analytical chem
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Diagram of electronic, vibrational and rotational energy levels
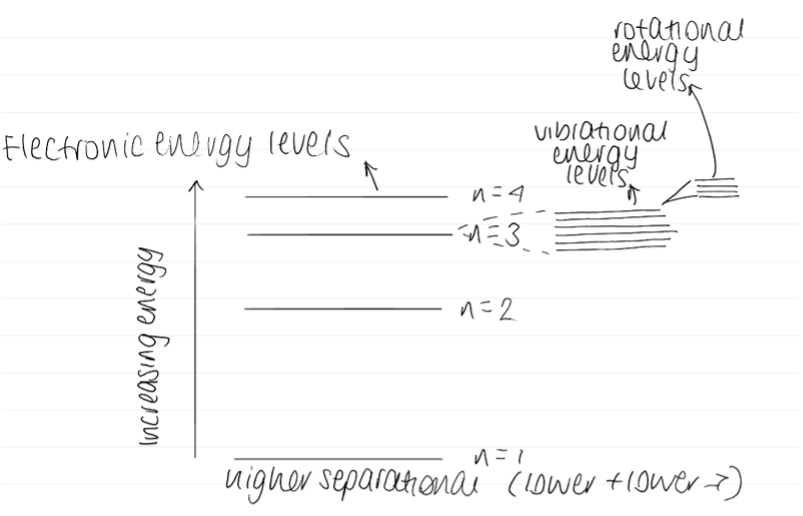
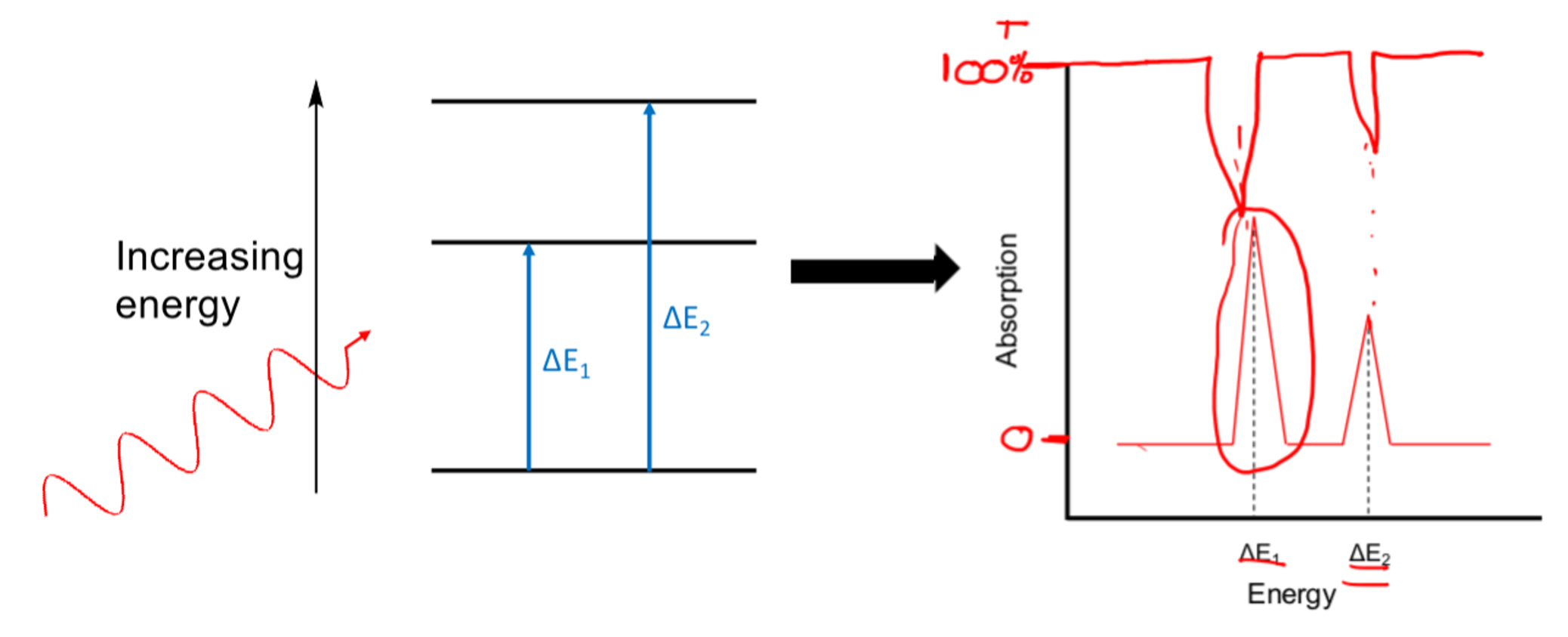
Diagram of absorption
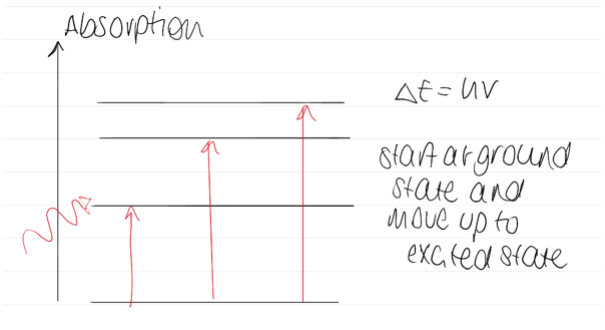
Diagram of emission
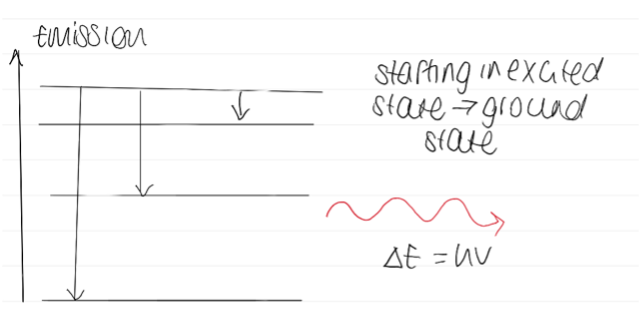
Diagram of fluorescence
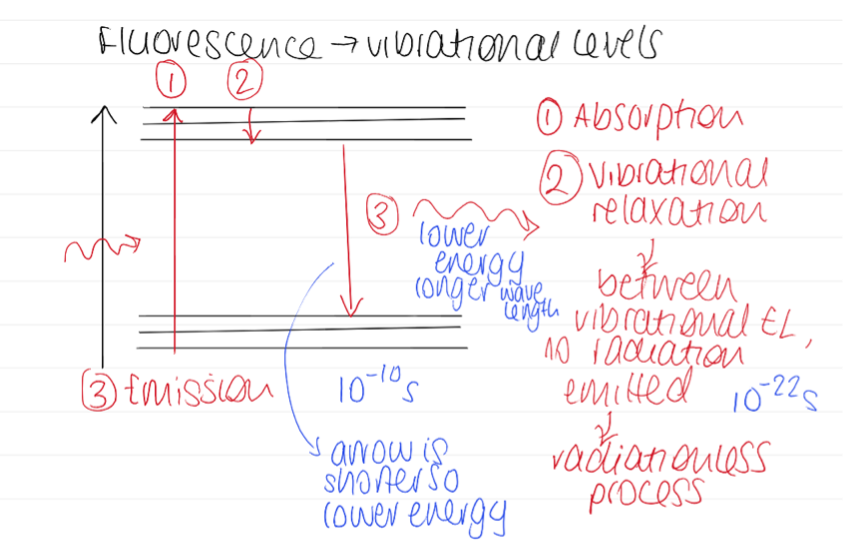
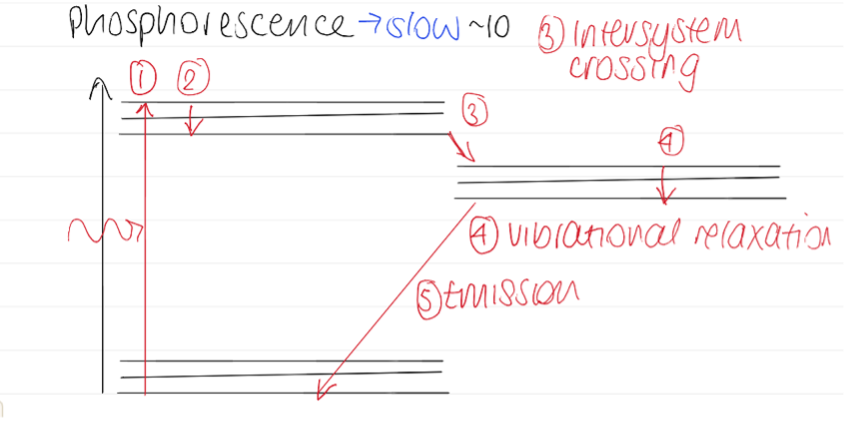
Diagram of phosphorescence
What is a monochromator used for?
To tune wavelength
What does position of the peaks in abs/emission spec depend on?
What does size of the peaks depend on?
position depends on the energies of transitions
size depends on the number of abs/emission events
sample conc
distance travelled by radiation (path length)
how many molecules in correct energy state (population of ELs)
how likely a transition is to take place
Diagram of absorption spectroscopy including transmission
What is the difference between transmitted light and incident light?
Intensity of transmitted light is lower than incident light due to absorption
What is the equation for transmittance?
T = It / I0
I is intensity
What is the equation for absorbance using transmittance?
A = - log10 T
What is transmittance a measure of?
The percentage of light going through the sample (not absorbed)
How does transmittance change with absorbance?
As absorbance increases, transmittance decreases
What is the Beer Lambert Law?
What do the terms mean?
A = ε x c x l
l is path length
ε is molar absorption coefficient
c is conc
What does ε show?
