Exam 1
1/155
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
156 Terms
Pathophysiology
the study of the changes of body function with disease.
patho-
disease
physiology
The study of body function
Disease
anything that is abnormal from your normal health/state of wellness. Inability to maintain homeostasis (internal balance).
What causes disease?
pathogens, abnormal function of cells, environmental factors, genetics, etc...
Pathogen
An organism that causes disease
Types of pathogens
viruses, bacteria, fungi, parasites
types of environmental factors that contribute to disease
water and air pollution, radiation, diet and exercise
Sedentary Lifestyle
low amount of exercise/physical activity
Predisposing factor (Risk factor)
Something that increases risk of developing a disease.
Homeostasis
ability to maintain an internal balance
What are the top 2 leading causes of death in the US?
Heart disease and cancer
what are the common cellular adaptations?
atrophy, hypertrophy, hyperplasia, metaplasia, dysplasia, and neoplasia.
Atrophy
cells decrease in size
atrophy
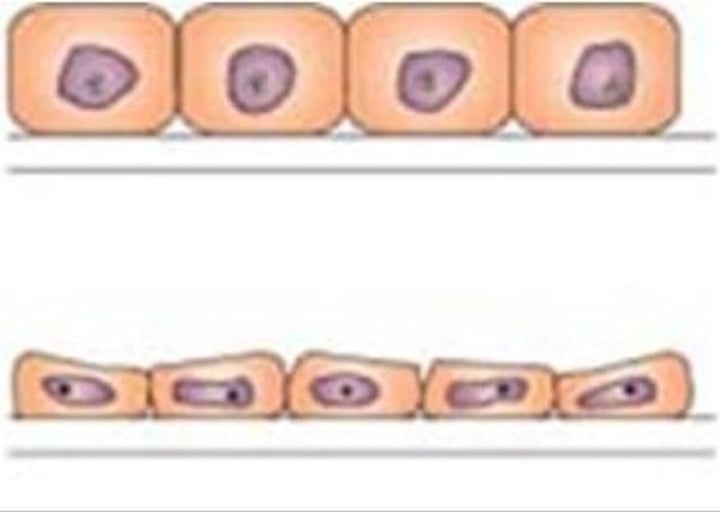
hypertrophy
cells increase in size
Hypertrophy
Hyperplasia
increased number of cells
hyperplasia
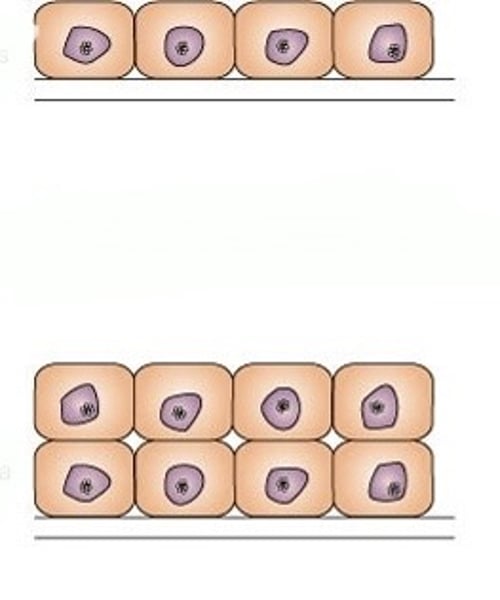
Metaplasia
replacement with a difference, but normal (non-canerous) cell/tissue type
metaplasia
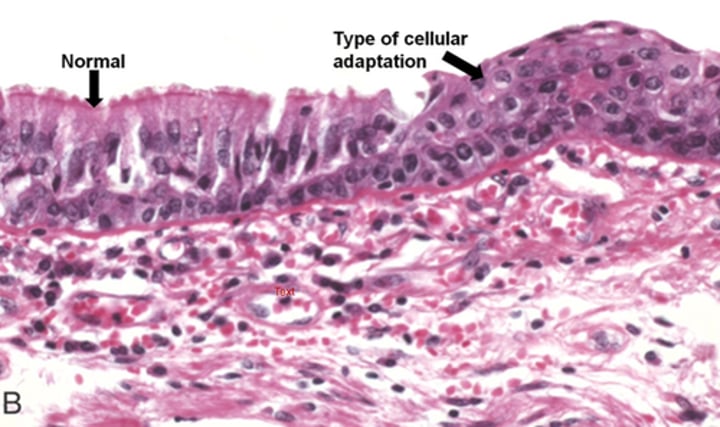
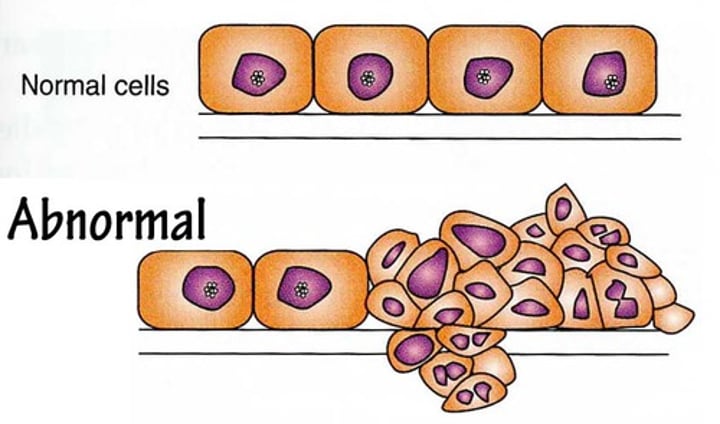
Dysplasia
increased number of cells, variable cell size, shape, and structure, loss of organization (possible pre-cancer).
dysplasia
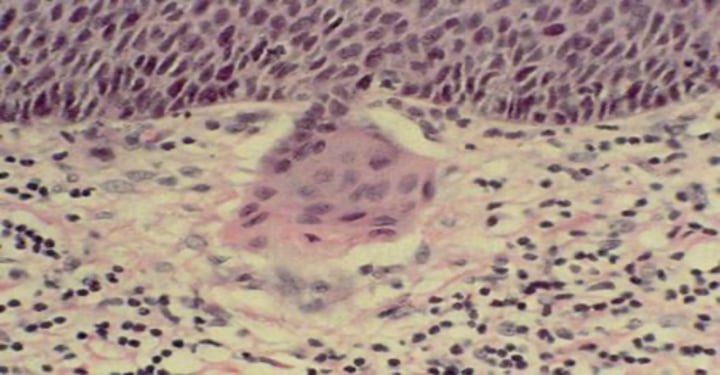
Neoplasia
increased number of cells, variable size and shape, loss of organization, variable nuclei, can be cancer
neoplasia
hyper-
increased
Apoptosis
process of programmed cell death
necrosis
traumatic cell death
what can occur with necrosis?
may cause local inflammation due to release of lysosomal enzymes
Types of necrotic tissue damage
liquefaction, coagulative, and fat necrosis
Liquefaction
dead cells are liquefied by enzymes
Coagulative
cell proteins are denatured and insoluble
