Final exam for A AND P i hate biol!
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
epithalamus function
contains pineal gland which secretes melatonin
functions of diencephalon
-processes, integrates, and relays information
-maintains homeostasis
-regulates biological rhythms
What is the limbic system?
emotional brain
What are the fornix of the limbic system
The fornix is a white matter bundle located in the mesial aspect of the cerebral hemispheres, which connects various nodes of a limbic circuitry and is believed to play a key role in cognition and episodic memory recall.
where is the location of the fornix in the brain
white matter bundle located in the mesial aspect of the cerebral hemispheres
subdivisions of the cerebrum
cerebral cortex and basal nuclei
What is the Occipital lobe contain
visual association area+visual cortex
What is the visual association area function
interprets activity in visual cortex
What is the visual cortex function
The visual processing areas of cortex in the occipital and temporal lobes.
What is the parietal lobe contain
primary somatosensory cortex+somatosensory association cortex
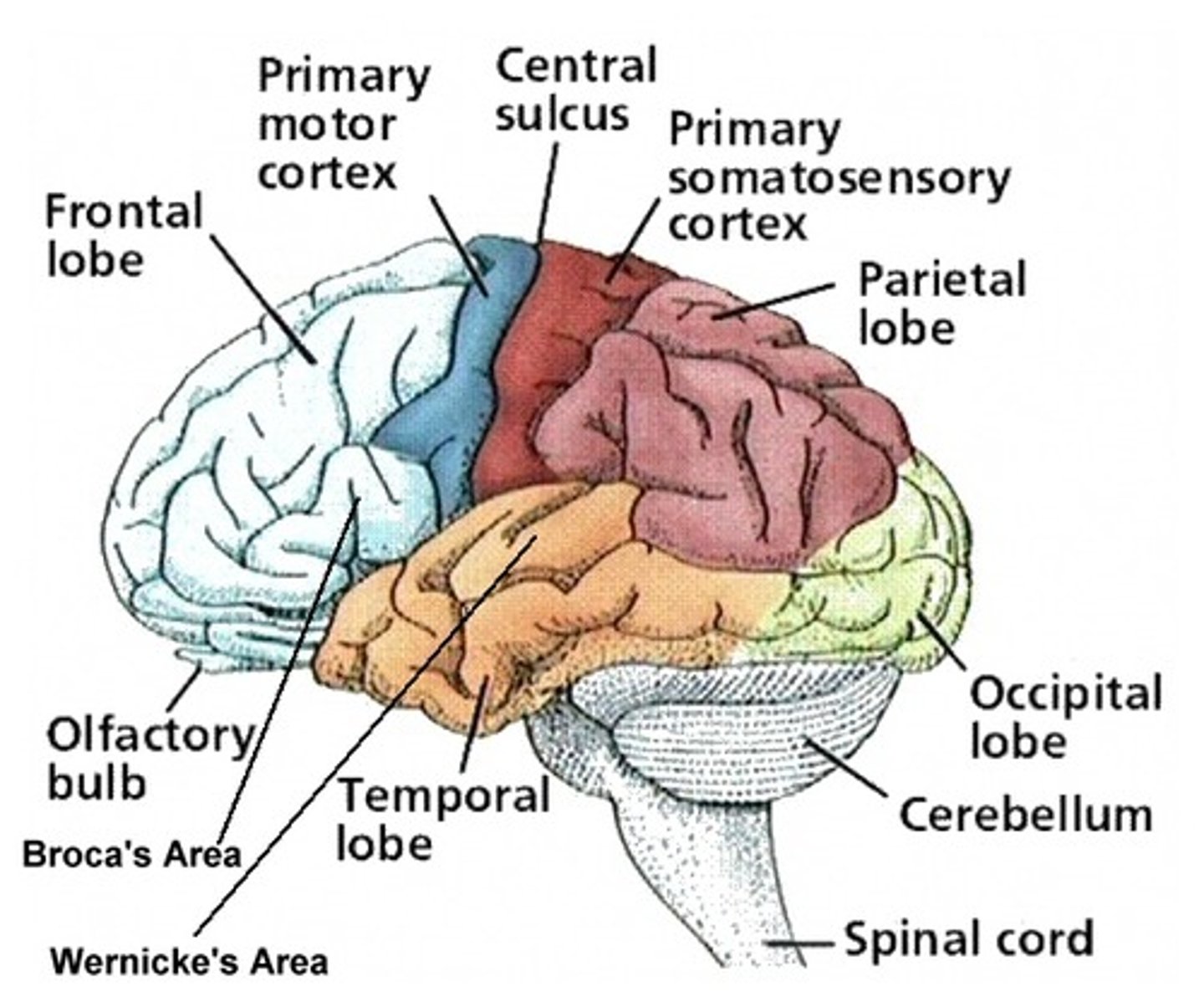
What is the function of the primary somatosensory
This cortex receives information regarding touch, pressure, pain, and temperature.
