Computer science (0984): Theory
1/183
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
184 Terms
Computer
A device that receives input, processes that input, and then produces the output.
Definitions

Denary
It has a base of 10
It uses ten values that are 0 to 9
Units increase by power of 10
Binary
It has a base of 2
It only uses two values that are 0 and 1
Units increase by power of 2
Why is data stored as binary in computers?
As computers consist of logic gates
Logic gates can only process data in two states (0 and 1)
Hexadecimal
It has a base of 16
It uses sixteen values that are 0 to 9 and A to F
Units increase by power of 16
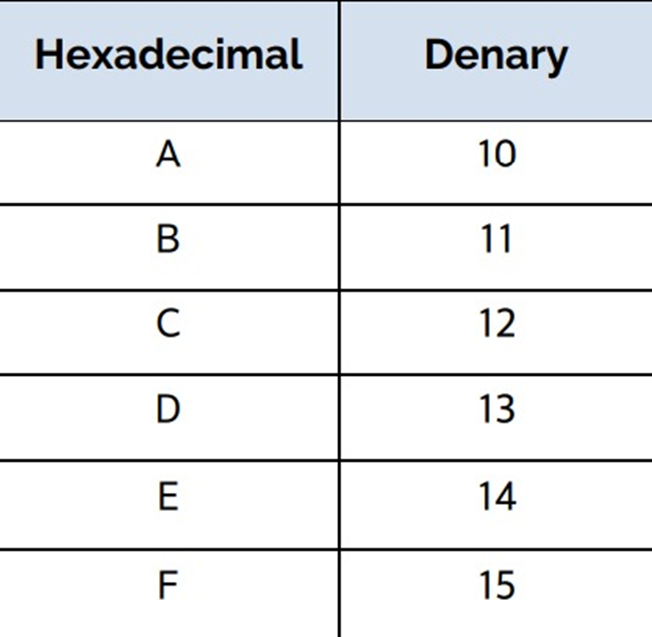
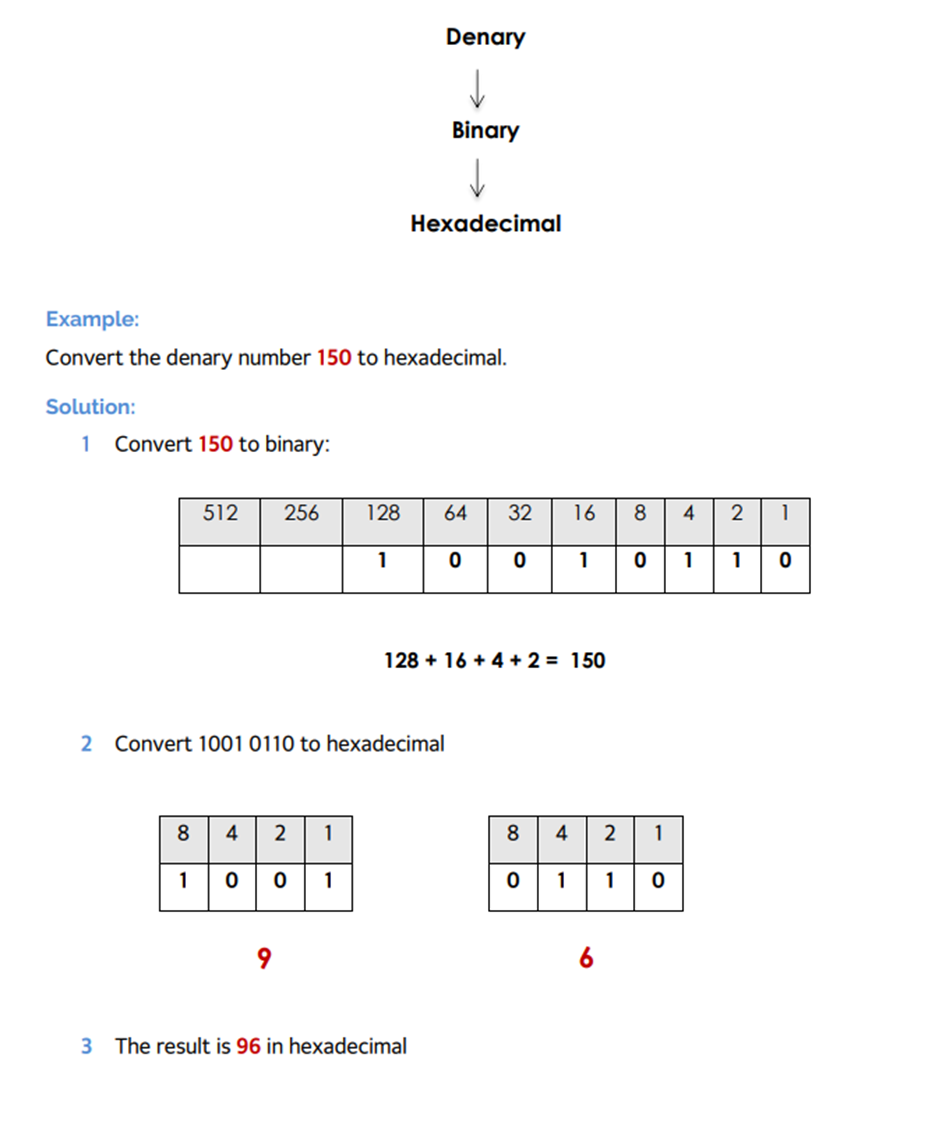
Conversion of Denary to Binary
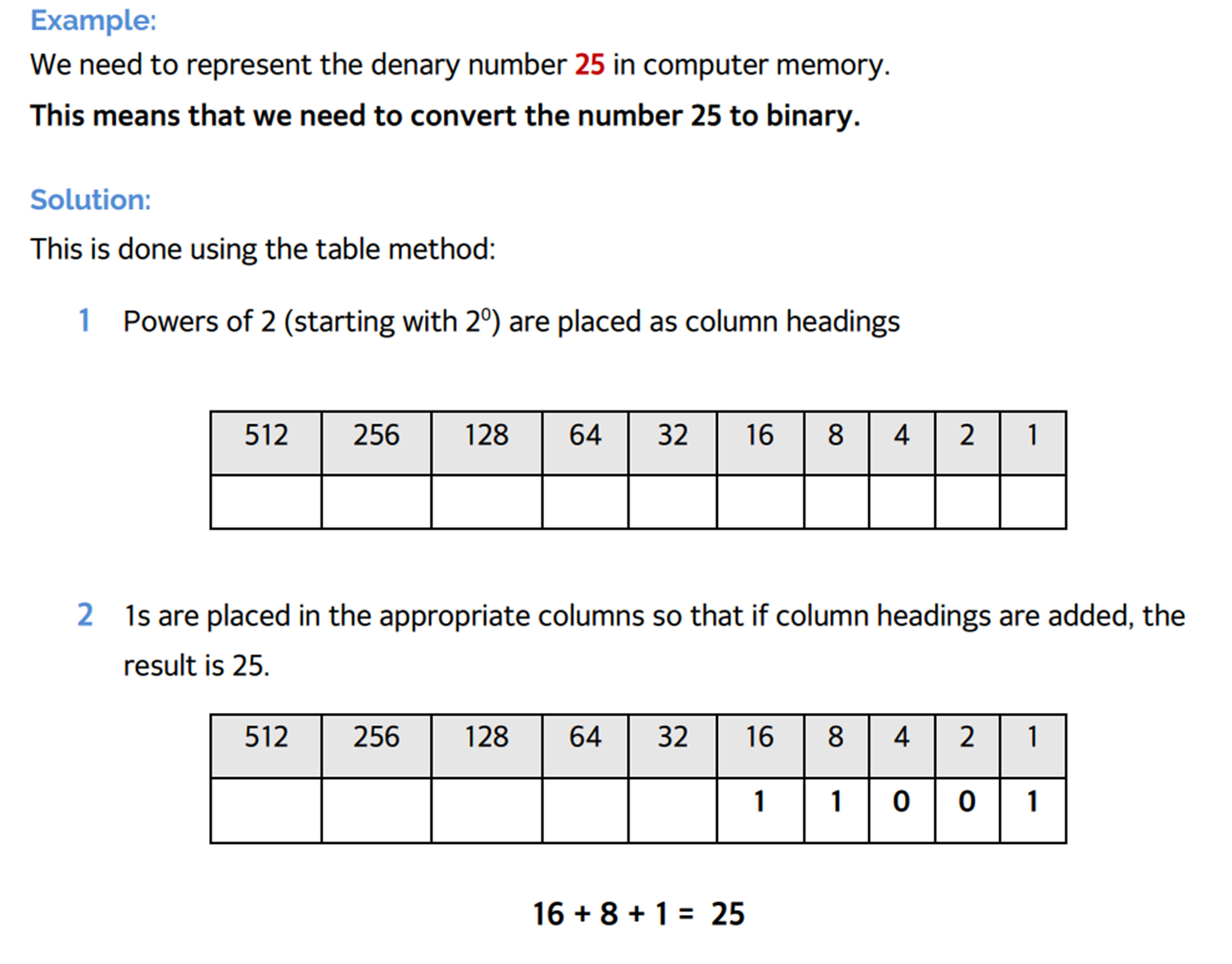
Conversion of Binary to Denary
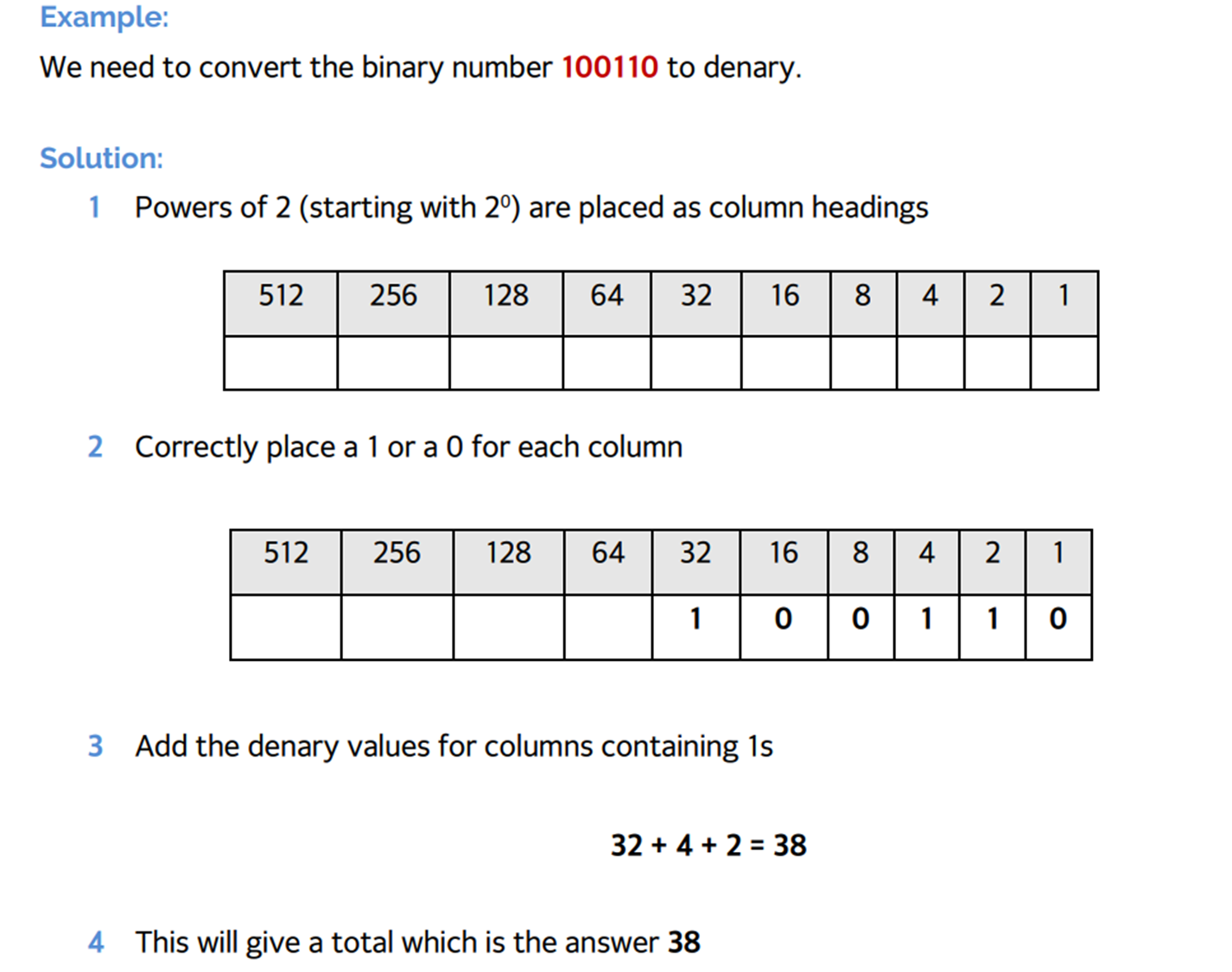
Conversion of Hexadecimal to Binary
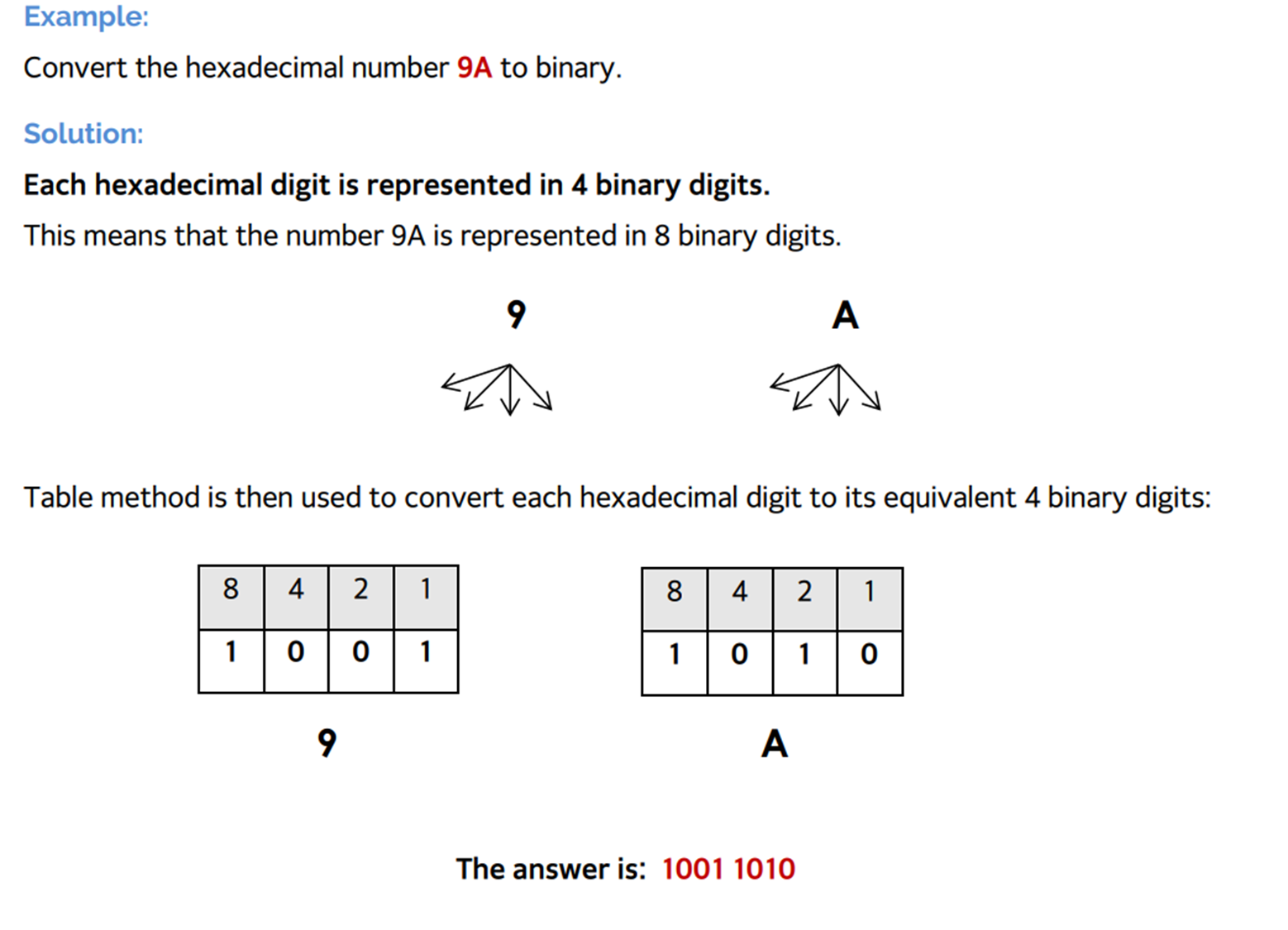
Conversion of Binary to Hexadecimal

Conversion of Hexadecimal to Denary
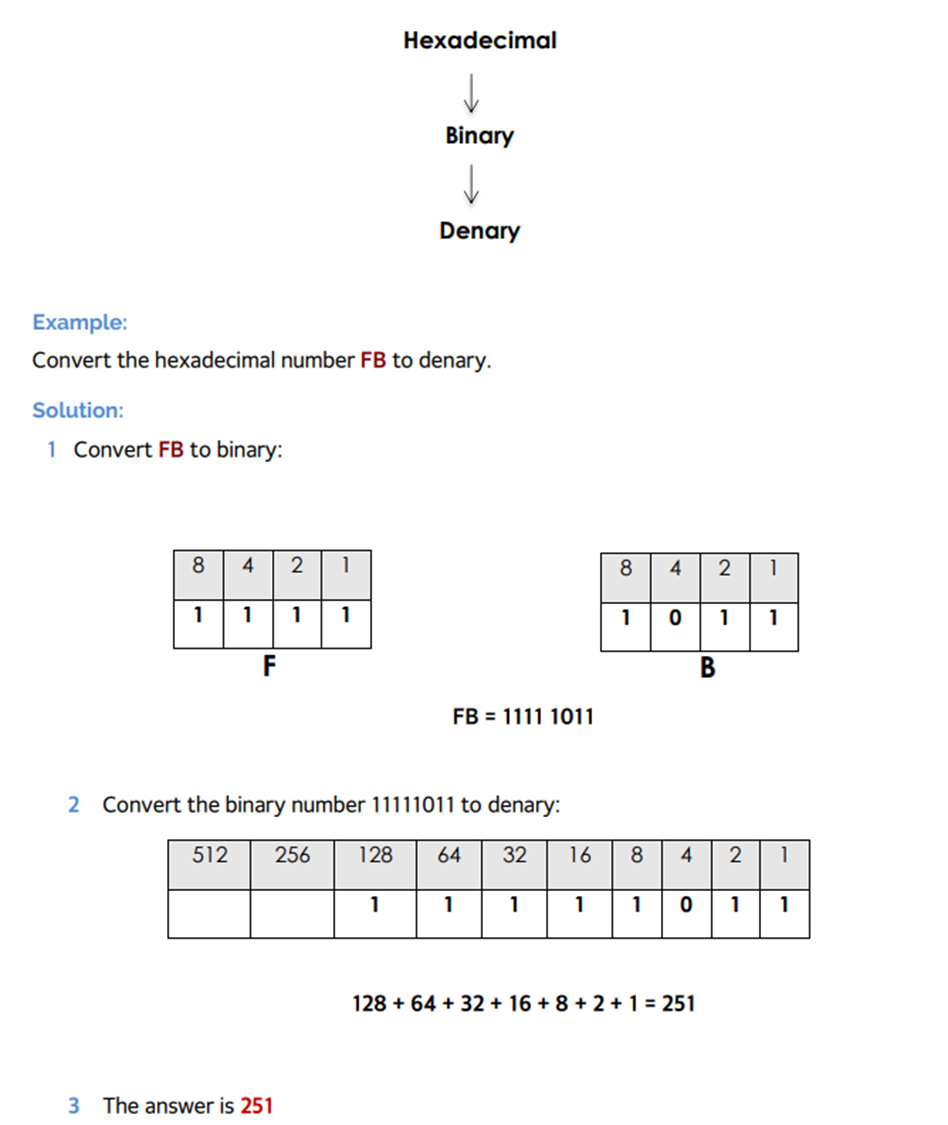
Conversion of Denary to Hexadecimal
Why is hexadecimal preferred by programmers rather than binary?
Easier for programmers to read and understand
Easier to debug
Takes up less space on the screen
Fewer errors made in data transcription
Uses of hexadecimal
MAC addresses
IPv6 addresses
ASCII // Unicode
Debugging
HTML colour codes
Bit
One binary digit.

