Geriatric Nursing Final Practice Questions
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topics 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 15 Chapters 11 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 29, 33
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What are some recommended practices to promote gastrointestinal health, particularly for older adults? (p. 275)
plenty of fluid intake
especially after increased fiber intake
diet rich in fruits and vegetables
regular exercise
establish a regular time for bowel elimination
useful for older adults to attempt a bowel movement after breakfast
What are some common causes of dysphagia? (p. 279)
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
stroke
structural disorders
What interventions can help manage dysphagia? (p. 279)
follow the recommendations of speech-language therapist
soft diet and thickening of liquids are recommended to promote ease of swallowing
eat in an upright position and remain upright for 30 minutes after
ingest small bites in an unhurried manner
have easy access to suction in the event of choking
monitor food intake and weight
What are some interventions to support patients with selected health conditions? (p. 282)
comfort measures
pain management
promoting nutrition
good fluid intake
diet rich in fruits and vegetables
physical activity
establishment of a regular time for bowel elimination
oral hygiene
infections of the oral cavity may lead to respiratory infections
listening to and talking with the patient
What are the most common nutrient deficiencies observed in older adults, as mentioned in the context of nutritional needs for this age group? (p. 151)
Niacin
Riboflavin
Thiamine
Vitamin B6
Vitamin C
Vitamin D
What are some potential adverse effects or risks associated with the excessive intake of various vitamin supplements? (p. 151)
Excessive Vitamin D can cause calcium deposits
Excessive Vitamin K can cause bleeding and prevent blood clotting
Folic acid can mask a vitamin B12 deficiency
Excessive calcium increases the chance of kidney stones
Excessive potassium may cause arrhythmias, cardiac arrest
How does calcium consumption affect kidney health? (p. 151)
Excess calcium consumption (i.e., more than 2,000 mg/d) can lead to problems such as kidney stones and an increased risk of cancer
NOTE: If calcium supplements are used, no more than 500 mg should be taken at any one time because larger amounts are not absorbed as well
What are some interventions for treating constipation? (p. 155)
Adequate amounts of fluids, vegetables, and physical activity can improve constipation
Senna is an effective natural laxative that can be consumed in tablet or tea form
Laxatives should only be considered AFTER other measures have proved unsuccessful
How can the elderly improve sleep patterns at night? (p. 167)
reduce or limit caffeine and alcohol consumption
managing pain before bedtime
regular activity during the day to promote rest and relaxation
noise control
exposure to sunlight during the day can facilitate sleep at night
a warm bath at bedtime
consuming foods high in carbs or protein snacks (e.g., warm milk)
What are some measures for managing stress effectively? (p. 168)
Respond to stress in a healthy manner
good nutrition, rest, exercise, and sound health practices strengthen the body’s ability to confront stress
Manage lifestyle
Relax
Pray
What are some health risks associated with stress? (p. 168)
unrelieved chronic stress can lead to heart disease, hypertension, cerebrovascular accident, ulcers, and other health disorders
What are the normal sleep patterns of the elderly? (p. 162)
older adults are more likely to fall asleep earlier in the evening and awaken earlier in the morning, a behavior referred to as phase advance
sleep latency and reduction in REM sleep are prevalent
How can nurses promote restful sleep in older adults? (p. 165 - 166)
Regular exercise, exposure to sunlight during the day, and non-caffeinated herbal teas at bedtime
Environmental noise should be controlled
A protein and carbohydrate snack at bedtime may encourage sleep
Manage stress
Valerian root or herbal tincture consumed 45 minutes before bedtime can also facilitate sleep
Reduce blue light before bed
What are the four stages of sleep? (p. 163 - 164)
Stage I → lightest sleep
heartbeat and breathing slows
slow, rolling eye movements
sudden jerks or muscle spasms
Stage II → light sleep
slow eye movements stop
heartbeat slows even more
body temperature begins to drop
Stage III → deep sleep
brain waves slow down even more
heartbeat and breathing at its lowest
Stage IV → Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep
dreams and memories form
heart rate and blood pressure increases
eye movements speed up
What are some common changes in older adults during the sleep stages? (p. 163 - 164)
Reductions in non–rapid eye movement stage sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) stage sleep begin to occur after midlife
Older adults have a decline in the proportion of time spent in the deeper sleep stages III and IV
Older people sleep less soundly
Tend to shift in and out of sleep stage I to a greater degree than do younger adults
Spend more time in sleep stages I and II
What are some common changes in sleep patterns associated with aging? (p. 165)
Older adults are more likely to fall asleep earlier in the evening and awaken earlier in the morning.