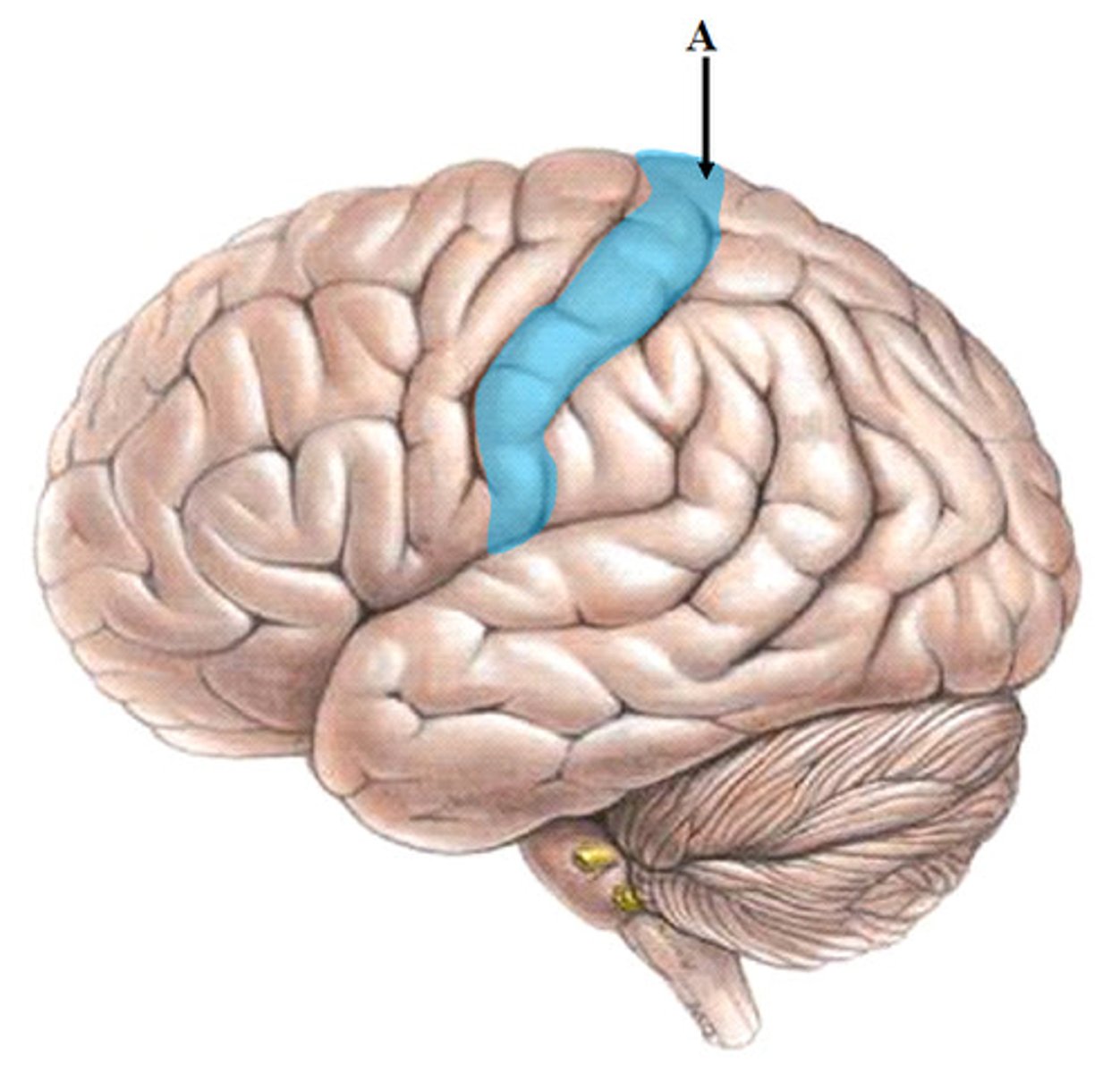
What is the somatosensory association cortex function
-Integrates sensory input from primary somatosensory cortex for understanding of object