coagulative necrosis looks
caseous
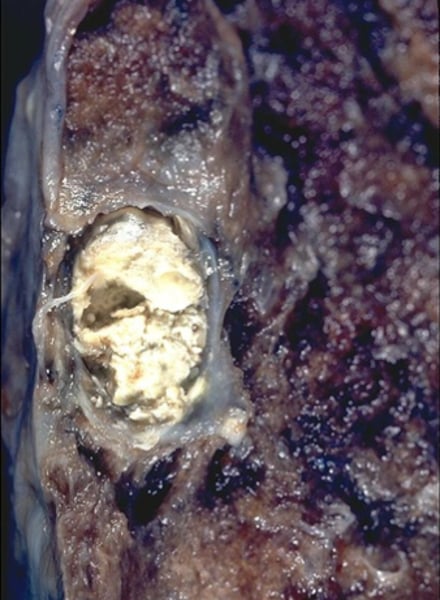
caseous
thick, yellowish, "cheesy" substance forms in tissue
caseous
liquefaction
fat necrosis
fatty tissue broken down into fatty acids
fat necrosis
denatured
unfold, bigger, not compact
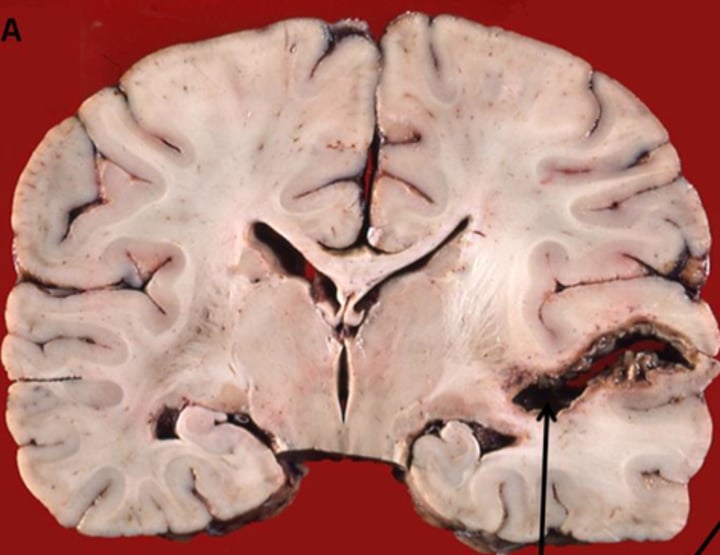
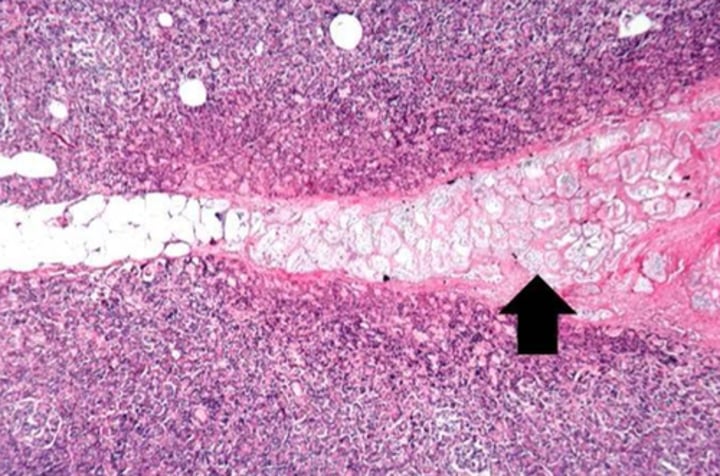
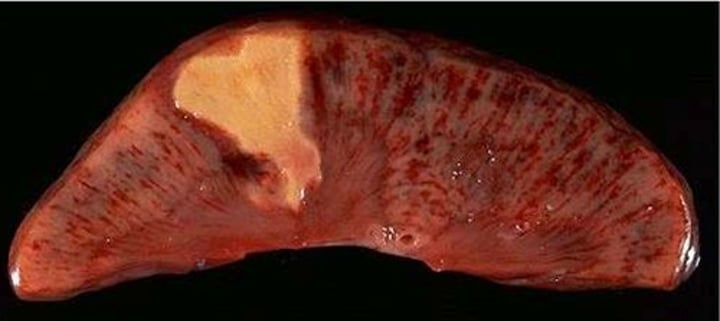
infarction
area of dead cells resulting from lack of oxygen
infarction
hypoxia
low oxygen levels
infarction is susceptible to
hypoxic damage that varies by cell type
Gangrene
areas of necrotic/dead tissue that has been infected by bacteria
gangrene
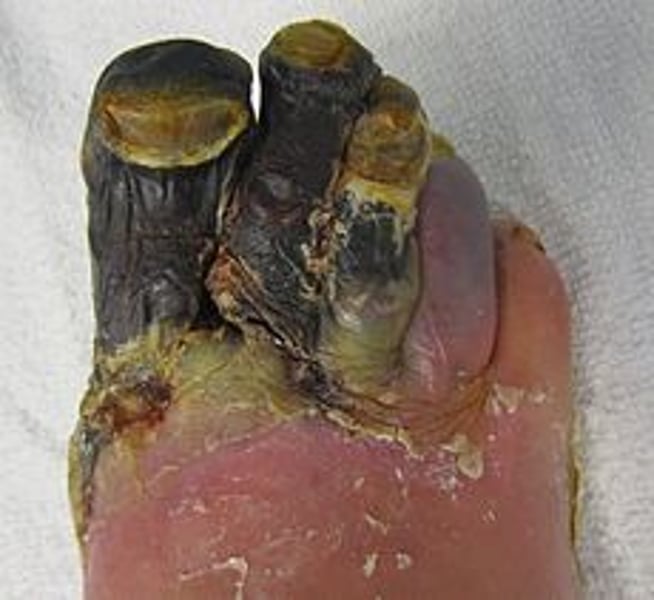
iatrogenic
disease related caused by medical treatments
Etiology
cause of disease
filtration
a process that causes ISF to flush out of capillary
absorption
a process that causes ISF to flush into a capillary
Hydrostatic pressure (HP)
force exerted by fluid pressing against wall (push)
osmotic pressure
the external pressure that must be applied to stop osmosis (pull)
What causes edema?
