AP STATS: Chapter 8
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Confidence interval general formula
Point estimate ± margin of error
Point estimate equation
A+B/2
M.E. equation
B-A/2
Confidence interval interpretation
“We are ___% confident that the interval from A to B captures the true parameter with context”
Standard error equation
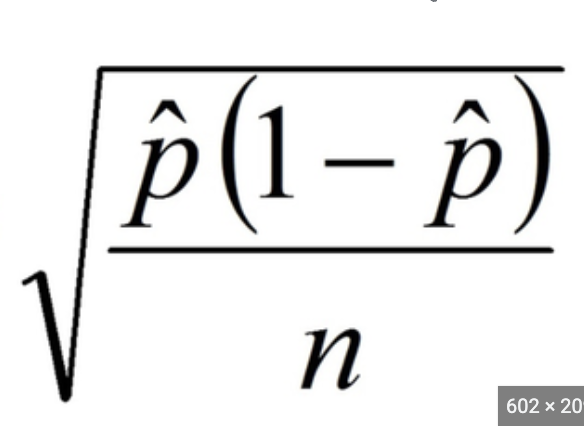
Confidence level interpretation
“If we take many, many samples and calculate a confidence interval for each one, about % of them will capture the true parameter with context”
as confidence level increases
me increases
as me increases
confidence level increases
as sample size increases
me decreases
as me decreases
sample size increases
conditions
random, 10%, LCC
random verifies
generalize population
10% verifies
independence: in sampling with out replacement. helps to not have biased results, you can use certain equations
LCC verifies
to assume sampling distribution is approximately normal, to find z critical in interval
critical value x standard error
margin of error
specific formula

(p) choose:
procedure: one-sample z-interval for p
define p (the parameter)
state confidence level
calculate
write formulas, plug in values, calculate CI
Conclusion
we are _% confident…”
find sample size
ME=z* x sq root p(1-p)/n
if we dont know p hat, use
0.5
if n is a decimal
round up
choose p1-p2
two-sample z-interval for p1-p2
define p1-p2
state confidence level
check p1-p2
independent random samples or random assignment+ 10+LCC
calculate p1-p2

evaluate a claim
(+,+) 1st proportion is greater
(-,-) 1st proportion is smaller
(-,+) no evidence of difference (0)
rate of increase me-n
quadruple to halve, me is proportional to 1/sq of n