-Determines size, texture, and relationship of parts of objects being felt
What does the temporal lobe contain
auditory cortex and Wernicke's area
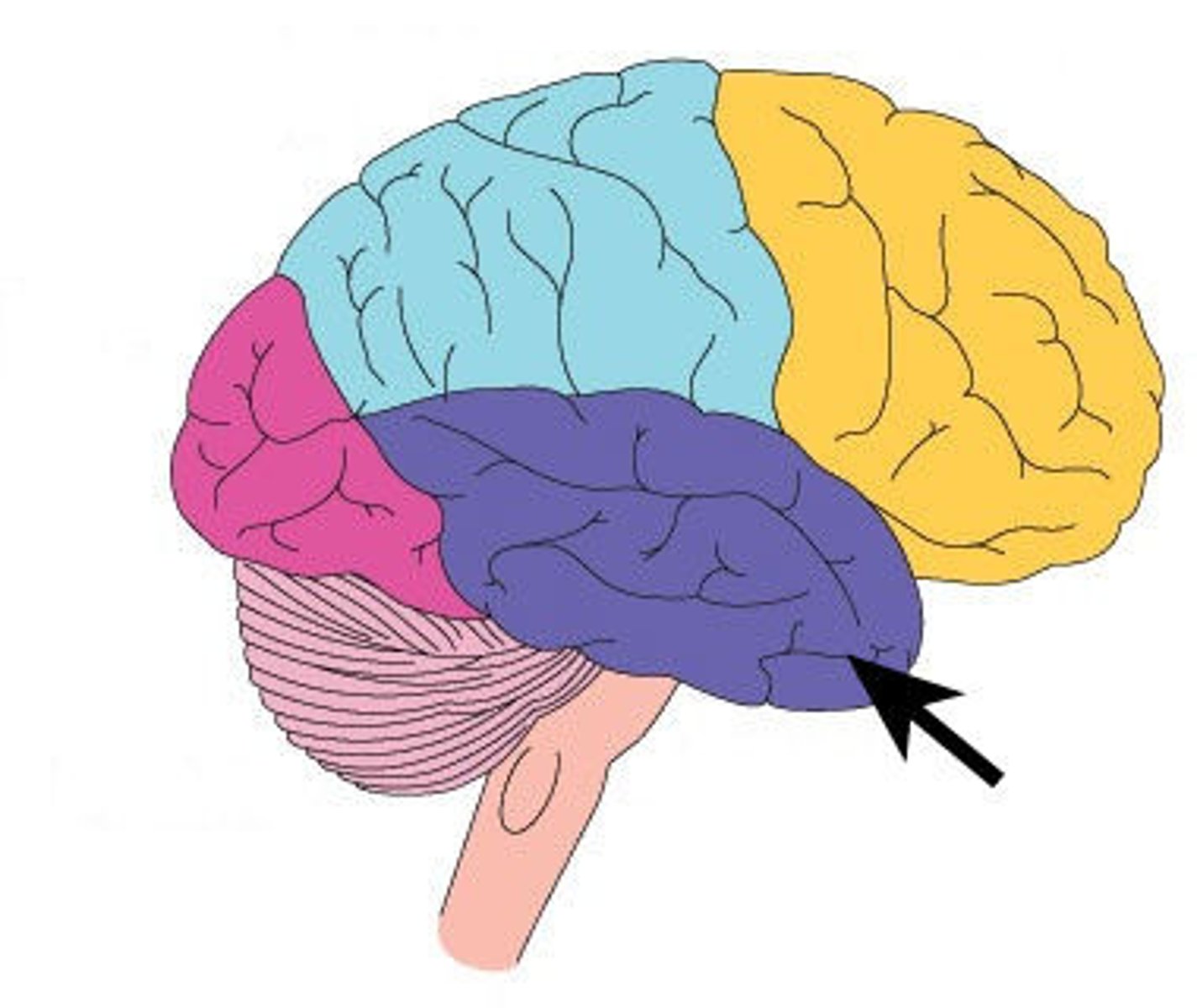
What does the auditory cortex do?