excess filtration, decreased absorption, increased capillary permeability, or blocked lymphatics
edema
swelling
If your Blood pressure decreases, the volume of ISF in a particular tissue would?
decrease, lower BP = Less push
Decreased levels of protein in the blood would cause the volume of ISF in a tissue to?
increase, less protein = less pull
Hypoalbuminemia
low albumin levels in the blood
high BP equals
ISF pushes out of capillary
manifestations
signs and symptoms of disease
signs
changes in a body that can be measured or observed as a result of disease. Ex: fever, BP
Symptoms
Subjective characteristics of disease felt only by the patient. Ex: headache, fatigue
First line of defense against pathogens
mechanical and chemical barriers
ex. fluids- tears, saliva, mucus
barriers- skin, mucus membranes. Do not change according to type of pathogen
Second line of defense against pathogens
innate immune responses Ex: phagocytosis, inflammatory response, and interferon
innate
existing from birth, inborn
Interferons
antiviral proteins
Thirds line of defense against pathogens
specific immune responses. Ex: B and T cells. Specific to type of pathogen
Inflammation
is a nonspecific defense mechanism that occurs in response to tissue injury or infection
-itis
inflammation of tissue
Complication
new conditions or diseases that result from the initial disease.
precipitating factor (triggers)
factors that precipitate an acute episode of a chronic illness
inflammatory responses can be triggered by
direct mechanical damage, chemicals, ischemia, allergic reactions, burns, infections, etc...
Process of Inflammation
1. injury or infection occurs
2. cells release chemical mediators
3. pain receptors activated by bradykinin
4. vasodilation/hyperemia
5. increased capillary permeability
6. proteins, water, and cells leave capillaries to form exudate
7. edema
8. Leukocytes move to site of injury/ chemotaxis occurs
9. phagocytes remove debris and prepare for healing
10. formation of blood clot that seals off the area
ischemia
Lack of blood supply
exudate
the interstitial fluid formed in the inflamed area
chemotaxis
movement of cells in response to a chemical
hyperemia
increased blood flow
Leukocytes
white blood cells
ISF
interstitial fluid
local manifestations of inflammation
redness, heat/warmth, swelling, pain, sometimes loss of function
mechanisms or rationale of pain
stimulation of pain-sensing neurons
mechanisms or rationale of redness and warmth
caused by hyperemia ( increased blood flow)
mechanisms or rationale of edema
caused by increase of capillary permeability
mechanisms or rationale of loss of function
depends on how severe
mechanism or rationale
how did we get there?
