Cardiovascular Imaging: Lecture Notes
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:03 PM on 3/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
1
New cards
What makes up the cardiac silhouette?
1. heart
2. pericardium
3. pericardial fat
4. fluid
2
New cards
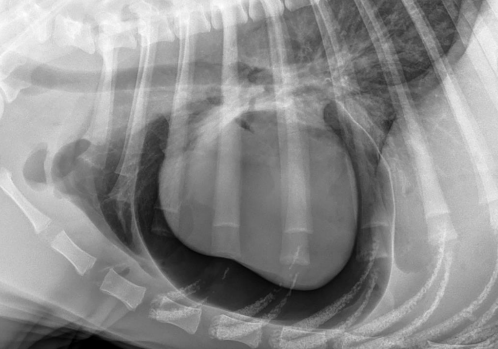
What is the abnormality?
Gas in the pericardial space
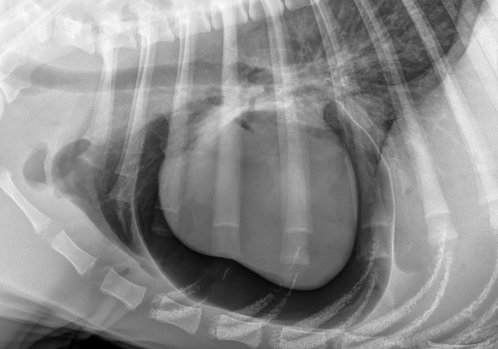
3
New cards
__******How big should the heart big on lateral rads?***__
How much sternal contact?
How much sternal contact?
Dogs: 2.5-3.5 ICS
Cats: 2-3 ICS
\
Sternal contact: 2.5-3 ICS
Cats: 2-3 ICS
\
Sternal contact: 2.5-3 ICS
4
New cards
On a lateral radiograph, what structures summate from 9-11 o’clock?
1. main pulmonary artery/pulmonary trunk
2. aorta
3. right auricle
5
New cards
Where is the left atrium located on a lateral projection?
At the carina