processes auditory information
What does the auditory association area do
stores memories of sounds and permits perception of sound stimulus
What is Wernicke's area?
speech comprehension
What is the cerebral cortex
outer layer of the cerebrum
What is the motor cortex?
voluntary movement
What is the prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
What is Broca's area?
speech production
What is the basal nuclei
islands of gray matter buried within the white matter
What does the frontal lobe contain
motor cortex, prefrontal cortex, Broca's area
what is the olfactory nerve
sense of smell (top of nose)
What is the optic (II) nerve?
transmitting visual information
What is the vestibulocochlear?
hearing and balance
What is the vestibule?
space between labia minora
What is the cochlea?
inner ear structure containing the central hearing apparatus
What is a commissure?
any collection of axons that connect one side of the brain with the other side
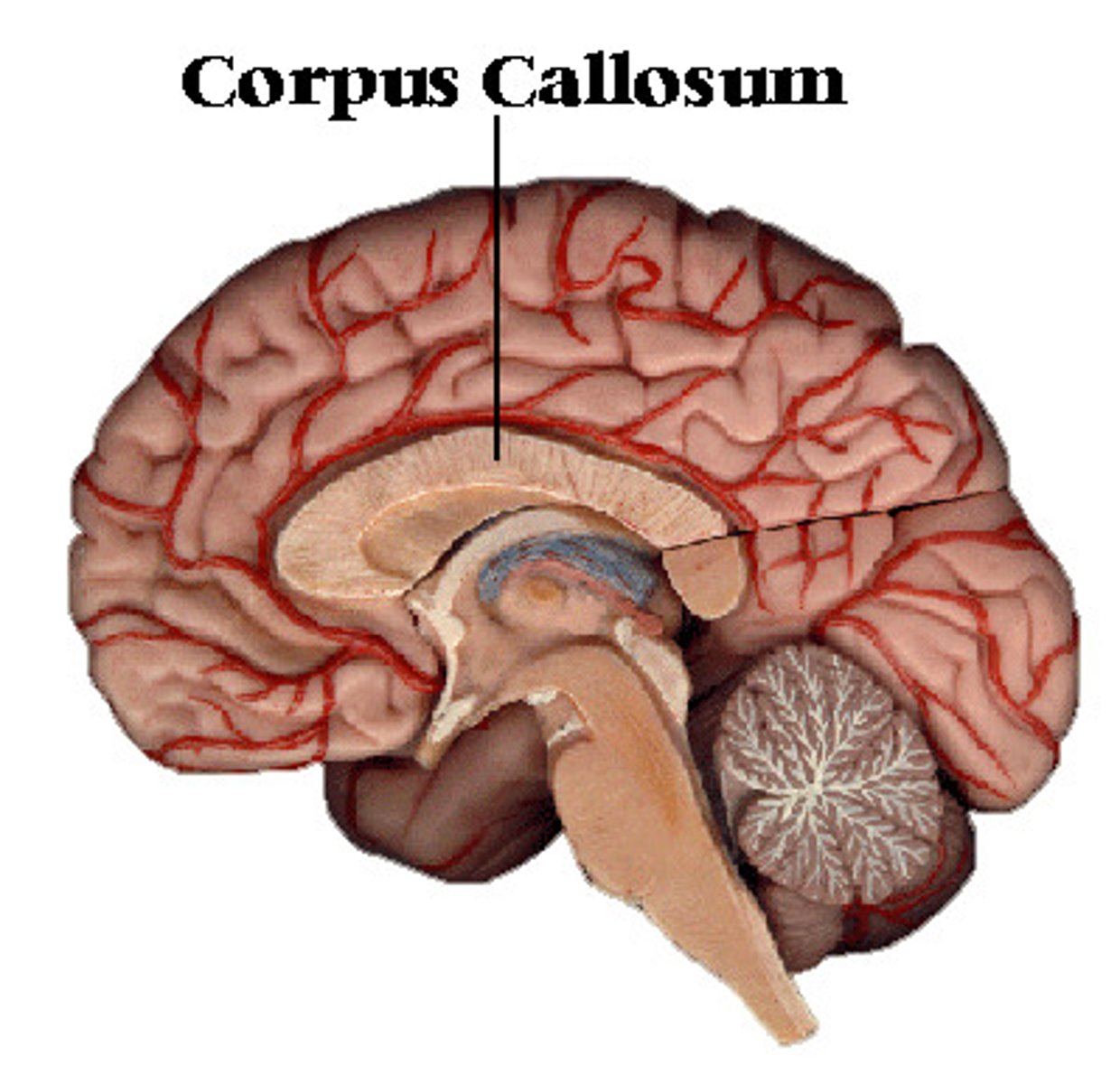
What is the corpus callosum?
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
What is the difference between association and articulation fibers
association fibers:within one hemisphere
articulate fibers: between gyri
What is the arcuate fibers
axons of second-order sensory neurons that compose the gracile and cuneate nuclei of the medulla oblongata
What are purkinje cells?
Large branded cells found in cerebellar cortex, they receive input from up to 200,000 synapses
What is the hippocampus
learning and memory (taxi)
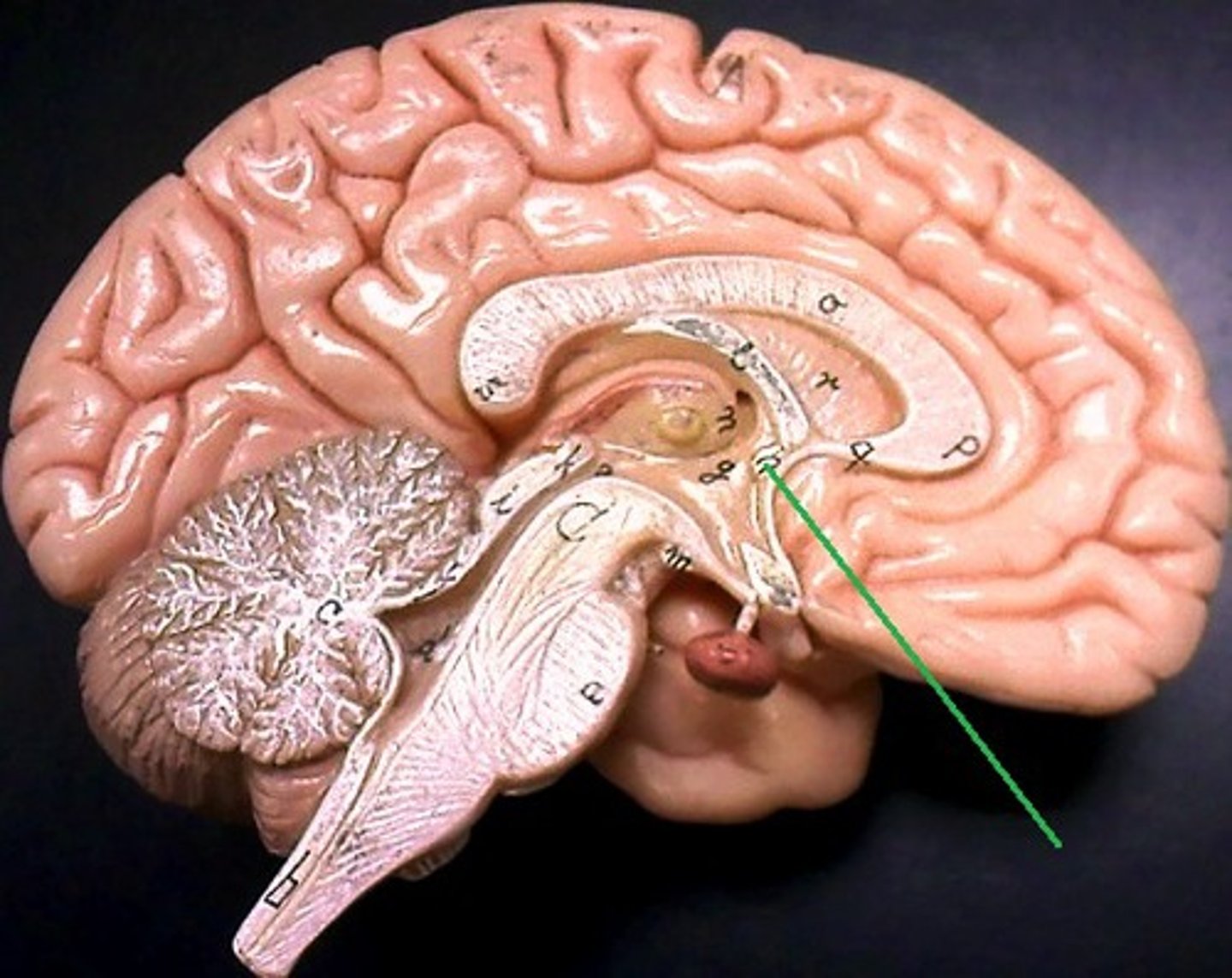
What is the mamillary body?
Terminal of the anterior fornix which connects impulses from the amygdala and hippocampus to the thalamus; important for episodic memory
What is Broca's area?
speech production
What is Wernicke's area?
language comprehension
What is the pineal gland
secretes melatonin
What is Infundibulum
A stalk that attaches the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus.
What is the pituatary gland
master gland that controls all hormones
What is the difference between afferent(sensory) and efferent (motor)
- Afferent neurons carry information from sensory receptors of the skin and other organs to the central nervous system (i.e., brain and spinal cord)
- , whereas efferent neurons carry motor information away from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands of the body.
What is the somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
Describe the different receptors for the general senses
nociceptors
thermorecptors
chemoreceptors
mechanoreceptors
What are the anatomical differences between the medulla oblongata and the spinal cord?
