Intro to Theater Final Exam
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
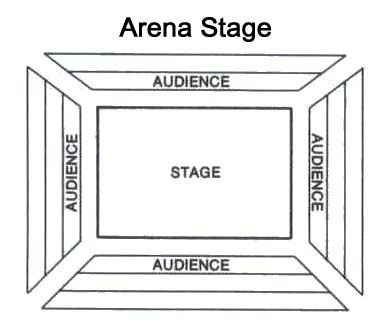
Arena Stage
aka “theater in the round” oldest type of stage originating from greeks where audience sits on all four sides of the stage
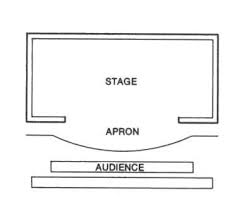
Thrust Stage
developed in Greece, audience sits on three sides of the stage
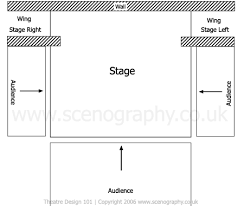
Proscenium Stage
developed during Italian Renaissance, audience sits on one side of the stage, most popular stage style
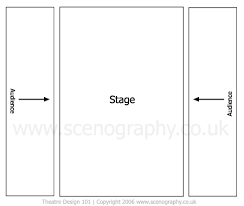
Traverse Stage
recently developed style, catwalk style stage, audiences sits on two sides facing each other with stage in between them
Flexible Stage
environmental/experimental style, audience can move during the performance
Black Box theater
usually square/rectangular shaped, painted black, minimal seating/intimate performances
Elements of Drama
plot, character, theme, diction, spectacle, music
plot
series of actions and events that unfold in front of the audience (opening scene, obstacles, complications, crises, climax
Character
refers to the agents of actions that unfold that plot one decision at a time (protagonist, antagonist)
theme
subject matter and universal message as supported by the unfolding of the plot and the development of the characters
diction/dialogue
how the plot, character development and revelation of the theme are all manifested with the written text of the script
music/melody
refers to anything heard from the performance space (instrumental music, songs, sound efects, volume of actions, pauses and silences
spectacle
anything seen in the performance (scenery, lights, costumes, make-up)
modern theatre elements
characters, plot, theme, dialogue, convention, genre, audience
convention
techniques and methods used by the playright or director to create the desired sylistic effect
genre
refers to the type of play (comedy, tragedy, drama)
audience
group of people gathered to watch a performance
initial incident
the event that gets the story going
preliminary event
whatever takes place before the actions of the play that is directly related to the play
rising action
a series of events following the initial incident and leading up to the dramatic climax
climax
the turning point or high point of a story, when events can go either way
falling action
the series of events following the climax
denouement
conclusion
commedia dell’arte
comedy of art, comedy of skills, italian comedy, comedy of professional artists, artistic comedy
characteristics of commedia
improvised performances based on scenarios
consistent themes
money, love food
mime, acrobatic tricks, music and masks were commonly used
stock characters
lazzi: short comedia physical acts of comedy within a scene
battute
set dialogue that always happens between two specific characters
burla
improvised comic bit or practical joke done by the servants, often involving 2 actors
concetti
a set character speech, something that a certain character always says
lazzi
a physical comic bit in the middle of the play unrelated to the plot
stock characters
commedia characters that are set and never change from play to play
zibaldone
reference book holding lazzi, concetti, battute, and stock phrase for a single character
three commedia character categories
clowns (zani), villains (vecchi), lovers (innamorati)
pantalone
rich & greedy
gullible
wears red pants and top with flowing black cloack and money bag
long point nose, has a mustache and busy eyebrows
hunch back, bent knees
arlecchino
servant who wants money and food
stupid and smart at the same time
colorful patchwork on costume
black mask with small eyes and cat like face
very quick paced
leads with knees and is very active
innamorati
romeo and juliet
dont wear masks but do wear make up
italian renaissance prince and princess style costumes
glide instead of walk - lead with chest and head
columbina
servant
quick witted character
moves with quick strong steps
II Dottore
not usually a real doctor
spouts knowledge but never has good timing
always wrong and makes no sense
never stops talking
movement is slow, character is large
brighella
tough servant
arrogant
dressed as a servant in a white costume
movement is cat like
II Capitano
a soldier/warrior who brags about his success
all talk and little action — hes cowardly
wears military garb
long pointy nose on the mask
pulcinella
hates all others
works alone
mostly a servant but could be a master as well
dresses in floppy clothes and floppy hateg
characteristics of melodrama
music was used to increase emotions or to show characters
episodic form: the villain poses a threat, the hero or heroine escapes
simplified moral univers; good and evil are embodied in stock characters
many special effects: fires, explosions, earthquakes
almost never five acts — usually 2-5
realisim
everything on stage is made to resemble observable everyday life
naturalism
extreme or heightened sense of realism
popular theatre
mainstream theatre
absurdism
based on the philosophy of existentialism
who was the founder of naturalism
Zola
true or false: realists believed that plays should be as much like real life as possible
true
gestures
movement of the arms or hands to communicate
blocking
large movements from one part of the stage to another in a performance
pantomime
non-verbal acting or acting without the use of props
stage whisper
a type of specialized speaking to simulate soft speech on stage, but be heard by the audience
cue
prompts a sound effect to play, lighting to change, or an actor’s entrance
rendering
a colored to scale representation of a design from the audience’s point of view
what is Stanisklavski most remembered for
acting
internal traits
make up a character’s personality
when did absurdism become popular
after world war II
En SL X SR, sit at ch, st, EX, SR translates to:
enter stage left cross stage right, sit at chair, stand, exit stage right
melodrama is
a play that is exaggerated
stake
level or degree of importance in meeting an objective
beat
a change in emotion or topic in a scene or monologue
sense memory
an actors memory of sight, sound, smell, taste, texture
stage presence
actor’s ability to command the audience’s attention through an actor’s energy on stage
ground plan
a diagram drawn to scale that shows the walls door windows and other props
given circumstances
information provided by the script that relates to the world of the play
external traits
characteristics that make up physical appearance - posture, gestures, mannerisms, clothing
flexible
stage that can be proscenium for one performance and a thrust for the next one
examples of time that the stage designer has to deal with
historical time
season
time of day
Shakespeare wrote in
iambic pentameter
Shakespeare was born in
Stratford upon avon, 1564
the theater
first permanent theatre in England
how many times did the globe theater burn due to cannon fire
twice
in naturalism, stage time is equal to
real time
SL
stage left (audiences right)
SR
stage right (audiences left)
DS
down stage (closer to audience)
US
upstage (further from audience)
Greek Theatre; a festival
5-6 days
14,000-15,000 people
outdoor performances
lines were chanted or sung
parts of a greek theatre
orchestra
skene — setting for plays
proskenion — frame around a wide shallow stage
thespian
greek word for actor
how many plays & sonnets did William shakespeare write
over 36 plays
154 sonnets
how did Shakespeare become successful
when he became a member of an acting company between 1564-1613
What was The Globe
a theater financed by Shakespeare and men from his company
who did Shakespeare perform his plays for
Queen Eilizabeth