Can sometimes see a backpack sign
Can sometimes see a backpack sign
6
New cards
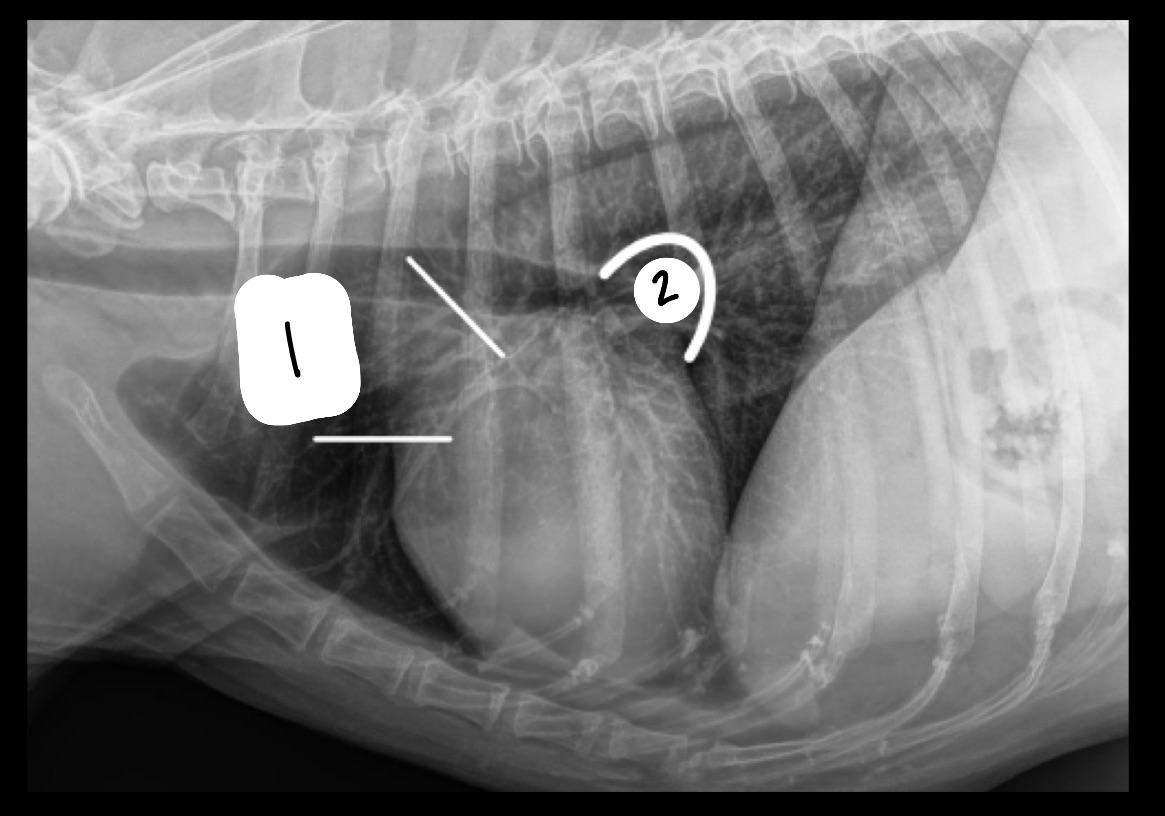
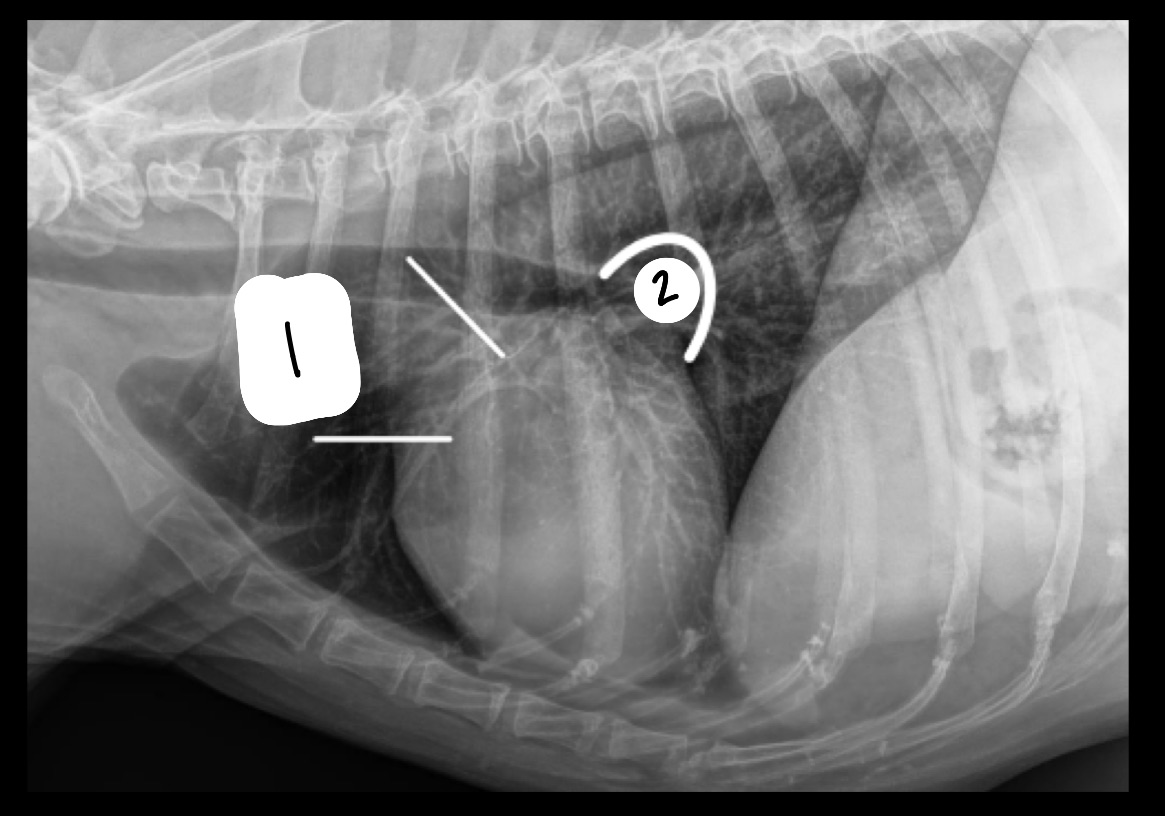
What is located at 1? At 2?
1 = right auricle, aorta, main pulmonary artery
2 = left atrium
2 = left atrium
7
New cards
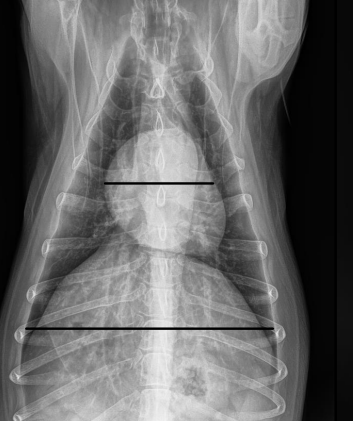
How large should the heart be on VD/DV view?
2/3 the width of the thoracic cavity
8
New cards
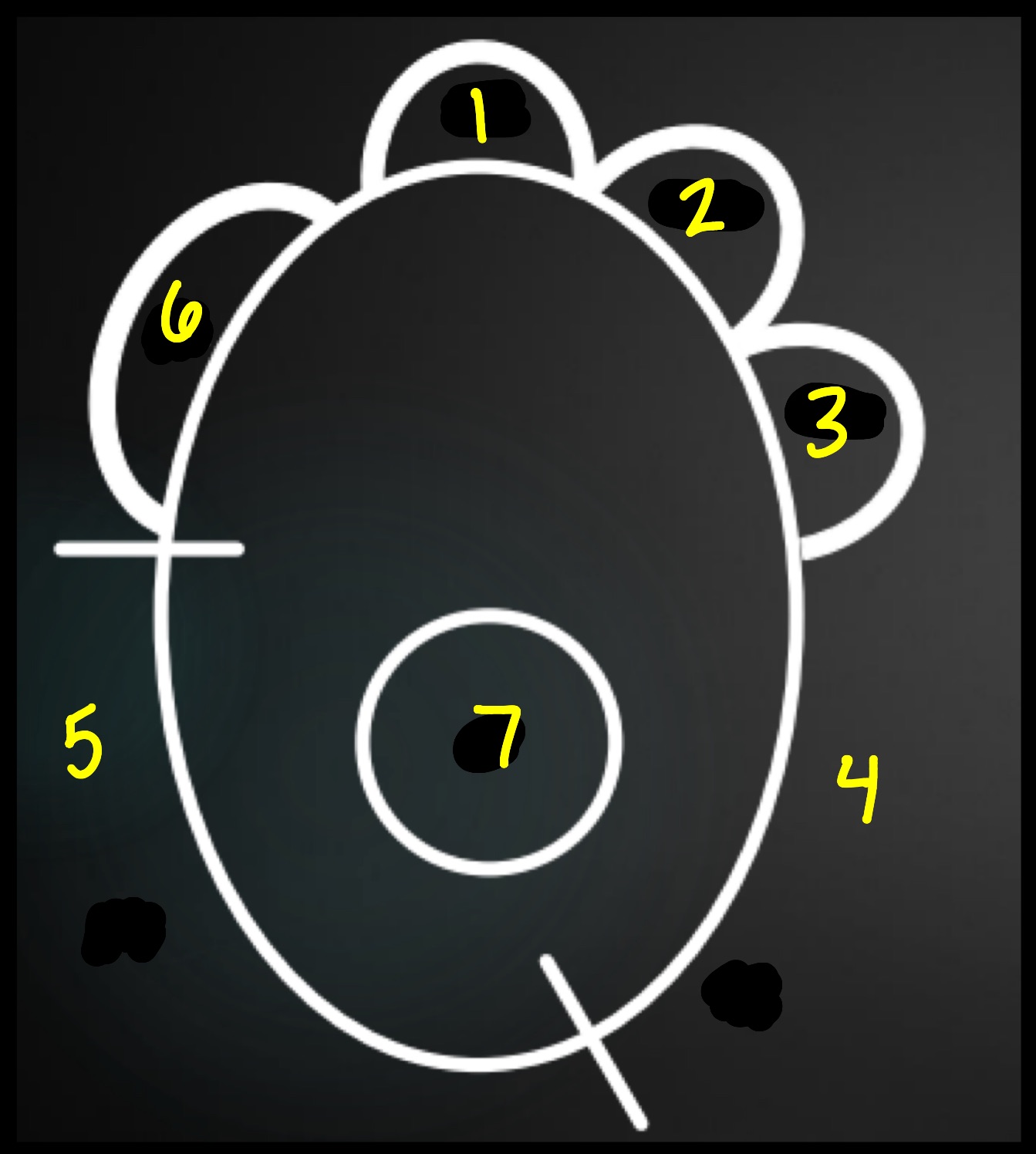
__******What is the DV/DV clock face analogy?***__
11-1 o’clock = aortic arch
1-2 o’clock = main pulmonary artery
2-3 o’clock = left auricle
3-6 o’clock = left ventricle
6-9 o’clock = right ventricle
9-11 o’clock = right atrium
1-2 o’clock = main pulmonary artery
2-3 o’clock = left auricle
3-6 o’clock = left ventricle
6-9 o’clock = right ventricle
9-11 o’clock = right atrium
9
New cards
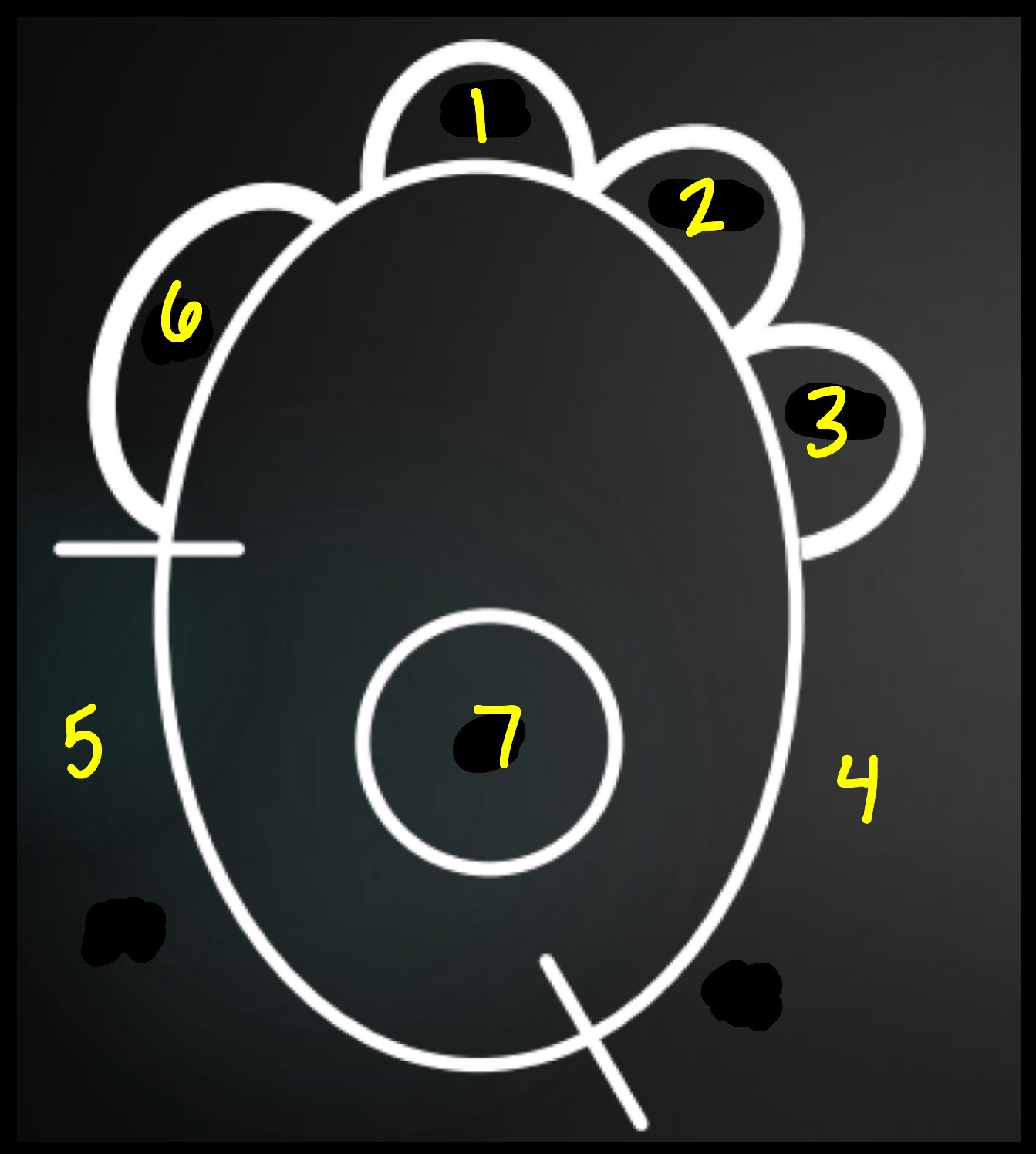