Nibble
A group of 4 bits.
Byte
A group of 8 bits.
More memory units:
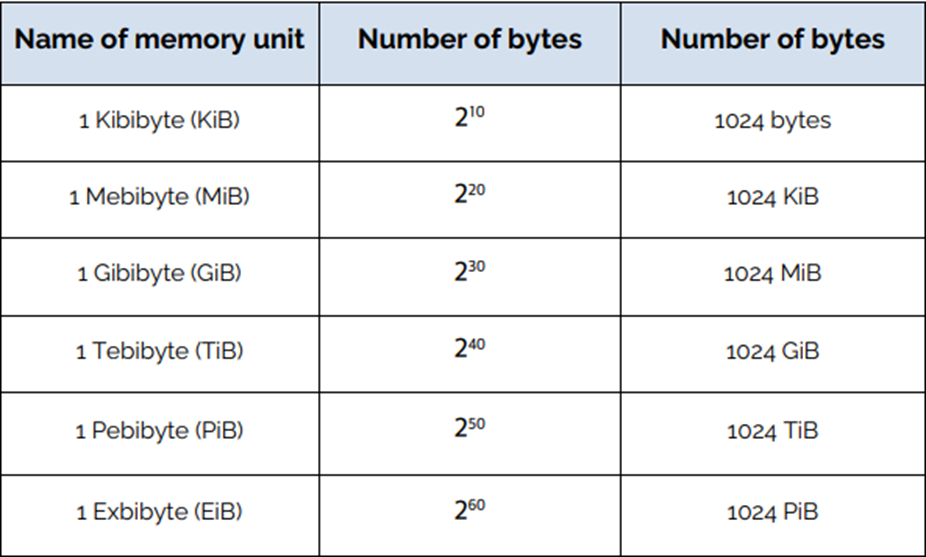
KMGTBE —→ The diff between each is 1024
Text is represented using a character sets:
ASCII
Unicode
Character set
A list of all characters and symbols that can be represented by a computer system
Each character/symbol is assigned a unique value.
ASCII
A character set for all the characters on a standard English keyboard
Each character is represented using 8 bits
Unicode
A character set which can represent all the languages of the world
Each character is represented using up to 32 bits
Differences between ASCII set and Unicode
Unicode has more characters than ASCII
Unicode includes more languages than ASCII
Unicode includes emojis while ASCII don’t
Text stored in Unicode takes up more storage space
Why does text stored using Unicode require more storage space than ASCII:
Unicode requires more bits per character than ASCII.
How text is converted to binary:
A character set is used
… such as Unicode/ASCII
Each character has a unique binary value
Images
An image is a series of pixels.
Important note:
The file size and quality of the image depend on the image resolution and the colour depth
Definitions
How an image is converted to binary:
Each pixel represents a colour and is given a binary value to be processed by the computer
Pixels are stored in sequence in the file
The image resolution is set that is the dimensions of the image
The colour depth is set that is the number of bits used to represent each colour
Effect of increasing the image resolution
The image will have more detail
The image will be closer to real-life
The file will require more storage space
Effect of increasing the colour depth
More bits are allocated to each pixel, so..
.. the image will have more detail
.. the image will be closer to real-life
.. the file will require more storage space
Size of an image file

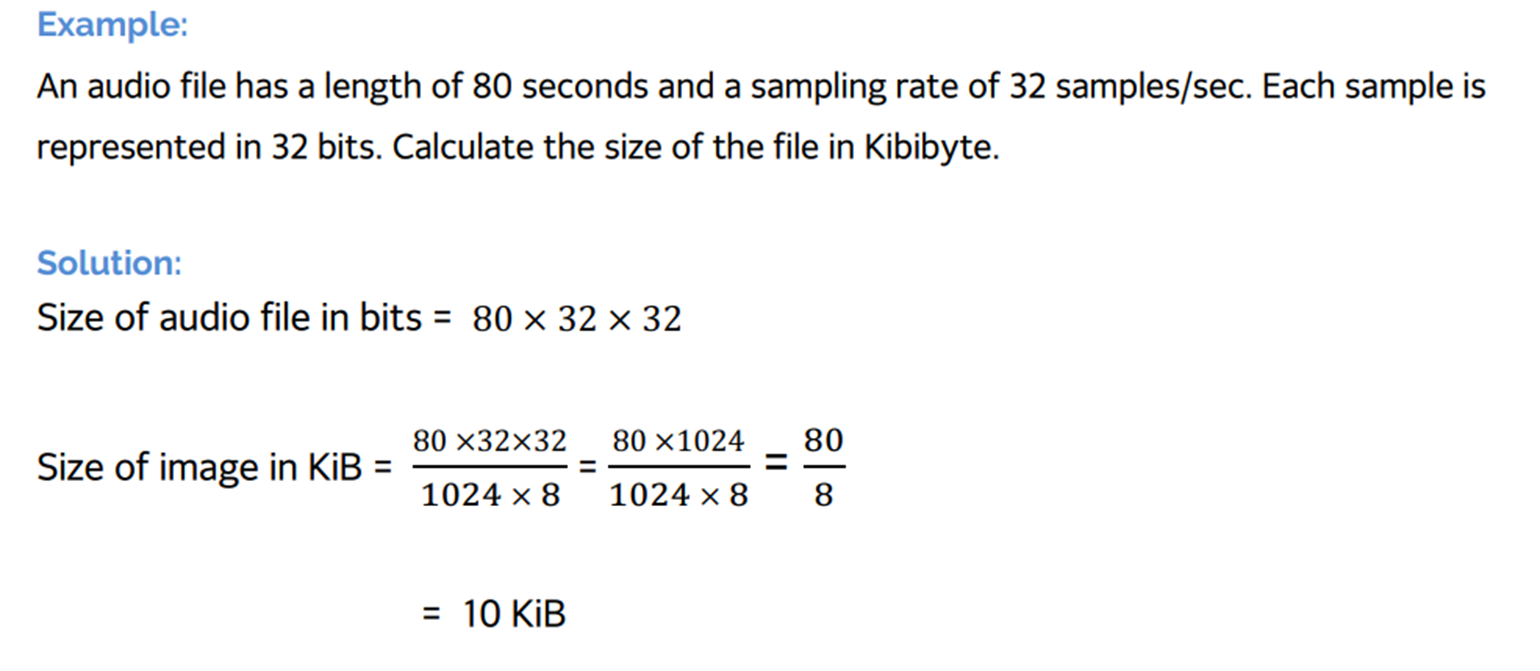
How audio is converted to binary:
The sound wave is sampled measuring the amplitude
Each amplitude has a unique binary value
The sampling rate is set that is the number of samples taken per second
The sampling resolution* is set that is the number of bits used to represent each sample
Each sample taken is converted to binary

Definitions

Effect of increasing the sampling resolution
More bits are allocated to each amplitude so..
.. amplitudes are closer to the original sound
.. a wider range of amplitudes can be recorded
.. the file will require more storage space
Effect of increasing the sampling rate
More amplitudes are taken per second, so..
..closer to the original sound
..the file will require more storage space
Size of an audio file

Register
A small fast memory location within the CPU.
Definitions

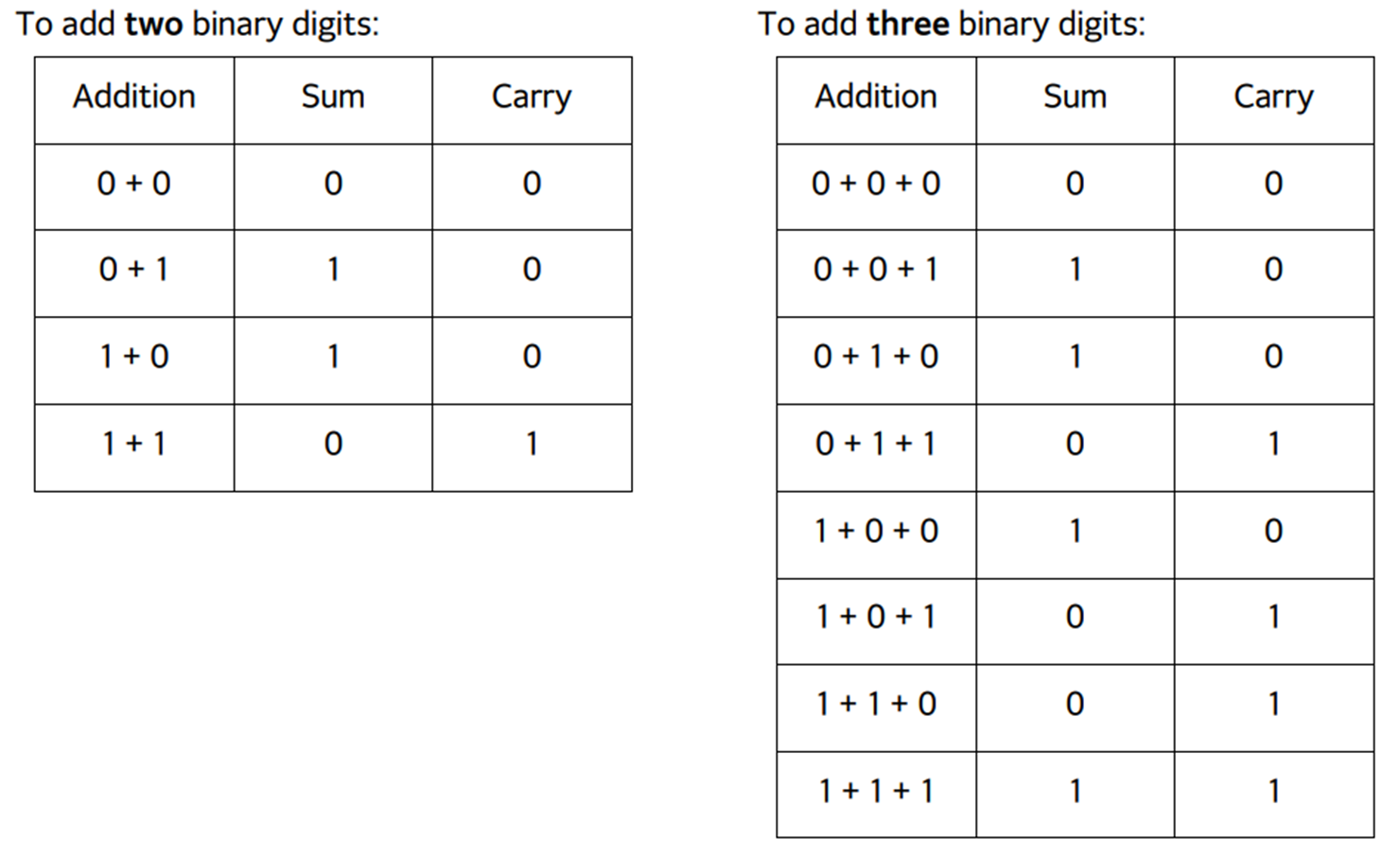
Binary Addition


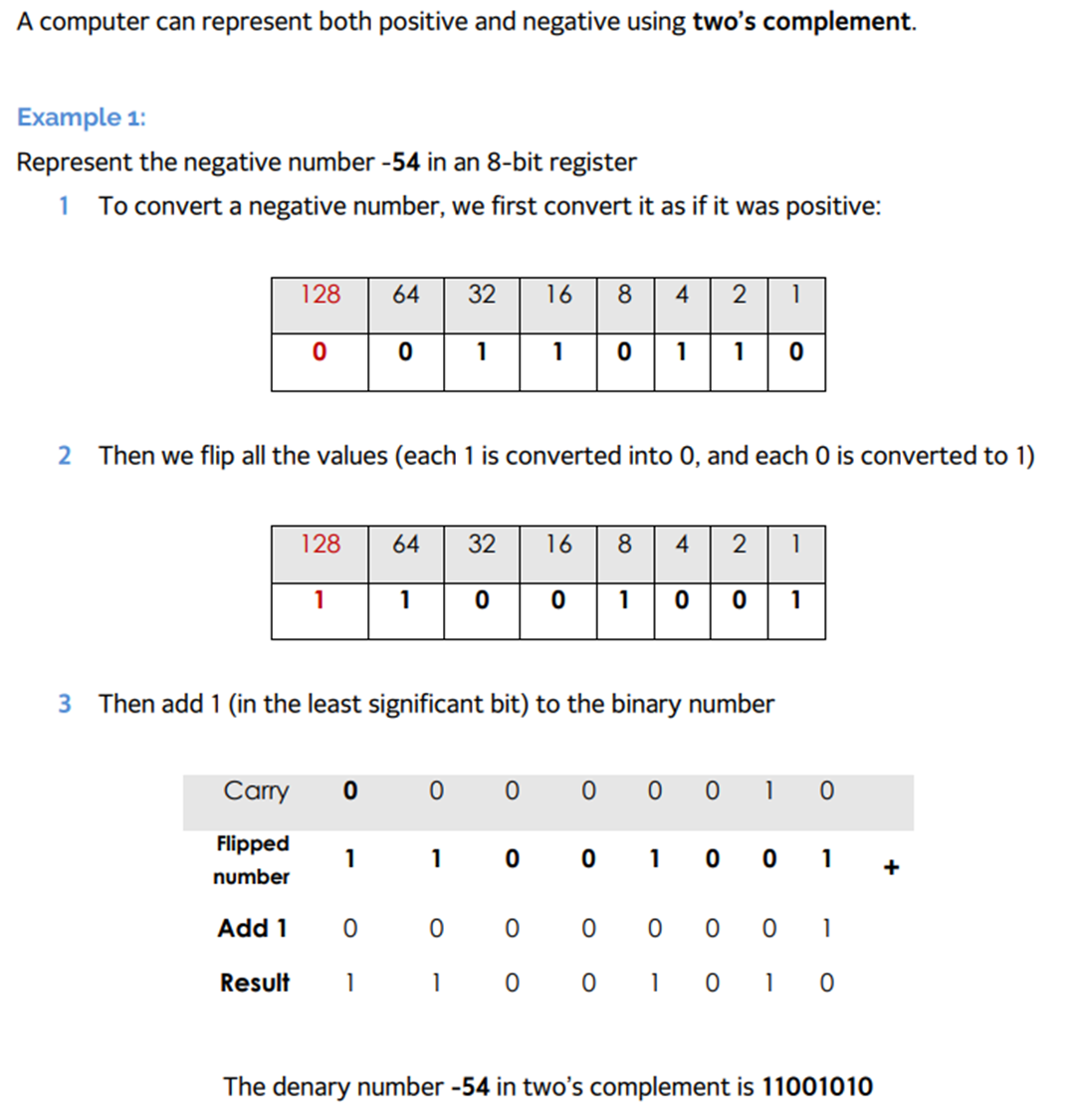
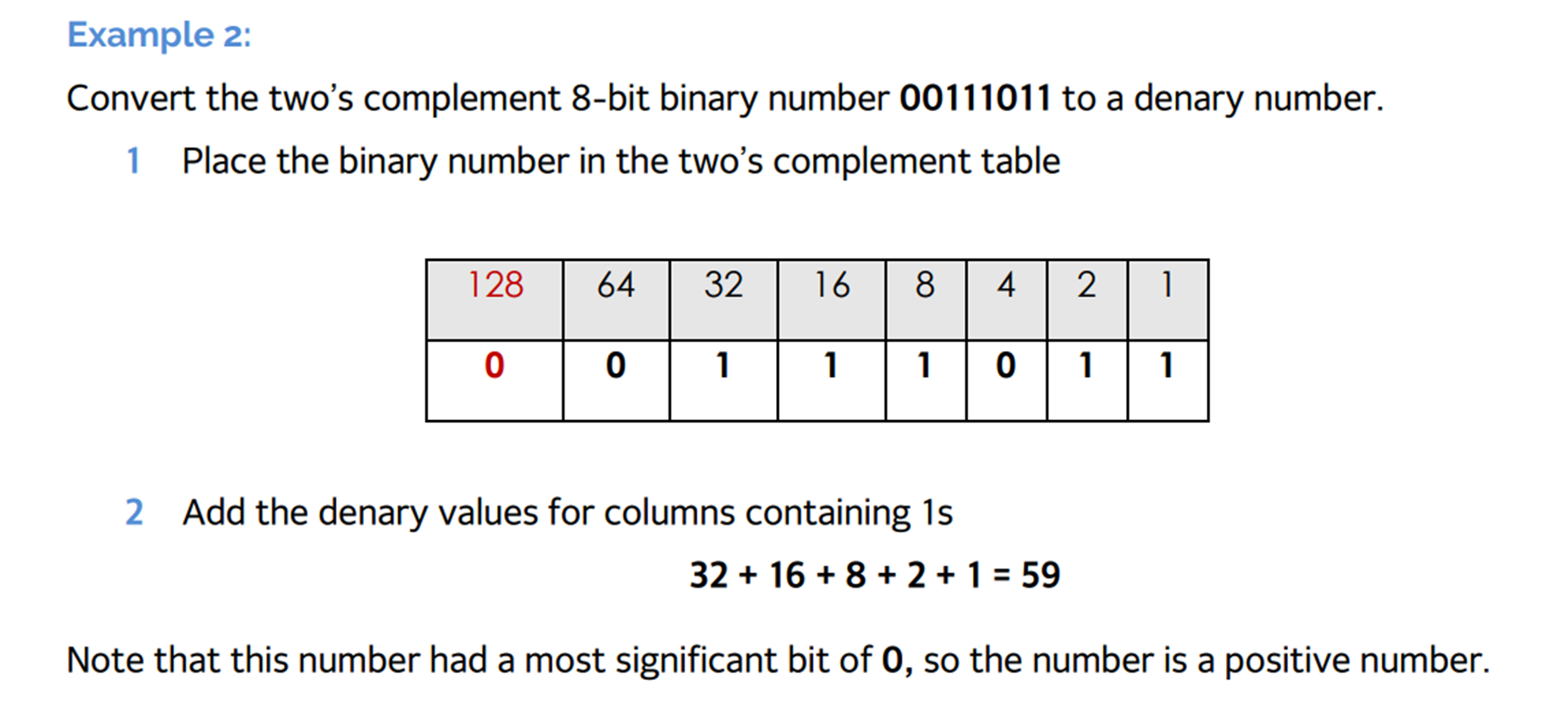
Negative Numbers

