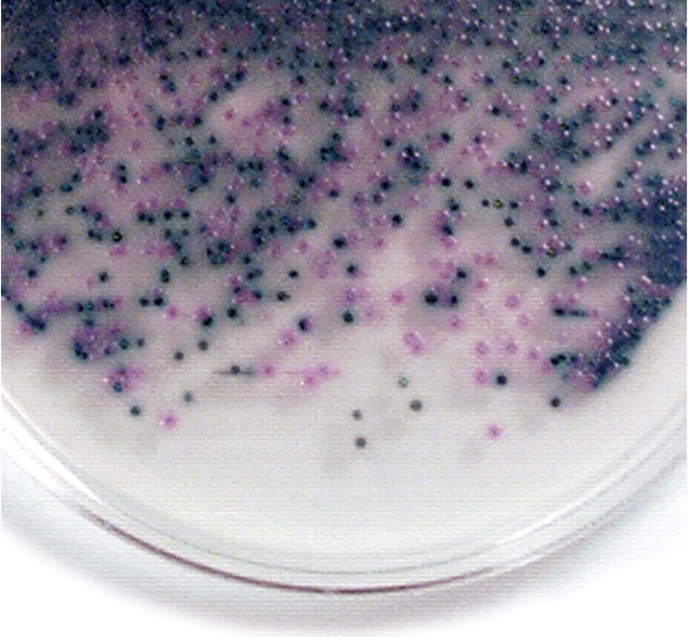
E. coli O157:H7 identified how?
Rapidly identified using Rainbow Agar: O157:H7 colonies appear black
Enterotoxigenic
E. coli causes severe diarrhea due to heat-labile toxin and heat-stable toxin – stimulate secretion and fluid loss; also has fimbriae
Enteroinvasive
E. coli causes inflammatory disease of the large intestine
Enteropathogenic
E. coli linked to wasting form infantile diarrhea