AP Calculus BC
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Quadratic Formula
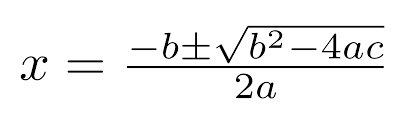
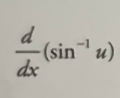
Inverse sin derivative
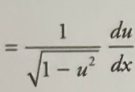
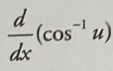
Inverse cos derivative
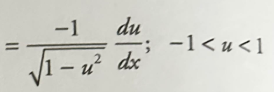
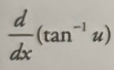
Inverse tan derivative
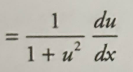
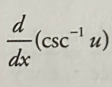
Inverse csc derivative
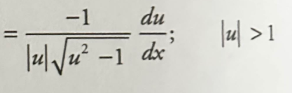
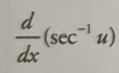
Inverse sec derivative
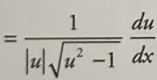
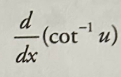
Inverse cot derivative
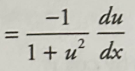
Linear Approximation
f(x) ≈ f(a) + f’(a) (x-a)
General Equation of Tangent Line
y = f(a) +f’(a) (x-a)
Newton’s Method
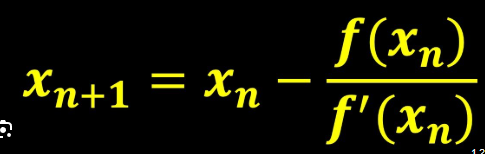
Exponential Growth
y = y0ekt
Exponential Decay
y = y0e-kt
Derivative of y = au
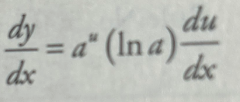
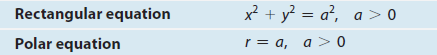

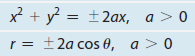
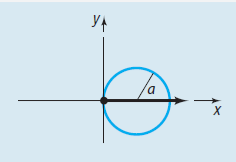
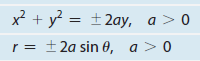
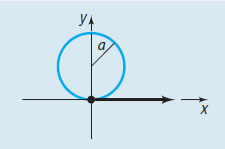
General equation of a Cardioid
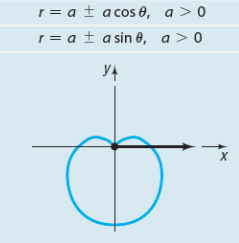
a + a cosθ
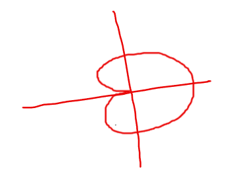
a - a cosθ

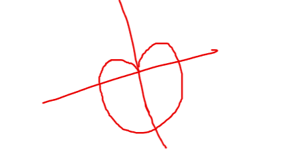
a - a sinθ
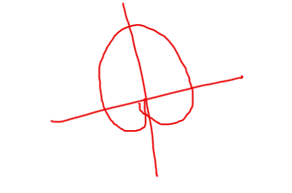
a + a sinθ
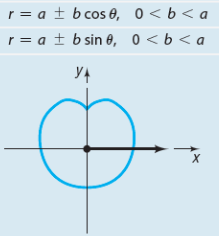
Limacon without inner loop
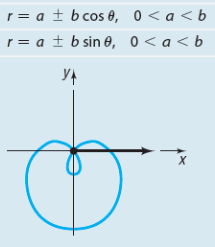
Limacon with inner loop
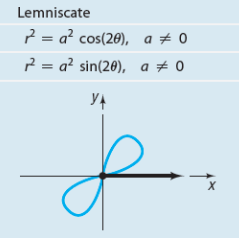
Leminscate
Rose with three petals
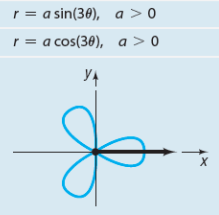
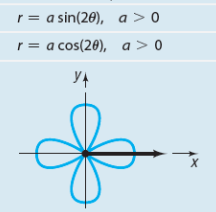
Rose with four petals
Logarithm notation
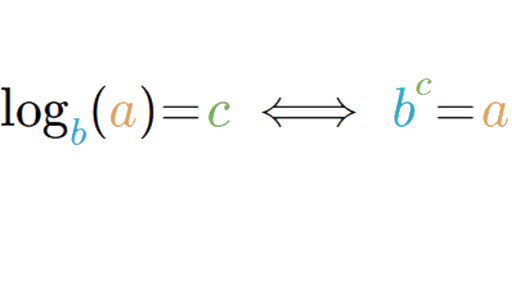
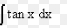
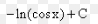
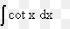
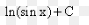
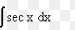
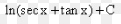
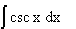
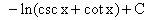
∫a^u du
1/ln a a^u + C
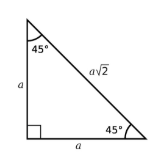
45-45-90 special triangle
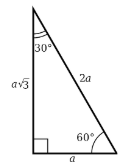
30-60-90 special triangle
Newton’s First Law
An object at rest will stay at rest, and an object in motion will stay in motion with the same velocity (speed and direction) unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
Newton’s Second Law
(F = ma) The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass
Newton’s Third Law
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force back on the first that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction