Unit 3 AP Psych
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sensation and Perception
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Sensation
Sensation refers to the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system detect and respond to stimuli from the environment. It involves the initial detection of sensory information, such as seeing, hearing, tasting, smelling, and touching. Sensation is the first step in the process of perception, where the brain interprets and gives meaning to the sensory information received.
Perception
ability to see, hear, or become aware of something through the senses.
Transduction
when you take an outside stimulus and it activates the sensory neurons (sensory receptors) and is transduced or transposes itself into an experience
Psychophysics
branch of psychology
deals with the relationships between physical stimuli and mental phenomena.
Subliminal
Hidden visual or auditory message that the conscious mind does not percieve
Weber’s Law
Physical proportion of change necessary before we “sense” the change.
The ratio of actual change in the stimulus compared to the perceived change.
Gestalt
Origin of cognitive psychology. Ways that we put together information into patterns. All principles based on how we simplify the world

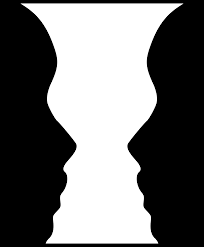
Figure Ground
Organization of the visual field onto objects (figure) that stand out from the surrounding (grounds).
Pragnanz
meaning good figure. Law of good figure or simplicity. Holds objects in the environment are seen inna way that makes them appear very simple.

Gestalt Grouping principles
Proximity
Similarity
Continuity
Conectedness
Closure
Proximity
how we organize and group things based on how close they are from oneanother.

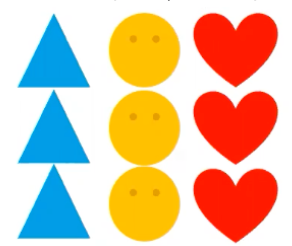
Similarity
objects that appear alike are grouped together.
Continuity
mind naturally follows a pattern that contains a continuous group.

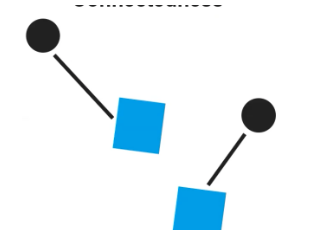
Connectedness
objects that move in the same direction tend to be seen as one object or grouped together.
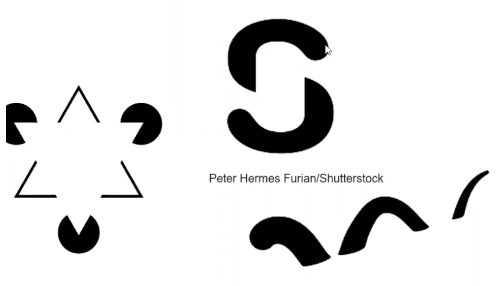
Closure
basis to fill in gaps in the mind. Sees pieces of images and mind fills it in.
Depth Perception
The ability to perceive distance of objects in one’s visual field
Perceive in Length, Width, and Depth
two different types
Binocular Cues
Monocular Cues
Binocular Cues
Require two eyes
convergence
retinal disparity
Monocular Cues
Relative size:
Interposition
light and shadow
Relative height
Texture gradient
Linear perspective
Wavelength
Distance between waves
Strobostopic Effect
objects appear to move at a slower speed than reality. This occurs when an object in motion is illuminated periodically with bursts of light.
Hue
Color
Convergence
Binocular Cue
Neuromuscular Cue
Two eyes move inward from near objects
Two eyes straighten for further objects
Retinal disparity
Binocular Cue
Images for eye differ
closer the object the larger the difference
further the object smaller the difference
Sensory Transduction
taking something physical and turning it sensory

Absolute Threshold
the stimulant has to reach this in order to produce snesory.
smallest amount of sensation you need to actually feel something
usually very low
chuldren’s are lower
Sensory Adaptation
Diminishes sensory awareness due to constant stimulation above the threshold
Difference Threshold
Smallest amount of change in a stimulus
Just- noticable differne
Weber’s Law: The ratio to actual change in the stimulus compared to the perceived change
Signal Detection theory
How much stimulation is necessary to meet out absolute threshold
Helps us understand when we notice or not notice things

Bottom-Up Processing
First sense the stimulus
Then perceive and process the experience
Top-down Processing
First perceive and process experience
expectations
experiences
motivation
culture
emotion
Then sense the experience
Perceptual Set
Tendency to perceive some parts of sensory data and ignore others
Infuences are the same that on Top-down Processing
Schemas
They are mental frameworks for organizing and understanding the world around us.
