giys this isnt funny
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What is a Pedigree chart
A chart which shows several generations of related families and how traits are passed down through the offspring.
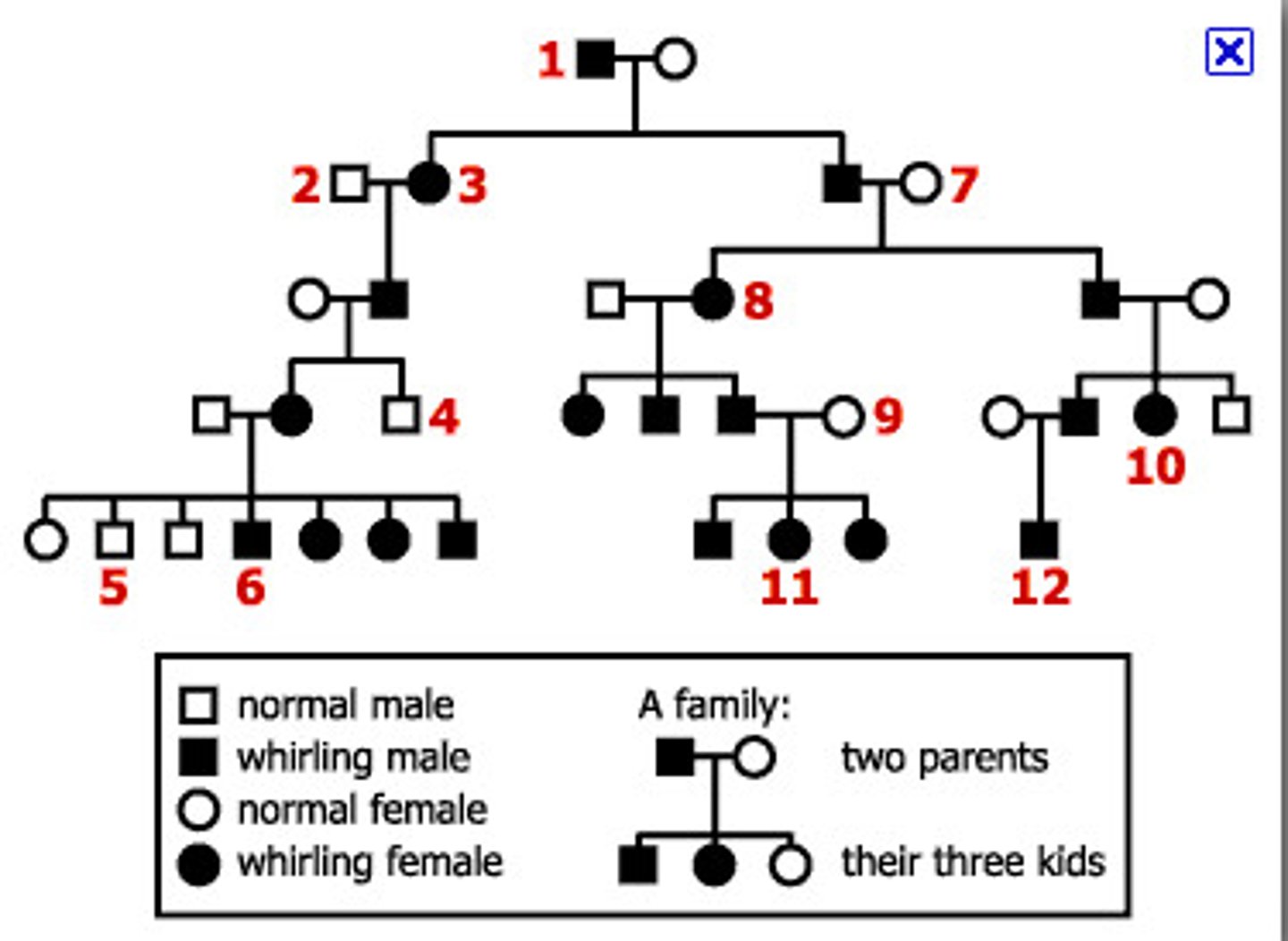
What is the component of a male that is not affected by the trait?