__******What is 1-7 on this image?***__
1: aortic arch
2 = main pulmonary artery
3 = left auricle
4 = left ventricle
5 = right ventricle
6 = right atrium
7 = left atrium
2 = main pulmonary artery
3 = left auricle
4 = left ventricle
5 = right ventricle
6 = right atrium
7 = left atrium
10
New cards
__***What are ddx for a globoid silhouette?***__
1. pericardial effusion
2. DCM
3. peritoneopericardial diaphragmatic hernia
4. tricuspid valve dysplasia
11
New cards
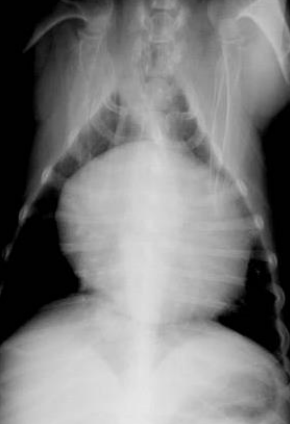
What is the shape of this heart? What are ddx?
Shape: globoid
1. pericardial effusion
2. DCM
3. peritoneopericardial diaphragmatic hernia
4. tricuspid valve dysplasia
1. pericardial effusion
2. DCM
3. peritoneopericardial diaphragmatic hernia
4. tricuspid valve dysplasia
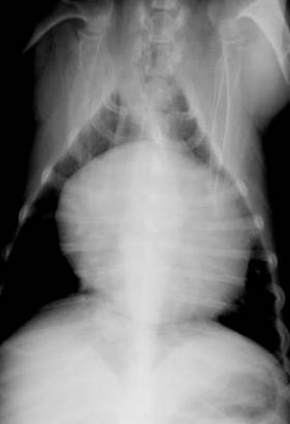
12
New cards
What is the diagnosis here?