How well a sample absorbs radiation
What are the units of ε?
mol-1 dm3 cm-1 /10 = mol-1 m2
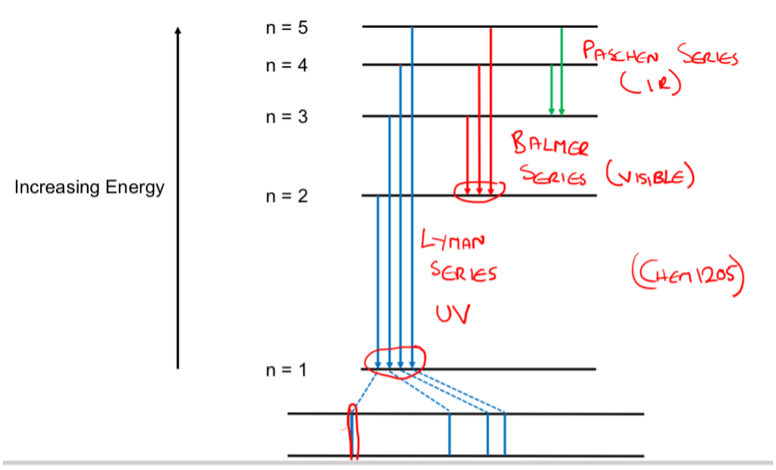
What are the different series of transitions?
How are intensity of radiaton and concentration related?
intensity ∝ concentration in sample
What does absorption and emission spectroscopy record? (i.e. intensity)
The intensity of radiation (either absorbing or emitting) at a specific wavelength
What are the steps for emission spectroscopy (flowchart)?
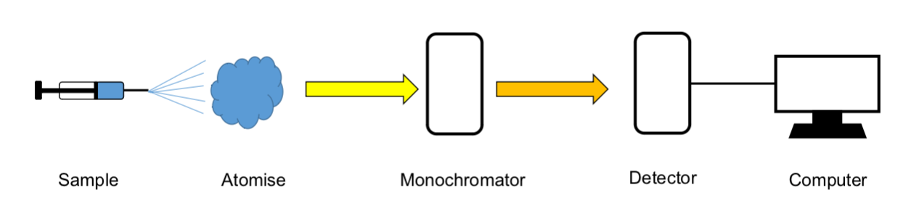
How is ICP (inductively coupled plasma) used in emission spec?
ICP is used to atomise samples
a stream of argon gas is passed through magnetic field which initiates a spark
argon is ionised and forms plasma
What is a plasma?
An ionized gas in which ions and electrons undergo electronic collisions
Steps for using emission spec to find unknown conc
measure emission intensity of a series of known concentrations at specific wavelength
plot emission intensity against conc (should go through origin)
calculate unknown conc (make sure sample is within range)
What are the steps for absorption spectroscopy (flowchart)?
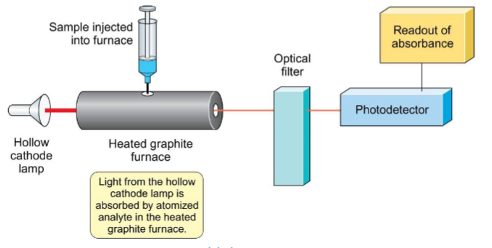
What is standard addition?
measure absorbance of unknown
add known amount of element (spiking) to sample and remeasure
change in absorbance is due to additional amount added
use difference to calculate relationship between absorbance and concentration
What are abs/emission spectroscopies used for vs UV-vis spectroscopy?
Absorption and emission are used for atomic species
UV-vis is used for molecular species
What are the three different types of electronic transitions?
between d orbitals in a transition metal
between ligand orbital and a metal orbital in a transition metal complex
between orbitals in conjugated compounds
How to calculate concentrations using the Beer Lambert law?
prepare calibration graph from series of known concentration
calculate ε from the graph
use this to determine unknown concentration
What happens at high concentrations (absorbance)?
molecules interact, which changes absorption behaviour as different chemical structure
scattering increases
properties of the solvent can change = refractive index
How to calculate wavenumbers?
frequency / speed of light in cm per second

How to calculate the period of motion of a vibration?
remember frequency = 1/time
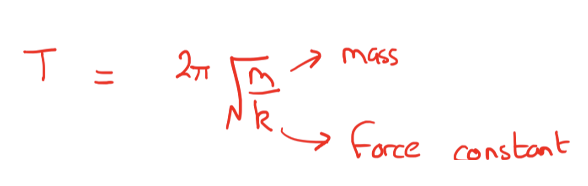
How to calculate reduced mass?

What is k? What does it show?
k is the force constant, and it relates to bond strength
Frequency equation including wavenumbers and reduced mass
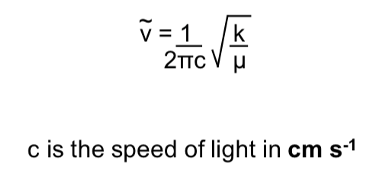
What happens when k increases / decreases?
When k increases, frequency increases
When k decreases, frequency decreases
-stronger bonds vibrate at higher frequencies
What happens when µ increases / decreases?
When µ increases, frequency decreases
When µ decreases, frequency increases
Why do bonds to H have higher frequencies?
They have lower reduced masses
What type of molecules are not observed in IR spectra? Why?
Homonuclear diatomics
for a vibration to be observed, there must be a change in the molecule’s dipole moment
there is no change in dipole moment when stretched in homonuclear diatomics (same electronegativity)