plain square
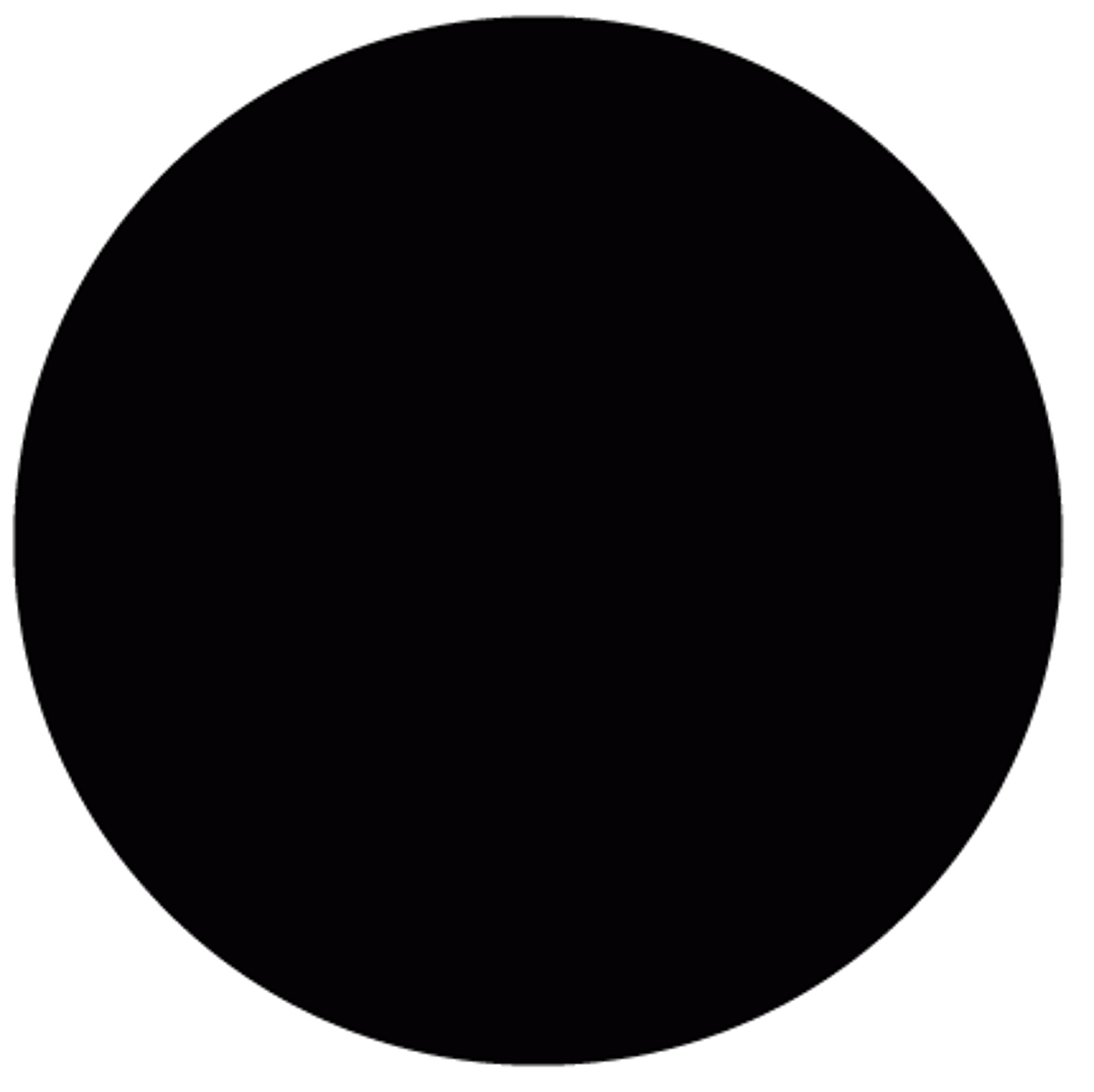
What is the component of a male that is affected by the trait?
dark square

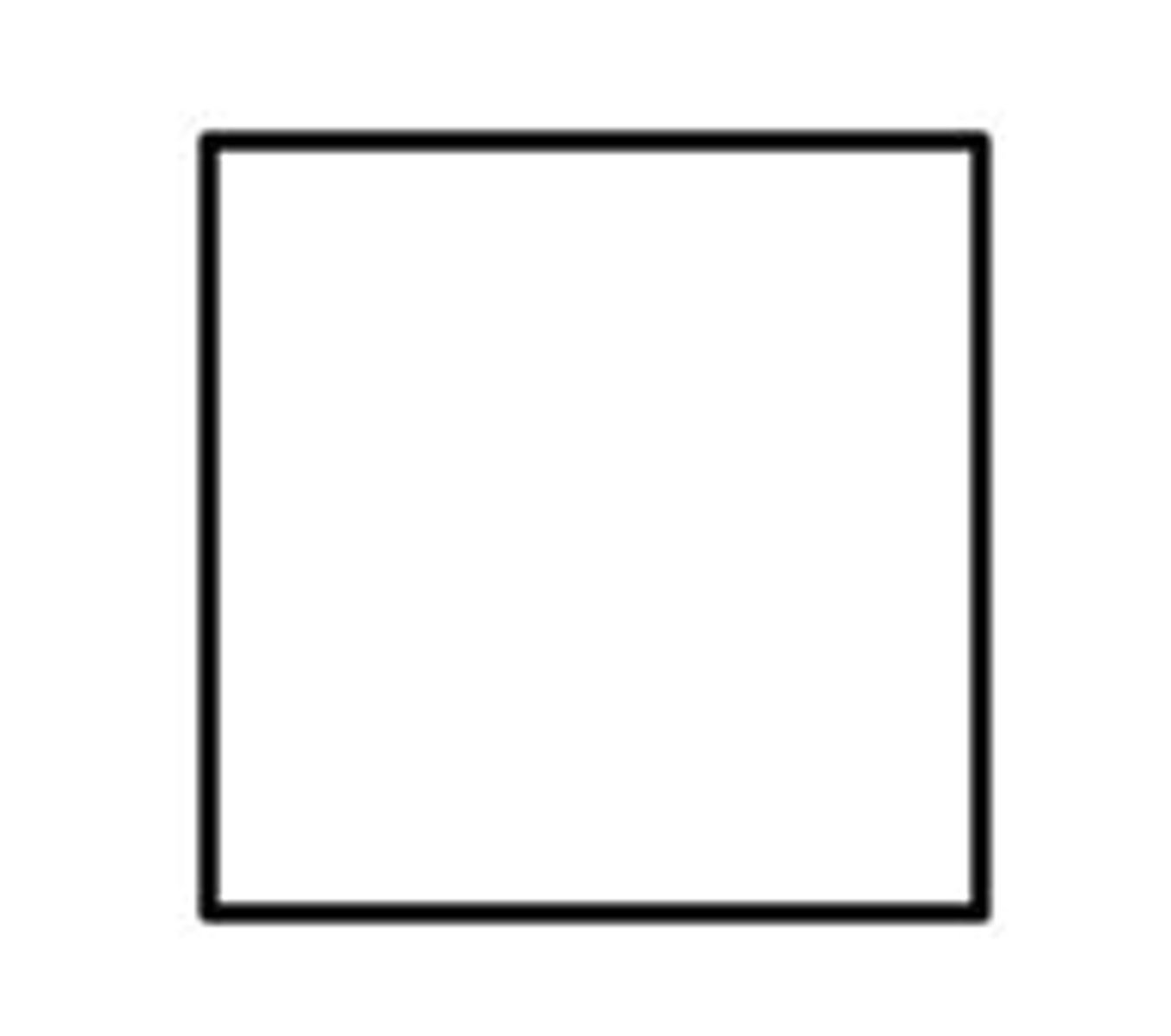