Peritoneal pericardial diaphragmatic hernia
\-not great diaphragm margins
\-has structure in cardiac silhouette
\-not great diaphragm margins
\-has structure in cardiac silhouette
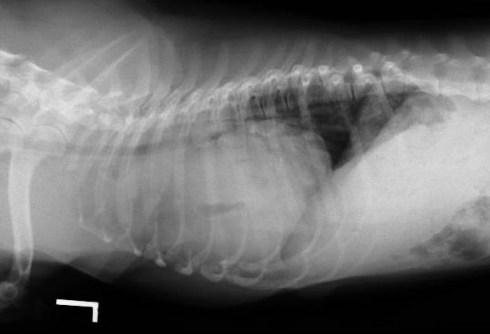
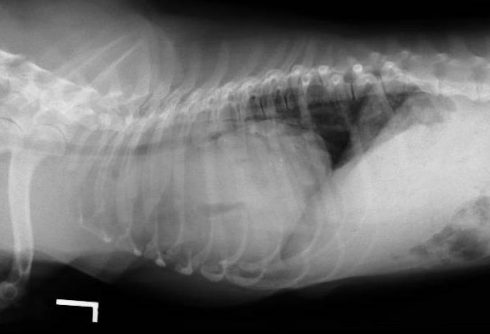
13
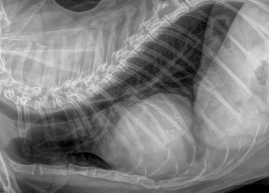
New cards
What is the heart shape?
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
Globoid
Pericardial effusion in this case
Pericardial effusion in this case
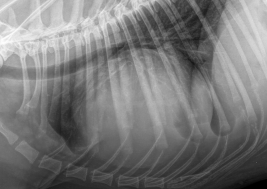
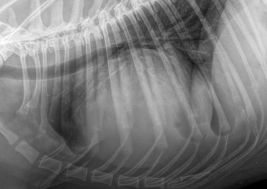
14
New cards
What are these examples of?
PPDH
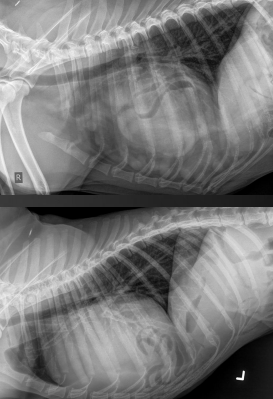
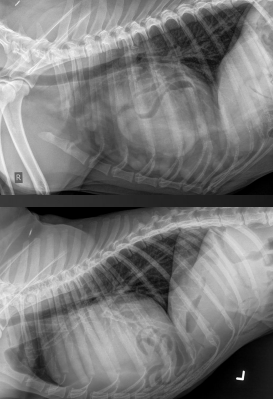
15
New cards
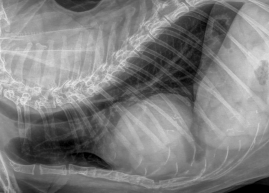
What is the diagnosis?
How do we know?
How do we know?
PPDH
* region of increased ST opacity
* possible stones in bile duct of liver
* region of increased ST opacity
* possible stones in bile duct of liver
16
New cards
What is a normal vertebral heart scale score?
9\.7 +/- 0.5 vertebrae, starting at T4
17
New cards
What is the vertebral heart scale useful for?
Monitoring
18
New cards
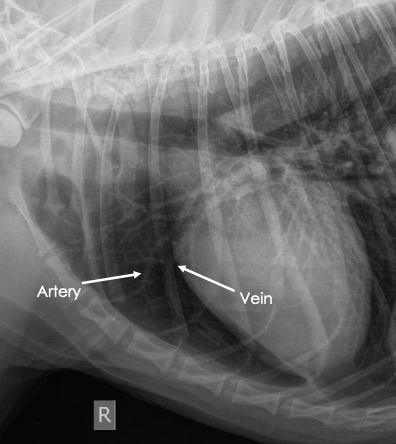
__******How to remember which are veins and which are arteries?***__
Veins: ventral and central
Arteries: up and away
Arteries: up and away
19
New cards
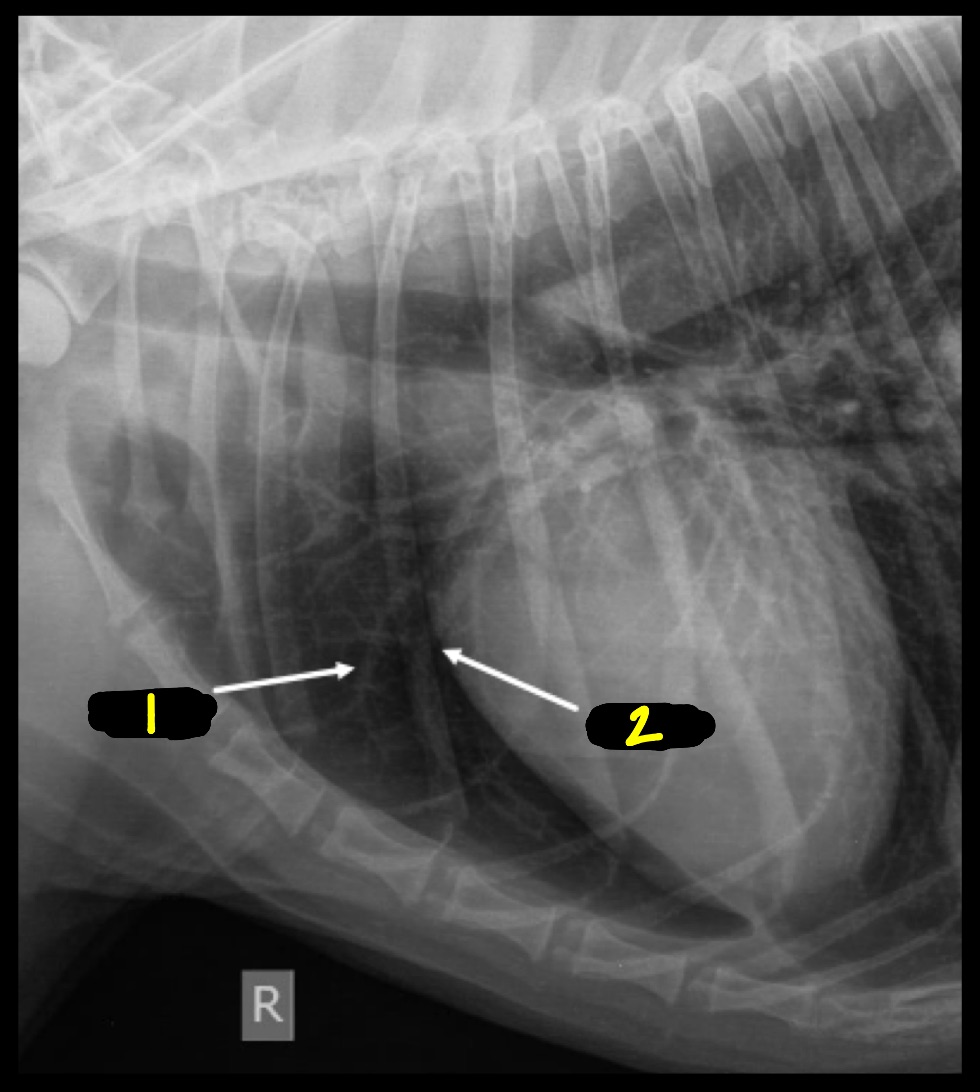
What is 1 and 2 in this image?
