CMB - Topic 1 - Introductory Chemistry - Atoms and Elements
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is an atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element, consisting of a nucleus made of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in orbitals. (dense positive core & negatively charged electrons.
How are atoms symbolised?
With the same abbreviation used for the element, e.g. C stands for both the element carbon and a single carbon atom
What is the mass number/atomic mass? and what is the atomic number
Atomic mass: sum of protons and neutrons
Atomic number: sum of protons
What is the unit Dalton used for and what other unit is it the same as?
Used for atoms and subatomic particles and is same as the atomic mass unit (amu)
Neutrons and protons are almost identical in mass, what is this mass?
1.7 × 10^-24 gram (g) // close to 1 Dalton
Why is the mass of an electron ignored in atomic mass?
Because the mass of an electron is only about 1/2,000 that of a proton or neutron
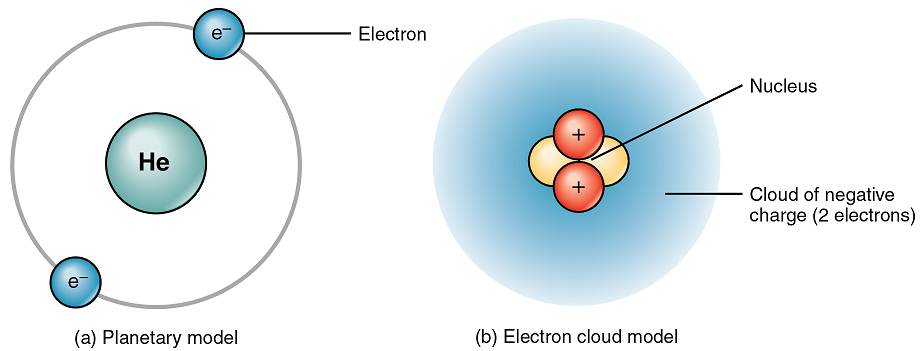
What are the two models of the atom and in which years were they established?
Planetary/Bohr model (1913)
Electron cloud model/Schrodinger (1926)
How do the two model differ?
The Planetary model is a more simplified model, electrons are shown as two small spheres on a circle around the nucleus.
The Electron cloud model shows the two electrons as a cloud of negative charge as a result of their motion around the nucleus.
What is an Element?
Any substance that cannot be broken down to any other substances by chemical reactions.
What is a Compound?
A substance consisting of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio.
What is an isotope?
Atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons.
All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons, but some have more neutrons than other atoms, therefore a greater mass.
In nature, an element may occur as a mixture of its isotopes
What is a Radioactive isotope?
A radioactive isotope is one in which the nucleus decays spontaneously, giving off particles and energy.
When the radioactive decay leads to a change in the number of protons, it transforms the atom to an atom of a different element.
Radioactive isotopes have many useful applications in biology. e.g radioactive tracers
Isotopes
Although the isotopes of an element have slightly different masses, they behave identically in the chemical reactions.
Both 12C and 13C are stable isotopes, meaning their nuclei do not have a tendency to lose subatomic particles, a process called decay.
The isotope 14C is unstable, or radioactive
Isotopes/ atomic mass
The atomic mass of some elements is not always an integer (whole number)
The atomic mass is an average of the different isotopes of the element.
What three types of radioactive decay exist?
Alpha decay
Beta decay
Gamma decay
What is radioactive decay?
Radioactive decay is the process in which a radioactive atom spontaneously gives off radiation in the form of energy or particles to reach a more stable state.
it is important to distinguish between radioactive material and the radiation it gives off.
How does radioactive decay present in the three types?
In Alpha decay, the nucleus loses two protons.
In Beta decay, the nucleus either loses or gains a proton.
In Gamma decay, no change in proton number occurs, so the atom does not become a different element.
What is electron configuration?
The description of how electrons are distributed among the various atomic orbitals within an atom e.g.
1s2, 2s2, 2p6
What does Valence mean?
Valence refers to the bonding capacity of a given atom; the number of covalent bonds that an atom can form, which usually equals the number of unpaired electrons in its outermost (valence) shell.
What is a Valence electron?
An electron in the outermost electron shell.
What is a Valence shell?
The outermost energy shell of an atom, containing the valence electrons involved in the chemical reactions of that atom.
What is an electrons energy level correlated to?
Its average distance from the nucleus.
Where are electrons found?
Electrons are found in different electron shells, each with a characteristic average distance and energy level.
Define a Covalent bond?
A type of strong chemical bond in which two atoms share one or more pairs of valence electrons.
What is the definition of electronegativity?
The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself in a covalent bond.
What is a non-polar covalent bond?
A type of covalent bond in which electrons are shared equally between two atoms of a similar electronegativity.
What is a polar covalent bond?
A covalent bond between atoms that differ in electronegativity.
The shared electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it slightly negative and the other atom slightly positive.
What is an Ion?
An atom or group of atoms that has gained or lost one or more electrons, thus acquiring a charge.
What is a Cation?
A positively charged Ion.
What is an Anion?
A negatively charged Ion.
What is an Ionic bond?
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Which chemical interactions are classed as weak?
Hydrogen bonds
Van der Waals Interactions
What is a Hydrogen bond?
A weak attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom (like oxygen or nitrogen) in another molecule or a different part of the same molecule.
What are Van der Waals Interactions?
They are dipole-dipole interactions , commonly existing in gases, liquids and solids.
How many types of Van-der-Waals interactions are there and what are they?
Dipole-dipole interactions
Dipole-induced dipole interactions
London dispersion forces.
The strongest type of Van-der Waals are dipole-dipole.