The quantity of sleep does not change, but the hours in which it occurs may. This change can prove frustrating for older adults who find themselves nodding off during evening activities and wide awake in the early morning hours when everyone else is asleep.
In addition, daytime naps may be needed to compensate for reductions in nighttime sleep.
What are some environmental interventions to prevent falls? (p. 190, 193)
lighting → a small light should always be on
floor surface → should be clear of any towels, hair dryers, rugs, leaks, and other items
faucets → color-code the faucet
tubs and shower stalls → should have grab bars on the wall and safety rails on the side of the tub + a shower or bath seat
toilets → should have grab bars or support frames
What interventions are suggested for individuals with visual deficits? (p. 197)
approach individuals from the front rather than from the back or side
furniture and frequently used items should be arranged in full view
What interventions are suggested for individuals with hearing deficits? (p.197)
individuals should live close to someone with adequate hearing who can alert them when fire alarms or other warnings are sounded
guide dogs
during the night, place the earpieces of a stethoscope into the impaired person’s ears and speak into the bell or diaphragm
What interventions are suggested for individuals with sensory deficits (excluding visual and hearing deficits)? (p. 197)
use gas stoves
reduced tactile sensation to pressure from shoes, dentures, or unchanged positions can lead to skin breakdown, and the inability to differentiate between temperatures can cause burns
What are some contributing factors for a hip fracture? (p. 194)
age-related health problems, weak or immobile state
sensory deficits
improperly fitted or used mobility aids
unsafe use of medications
unsafe environment
altered mood or cognitive function
What interventions are suggested for individuals with a risk of hip fracture? (p. 194)
assess risk of injury
orient to new environments
encourage patients to wear prescribed eyeglasses, hearing aids, and prosthetic devices
ensure patients use canes, walkers, and wheelchairs properly
advise patients to change positions slowly, holding on to a stable object as they do
keep floors free from litter and clutter
provide good lighting in all areas
encourage patients to use handrails and grab bars
be sure patients wear well-fitted, low-heeled shoes, and robes and pants of an appropriate length
review home environment for safety risks
What observations can be noted during the assessment of gait abnormalities? (p. 323)