What is the component of a female that is not affected by the trait?
plain circle
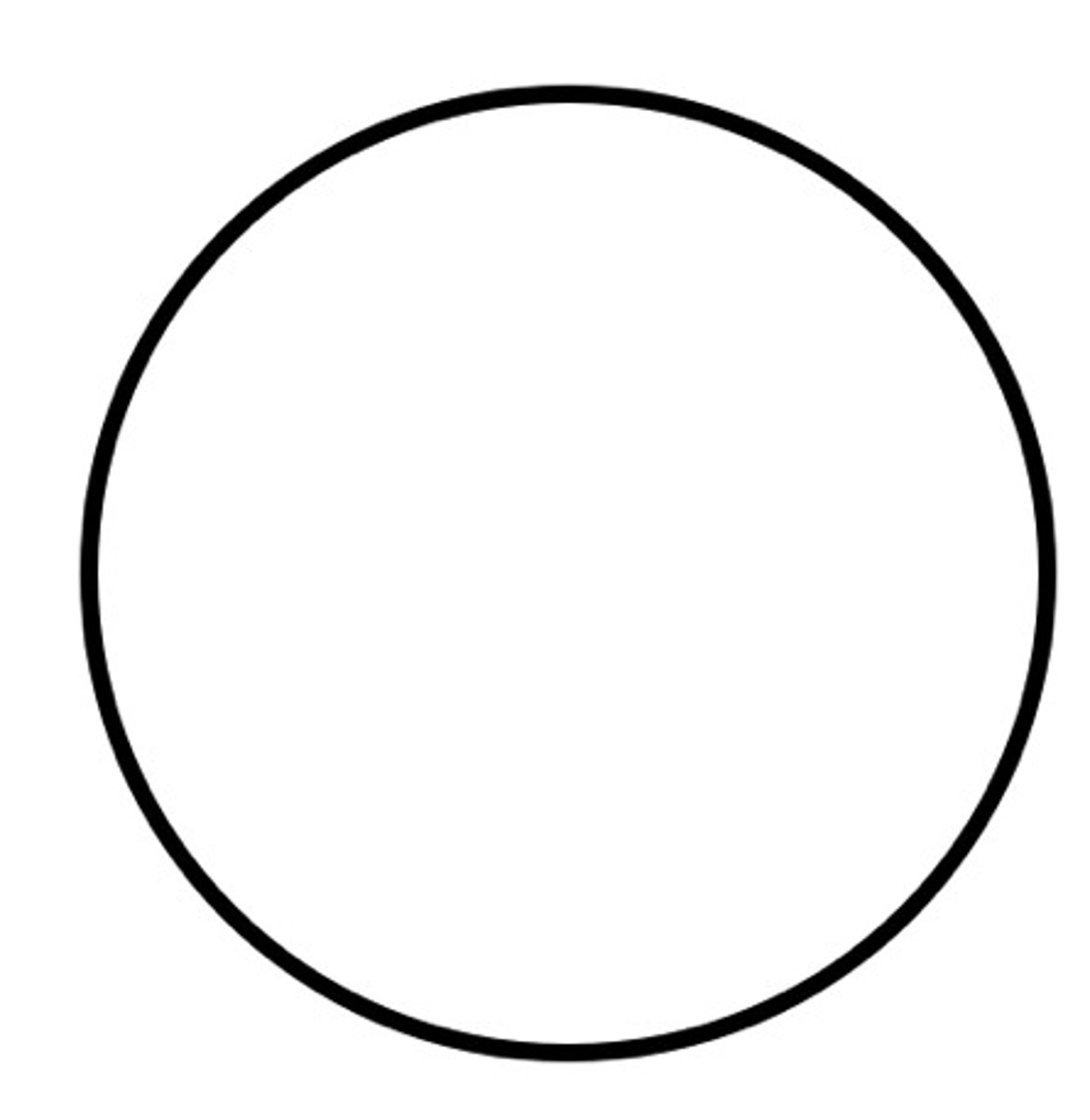
What is the component of a female that is affected by the trait?