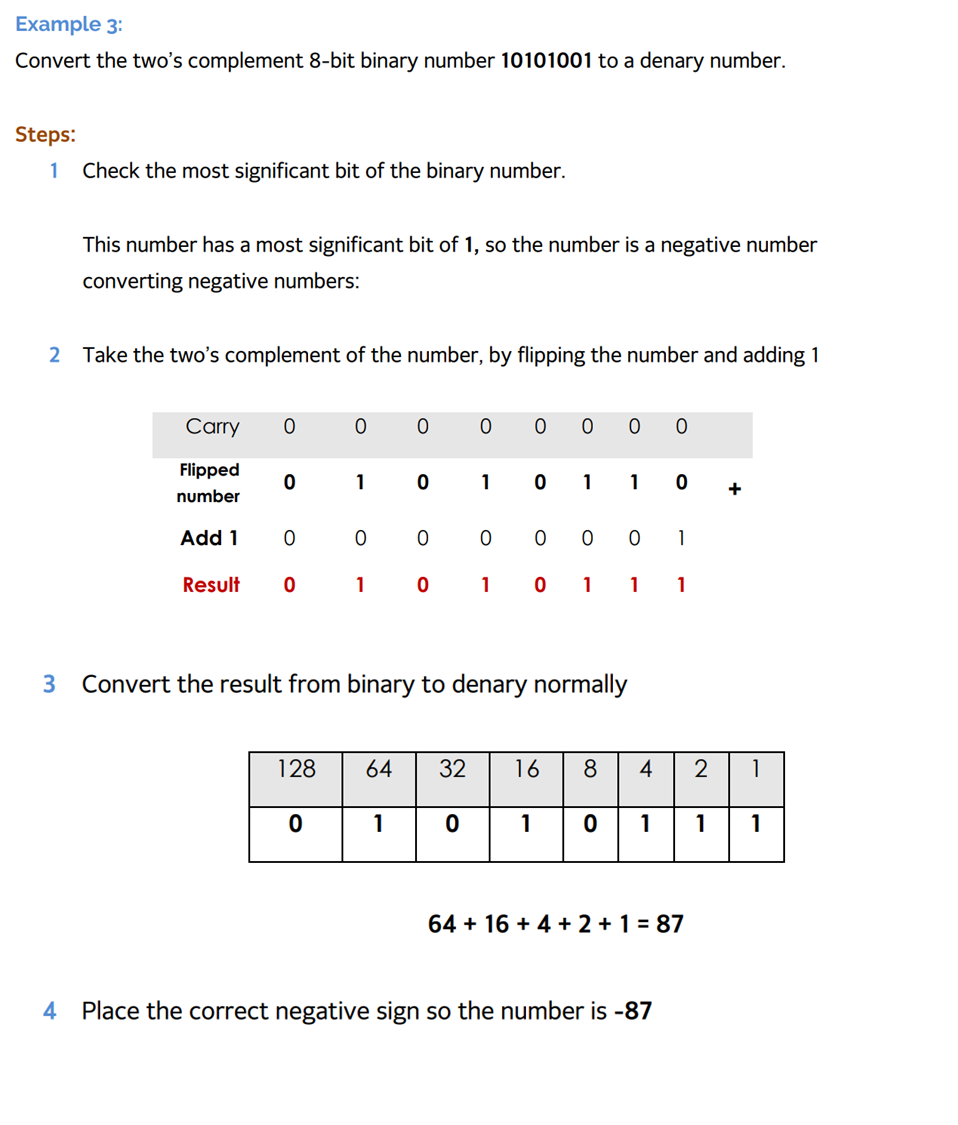
Logical Shift
A binary operation that moves bits to some places to the left or right.
Left logical shift: Multiply by 2
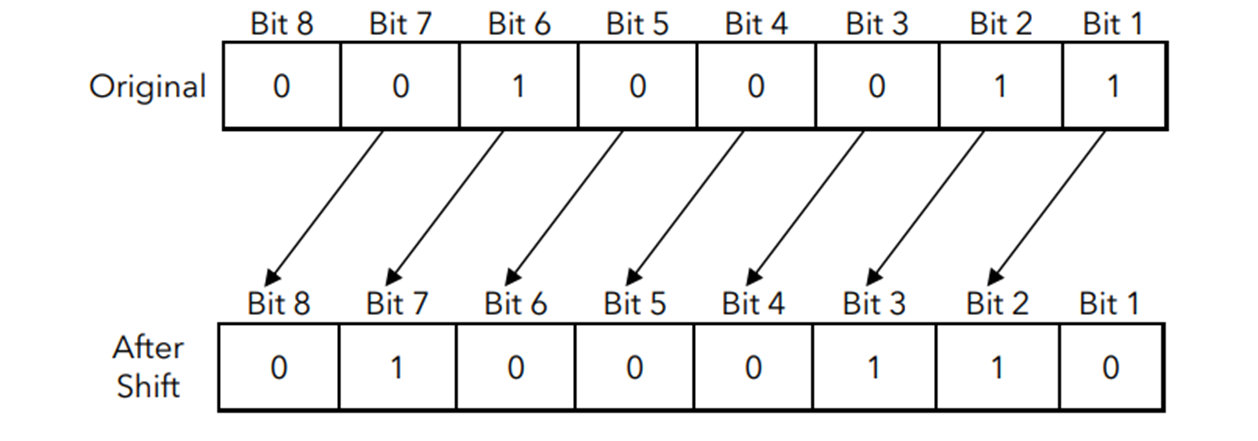
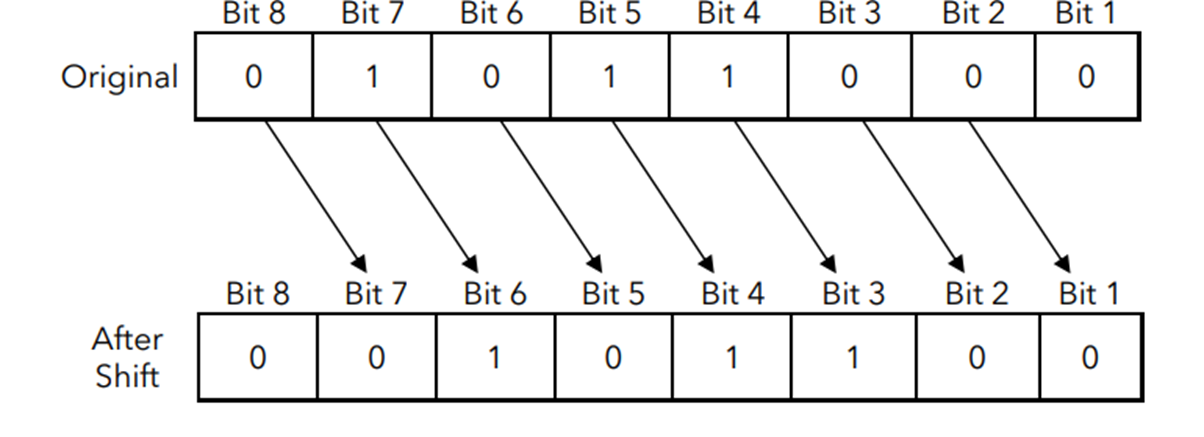
Right logical shift: Divide by 2
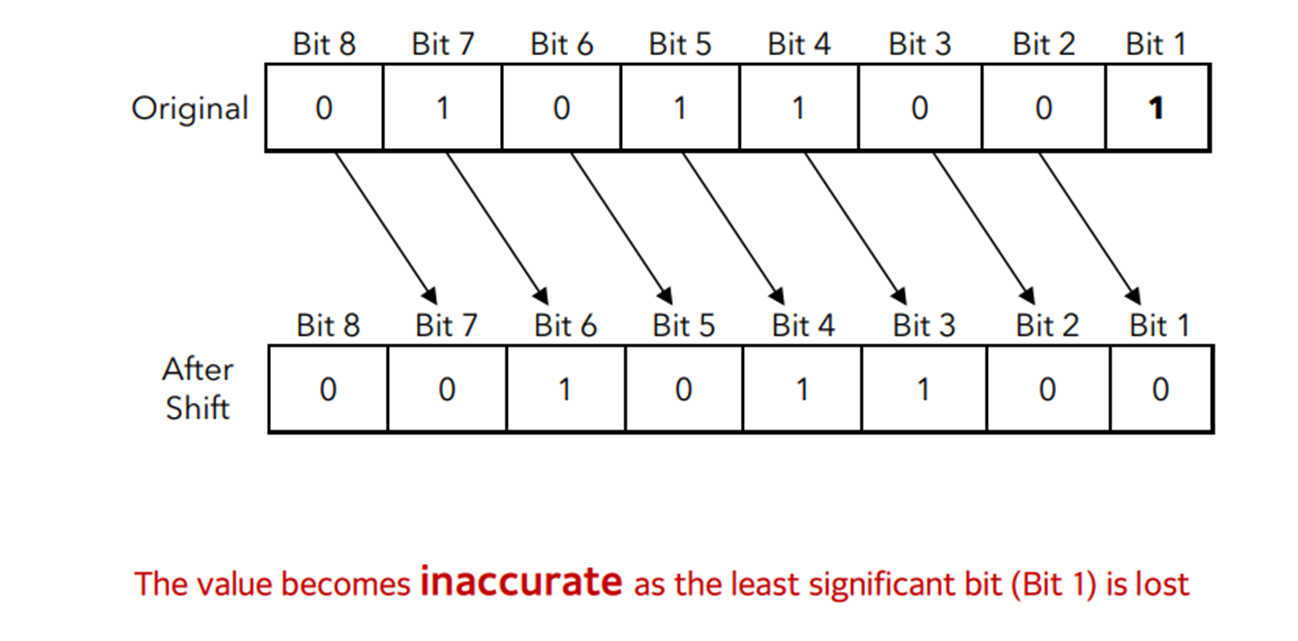
Issues with logical shift:
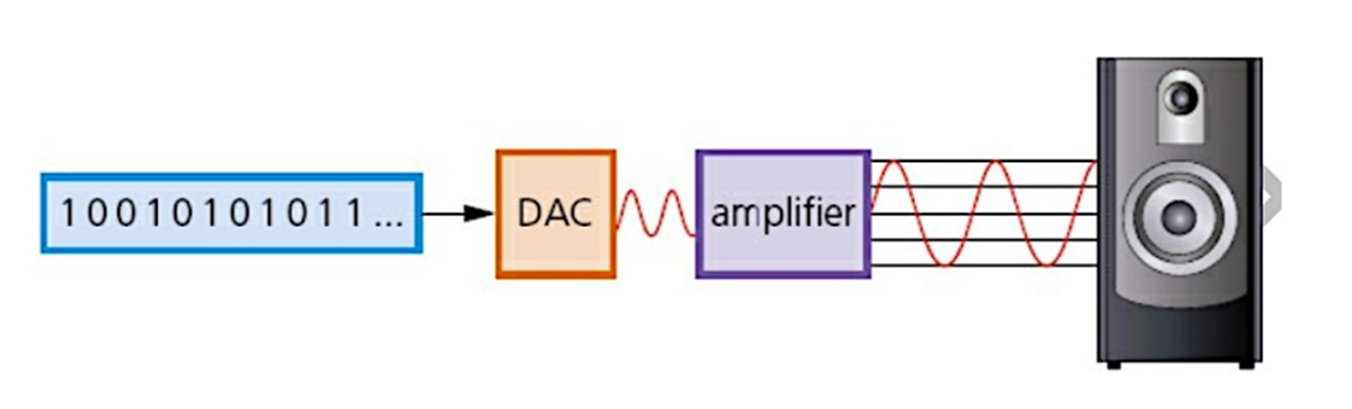
Analogue & digital data:
Why are converters used?
As humans, we use analogue data while computer only understand digital data.
Thus converters are used to convert from analogue to digital or vice versa
Converters
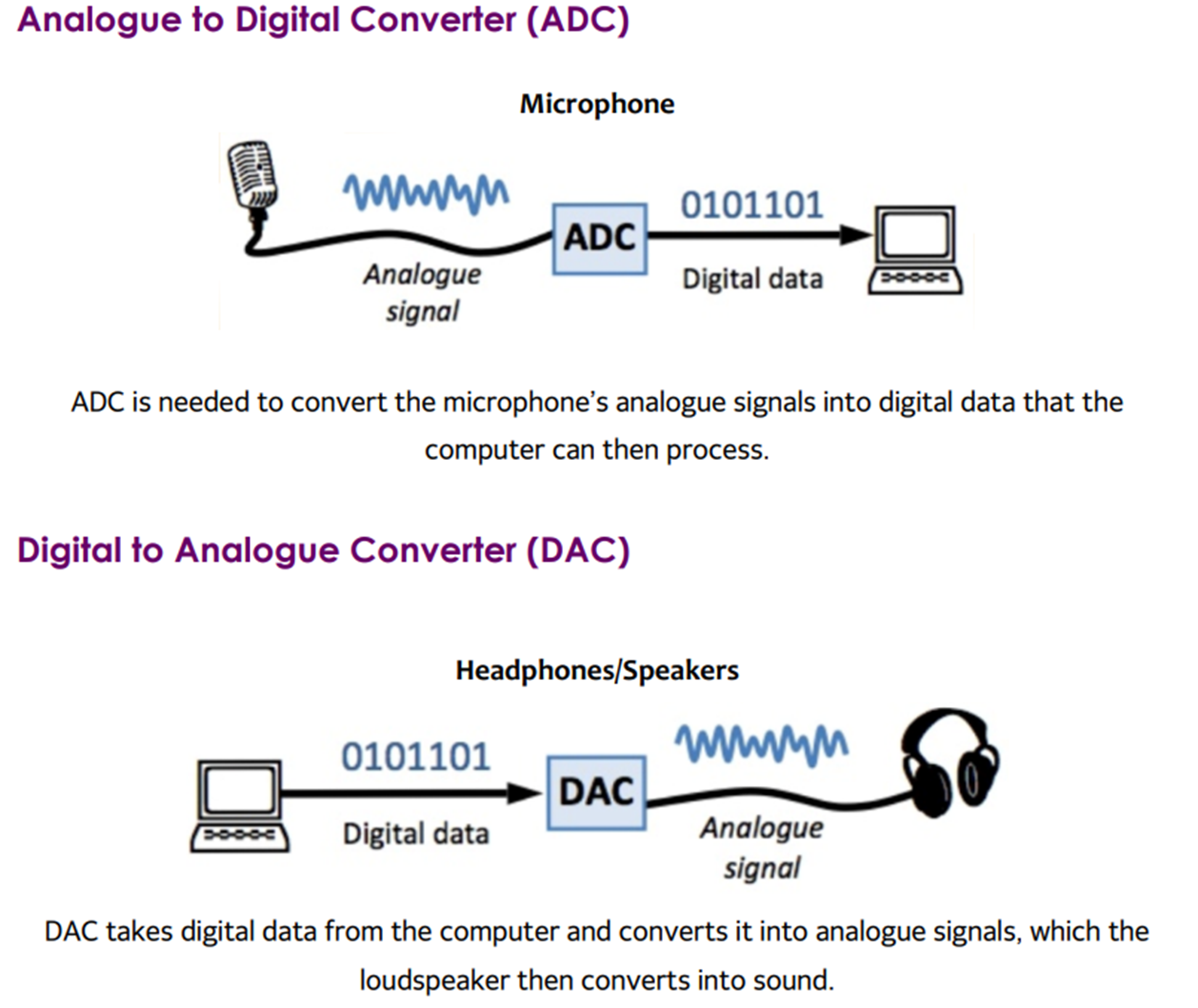
Input device, part 1:
Device used to enter data into a computer
Keyboard:
An input device used to type in data
Optical mouse:
An input device used to control a pointer/cursor on a screen
Uses laser and optical sensor to detect movement
Microphone:
An input device used to input sound to a computer
Uses:
Used to input sound in voice recognition software to enhance security
Used to input sound in speech recognition software to convert voice into text

Digital camera:
Input device used to capture digital photographs
It uses a lens and a sensor to capture light
Scanners:
2D scanner:
An input device used to convert hardcopy images/document into a digital format
Software that works with 2D scanners: OCR & OMR