1 = artery
2 = vein
2 = vein
20
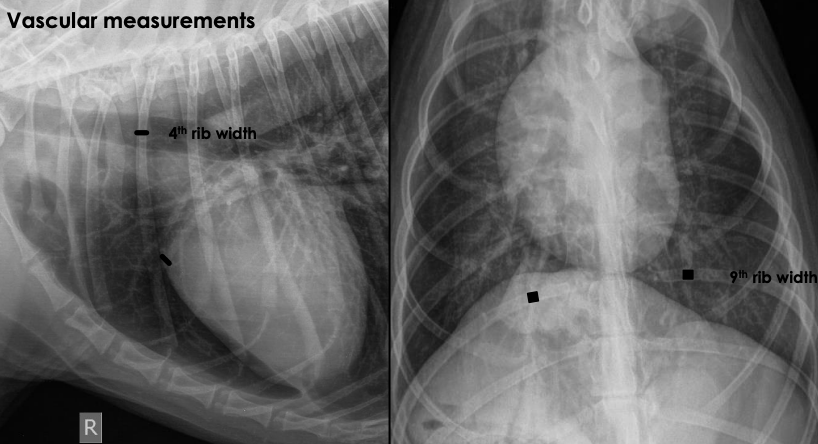
New cards
__******How big should pulmonary arteries and veins be?***__
Should be __**same size**__
* Lateral projection: cranial vessels
* size of __**proximal 4th of 4th rib**__
* VD projection: caudal vessels
* size of __**9th rib**__ where they overlap
\
1\.22 right caudal vein to 9th rib
(right caudal vein can be a little large than the 9th rib and still be normal)
* Lateral projection: cranial vessels
* size of __**proximal 4th of 4th rib**__
* VD projection: caudal vessels
* size of __**9th rib**__ where they overlap
\
1\.22 right caudal vein to 9th rib
(right caudal vein can be a little large than the 9th rib and still be normal)
21
New cards
\*\*\*\*
1. What type of hypertrophy does __***volume overload***__ cause?
2. Does this cause apparent cardiac enlargement?
3. Example?
1. What type of hypertrophy does __***volume overload***__ cause?
2. Does this cause apparent cardiac enlargement?
3. Example?
1. eccentric hypertrophy
1. TIP: think eccentric person is outgoing, pushing out
2. apparent cardiac enlargement (large lumens)
3. shunting lesions
22
New cards
\*\*\*
1. What type of hypertrophy does __***pressure overload***__ cause?
2. Does this cause apparent cardiac enlargement?
3. Example?
1. What type of hypertrophy does __***pressure overload***__ cause?
2. Does this cause apparent cardiac enlargement?
3. Example?
1. concentric hypertrophy
2. thickened muscles, small lumens, not really outwardly apparent enlargement
3. stenotic lesions
23
New cards
__******What are the 4 most common congenital cardiac diseases in small animals? What is most common in large animals?***__
Small animals
1. aortic stenosis
2. pulmonic stenosis
3. patent ductus arteriosus
4. tricuspid valve dysplasia
\
Large animals
1. ventricular septal defect
1. aortic stenosis
2. pulmonic stenosis
3. patent ductus arteriosus
4. tricuspid valve dysplasia
\
Large animals
1. ventricular septal defect
24
New cards
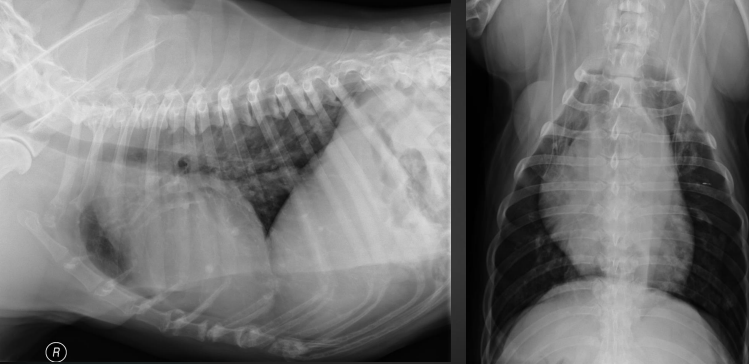
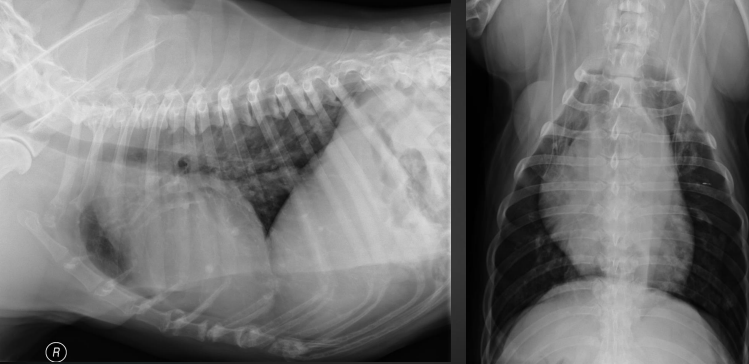
What are the radiographic findings?