Darkened circle
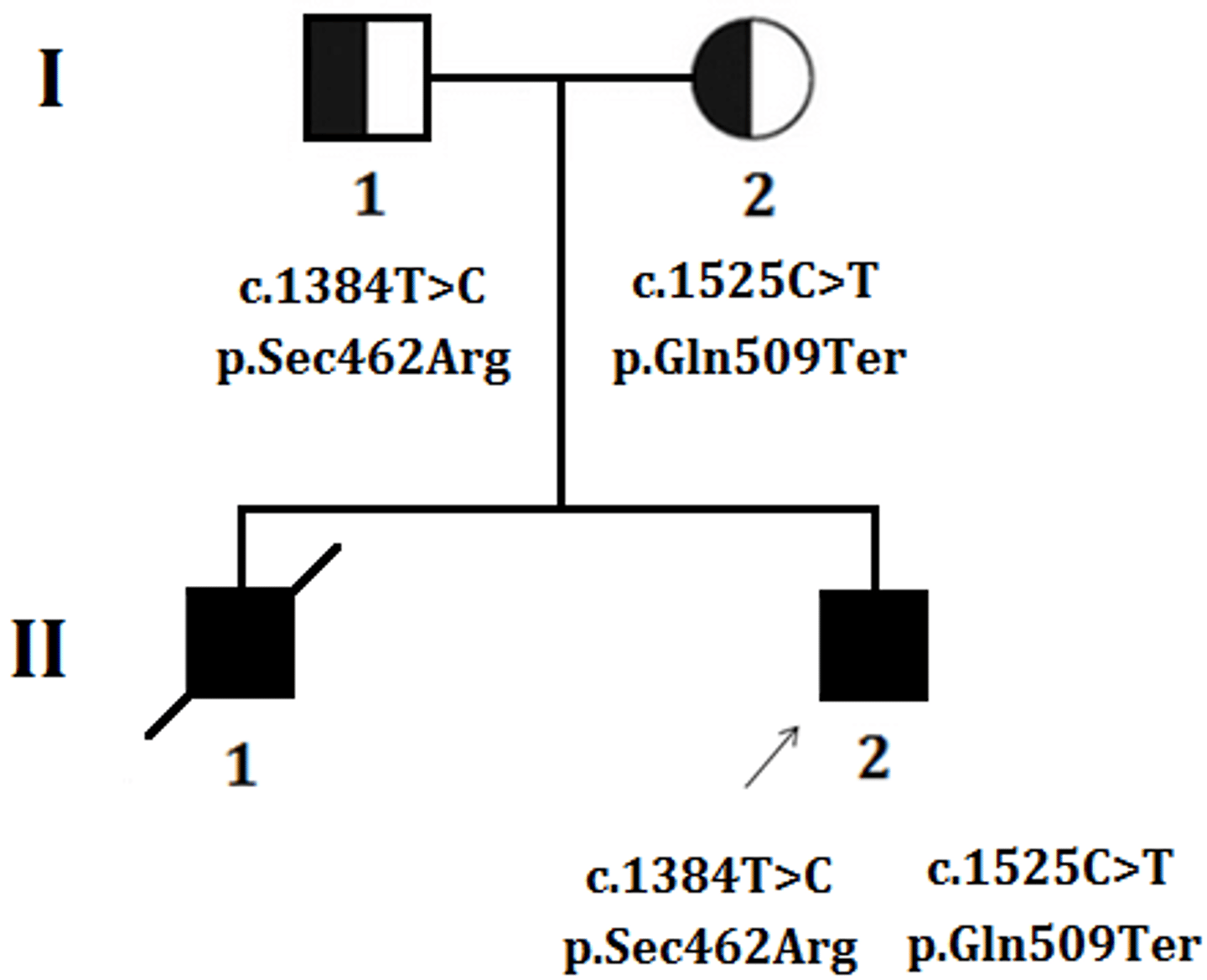
What is the component of a male with a hybrid?