3D scanner:
An input device to scan solid objects & produce a 3D digital model
Part 2:
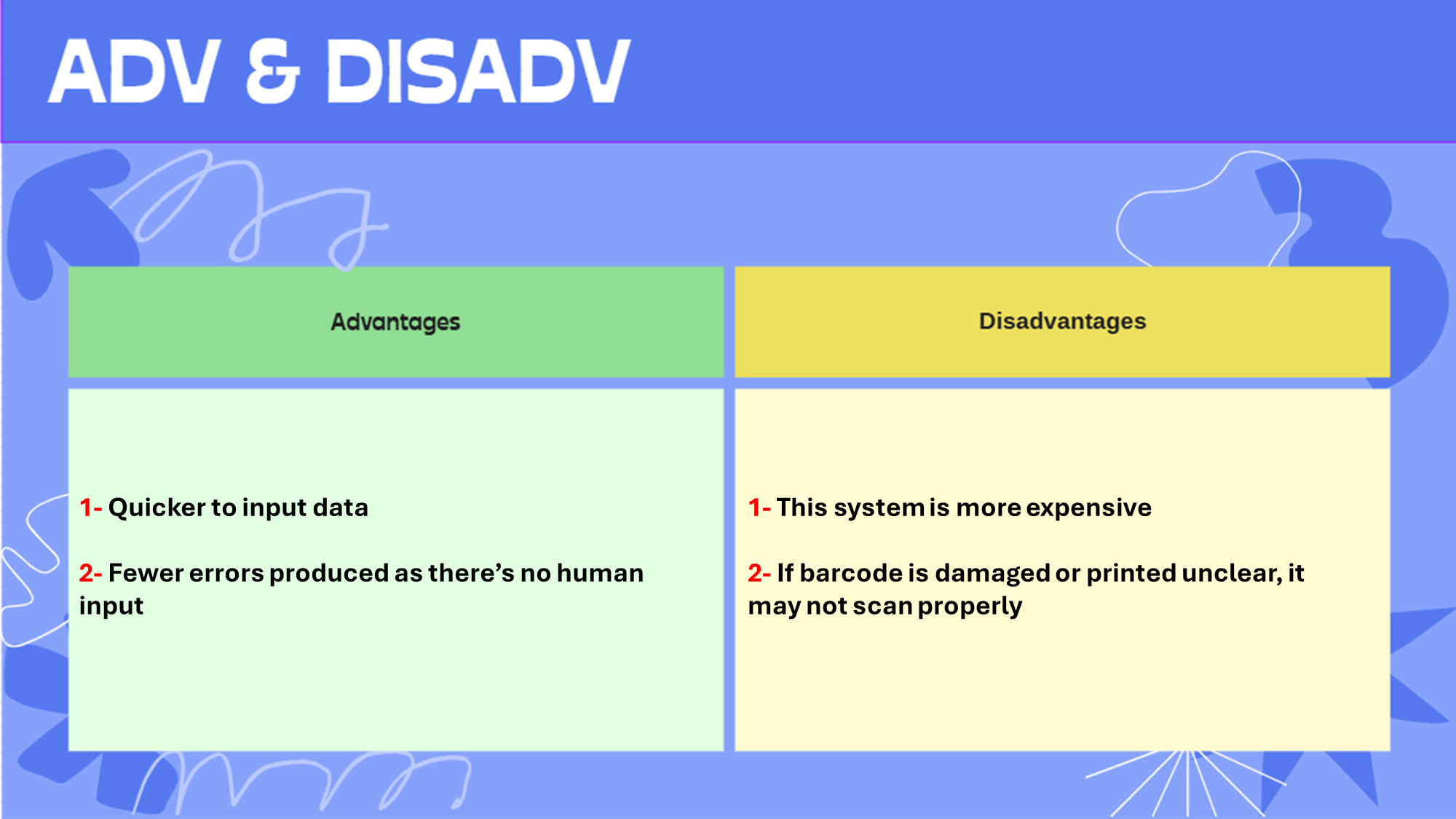
Barcode scanner:
Barcode: a series of black & white lines of varying thickness and is used to represent numeric digits or characters
Barcode scanner: An input device used to scan barcodes
Compared to entering data manually:
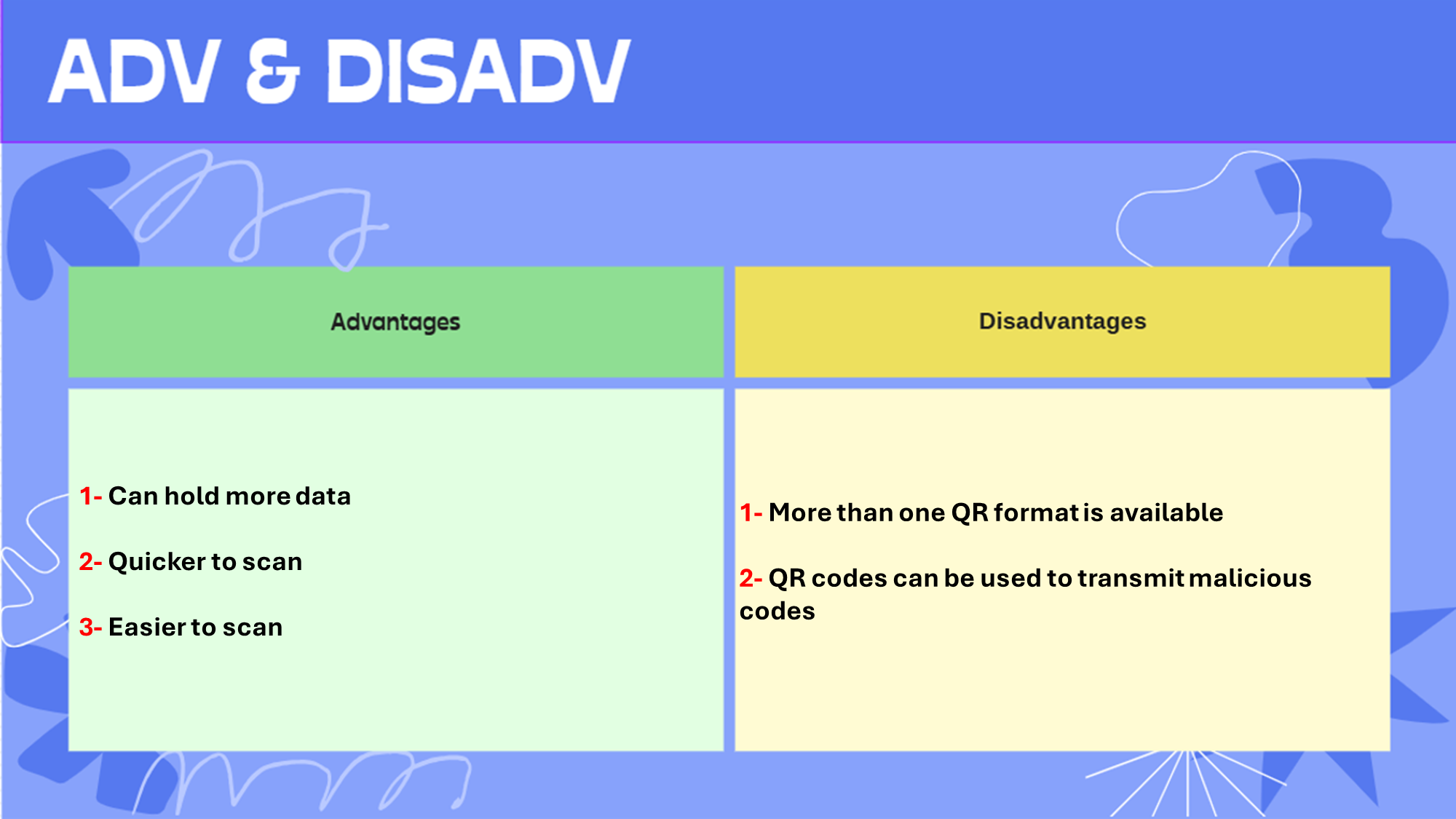
QR scanner:
QR code: Matrix of black & white squares that can link into things.
QR code scanner: An input method used to scan QR codes. It uses red laser & sensors to convert QR code into binary values
Compared to traditional barcodes:
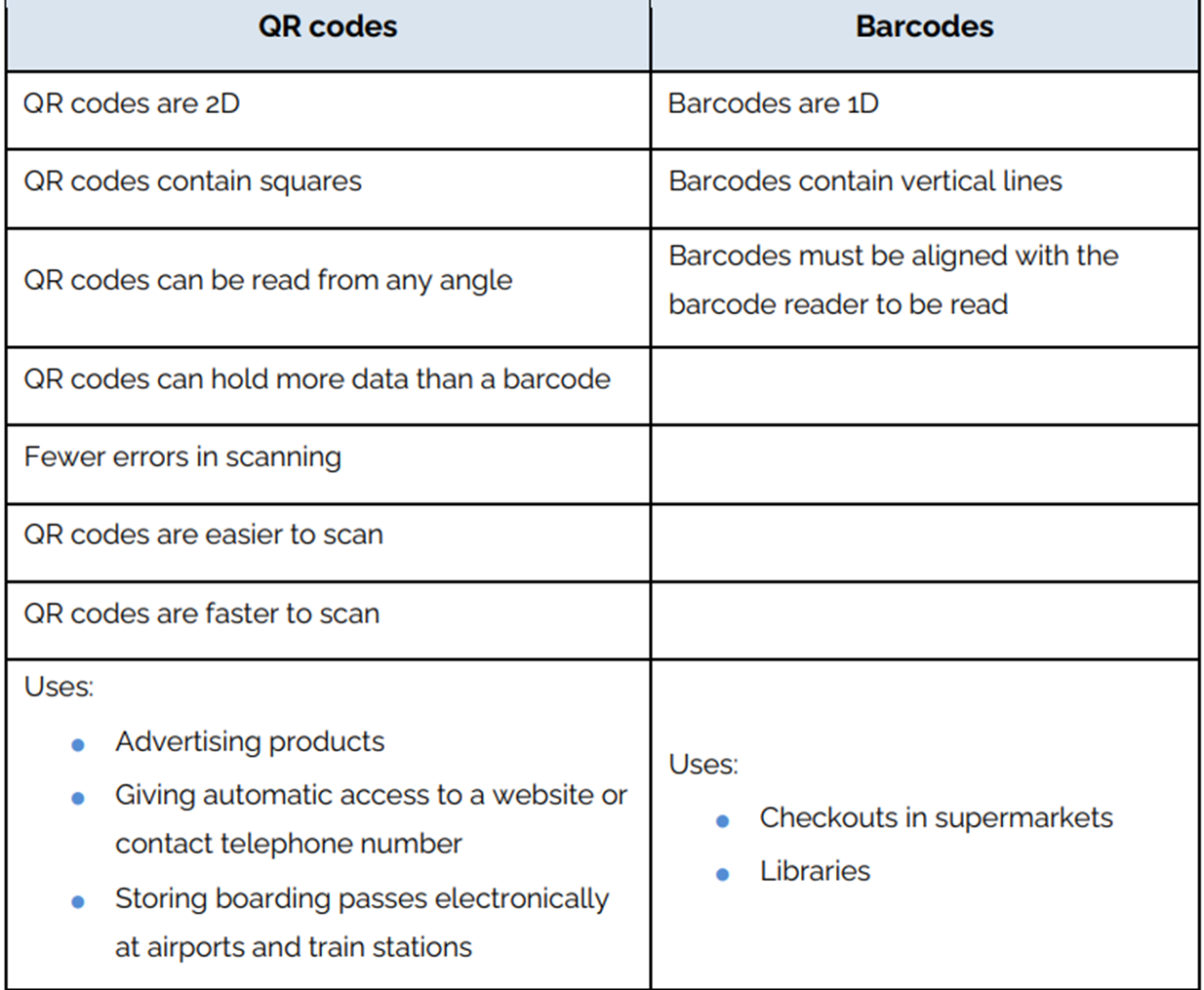
Diff between QR codes & barcodes:
Part 3:
Touchscreen: An input device that allows simple touches to carry out many functions of a pointing device
Compared to Keyboards & mouses:

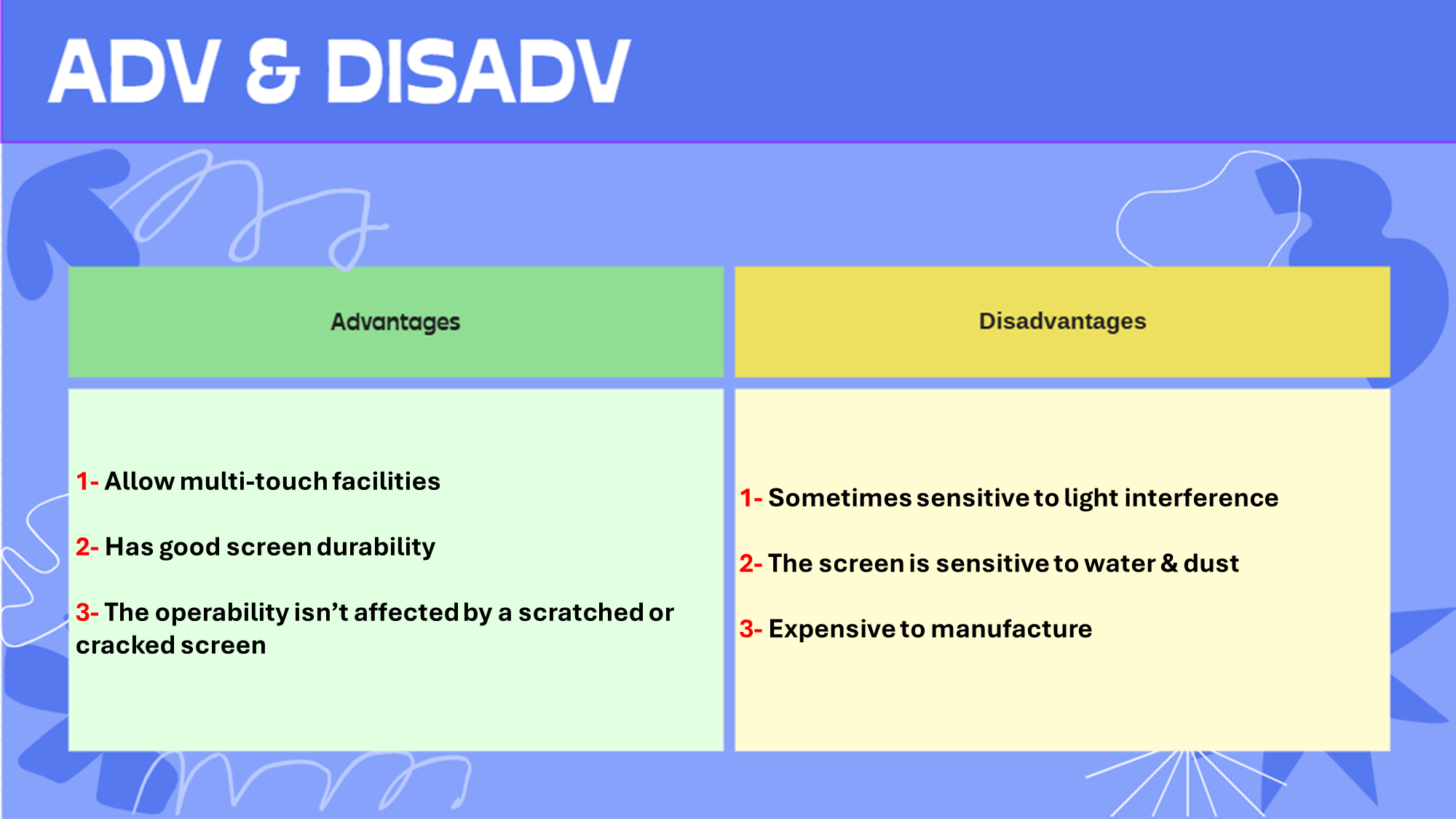
Capacitive touchscreen:
Touchscreen that operates by using the conductive properties of the object/finger that is used to touch the screen
Adv & Disadv:
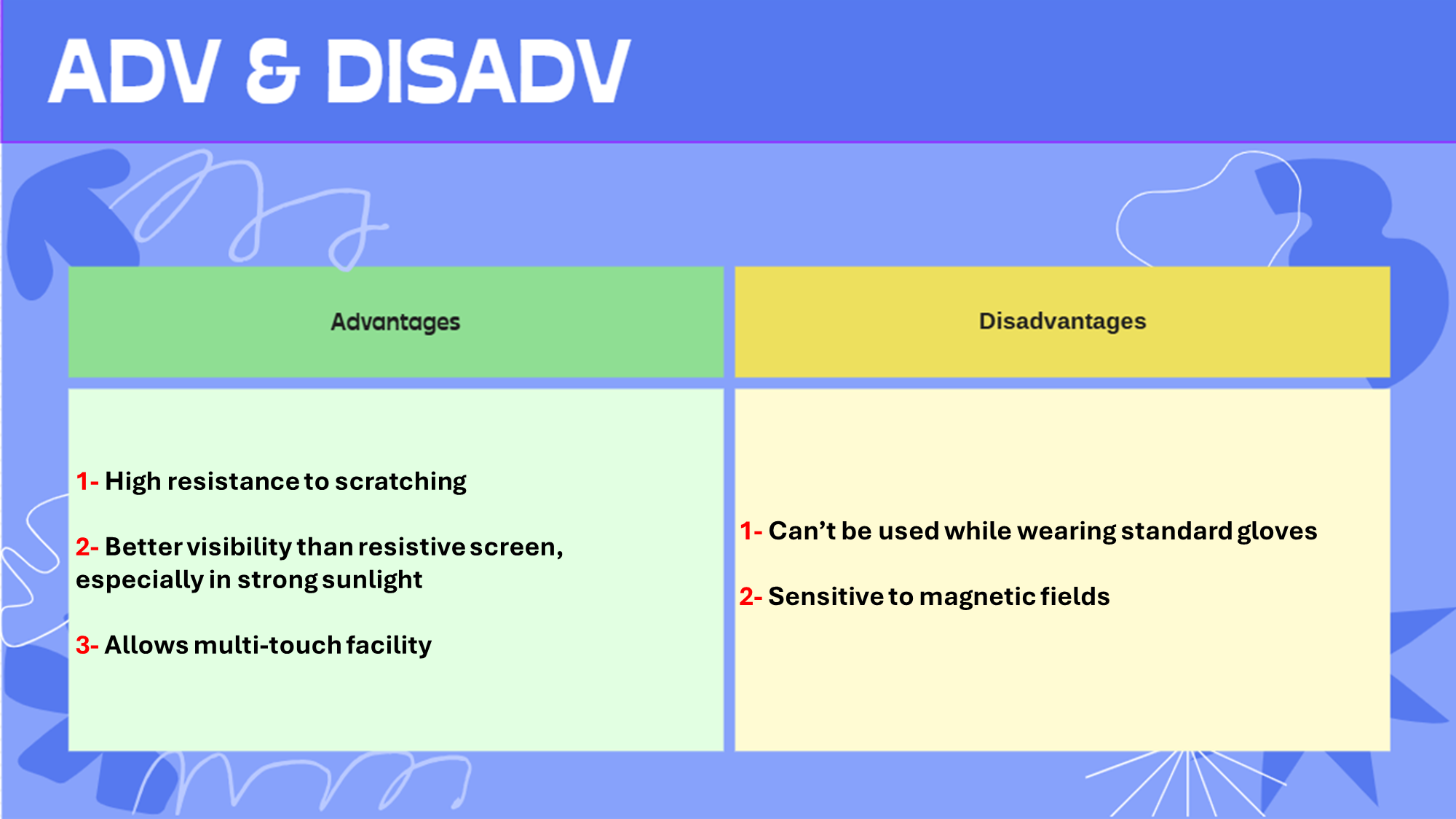
Resistive touchscreen:
Touchscreen that makes use of two layers, when top layer is touched, top & bottom layers complete a circuit at the point of touching
Adv & Disadv:
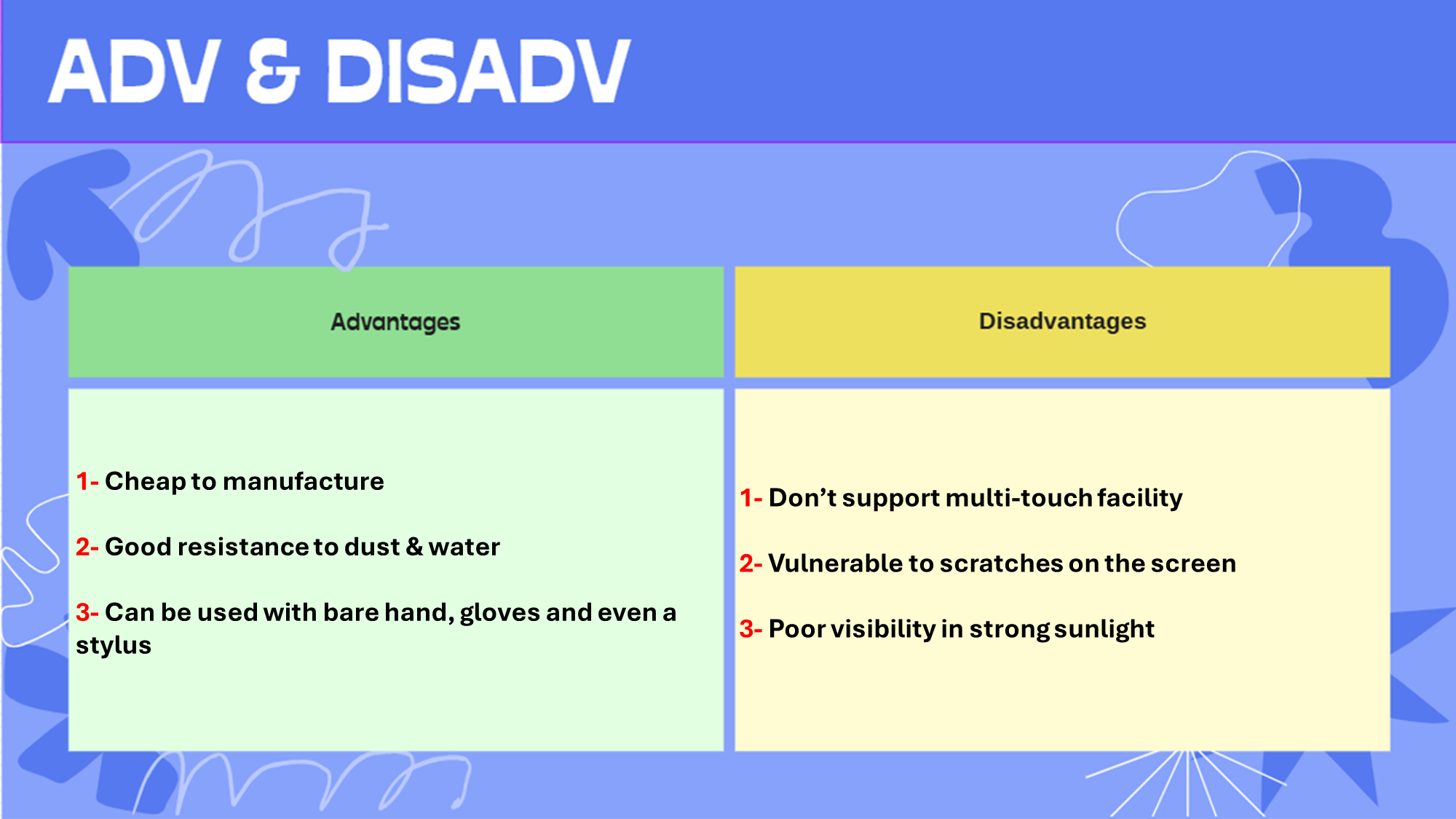
Infrared touchscreen:
Touchscreen that uses sensors & infrared beams, sensors detect the point of touching through a break in a beam
Adv & Disadv:
Output devices, part 1:
A piece of hardware that produces the processed data to the user
Screens:
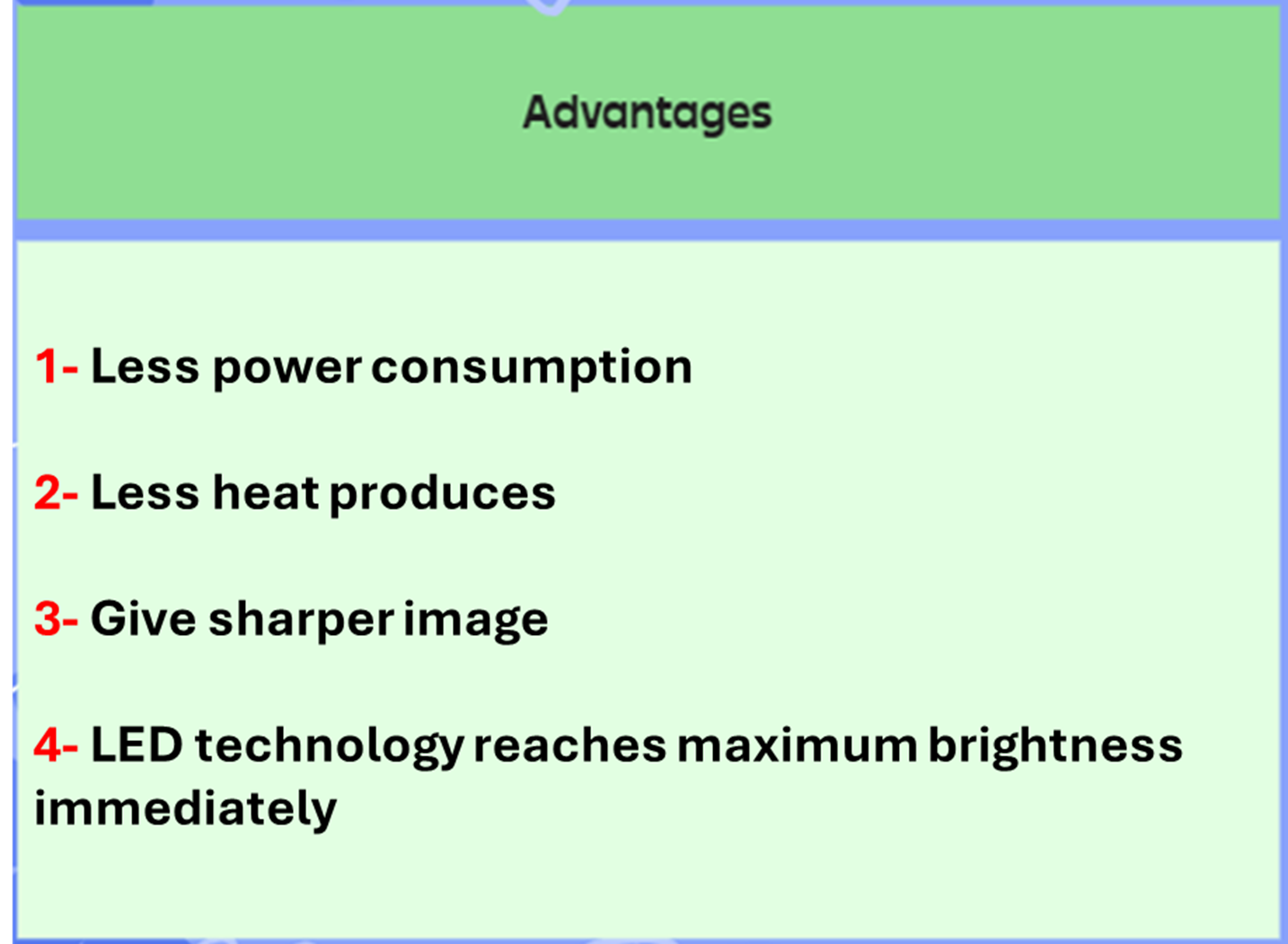
LED screen: A screen that is made of tiny LEDs, LED brightness can vary by varying the current sent to each LED
LCD screen: A screen that is made up of tiny liquid crystals & backlighting. Backlighting can be either LED technology or CCFL technology
Adv of using LED backlighting over CCFL backlighting:
Part 2:
Projectors:
LCD projector: A projector that uses LCD screens & a special prism to project an image
Adv of LCD projector over DLPs:
DLP: A projector that’s composed of millions of micro mirrors on a small DMD chip
Adv of DLP projectors over LCD projectors:

Part 3:
Printers:
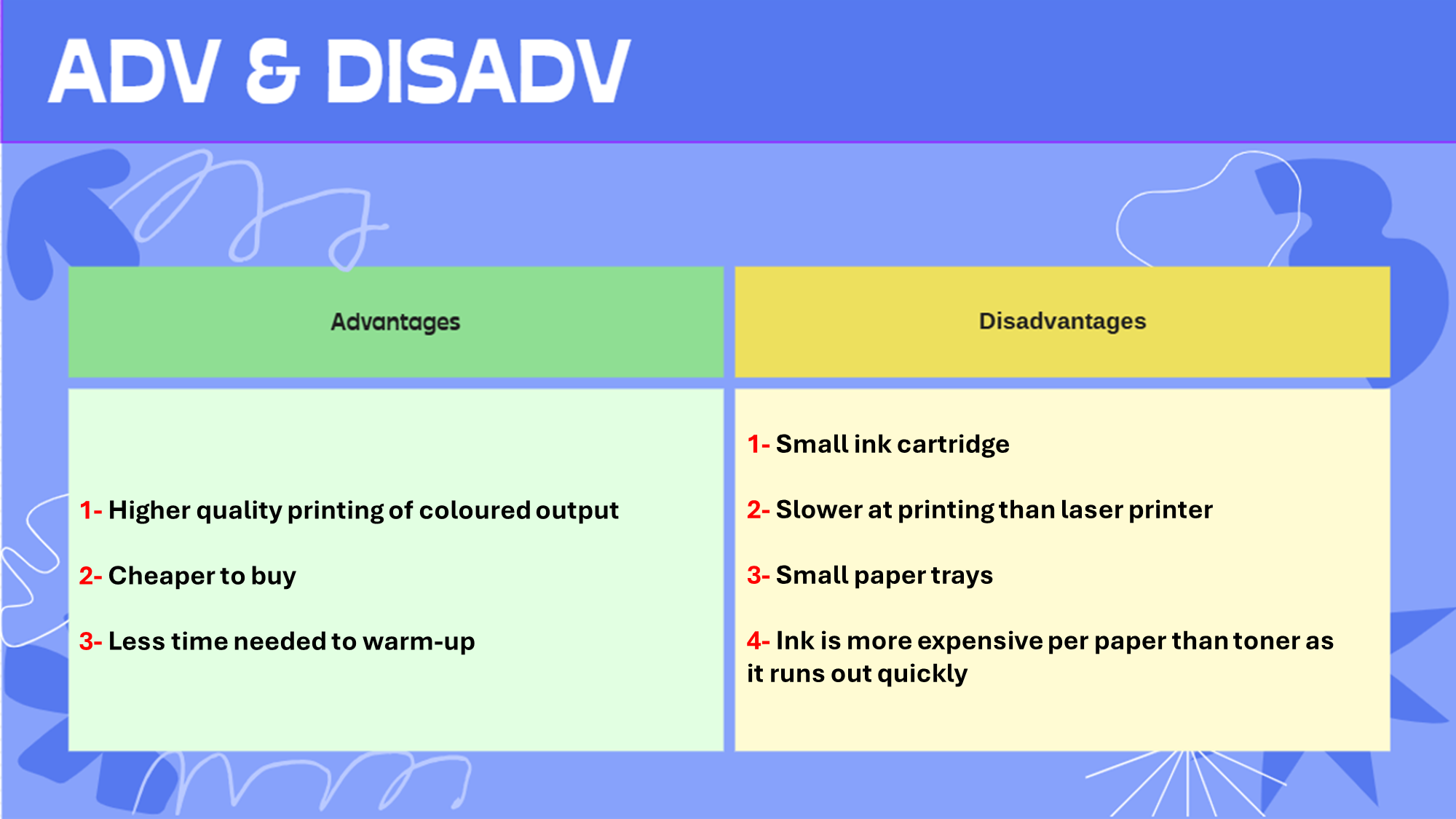
Inkjet printer: A printer that uses liquid ink & a moving printing head to print out data
Use: Printing photographs
Adv & Disadv:
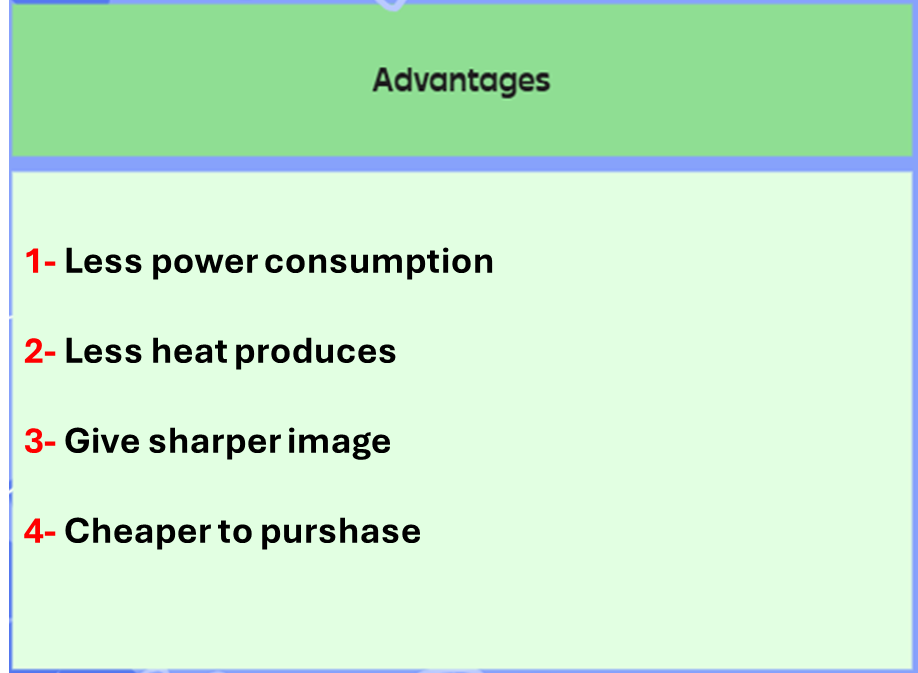
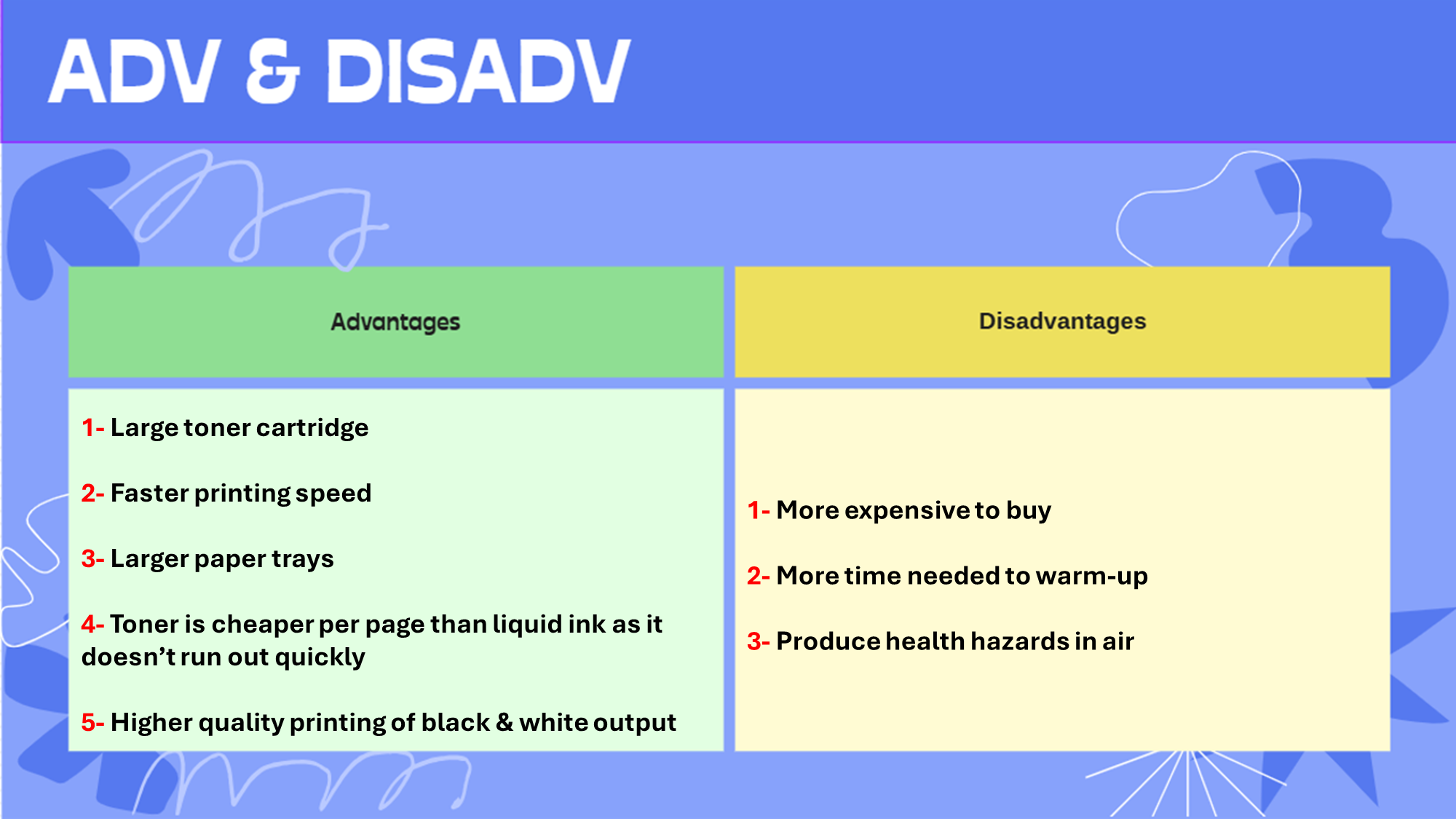
Laser printer: A laser printer that uses toner & static electricity to print out information
Use: Producing a large number of high quality flyers & posters for advertising
Adv & Disadv:
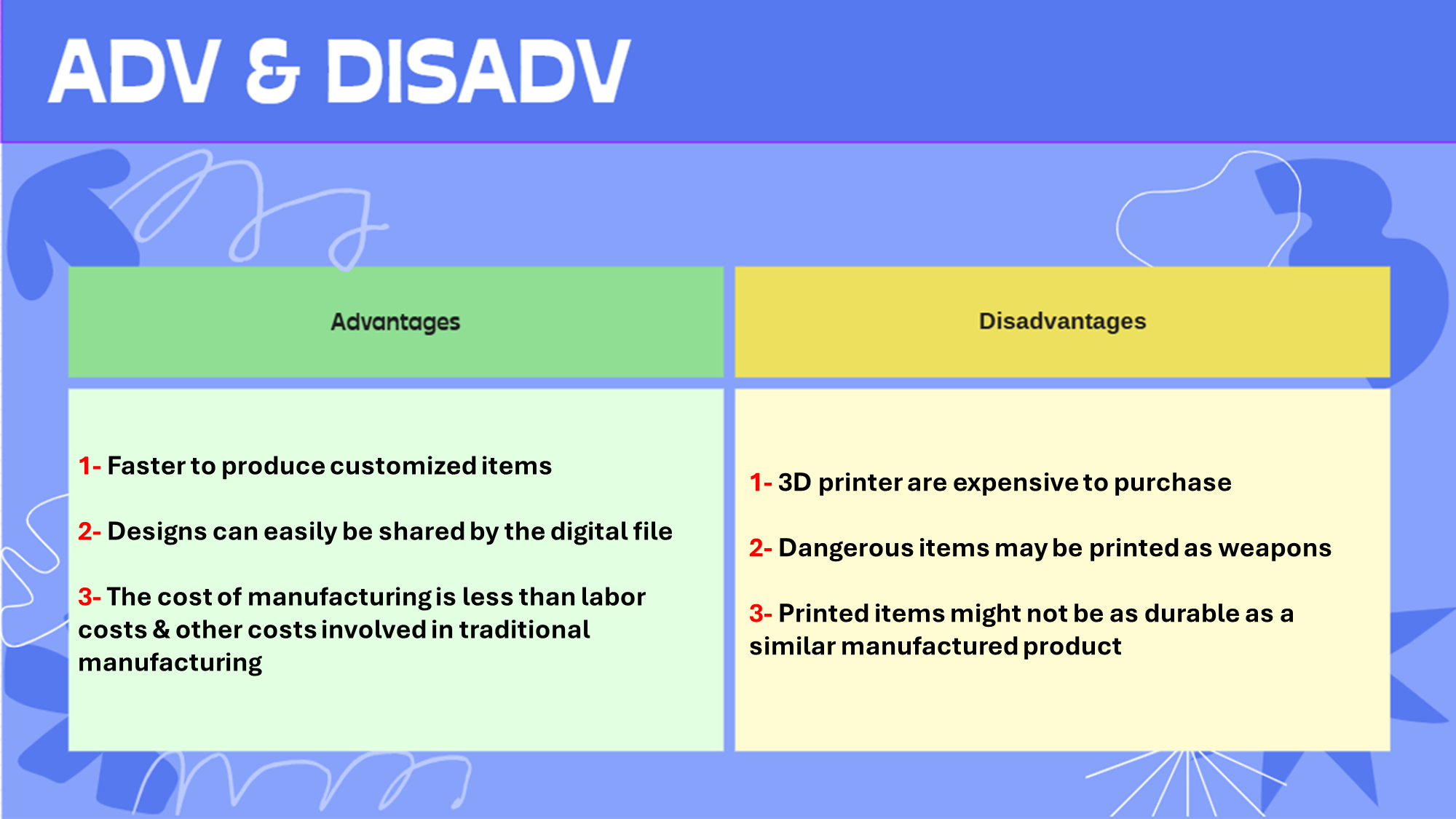
3D printer: Output device used to produce 3D solid objects, the solid objects are built layer by layer using a specific material
Use:
Produces:
..Prototypes
..Customized items like prosthetic limbs to exactly fill the recipient
..Customized items for surgical equipment
..Making parts for items no longer in production
Adv & Disadv of using 3D printer over traditional manufacturing:
Part 4:
Speakers & headphones: Output devices that produces sound
Actuators: A mechanical output device that produces movement, they can rotate, close, push and pull an object
Use:
1- controlling robot arm.
2- spinning a fan.
3- pumping water
Adv & Disadv:
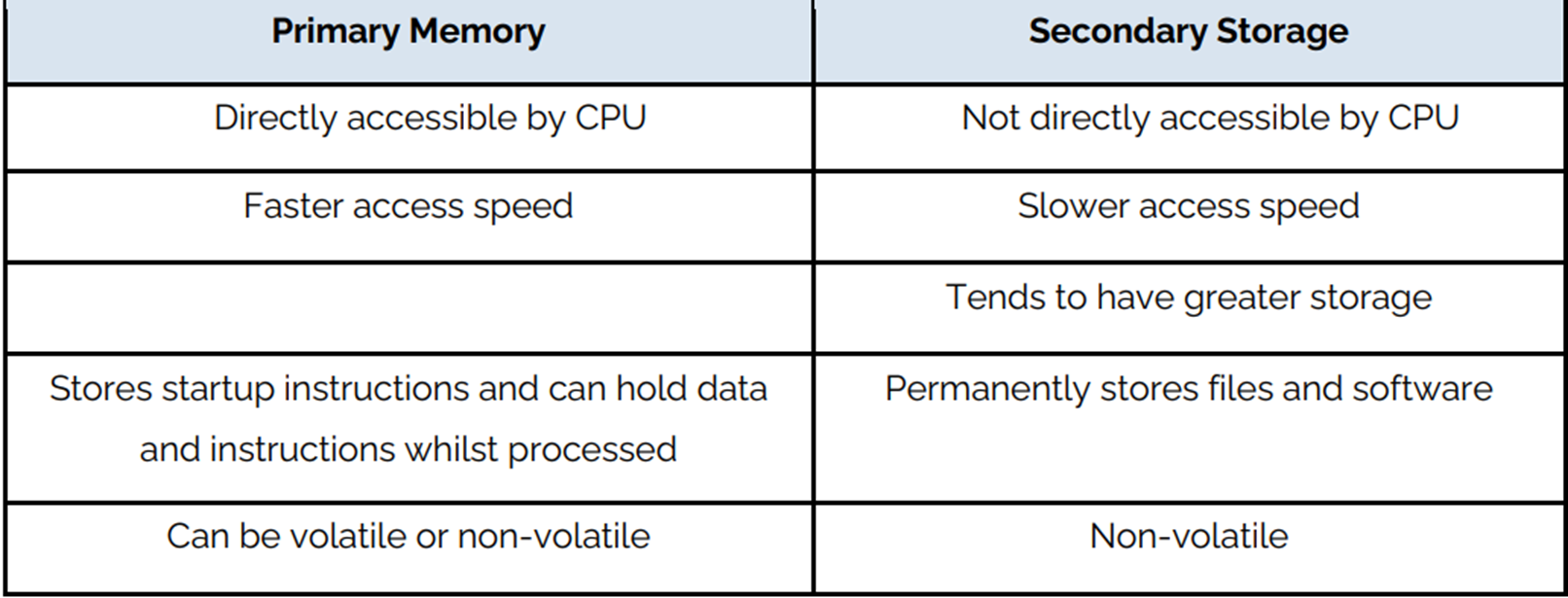
Primary memory
Main memory inside the computer that is directly accessible by the CPU
Secondary storage
Non-volatile storage that is not directly accessible by the CPU
Purpose of secondary storage:
For permanent storage of data
To store data that isn’t currently required by the CPU
To allow software to be installed on the computer
To store data to transfer it to another computer
For the creation of virtual memory
Technologies of secondary storage:
Magnetic
Optical
Solid-state
Diff between Primary Memory and Secondary Storage:
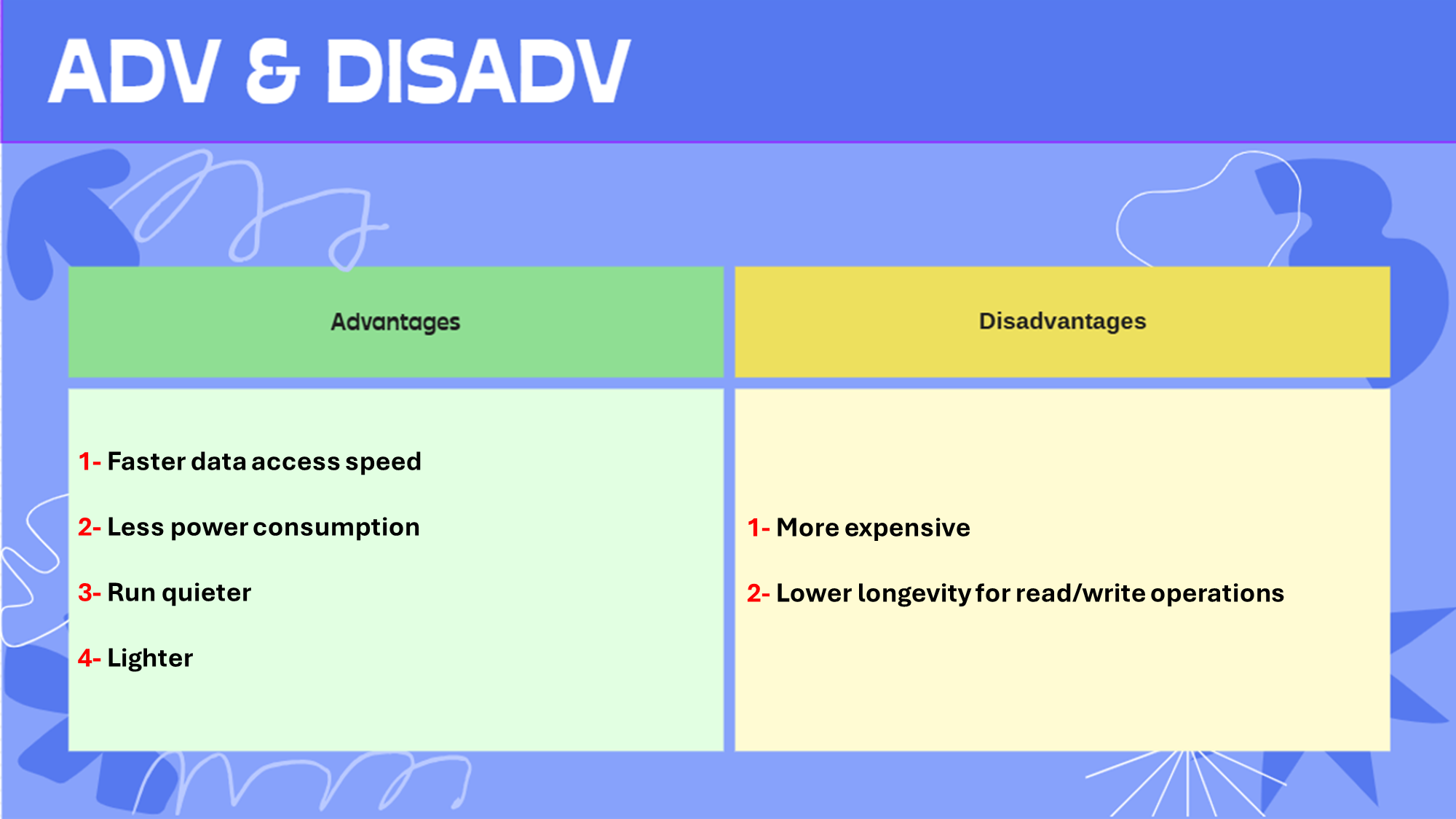
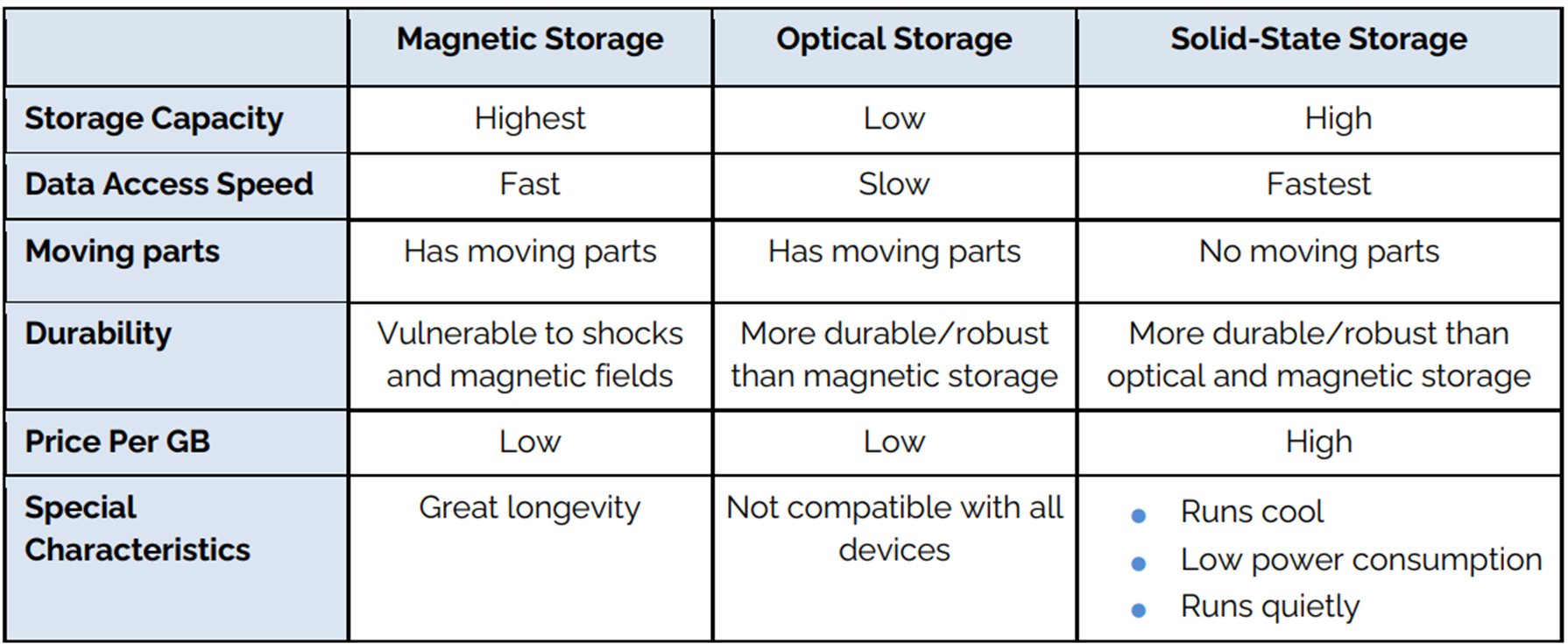
Solid state devices
Eg:
SSD
Portable SSD
SD card
Usb flash memory
Feature/Characteristics:
Uses NAND/NOR to store data
They are made of transistors that are laid out on a grid
Transistors are used to control gates & floating gates to control the flow of electrons
How data is stored/written on it:
NAND/NOR chips are made of transistors
Data is stored by flashing it onto the chips
The flow of electrons is controlled using transistors
Data is stored sequentially as 0s & 1s inside the transistors
How data is read from it:
Data is read sequentially by retrieving the binary values of transistors
Optical storage
Eg:
CD
DVD
Blu-ray disc
Feature/Characteristics:
Data is represented as pits & land
Optical device lasers on the disk
An arm is used to move the optical devices across the disk