Ex. what a true friend, what food we like or not
Functional Fixedness
cognitive bias that limits a person to use an object only in the way it is traditionally used
Context Effect
describes the influence of environmental factors on one's perception of a stimulus. The impact of context effects is considered to be part of top-down
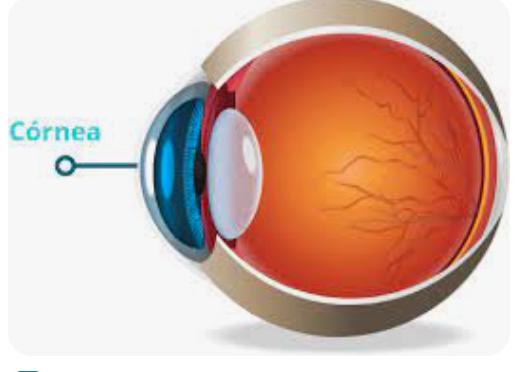
The Vision Process
Light Waves enter the eye through Cornea, then it hits the Pupil, then goes through the lens and that sends it back to the retina which has the fovea for color and focus. Once the retina is stimulated neurons fire and form the optic nerves which which take the signal to the visual cortex.
Cornea
Thin outer covering of the eye
Iris
What allows light to come in by expanding and contracting the pupil
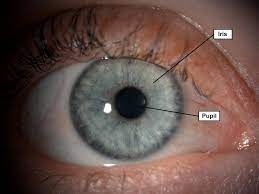
Pupil
The dark part of the eye where light actually comes in
Retina
what contains the receptors for vision
contains fovea (fovea=focus)
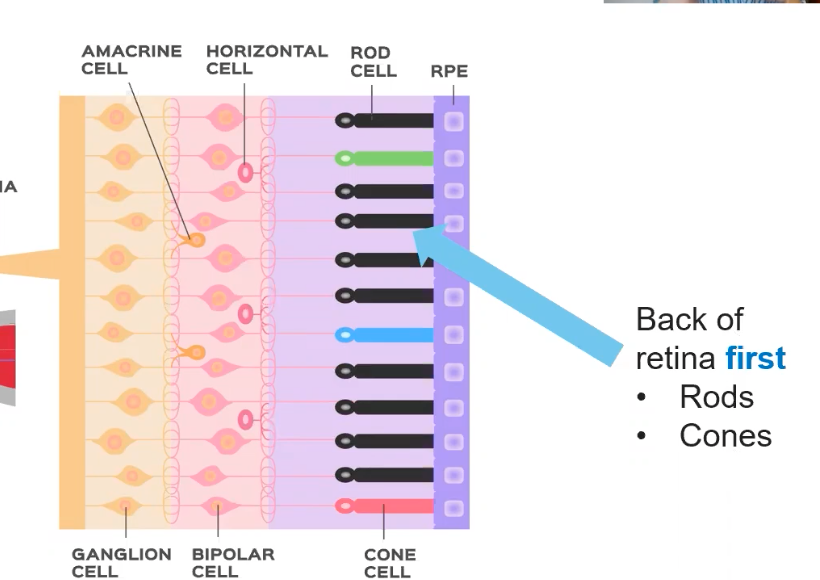
Optic nerve
When retina is stimulated neurons start to fire and form the optic nerve
Ganglions cells
For the optic nerve
Rodes and Cones
Rodes: receptors in the eye that detect movement
Cones: types of photoreceptors that work best in bright light conditions. Cones are very sensitive to acute detail and provide tremendous spatial resolution. They also are directly involved in our ability to perceive color.
Primary Visual Cortex
Occipital lobe. Vision is processed here
Feature detectors
light
line
shape
angle
motion
Feature detectors
respond to lines and spheres and angles
Parallel Processing:
refers to our ability to deal with multiple stimuli simultaneously.
Hubel and diesel
Discovered that vision was processed in the Occipital lobe by doing experiments of cats. it was accidental.