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
* bulge of aorta
* 11-1 o’clock on VD
* can’t distinguish from aorta, pulmonary artery, or right auricle on lateral
Aortic stenosis
* 11-1 o’clock on VD
* can’t distinguish from aorta, pulmonary artery, or right auricle on lateral
Aortic stenosis
25
New cards
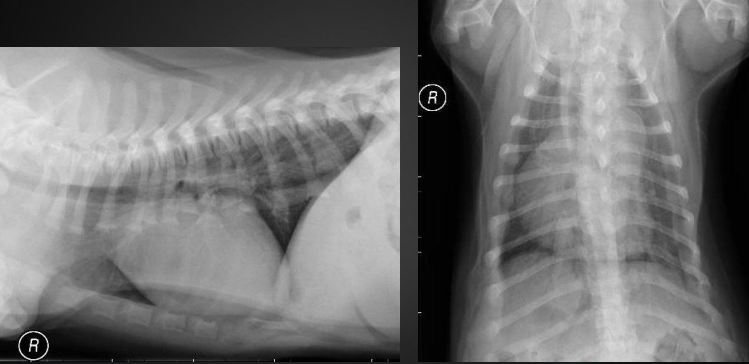
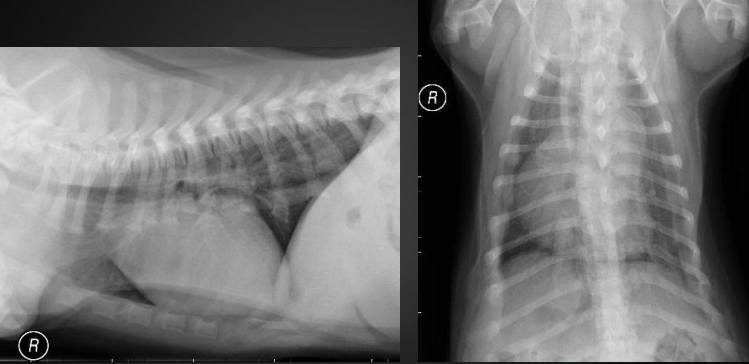
What are the radiographic findings?
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
* bulge of main pulmonary artery
* 1-2 o’clock on DV/VD
* can’t distinguish from aorta, pulmonary artery, or right auricle on lateral
* 1-2 o’clock on DV/VD
* can’t distinguish from aorta, pulmonary artery, or right auricle on lateral
26
New cards
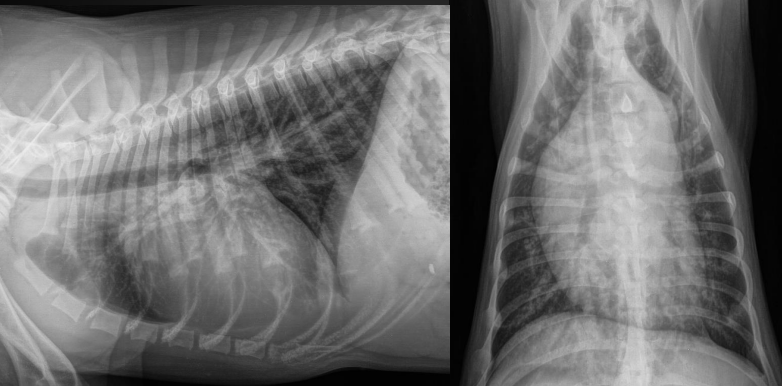
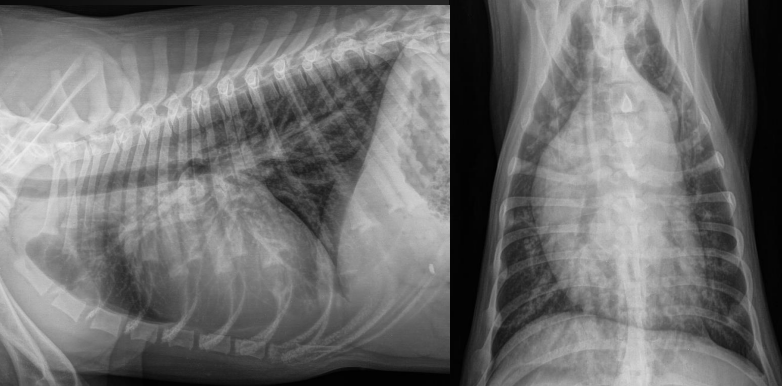
What are the radiographic findings?
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
* aorta bulge, MPA bulge
* three knuckle appearance (aorta bulge, main pulmonary artery bulge, left auricle bulge) - not seen here, but common in PDA dogs
* enlarged vessels
\
PDA
* three knuckle appearance (aorta bulge, main pulmonary artery bulge, left auricle bulge) - not seen here, but common in PDA dogs
* enlarged vessels
\
PDA
27
New cards
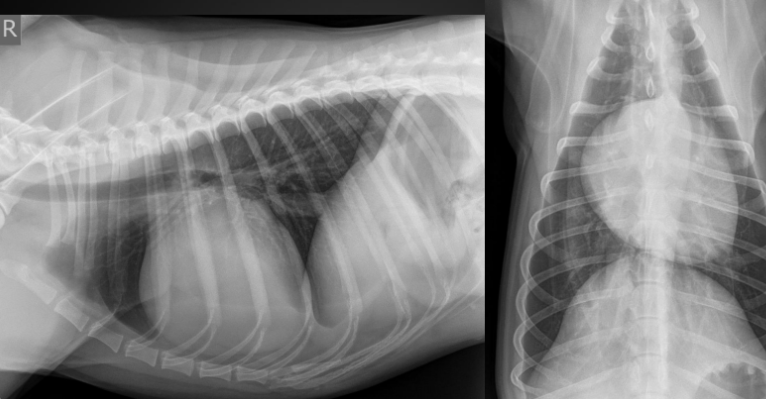
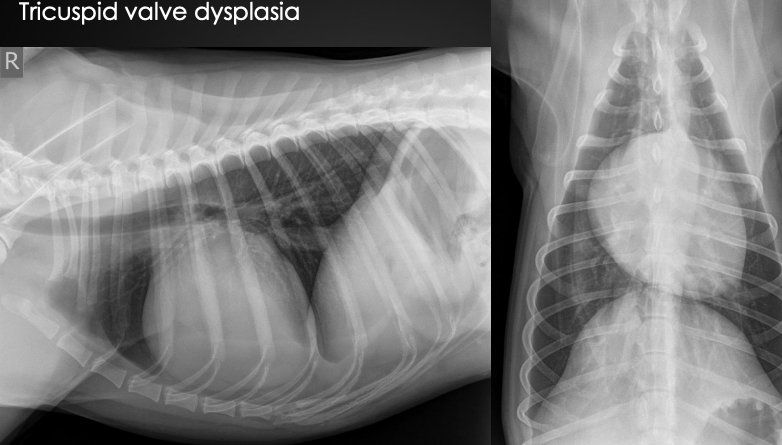
What are the radiographic findings?