How data is stored/written on it:
Disk is spun
Laser beam is shone onto the surface of disk
An arm moves the laser across the surface of disk
The laser burns pits onto the surface of the disk
Both pits & land represent binary values of 1 & 0
How data is read from it:
laser is used to read the pits & lands
Reflected light from the laser shining on disk is captured by a sensor
Magnetic storage device
Eg:
HDD
Portable HDD
Magnetic tape drive
Feature/Characteristics:
Data is stored in the form of magnetic dots
It consists of several platters, where magnetic dots are stored
Data is read, written or erased as the magnetic dots under read/write heads
How data is stored/written on it:
Data, in the form of magnetic dots, is stored on the surface of multiple platters
Platters are spun at high speed
Read/write heads move quickly back & forth to access all tracks & platters
Read/write heads apply magnetic field to control magnetic dots
How data is read from it:
Data is read as dots pass under read/write head
Adv & Disadv of using Solid state storage over Magnetic technology
Comparison between diff types of secondary storage
Cloud storage
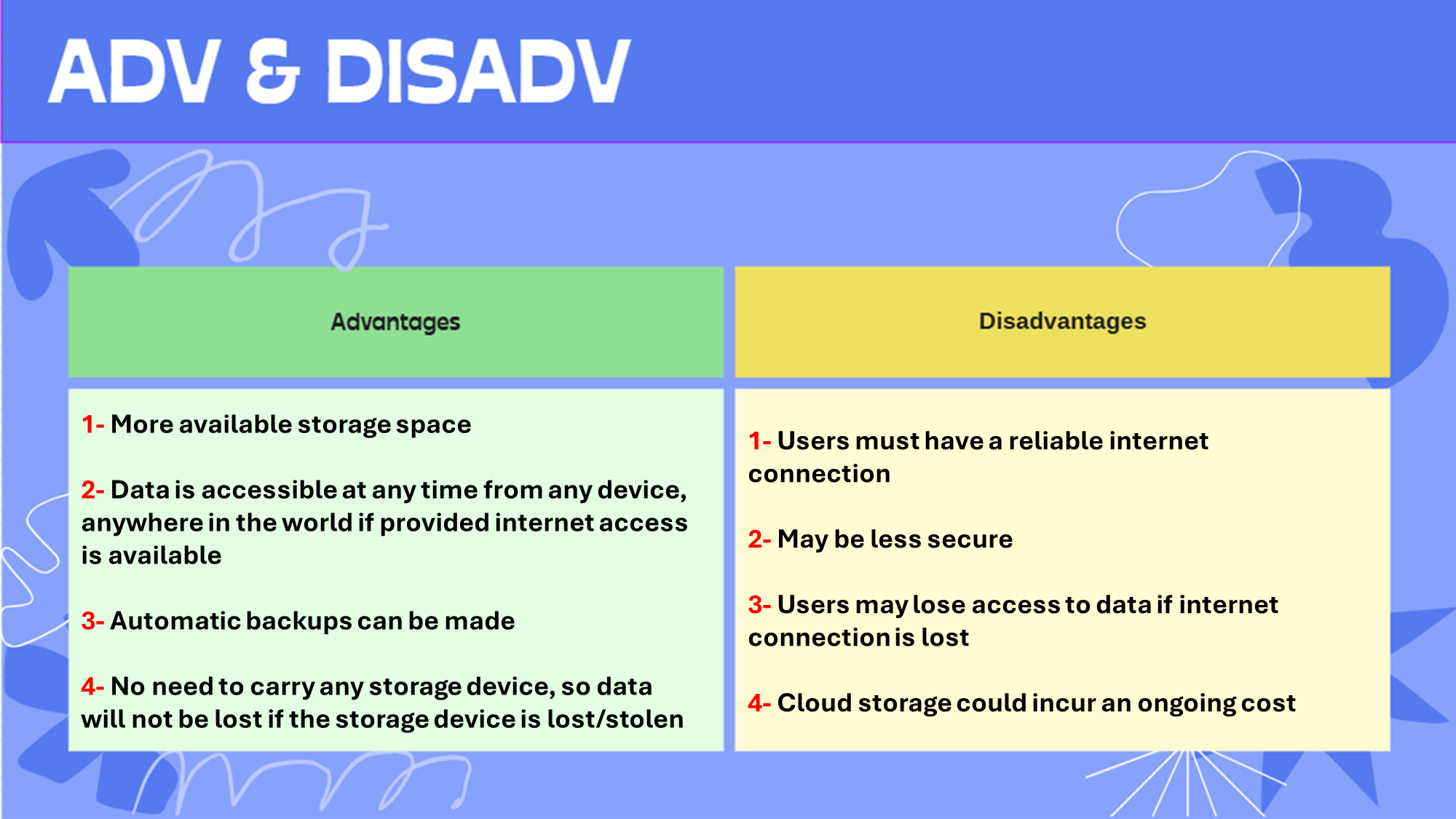
Online storage platform. Data is stored in a remote physical location, using hundreds of interlinked data servers.
Adv & Disadv of using cloud storage over storing data locally:
File compression:
Effect of compression: It reduces the file size
Reasons to compress a file:
To save storage space
To reduce bandwidth needed to transmit
To make it quicker to transmit
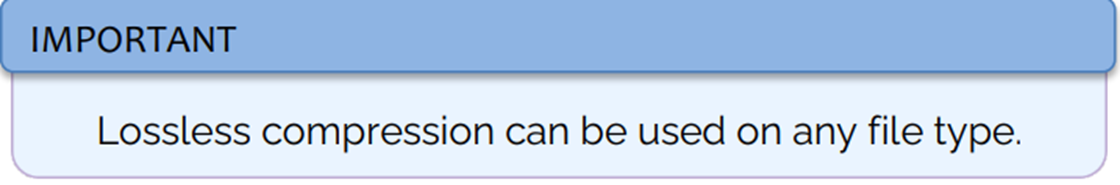
Lossless compression:
Method of compression that loses no data in the process, used when it is essential that no data is lost during compression process.
Code
Text file
Database file
RLE: The repeated pattern of characters/pixels/samples are identified, then encoded into two values:
Number of identical characters in the run (run count)
Value of the pattern (run value)
Data dictionary: The repeated characters/pixels/samples are identified, then put into index & replaced by their index. The number of occurrences is stored in the table. The position of characters/pixels/samples in the file is stored in the table.
Lossy compression, part 1:
Method of compression where redundant details are permanently removed from the file without significantly affecting the quality of the file.
Used when there is no requirement for the files to be the same as the original file
Images
Audio files
Video files
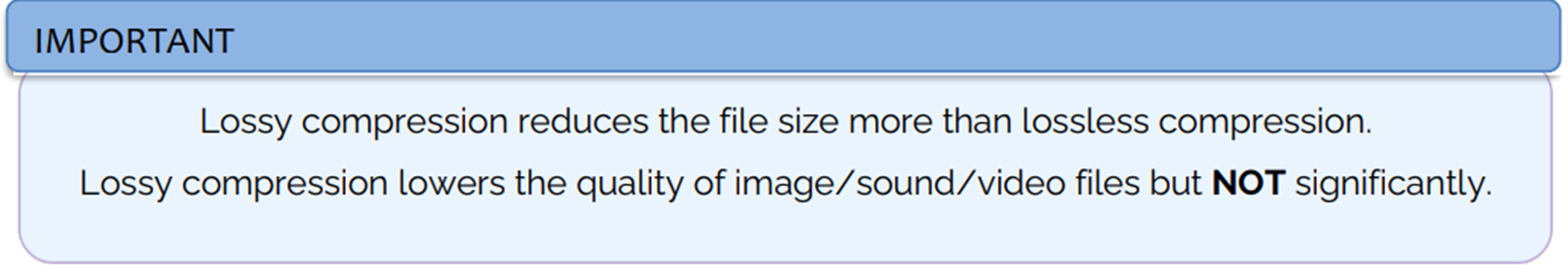
Adv of using Lossy compression instead of lossless compression:

Part 2:
How to compress an image using lossy compression:
A compression algorithm is used, where redundant details are permanently removed
Colour depth could be reduced
Image resolution could be reduced
How to compress a sound file using lossy compression:
A compression algorithm is used, where redundant details are permanently removed
Sampling rate could be reduced
Sampling resolution could be reduced
Unnecessary sound could be discarded
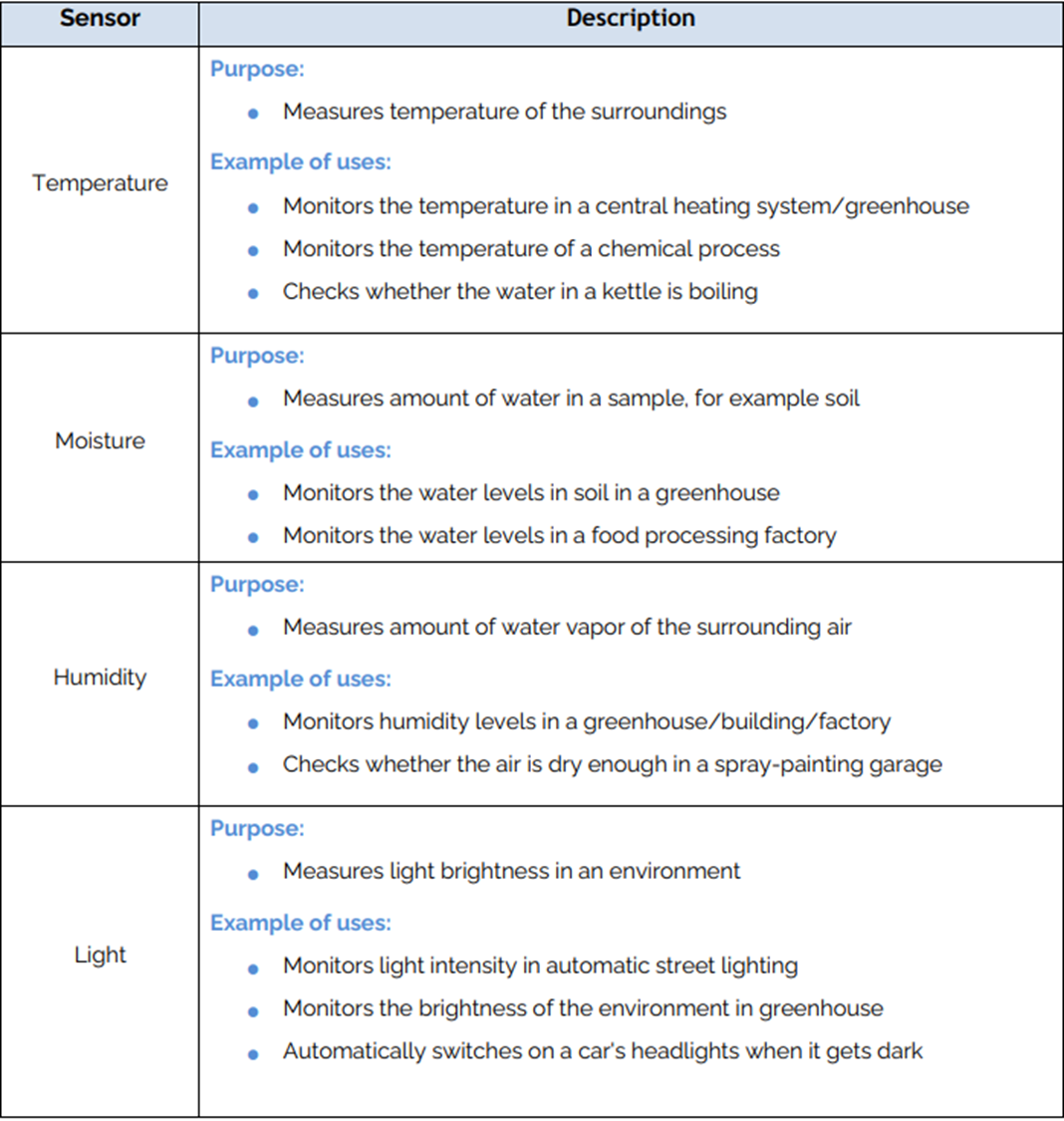
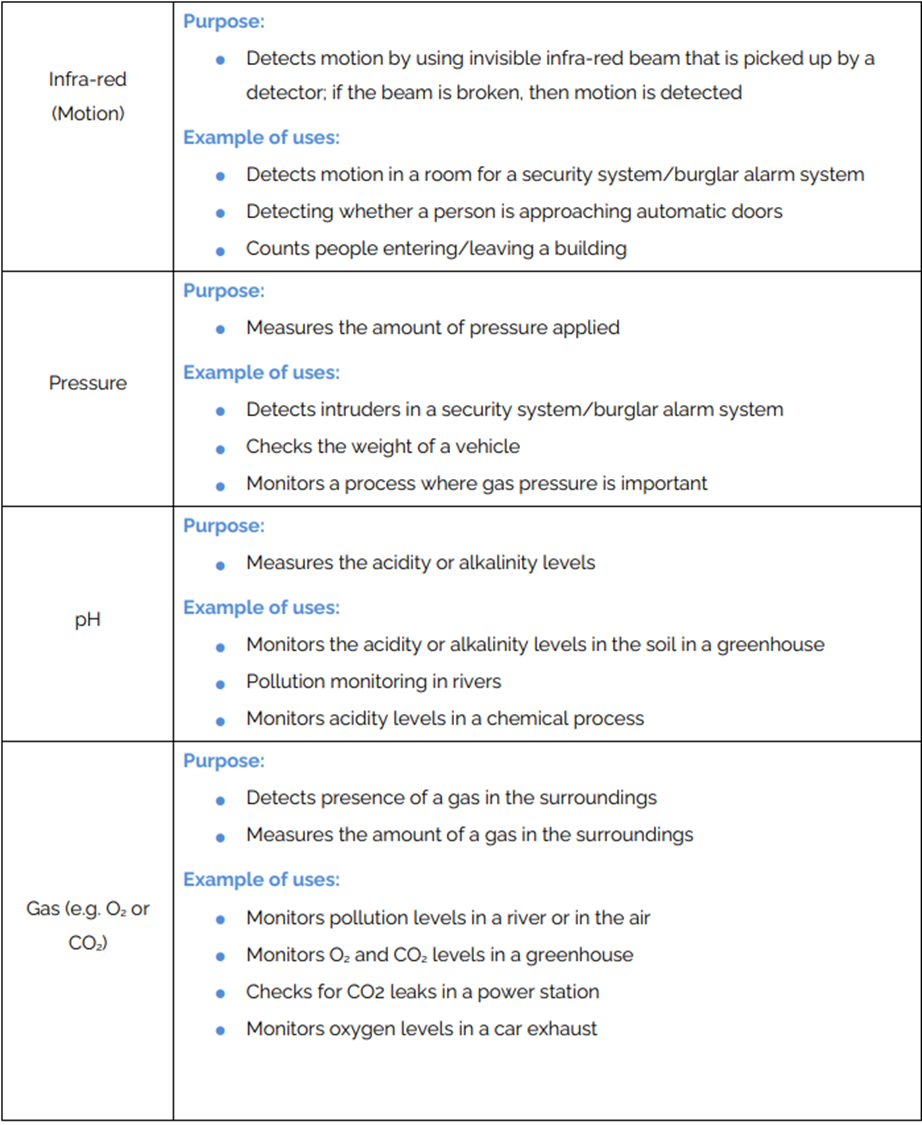
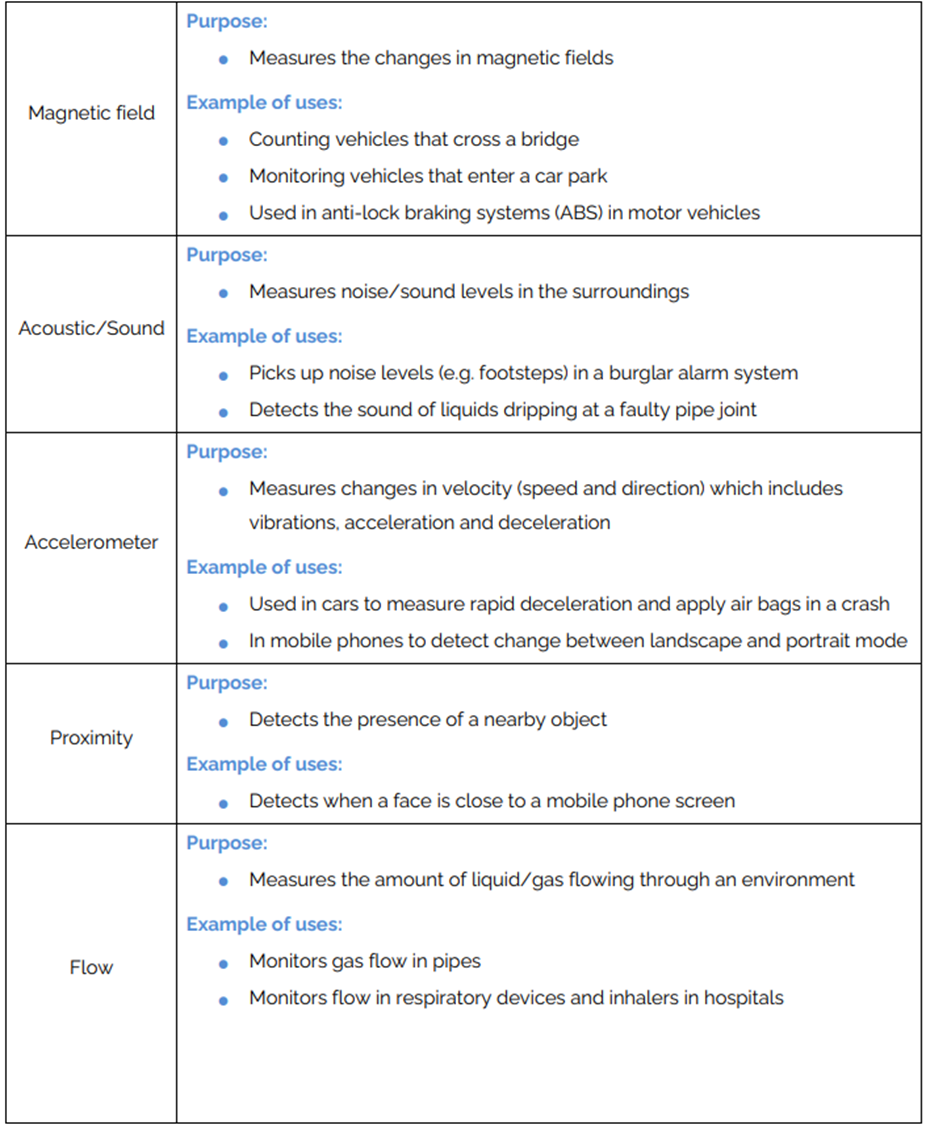
Sensors
An input device used to measure the physical properties of the surrounding envronment

Automated system
A combination of software & hardware designed & programmed to work automatically without the need for human intervention
It consists of:
Sensors to take reading
Microprocessor to process data
Actuator to do mechanical output

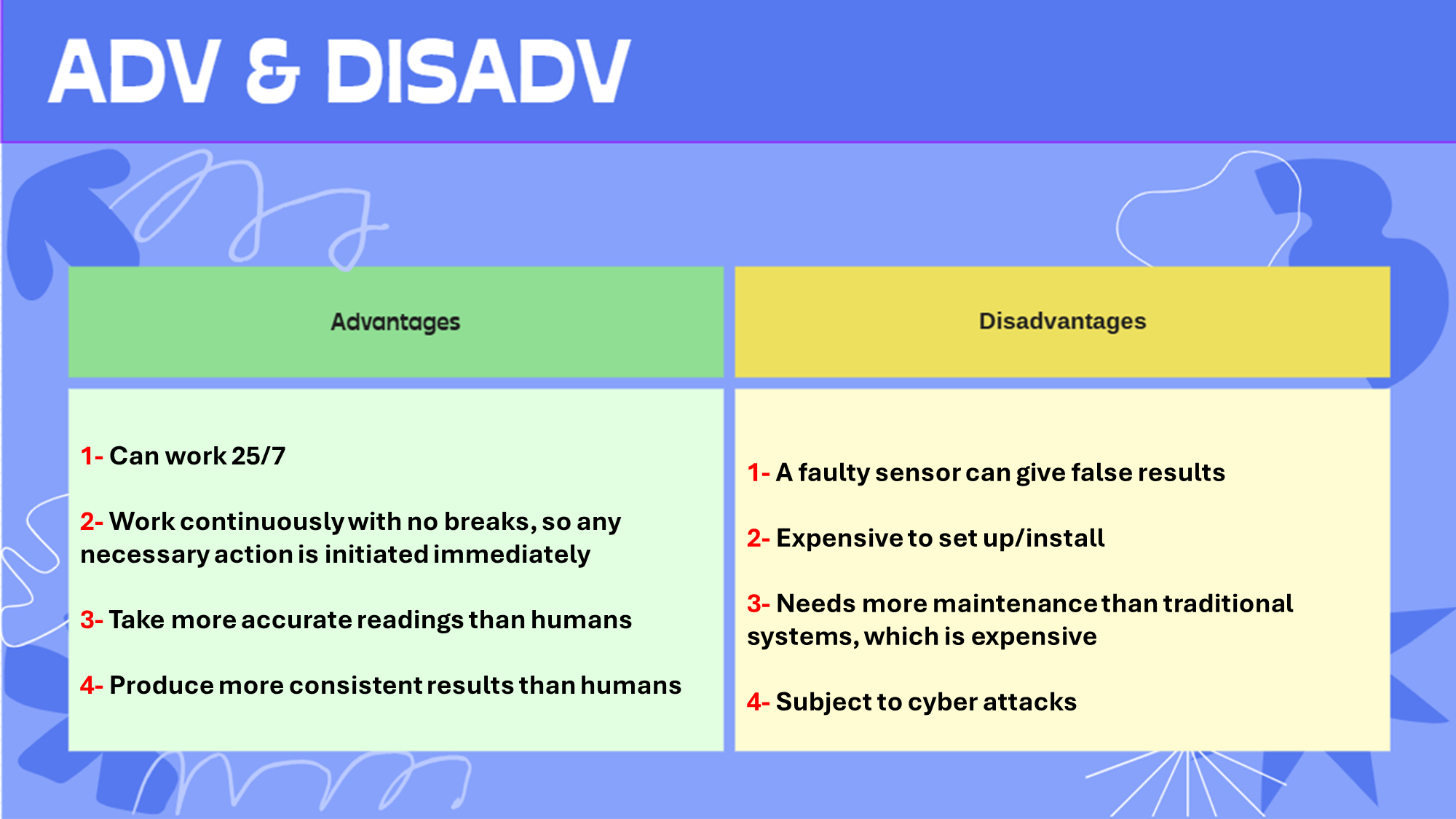
Adv & Disadv:
Automated steps:
1- (…) sensor is used
2- The sensor sends digitised data to the microprocessor
3- the microprocessor compare the value taken from the sensor with the stored value
4- if the value taken is (…) then the microprocessor sends signals to the actuator to (…)
5- if not, it operates normally
6- the process is a loop
Eg of automated systems:

Temperature sensor is used.
The sensor sends digitised data to the microprocessor .
The microprocessor then compares the value taken from the sensor with the stored value.
If value is less than 21 c or higher than 24 c, then the microprocessor sends a signal to the actuator to change the temperature to be between 21 c to 24 c.
If it is between 21 c to 24 c, then it operates normally.
The process is a continuous loop.