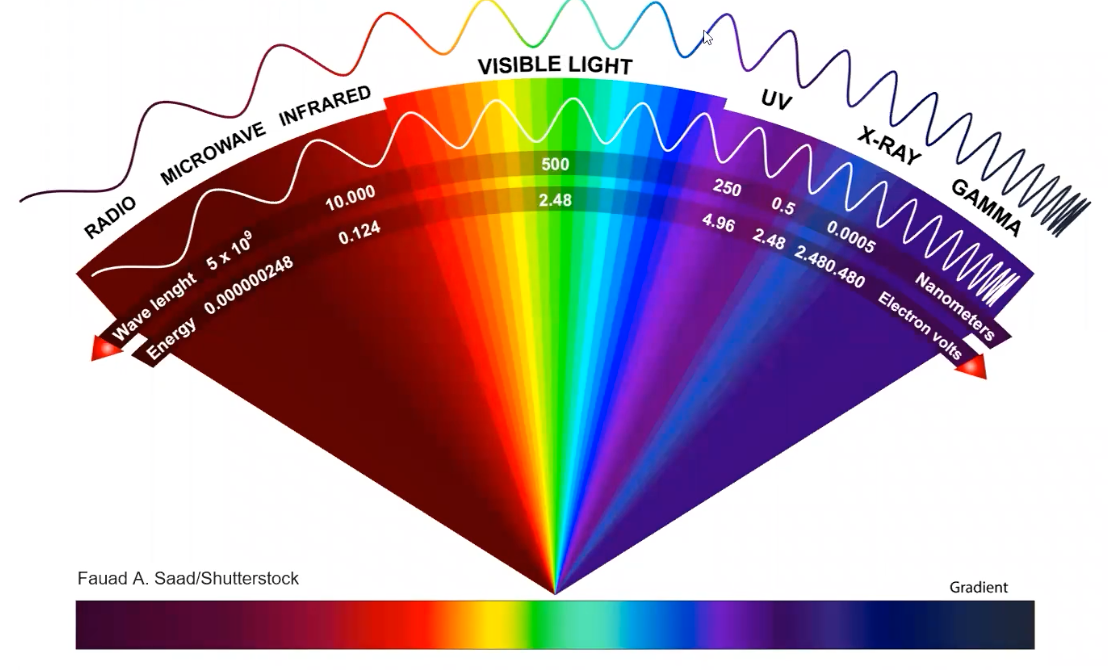
Light Waves
the Stimuli
Wavelength: distance between each wave. Determines hue. Short =cool (Purple= 400nm). Long =warm (red=650nm)
Amplitude; height of the wave . intensity of the color.
Trichromatic Theory
First stage of color processing.
Ypung and Helmohits (1802)
Photoreceptors ( cones) work in teams of three
red
green
blue
Combinations of cones firing make up all the colors in the visual spectrum
The strength of the signal determines how the brain interprets color
as light hits the retina cones are stimulated and create sensation of color.
Opponent.process theory
Second stage of color
As visual information is transferred from the photoreceptor cells (cones) to the ganglion cells, some neurons are excited (turned on), while others are inhibited (turned off).
They work through opponent process
neurons turn on and off during this process
explains phenomenon of afterimages
Color blindness
Result of lack of functioning color receptors for color. Inability to distinguish excitatory form inhibitory signals or may have unresponsive cones.
Monochromat
Most rare. Can only see black white or gray
Dichromat
Common. have trouble distinguishing Red and green or Yellow and blue.
Trichromat
No limitations of color
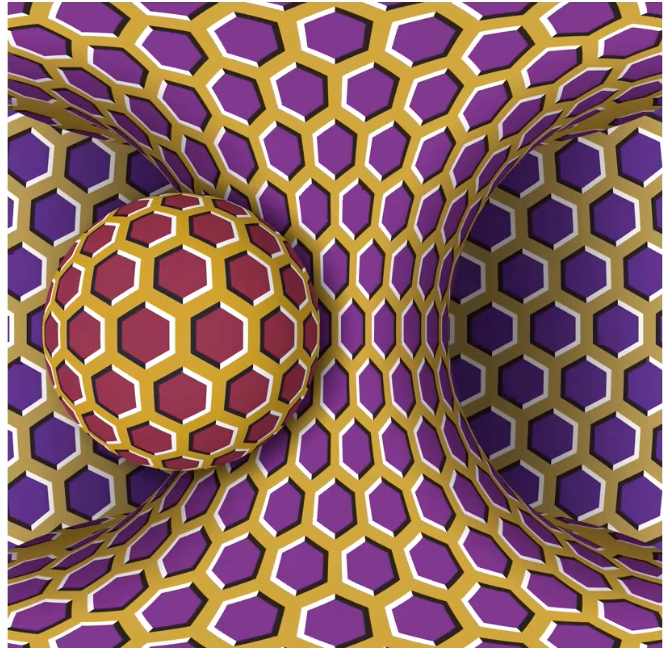
Physical illusion
A type of illusion
distortions of scale
based on manipulation of monocular cues for depth perception
Physiological Illusion
A type of illusion
visual system gets overstimulated
excitement or fatigue of photoreceptors
fatigue of stimulation of feature detectors in visual cortex.