abnormal gait patterns
ataxia
foot slapping
hemiplegic gait
Parkinsonian gait
scissors gait
spastic gait
structural abnormalities
limb dysfunction
favoring one side
presence of tremors
paralysis
weakness
limb atrophy
redness, swelling of a joint
the use of assistive devices like canes, walkers, or wheelchairs
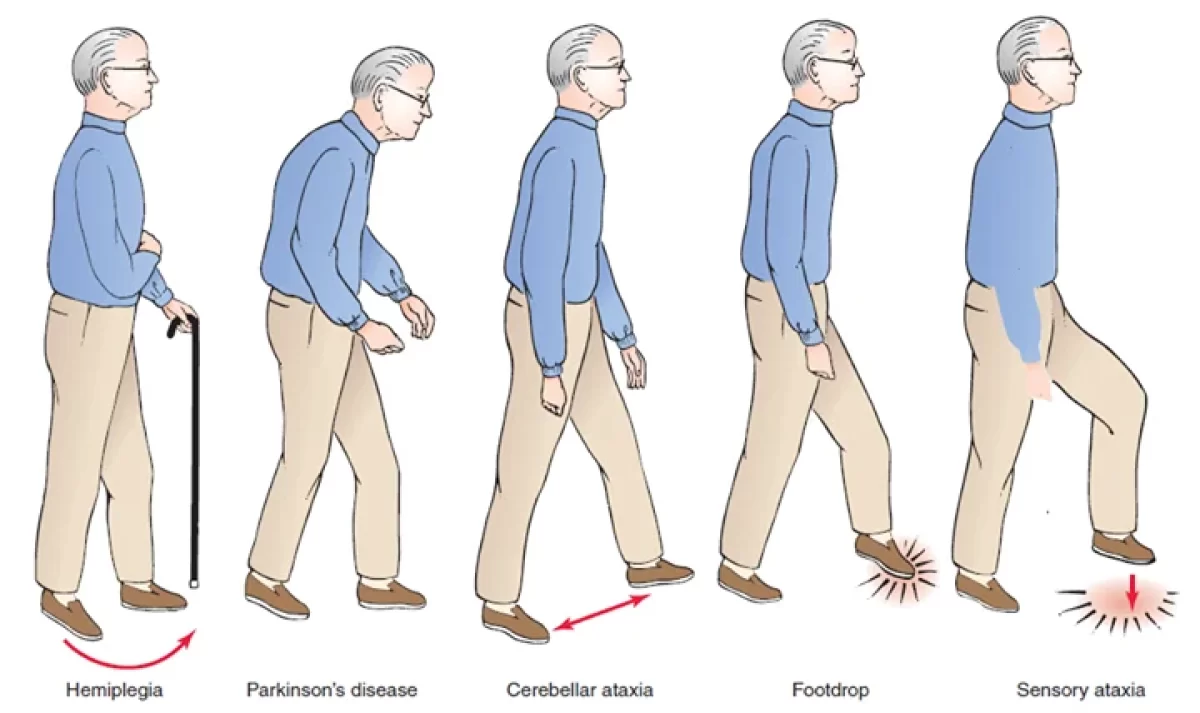
What is ataxia? (p. 323)
unsteady, uncoordinated, feet raised high while stepping and then dropped flat on floor
What is foot slapping? (p. 323)
wide-based, feet raised while stepping and then slapped down against floor, no staggering or weaving
What is a hemiplegic gait? (p. 323)
unilateral foot drop and foot dragging, leg circumducted, arm flexed and held close to side
What is a Parkinsonian gait? (p. 323)
trunk leans forward, slight flexion of hip and knees, no arm swing while stepping, short and shuffling steps, starts slowly and then increases in speed
What is a scissors gait? (p. 323)
slow, short steps, legs crossed while stepping
What is a spastic gait? (p. 323)
uncoordinated, jerking gait; legs stiff; toes drag
What interventions are recommended for individuals with low bone density or osteoporosis? (p. 328)
Avoid heavy lifting, jumping, and other activities that could result in a fracture
Persons providing care for these patients must remember to be gentle when moving, exercising, or lifting them because fractures can occur easily
Compression fractures of the vertebrae are a potential complication of osteoporosis
Range-of-motion exercises and ambulation are important to maintain function and prevent greater damage
Increase vitamin D, vitamin C, protein, and calcium intake.
Physical therapists may be able to suggest appropriate exercises to promote strength and function
What is onychomycosis, and how does it typically affect the appearance and condition of the nail? (p. 330)
a fungal infection of the nail or nail bed in which the toenail appears enlarged, thick, brittle, and flaky
as the fungus forms under the nail and displaces it up, the sides of the nail are pushed into the skin and cause pain
antifungal preparations assist in eliminating the infection, but these infections are challenging to treat
What are the rights of safe medication administration (p. 211)?
right medication
right patient
right dose
right route
right time and frequency
right education
right documentation
What precautions should be considered for safe medication administration in older adults? (p. 211)
To ensure that oral medications achieve full benefit, encourage good oral hygiene, ample fluids, and proper positioning to facilitate swallowing.