Light sensor is used.
The sensor sends digitised data to the microprocessor.
The microprocessor then compares the value taken from the sensor with the stored value.
If value is different than the stored value, then the microprocessor sends a signal to the actuator to turn on/off the street light for a period amount of time like 10 minutes..
If the value is the same, then it operates normally.
The process is a continuous loop
Primary memory
Main memory inside the computer that is directly accessible by the CPU
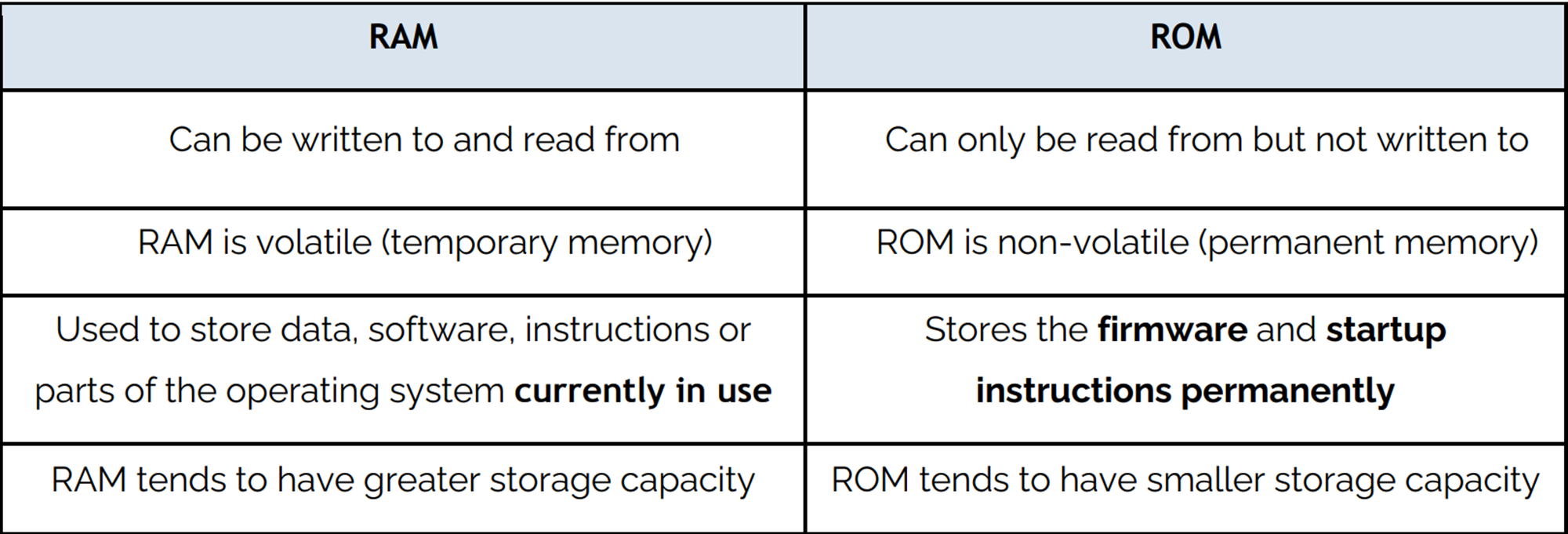
RAM
Volatile memory, that’s directly accessible by the CPU. Can be read from & written to.
Purpose:
Used to store data/files currently in use
Used to store software/programs/instructions/parts of OS currently in use
Used to store data temporarily
To speed up the fetch stage of FDE cycle

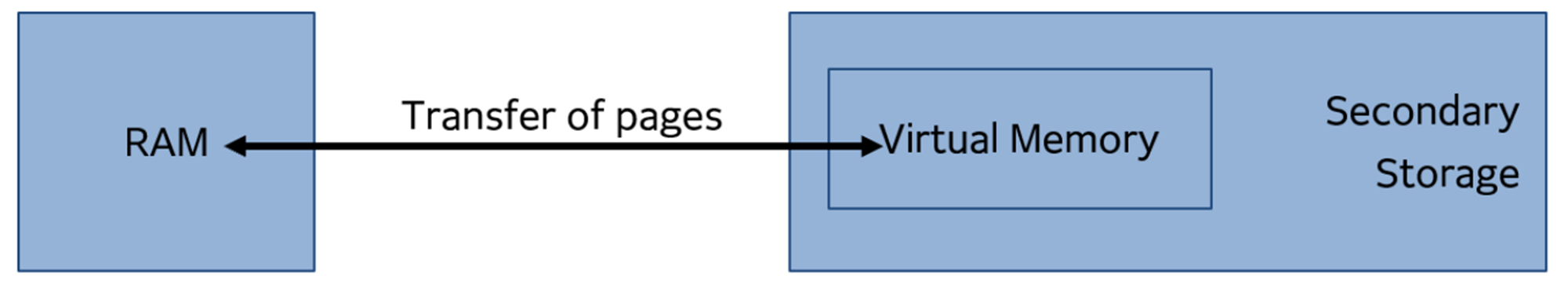
Virtual memory
A memory management system that makes use of secondary storage & software to extend RAM capacity
How virtual memory is created:
Secondary storage is partitioned to create virtual memory
When RAM is full, pages of data that are not required are transferred from RAM to virtual memory
When data is required again, pages are transferred back to RAM
Purpose of using virtual memory:
To extend RAM capacity when required
Reduces the need to buy & install more expensive physical RAM
Stops program from crashing when RAM is full
To allow computer to process large amount of data
ROM
Non-volatile, directly accessible by the CPU. Can only be read from but not written to
Purpose:
To store start-up instructions
To store firmware
To store BIOS
To store bootstrap/bootloader
To store data permanently
Diff between RAM & ROM
Application where RAM & ROM are both used

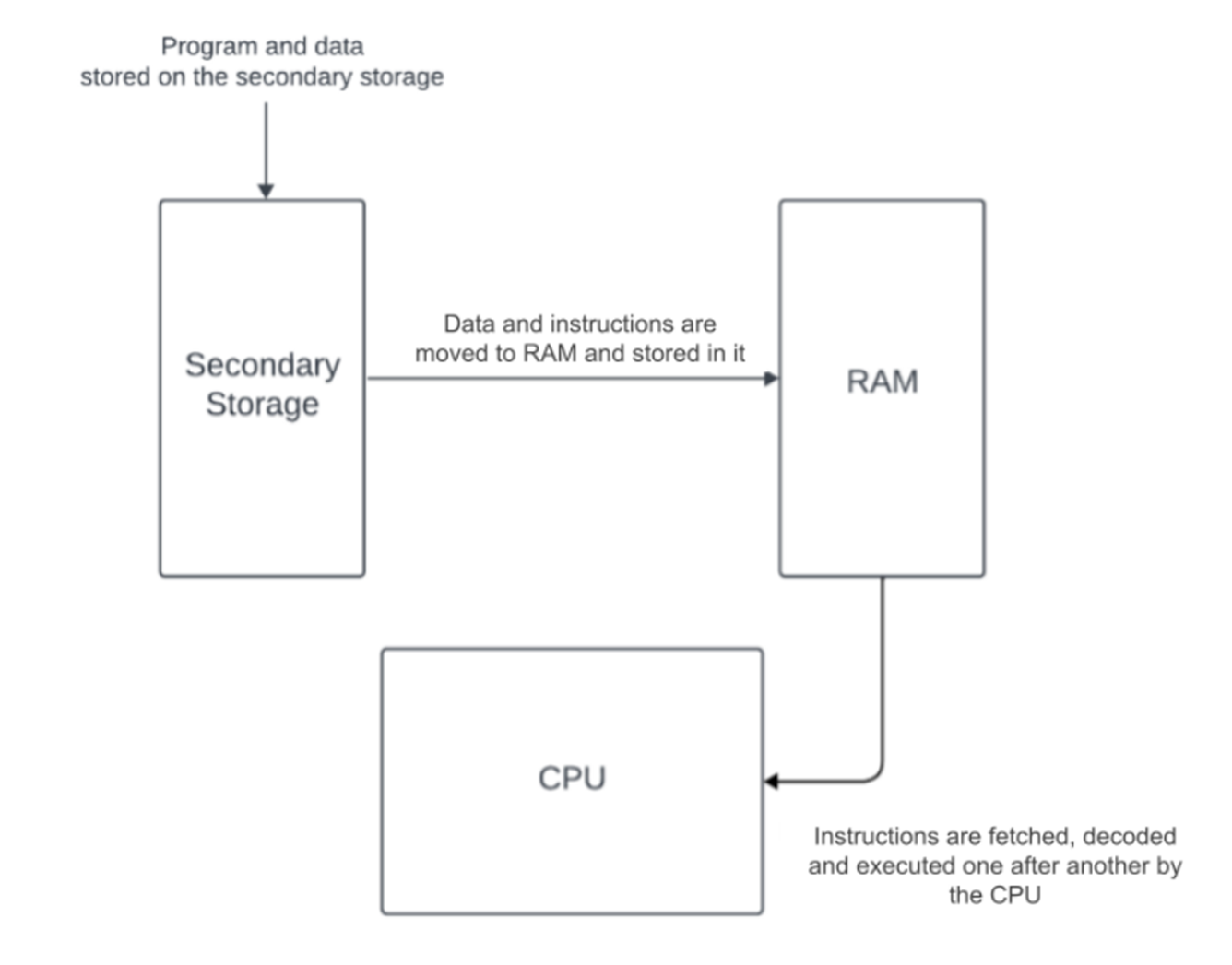
Von Neumann architecture (stored program concept)
Programs are stored on a secondary storage device
Data & instruction are moved to RAM & stored in it
Instructions are fetched, decode and executed one after another by the CPU
Related components to Von neumann architecture:
Secondary storage purpose:

RAM: Ram is made up of partitions, each partition consists of an address & its contents
Purpose:

CPU: A type of integrated circuit contained on a single ship that is used to process the instructions
Structure: It consists of an ALU, CU and registers
purpose: to perform an FDE cycle // to process an instruction
CU
Purpose:
sends control signals that manage the transfer of data & instructions within the CPU
Responsible for decoding instructions using an instruction set
ALU
Purpose:
Carries out arithmetic calculations
Carries out logic operations
Stores interim results of calculations in a register called accumulator
Registers
A small fast memory location within the CPU
Purpose: To store data/address/instruction temporarily
Eg:
PC: Temporarily stores the address of the next instruction to be fetched/executed
CIR: Temporarily stores the current instruction during processing
MAR: Temporarily stores the address of the next instruction/data to be fetched from RAM
MDR: Temporarily stores the instruction/data that is in use from the address in MAR
ACC: Temporarily stores interim results during calculations
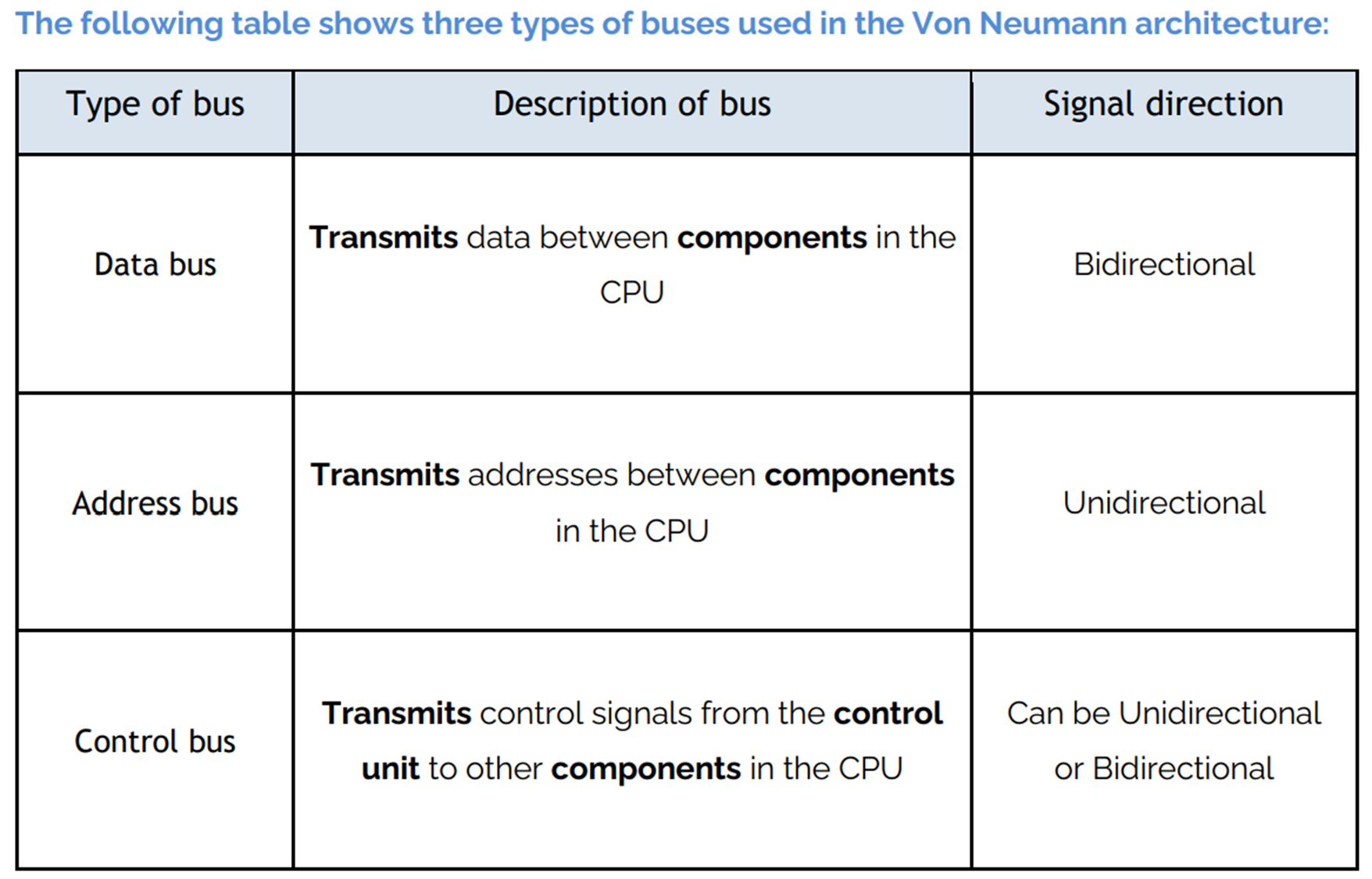
Buses
Pathways to transmit data, addresses and control signals between the internal components of the CPU & between CPU and RAM
Input/Output devices
Purpose: Main method of entering data into & getting the data out of computer systems
FDE cycle
Fetch:
PC contains the address of the memory location of the instruction to be fetched
This address is copied from PC to MAR using the address bus
The contents (instruction) of the memory location contained in MAR is copied to MDR
The instruction in MDR is then copied to CIR using data bus
The value of the PC is incremented by one to point to the next instruction that has to be fetched
Decode:
(Step 4)
CU decodes the instruction using an instruction set
Execute:
The CPU then executes the instruction
Steps of how MDR & ALU are used in FDE cycle:

Interrupt
A signal sent from a device or software that informs the CPU that its attention is required. Interrupts have diff priorities
Purpose:
Informs the CPU that its attention is required
Allows the CPU to pause the current process until the interrupt is serviced
Allows the CPU to deal with vital tasks immediately based on their priority
It enables multi-tasking to be carried out on a computer
Hardware Eg:
A key on a keyboard is pressed
A mouse button is moved
A paper has jammed in a printer
A printer runs out pf paper
A printer runs out of ink
Software Eg:
Opening an app
Switching from one app to another
Runtime errors
Steps of handling an interrupt:
Interrupt is given a priority by OS & placed in the interrupt queue
CPU finishes the current FDE cycle for the process & checks the priority of the interrupts in the interrupt queue
If all interrupts in the queue have lower priority than the process, then the CPU runs the next FDE cycle for the process
If an interrupt in the queue has higher priority than the process, the CPU pauses the process
Processor checks the source of the interrupt & calls ISR to handle the interrupt
If there’s no another higher priority interrupt than the process, then repeat, otherwise , CPU resumes the process by running its next FDE cycle

ISR
A piece of software that contains the code that handles the interrupts. It’s a part of the OS
Factors that determine CPU performance:
Core: A unit on a CPU that’s made up of an ALU, Cu & registers
Purpose: To perform an FDE cycle // To process an instruction
Effect of increasing No. of cores on CPU performance:
Allows the CPU to process multiple instructions at the same time, increasing the CPU performance
System clock: A component that regulates the number of FDE cycles the CPU can perform in a seconds
clock speed: The max number of FDE cycles a CPU can process/execute in a second
2.4 Ghz: CPU completes 2.4 billion cycles per second
Effect of increasing the clock speed on CPU performance:
increases the max number of FDE cycles the CPU can process/execute in a second, increasing CPU performance
CPU cache: It is a type of storage that stores frequently used data/instruction to speed up access as it is faster to access than RAM
Effect on CPU performance:
Allows more frequently used data/instruction to be stored
..which allows the CPU to speed up access to more frequently used data/instructions
..increasing the CPU performance
Embedded systems
Dedicated hardware
Dedicated function
Has a microprocessor
Uses firmware
Doesn’t require much power
Cheap to manufacture
Works automatically
Small in size
Real-time system
Eg:
Domestic appliances
Cars
Security systems
Lighting systems
Vending systems
Examples of software
Software programs can be System software or Application software.
.
Application software: programs that provide the services that the user requires to perform specific tasks
General features:
Run on OS
Provides services that the user requires
Allows user to perform specific tasks

System software: Programs that provide the services that the computer requires to manage/maintain the hardware
General features:
Run on firmware
All OS functions
Provides services that the computer requires

OS
A piece of system software that performs many basic tasks & allows the user to communicate with the computer hardware
Functions:
Memory management
Managing peripherals
Manage multi-tasking
Manage files
Manages user accounts
Provides an interface
Provides system security
Provide a platform for running apps
Handling interrupts
OS function explanation
Managing memory:
Managing the movement of data to and from RAM
Allows multitasking
Manage the transfer of pages between virtual memory and RAM
Managing peripherals:
Transmits data to hardware
Receives data from hardware
Allocates data to buffers
Manage multi-tasking
Gives the process a priority
Allocates resources for each process for a specific time limit
Interrupts the running process when it exceeds its time limit
Manage files
Create/Copy/Open/Close/Rename/Save a file
Manages user accounts
Allowing multiple user accounts to be created on a computer
Allows the user to customize their screen layout
Uses separate folders and files to allow users to manage them
Provides an interface
Allows the user to interact with the computer
Eg: GUI & CLI
Provides system security
Help prevent hacking
Communicates with firewall
Ensures anti-virus is always up-to-date
Carries out OS updates when they become available
Provide a platform for running apps
Allowing communication between the applications software and the hardware.
Handling interrupts
Gives the interrupt a priority
Includes the ISR, which is a piece of software that contains the code that handles the interrupts
Utility software
A program that performs a specific task required for the operation of the computer system
Eg:
Antivirus
Disk repair
ackup software
Screensaver
Firmware
A piece of software that runs directly on the hardware
Purpose:
Controls/Allows communication with the hardware
Stores instructions to boot up/start up the computer
Provides the OS with a platform to run on
Eg of firmware:
Bootloader/Bootstrap: Software that is responsible for loading the OS into the RAM
BIOS: Carries out a hardware check to find out if all the devices are present & whether they are functional
How hardware, firmware and an OS are required to run applications software:
App software runs on the OS
The OS runs on the firmware
The firmware runs on the hardware
Types of programming languages:
High level language
A type of programming language that is close to human language
Machine independent
One line of high level language code can perform several low level language operations
It has built-in functions which save time when writing a program
Low level language
A type of programming language that is close to native language of the computer
Machine dependent
Allows direct manipulation of memory
Allows for use of specialized hardware
Eg: Machine code & Assembly language
Machine code: The binary instructions that a computer understands & executes directly
Assembly language: A form of low level language that uses mnemonics. An assembler is needed to translate an assembly language program into machine code
Adv of using High level language over Low level language
Closer to human language, so fater to write codes & the programmer is less likely to make mistakes while writing the code
Easier to debug, so programmers can find & correct errors in less time
Machine independent // Portable, so program can be used on any computer without need for understanding the hardware
One line of code can carry out multiple commands, so the code is more compact
It has built-in functions, so faster to wrte cod
Adv of using Low level language over High level language
Allows direct manipulation of memory
Code executes faster
Code requires less memory
Allows for use of specialized hardware
Instruction Set
A list of all machine code commands that can be processed by a CPU
Purpose:
Used to define the commands that can be carried out by the CPU
Used by the CU to decode instructions during processing
Language translators, part 1:
Software used to convert programming language code to machine code to be executed by the computer
Compiler: A program that translates a high level language code to machine code

Interpreter: A program that translates a high-level language to machine code

Assembler: A program that translates a low-levl language code to machine code

Part 2:
How the compiler translates the computer program:
It translates the high level language to low'-level language/machine code
It translates all the code before it is executed
It creates an executable file
How the Compiler reports errors:
It creates an error report after trying to compile
..Displaying all errors in the code
..That require correction before execution can take place