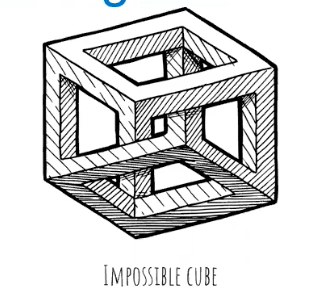
Cognitive Illusion
A type of Illusion
mismatch between what you perceive and what you sense
top-down processing
perceptual set
context cues
manipulation of Gestalt principle

Audition
Ability to process sound and interpret sensations.
Frequency
Number of waves that occur at a certain time
Pitch
Quality of a sound governed by the rate of vibrations producing it; the degree of highness or lowness of a tone.
Outer ear
Pinna, auditory canal, and tympatic membrane
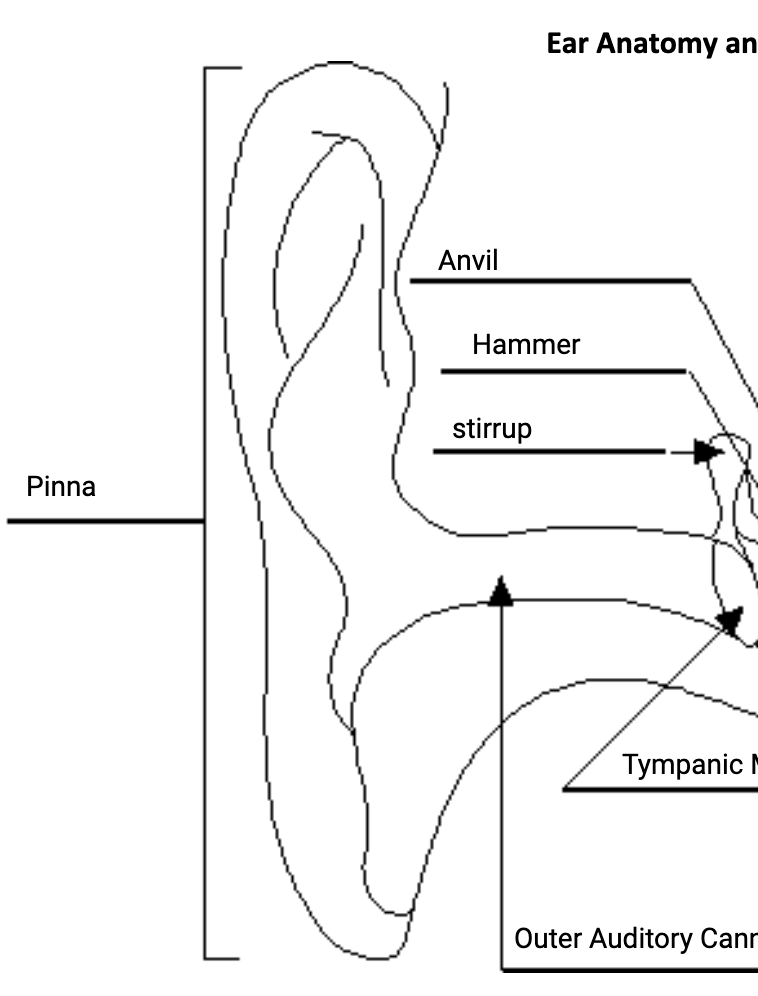
Middle ear
Three solid tiny bones
the hammer, or malleus;
the anvil, or incus;
the stirrup, or stapes.