types of exudate
serous, fibrinous, purulent, hemorrhagic
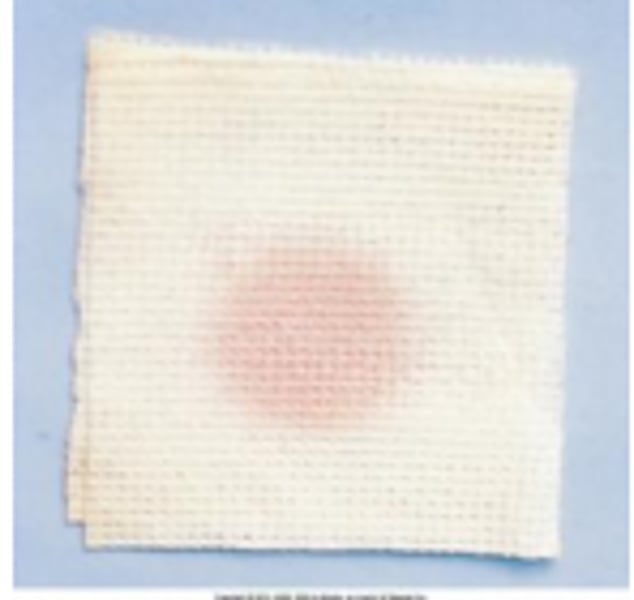
serous
mostly fluid, some protein and leukocytes (thin, watery)
serous
fibrinous
thick, sticky, high levels of fibrin and leukocytes
fibrinous
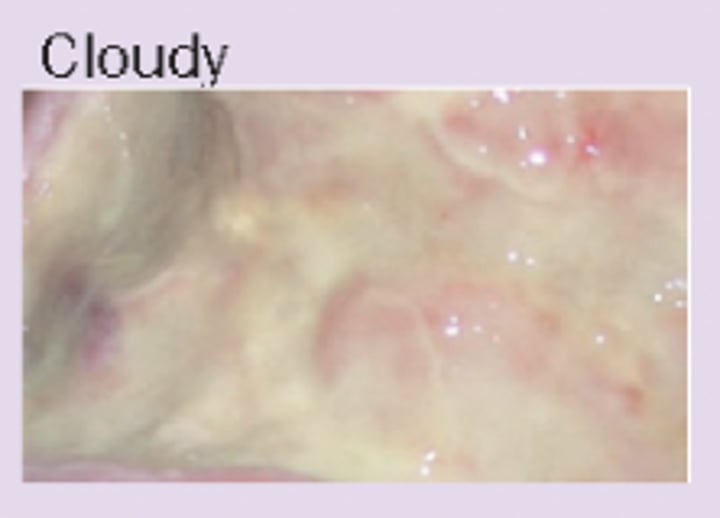
purulent
thick, yellow-green, high levels of leukocytes, cell debris, and bacteria (pus)
purulent
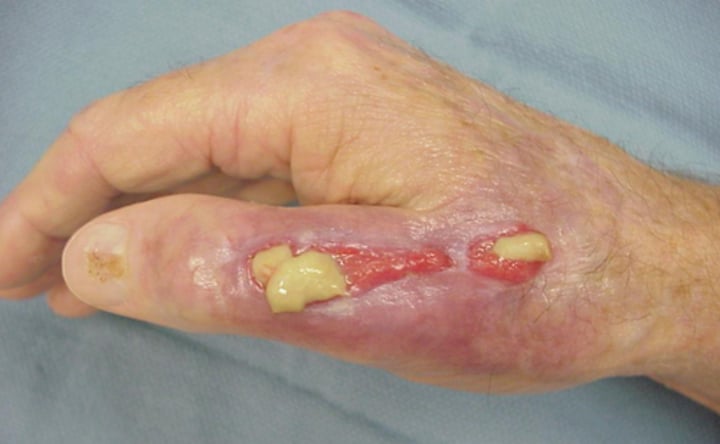
hemorrhagic
bloody, can be combined with other exudate types
hemorrhagic
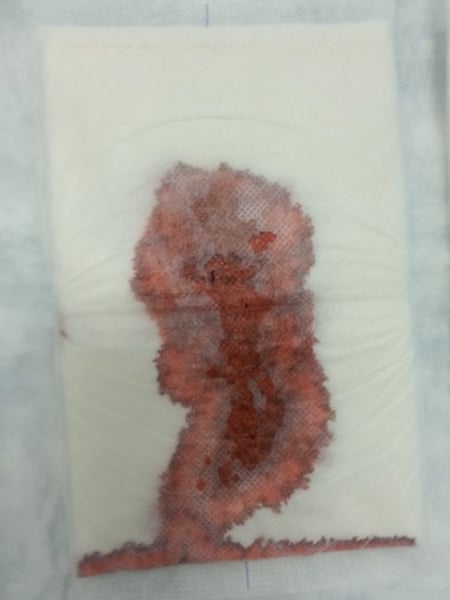
systemic manifestations of inflammation
distant or away from sight of injury or infection
systemic
whole body
malaise
general feeling of unwellness
fatigue
tired
anorexia
loss of appetite
acute phase responses
changes in certain plasma proteins, leukocyte numbers
plasma
liquid part of blood
plasma proteins
blood proteins