older adults are at higher risk for adverse effects
older adults are at risk for circulatory overload during intravenous drug therapy
What effects does furosemide have on the excretion of certain minerals? (Table 5-2 p. 206)
furosemide increases the excretion of calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, and zinc
How can aspirin impact the effects of oral anticoagulants? (p. 216 - 217)
Aspirin can increase the effects of oral anticoagulants
↑ bleeding
What should nurses monitor for patients taking anticoagulants? (p. 216 - 217)
prothrombin time (PT) → evaluates ability to clot
international normalization ratio (INR) → ensures that results from a PT test are the same
What should be considered when administering anticoagulants to maintain consistent blood levels? (p. 216 - 217)
Administer anticoagulants at the same time each day to maintain a constant blood level
What should nurses teach patients to observe when taking anticoagulants? (p. 216 - 217)
signs of bleeding
blood in urine
blood in stool
severe bruising
prolonged nosebleeds
How can diet affect the effectiveness of anticoagulants? (p. 216 - 217)
A large intake of vitamin K–rich foods can reduce the effectiveness of anticoagulants
asparagus
bacon
beef liver
cabbage
fish
cauliflower
green leafy vegetables
What foods can increase INR? (p. 216 - 217)
mango
papaya
Which vitamin can increase risk of bleeding? (p. 216 - 217)
Vitamin E
Why should vitamin K be readily available for patients receiving anticoagulants? (p. 216 - 217)
Vitamin K acts as an antidote for excessive bleeding
What dietary recommendations are suggested for managing hypertension? (p. 267)
Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet
rich in n fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy foods
Heart-healthy diets include…
high intake of nuts, fish, as well as fiber-rich whole grains
less than 1,500 mg of sodium per day
fruits and green vegetables that are rich in essential nutrients, including antioxidants
Low-sodium diet
What dietary approach is recommended for individuals with poor appetite? (p. 238)
small, frequent meals
What interventions are recommended to manage asthma? (p. 237)
instruct the patient in breathing exercises
A. With one hand on the stomach (below the ribs) and the other over the middle anterior chest, the patient should inhale deeply to the count of one. The hand over the stomach should move outwardly as the diaphragm and stomach move downward; the hand over the chest should not move.
B. Expire air slowly to the count of three. The hand over the stomach should be pulled closer to the body as the diaphragm and stomach move upward; the hand over the chest should not move.
control symptoms (e.g., pain) that could threaten effective respirations
raise the head of bed at least 30 degrees
instruct the patient to turn, cough, and deep breathe at least once every 2 hours
monitor rate, depth, and rhythm of respirations
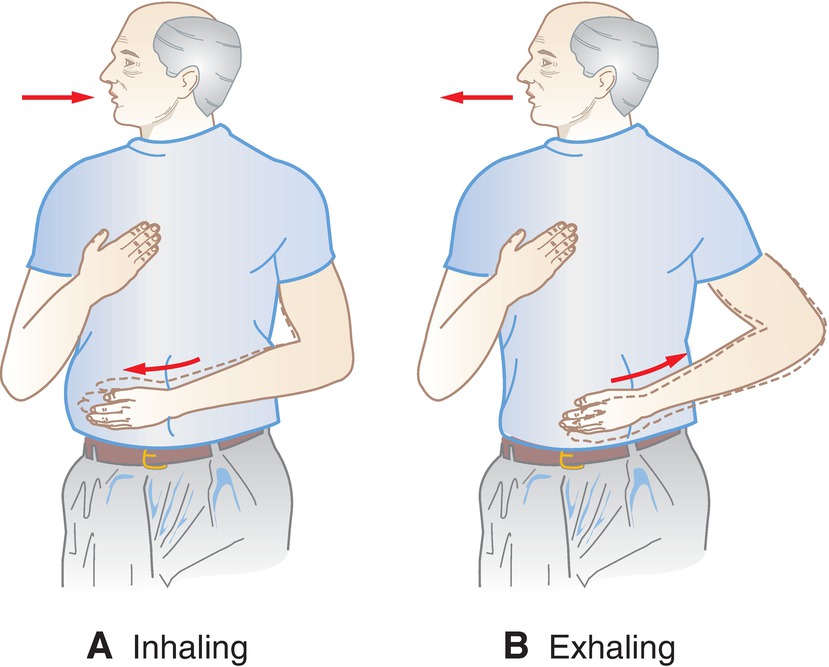
What position adjustment is recommended for patients experiencing shortness of breath while lying down? (p. 237)
raise the head of the bed at least 30 degrees
What potential conditions or factors are associated with different abnormal colors in urine? (p. 291)
dark colors can indicate increased urine concentration
red or rust color usually is associated with the presence of blood.