-Allows brain and spinal cord to communicate-Coordinates complex autonomic reflexes
-Controls visceral functions-Nuclei in the medulla-Autonomic nuclei control visceral activities
-Sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves-Relay stations along sensory and motor pathways
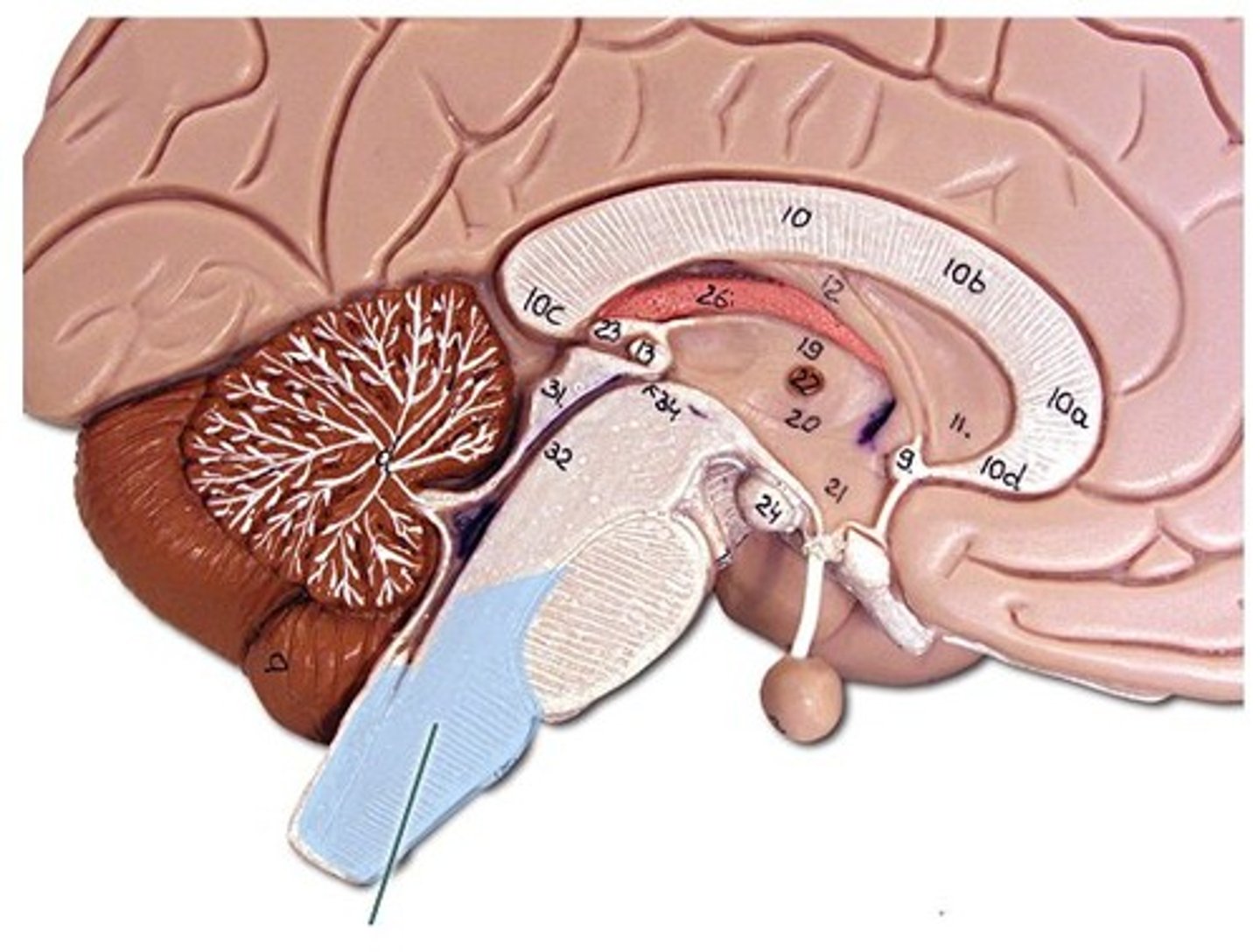
What are the functions of the medulla oblongata?