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
Globoid cardiac silhouette
* centered around right atrium (we don’t need to be that specific)
* centered around right atrium (we don’t need to be that specific)
28
New cards
What are clinical signs/signalment of tricuspid valve dysplasia?
1. young dog
2. right sided murmur
29
New cards
__******What are examples of acquired left-sided heart disease?***__
1. degenerative mitral valve disease (75% of cases)
2. DCM
1. may also cause right-sided disease
3. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (cats)
30
New cards
__******What are examples of acquired right-sided heart disease?***__
1. heartworms
2. tricuspid valve disease
1. can be acquired or congenital
2. acquired: can have right-sided changes as well if MVD present
31
New cards
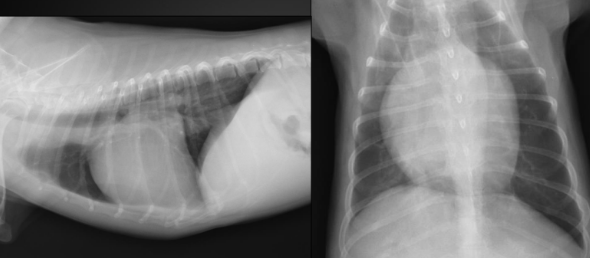
What are the radiographic findings?
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
Findings on lateral:
1. loss of caudal cardiac waist (flat line)
2. bulge of left atrium
3. dorsal deviation of trachea
Findings on DV/VD:
1. bulge at 2-3 o’clock = left auricle
2. enlarged left atrium (double wall sign)
3. a little right sided rounding
\
Diagnosis: mitral valve degeneration
* probably some tricuspid valve degeneration as well b/c of right-sided rounding
1. loss of caudal cardiac waist (flat line)
2. bulge of left atrium
3. dorsal deviation of trachea
Findings on DV/VD:
1. bulge at 2-3 o’clock = left auricle
2. enlarged left atrium (double wall sign)
3. a little right sided rounding
\
Diagnosis: mitral valve degeneration
* probably some tricuspid valve degeneration as well b/c of right-sided rounding
32
New cards
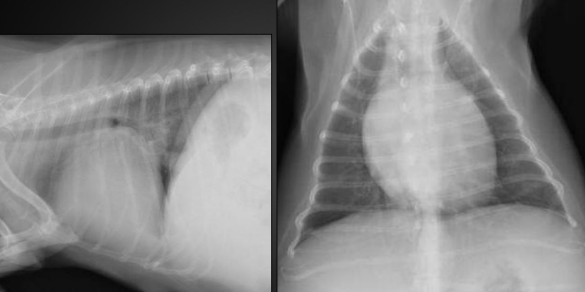
What are the radiographic findings?
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
Findings:
* loss of cardiac waist
* rounding of right side
* left atrial enlargement
\
Not definitive diagnosis until echo performed
* likely DCM
* loss of cardiac waist
* rounding of right side
* left atrial enlargement
\
Not definitive diagnosis until echo performed
* likely DCM
33
New cards
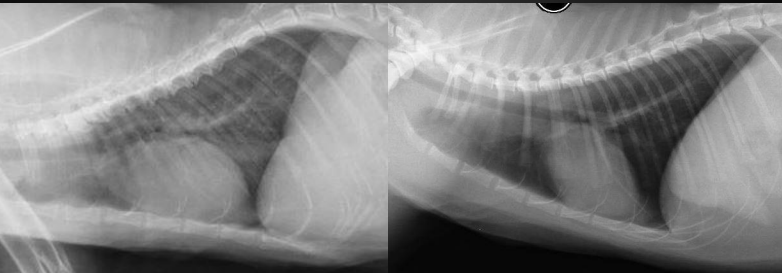
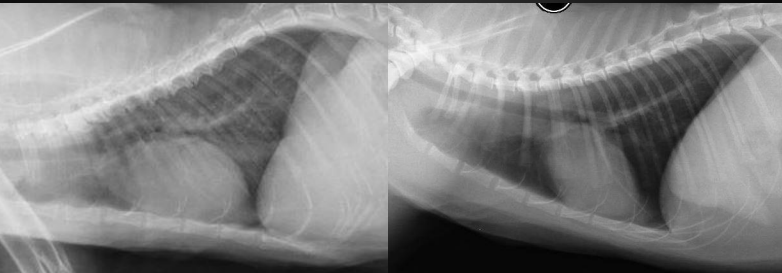
What are the radiographic findings in this cat on the left? (normal on right)
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
Findings:
* fat potato heart
\
Likely HCM
* fat potato heart
\
Likely HCM
34
New cards
__******Ddx for enlarged hearts in cats?***__
1. __**HCM (most common)**__
2. restrictive CM
3. thyrotoxic CM
4. dilated
5. unclassified CM