yellow-brown or green-brown color can be caused by an obstructed bile duct or jaundice
orange urine results from the presence of bile or the ingestion of phenazopyridine
very dark brown urine is associated with hematuria or carcinoma
What might different odors in urine indicate? (p. 291)
strong odor can indicate concentrated urine associated with dehydration
ammonia-like odor can accompany infections
What are some reproductive system health concerns for females? (p. 303)
vulvitis: itchy and inflamed vulva
vaginitis
soreness
pruritus (itching)
burning
reddened vagina
foul-smelling vaginal discharge that is either clear, brown, or white
breast cancer
incidence increases with age
older women are least likely to receive mammograms and breast examinations
vaginal cancer
cervical cancer
endometrium cancer
ovarian cancer
perineal herniation
dyspareunia: pain that occurs in the genital area before, during, or after sex
Which type of medication is known to potentially cause nocturia (frequent nighttime urination)? (p. 289)
long-acting diuretics (e.g., thiazides)
How can independence be promoted for patients with neurological conditions? (p. 344)
encouraging the use of assistive devices
periodic home visits by a nurse, regular contact with a family member or friend, and a daily call from a local telephone reassurance program can help the patient feel confident and protected
continuing patience, reassurance, and encouragement are essential to maximize patients’ capacities for independence
What strategies can help compensate for visual deficits? (p. 353)
face the person when speaking
use several soft indirect lights instead of a single glaring one
avoid glare from windows by using sheer curtains or stained windows
use large print reading material
place frequently used items within the visual field
avoid the use of low-tone colors and attempt to use bright ones
use contrasting colors on doorways and stairs and for changes in levels
identify personal belongings and differentiate the room and wheelchair with a unique design rather than by letters or numbers
What potential risks or complications might occur following cataract surgery? (p. 353)
a secondary membrane may form, requiring an additional procedure for discission of the membrane
eye infection
loss of vitreous humor
slipping of the implant
What is age-related hearing loss, and what steps are advised for older adults experiencing this condition? (p. 358)
presbycusis: age-related hearing loss
encourage audiometric examination
physical, emotional, and social health can be seriously affected
What are some considerations for cosmetic surgery in older adults? (p. 385)
some older adults want to have a more youthful look
nurses should also explore patients’ reasons for seeking cosmetic surgery to ensure that it is a rational decision rather than a symptom of an underlying problem, such as depression or a neurotic disorder
counseling and therapy may be a more pressing need than surgical intervention in some circumstances
What advice is provided to assess changes in moles for potential signs of melanoma (skin cancer)? (p. 384)
think “ABCD”
A - asymmetry
if one half of the mole is not like the other, it could be a sign of melanoma
B - border irregularity
borders may be uneven, ragged, notched, or blurred
C - color
a mole that has changed color over time or is varied in a shade of brown, tan, and black may be cancerous
if melanoma has progressed, the mole may become red, blue, or white
D - diameter
cancerous moles may be more than 6 mm in diameter (or ¼ inch)
NOTE: Other mole variations that may indicate melanoma include elevation in height from the skin surface both horizontally or vertically; a change in feeling, such as itchiness, tenderness, or pain; and the tendency to bleed if scratched
What condition involving fixed flexion of the hands might individuals with diabetes mellitus be at risk for? (p. 367)
Dupuytren’s contracture
What are some signs of cancer indicated by the acronym "CAUTION”? (p. 400)
think “CAUTION”
Change in bowel or bladder habits
A sore throat that does not heal
Unusual bleeding or drainage
Thickening or lump in the breast or elsewhere
Indigestion or swallowing difficulty
Obvious change in a wart or mole
Nagging persistent cough or hoarseness
What are the primary goals of palliative care? (p. 440)
Palliative care focuses on helping patients effectively live in harmony with, rather than cure, the condition.
maintain or improve self-care capacity
manage the disease effectively
boost the body’s healing abilities
prevent complications
delay deterioration and decline
achieve the highest possible quality of life
die with comfort and dignity
Why might the incidence of cancer increase with age? (p. 396)
the increased incidence of cancer with age could result from age-related changes that reduce the ability to resist the disease or prolonged exposure to carcinogens
What is the most important action to keep hospitalized patient free of infection? (p. 497)
good hand hygiene
promoting good hydration and nutritional status
monitoring vital signs, mental status, and general health status
maintaining intact skin and mucous membrane
avoiding immobility
ensuring pneumococcal and influenza vaccines have been administered (unless contraindicated)
maintaining a clean environment
restricting contact with persons who have infections or suspected infections
storing foods properly
preventing injuries
adhering to infection control practice