I-1 (Half filled square)
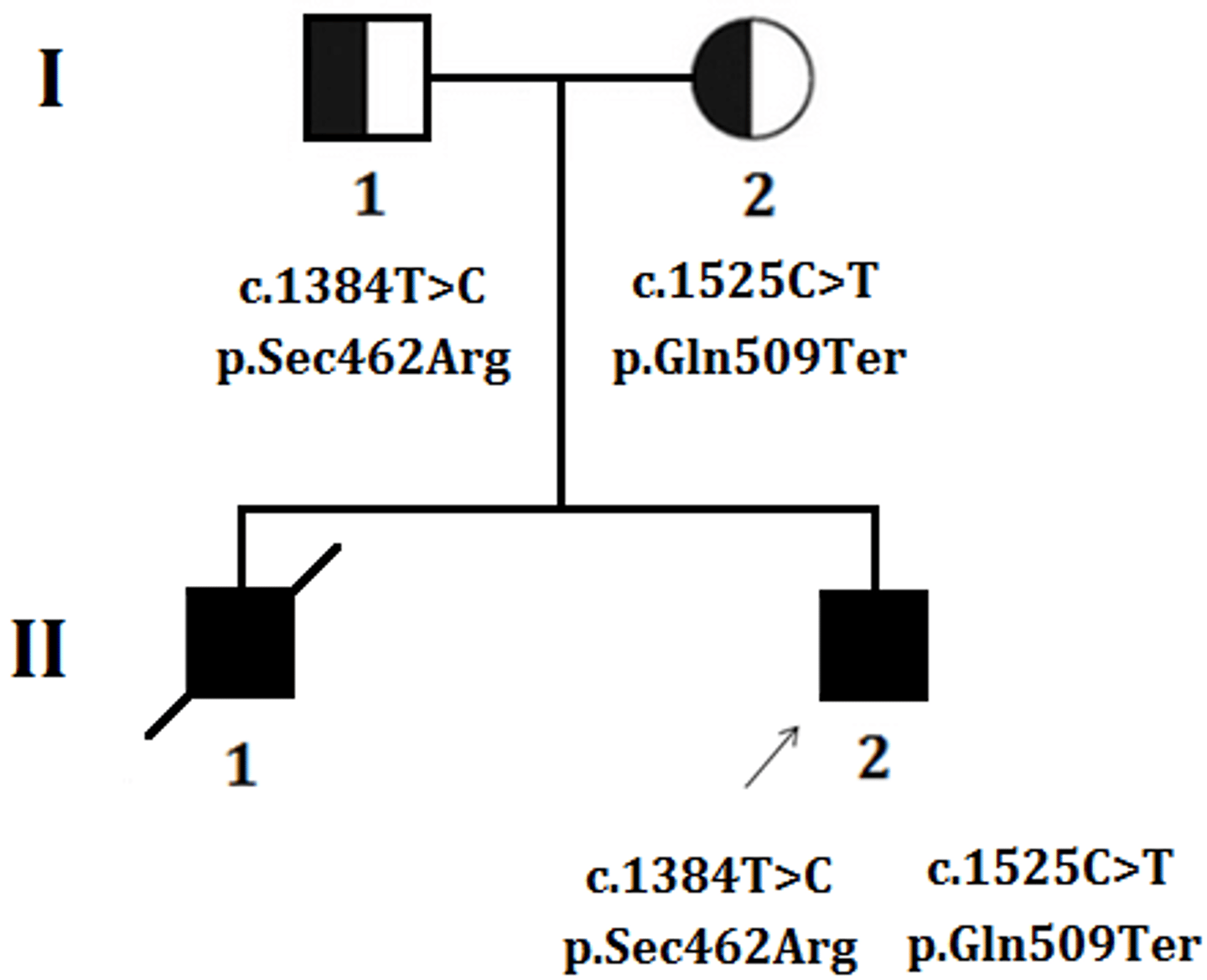
What is the component of a female with a hybrid?
I-2 (Half filled circle)
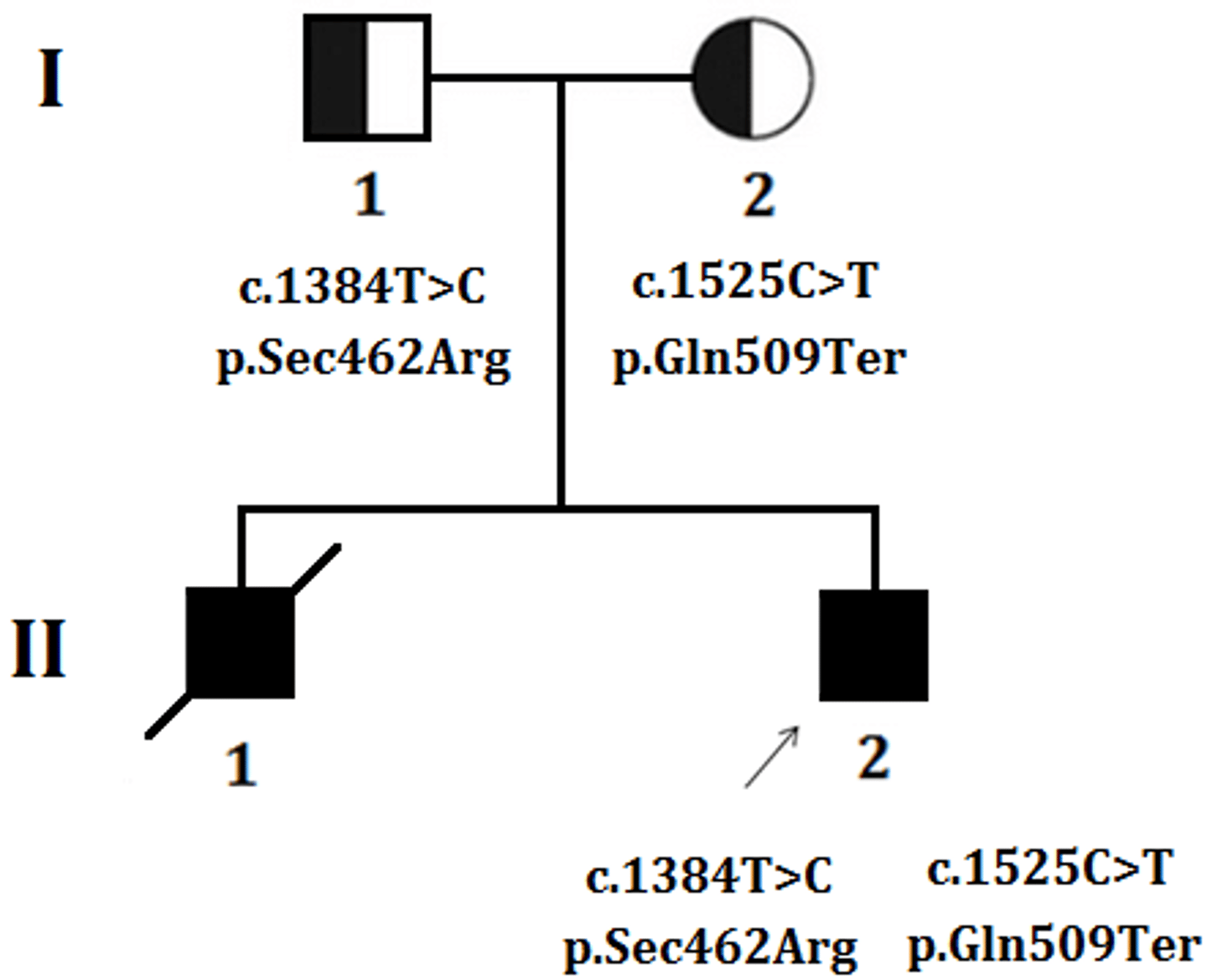
How does a trait skip a generation?