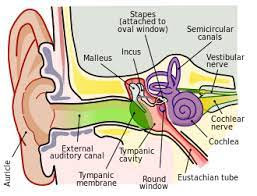
Inner Ear
Cochlea: Hearing
Semicircular Canals: Balance
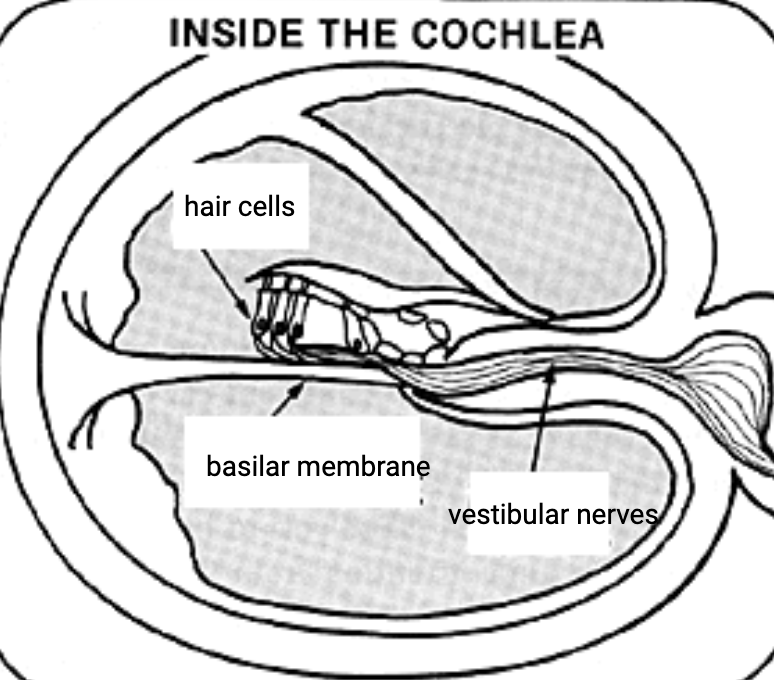
Cochela
fluid-filled, spiral-shaped cavity found in the inner ear that plays role in hearing and participates in the process of auditory transduction.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
affects loudness, clarity, and range of sounds.
Solution: hearing aids and/or cochlear implants
Conduction Hearing Loss
Sound waves don’t process normally through outer and middle ear
Solution: medicine or surgery,
Place Theory
proposes an explanation of how human beings perceive pitch. According to place theory, the hair cells and nerve fibers of the cochlea are divided into different regions that detect specific sound frequencies.
Pinna
external flop of skin and cartilage that regulates vibrations and protects the ear
Auditory canal
part of the outer ear that leads to tympanic membrane
Tympanic Membrane
the eardrum. separates outer from middle ear and vibrates with sound
Hammer, Anvil, and Stirrup
bones inside of the ossicles that transmit sound to the oval window
Hair cells
Trigger neural impulses to the brain via auditory nerve
Organ of Corti
produces nerve impulses to respond to sound vibrations (inside cochlea)
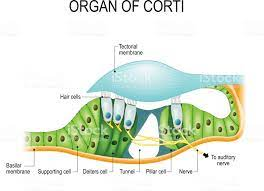
Basilar Membrane
pressure changes in cochlear fluids
Oval WIndow
Get sound vibrations to the cochlea
Place theory
an explanation of how human beings perceive pitch. According to place theory, the hair cells and nerve fibers of the cochlea are divided into different regions that detect specific sound frequencies.
Touch
ability to perceive an object or other stimulus that comes into contact with the surface of the skin
Gate Control Theory
mechanism in the spinal cord, in which pain signals can be sent up to the brain to be processed to accentuate the possible perceived pain, or attenuate it at the spinal cord itself.
Kinesthesis:
provides information through receptors in the muscles, tendons, and joints, enabling humans and other animals to control and coordinate their movements, including walking, talking, facial expressions, gestures, and posture.
Vestibular sense
carries impulses involved in maintaining equilibrium. It arises in the primary vestibular bipolar neurons whose cell bodies make up the Scarpa ganglion in the internal auditory canal.
Gustation
Taste
Chemical sense
Olfaction
Smell
Chemical Sense
Synesthesia
Synesthesia is when your brain routes sensory information through multiple unrelated senses, causing you to experience more than one sense simultaneously.
Extrasensory Perception
perception that occurs independently of the known sensory processes.
Gustav Fechner
founded the field of psychophysics and is considered to be the founder of modern experimental psychology as a field. He discovered the Fechner Color Effect which is the observation of different colors when black and white patterns are moving at a high speed.
David Hubel:
Demonstrated that neurons in the occipital lobe's visual cortex receive information from individual ganglion cells in the retina (feature detector cells). Also proved that the brain divides a visual scene into several subdimensions(color, movement, etc.) and processes each separately.
Ernst Weber
Weber's law is the principle that states that the just-noticeable difference between two stimuli is a function of the magnitude of the original stimulus.
Torsten Wiesel
discovery of the critical period in visual system development as well as research on visual information processing by the visual cortex of the brain.