\
\*Radiographs are not definitive for underlying cause for feline heart disease
\*__**Echocardiogram**__ needed to further investigate
35
New cards
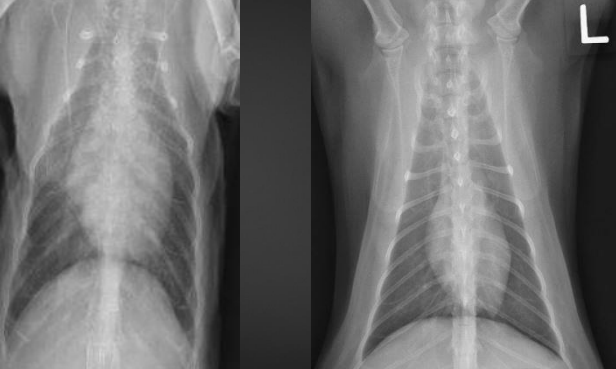
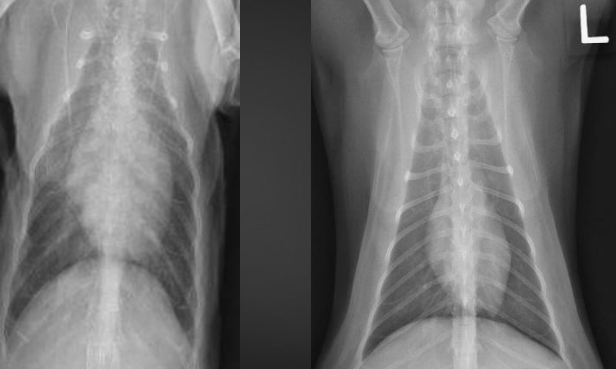
What are the radiographic findings for the cat on the left? (normal on right)
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
Findings:
1. fat potato heart
2. left-sided enlargement
Diagnosis
1. HCM most likely
1. fat potato heart
2. left-sided enlargement
Diagnosis
1. HCM most likely
36
New cards
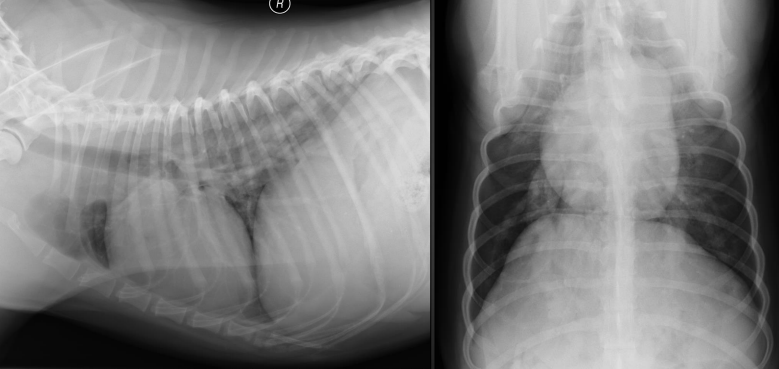
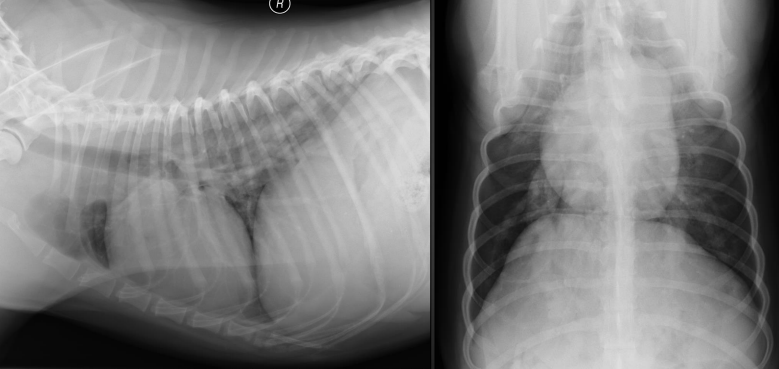
What are the radiographic findings?
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
Findings on VD:
* pulmonary artery enlargement
* bulge of MPA
* reverse D
Findings on lateral:
* possibly increased sternal contact (right ventricular enlargement)
\
Diagnosis: HW disease
* pulmonary artery enlargement
* bulge of MPA
* reverse D
Findings on lateral:
* possibly increased sternal contact (right ventricular enlargement)
\
Diagnosis: HW disease
37
New cards
__******What are radiographic signs of left-sided heart failure?***__
1. cardiogenic pulmonary edema'
1. unstructured groundglass opacity, possibly consolidation
2. pulmonary __***venous***__ congestion
3. left sided cardiac changes
1. atrial/ventricular enlargement
2. dorsal deviation of trachea
4. cats: can have pleural effusion
\
\*Diuretics can cause vessels to be normal or small
38
New cards
__******What are radiographic signs of right-sided heart failure?***__
1. distended CVC
2. hepatomegaly
3. peritoneal effusion
4. pleural effusion
5. right sided cardiac changes
1. rounding of atrioventricular region, possible bulge of main pulmonary artery depending on disease location
39
New cards
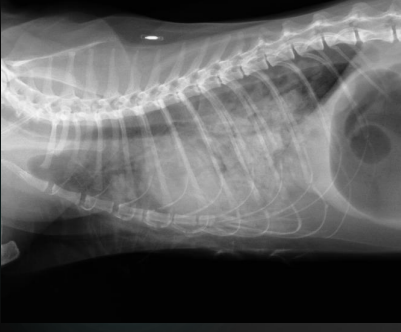
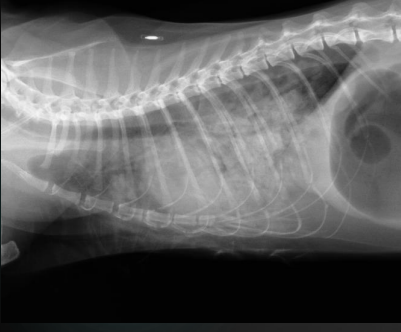
What are the radiographic findings in a cat?
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
Findings:
* more ventral distribution of increased opacity
* groundglass opacity
Diagnosis:
* CHF
* more ventral distribution of increased opacity
* groundglass opacity
Diagnosis:
* CHF
40
New cards
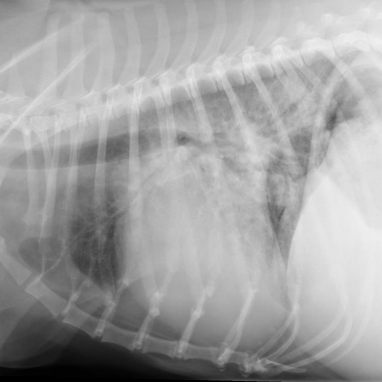
What are the radiographic findings in a dog?
Diagnosis?
Diagnosis?
Findings:
* peri-hilar or caudodorsal ground-glass opacity
\
Diagnosis: CHF
* peri-hilar or caudodorsal ground-glass opacity
\
Diagnosis: CHF
41
New cards
What start of MVD do we start using medical mangement?
Stage B2 (left atrial or ventricular enlargement on radiograph)