Recessive traits can skip generations because they can hide out in a carrier behind a dominant trait. The recessive trait needs another carrier to be seen.
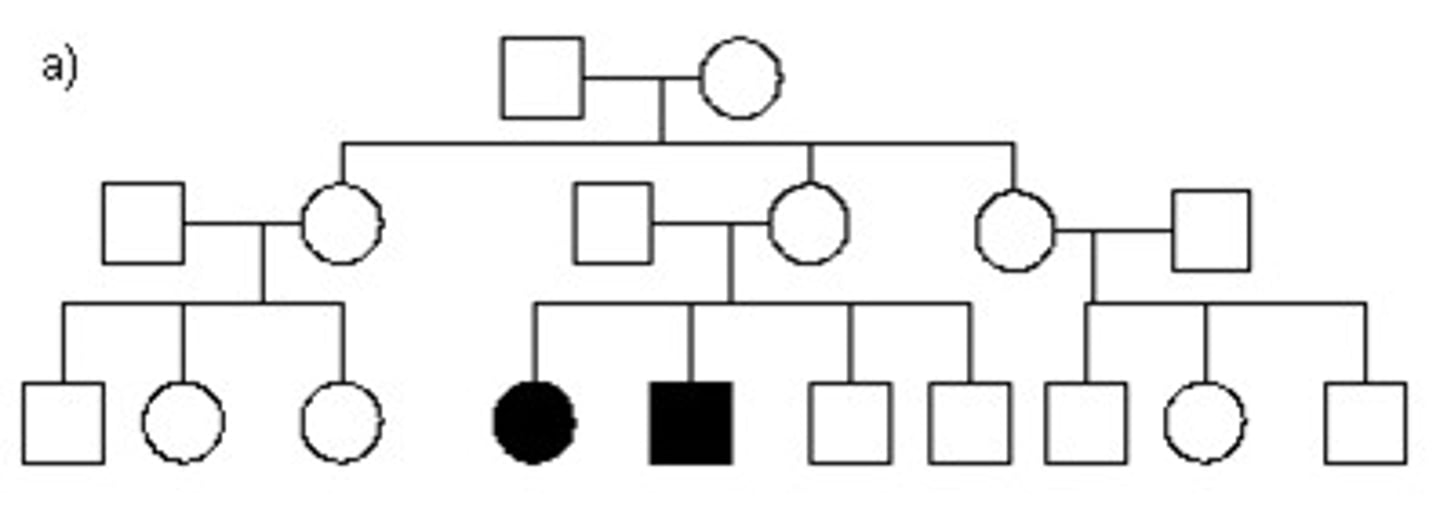
How does a trait get found in every generation?
It’s a dominant trait.
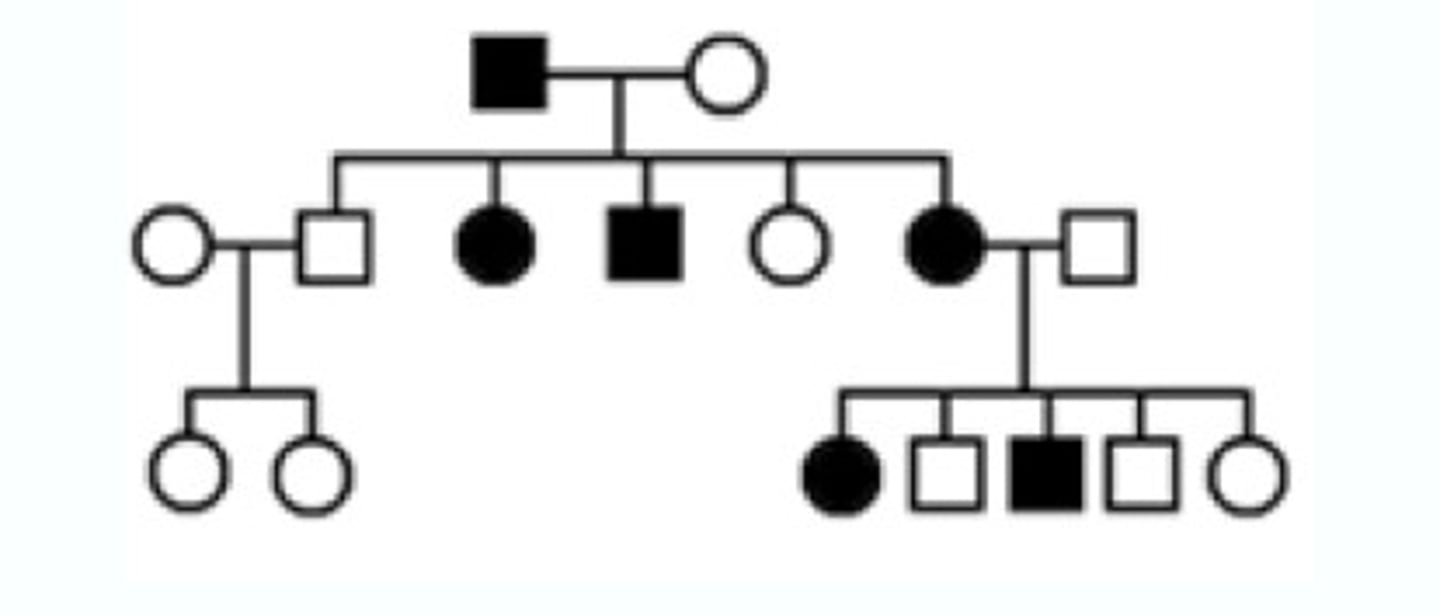
What is the process of meiosis?
The process by which gametes (sex cells) are produced.
How does meiosis happen?
1 parent cell equally distributes 2 full sets of DNA (chromosomes) into 4 genetically different daughter cells.
How many cell divisions are there in meiosis?
There’s 2 cell divisions (meiosis 1 & meiosis 2) but with only one DNA replication before meiosis 1.
What is crossing over?
The exchange of genes between homologous chromosomes resulting in a mixture of parental traits in offspring.
What is independent assortment?
The random moving of chromosomes to poles causing various gene combinations.
What is the product of independent assortment?
The product is 4 haploid daughter cells that are different from each other and from the parent cell.
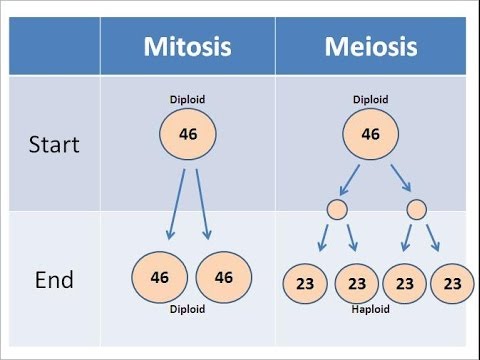
In MITOSIS, how many cells do we start with?
46 DIPOLOID cells
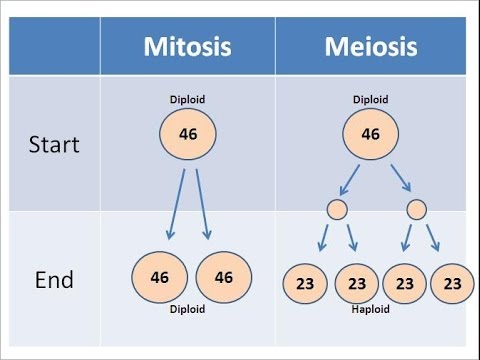
In MITOSIS, how many cells do we end up with?
92 DIPLOID cells (46 & 46)
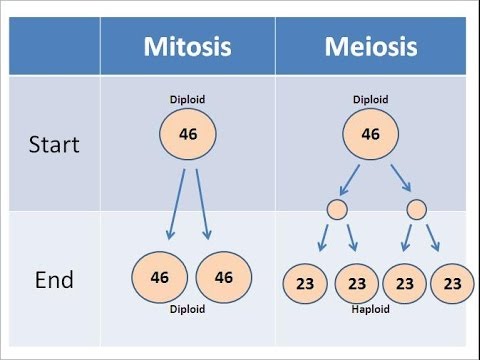
In MEIOSIS, how many cells do we start with?
46 DIPLOID cells
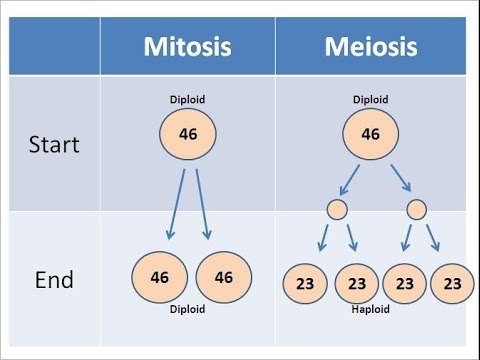
In MEIOSIS, how many cells do we end with?
92 HAPLOID cells (23 & 23 & 23 & 23)
What is meiosis?
A special type of cell division that produces 4 genetically distinct cells.
What type of cells undergoes meiosis?
Germ cells.
Meiosis produces __ reproductive cells called _______.
4, haploid.
What effect does meiosis have on the chromosome number of a cell? What is this ploidy called?
It’s called a haploid and it has half as much DNA.
The fusion of a _____ and an ____ produces a zygote with 46 (2n) chromosome number.
Sperm & egg
How do the cells produced by meiosis reestablish a complete set of chromosomes?
Joins two haploid.
In which stage of meiosis is crossing-over found?
In prophase 1.
What type of material is exchanged during crossing-over?
Alleles.
What does crossing over result in?
Genetic Variation.
Is DNA copied directly before Meiosis II?
No it is not.
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid.
What is DNA built out of?
Nucleotides.
What is the shape of DNA?
Double Helix and it’s antiparallel (running in opposite directions)
What is the backbone of DNA made out of?
Sugar.
What are the rungs of DNA made out of?
Nitrogen bases (complementary base pairs)
What is a nucleotide?
Sugar molecule & it attaches to a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.
What are the 4 purposes of DNA?
To store genetic information, pass on hereditary information, controls cell cycle, and controls protein synthesis.
What is the goal of DNA replication?
The goal of replication is to produce a second and identical double strand.
What is the cell cycle?
A repeating series of events a cell goes through constantly, includes growth, replication, & division.
What is DNA replication?
Semi-conservatives and identical copy of DNA is made in somatic (body) cells.
What does semi-conservative mean?
Two copies of DNA that each contain one of the original strands and one new strand.
What is helicase?
an enzyme that unwinds the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases & 2 single strands of DNA remain. (Unzipping)
What is ligase?
an enzyme that helps to connect the DNA strands
What is a polymerase?
an enzyme that builds DNA and checks for errors
What is a mutation?
Anytime DNA is damaged or miscoded
What are the 3 types of mutations?
Point (substitution), insertion, & deletion.
What is the process of protein synthesis?
The process of individual cells build specific proteins through transcription of DNA to mRNA & translation of mRNA into a protein.
What is transcription?
In the nucleus, a section of DNA is written as an mRNA message, base pairs stay the same but instead of thymine there’s URACIL.
What is translation?
In the cytoplasm at a ribosome, the mRNA message is read in groups of three (codons), each codon codes for an amino acid and a chain of amino acids makes a protein.
What is RNA?
A brief genetic message from DNA and is read by a ribosome. Built of nucleotides, single helix, sugar is ribose, there are four nitrogen bases: A, U, C, G, there’s only a copy of a gene from DNA.
List the 3 enzymes involved with DNA replication and describe their roles.
DNA Polymerase: It helps in the replication of double-stranded DNA into two identical DNA molecules. Helicase: It helps in the separation of double-stranded DNA into single strands allowing each strand to be copied. Ligase: It acts as glue by joining 2 DNA fragments to form a new DNA strand.
What are the four steps of DNA replication? (In order)
Unwinding, base pairing, joining, and checking.
What can happen if replication has uncorrected errors?
the deletion of one or more base pairs (mutation)
Describe what a point mutation is and its effect.
One or two bases switches and it is positive. (Color vision)
Describe what an insertion mutation is and its effect.
Base pairs get added - its harmful
Describe what a deletion mutation is and its effect.
One or more bases are removed and there is no change if same amino acids are selected but any change in the code can result in the loss of one or more amino acids from the protein
What is cell specialization?
Cells produce certain proteins and are structured for a specific job.
What causes cell specialization?
Certain genes are turned on/off in the cell’s DNA
Define mitosis.
The process by which a single parent cell divides to make two new daughter cells.
Give three reasons why mitosis occurs
Growth, repair, and asexual reproduction
What kind of cells complete mitosis?
Somatic cells
Compare the parent and daughter cells.
mitosis creates two identical daughter cells that each contain the same number of chromosomes as their parent.
What does polymerase do during base pairing?
Adds the new base pairs & one strand is the leading strand (copied in a straight line) while the other is the lagging strand
Why do we get larger as we age?
Our cells divide to make more cells
How do cancer cells develop?
Cancer cells divide too frequently.
What is apoptosis?
It’s when the cell self destructs. There is an issue in the cell cycle and it cannot be fixed. Insures the damaged dell cannot divide.