all vital functions for living (if damaged instant death)
main components of the pons
1. Sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves
2. Nuclei involved with control of respiration
3. Nuclei and tracts that process and relay information sent to and from the Cerebellum
4. Ascending, descending, and transverse tracts
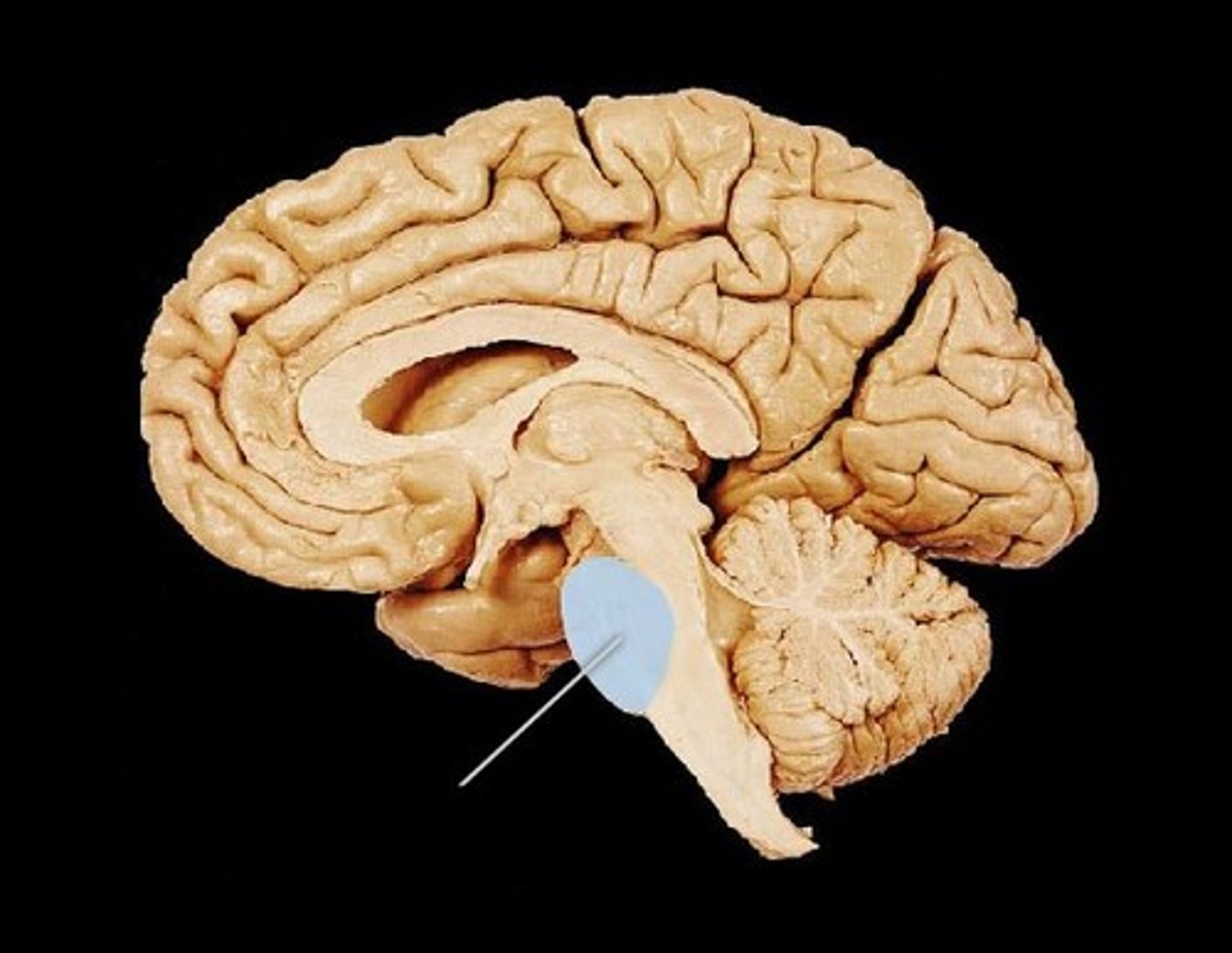
Functions of the pons
-receives sensory information and returns motor info for the jaw muscles, anterior surface of the face, eye muscles, & internal ear
-modifies breathing rhythm set by the medulla oblongata through the apneustic and pneumotaxic centers
-relays info to and from the cerebellum (relay centers)
components of midbrain
inferior and superior colliculi
What is the superior colliculi
visual reflexes
What is the inferior colliculi
auditory reflexes
corpora quadrigemina of midbrain
coordinates visual and auditory reflexes
substantia nigra (midbrain)
part of the midbrain; a motor area; gives rise to dopamine path that deteriorates in Parkinson's disease
Functions of the midbrain
-processing of visual and auditory data
-generation of reflexive somatic motor responses
-maintenance of consciousness
Components of Cerebellum
vermis, arbor vitae
What is the vermis?
connects the two cerebellar hemispheres
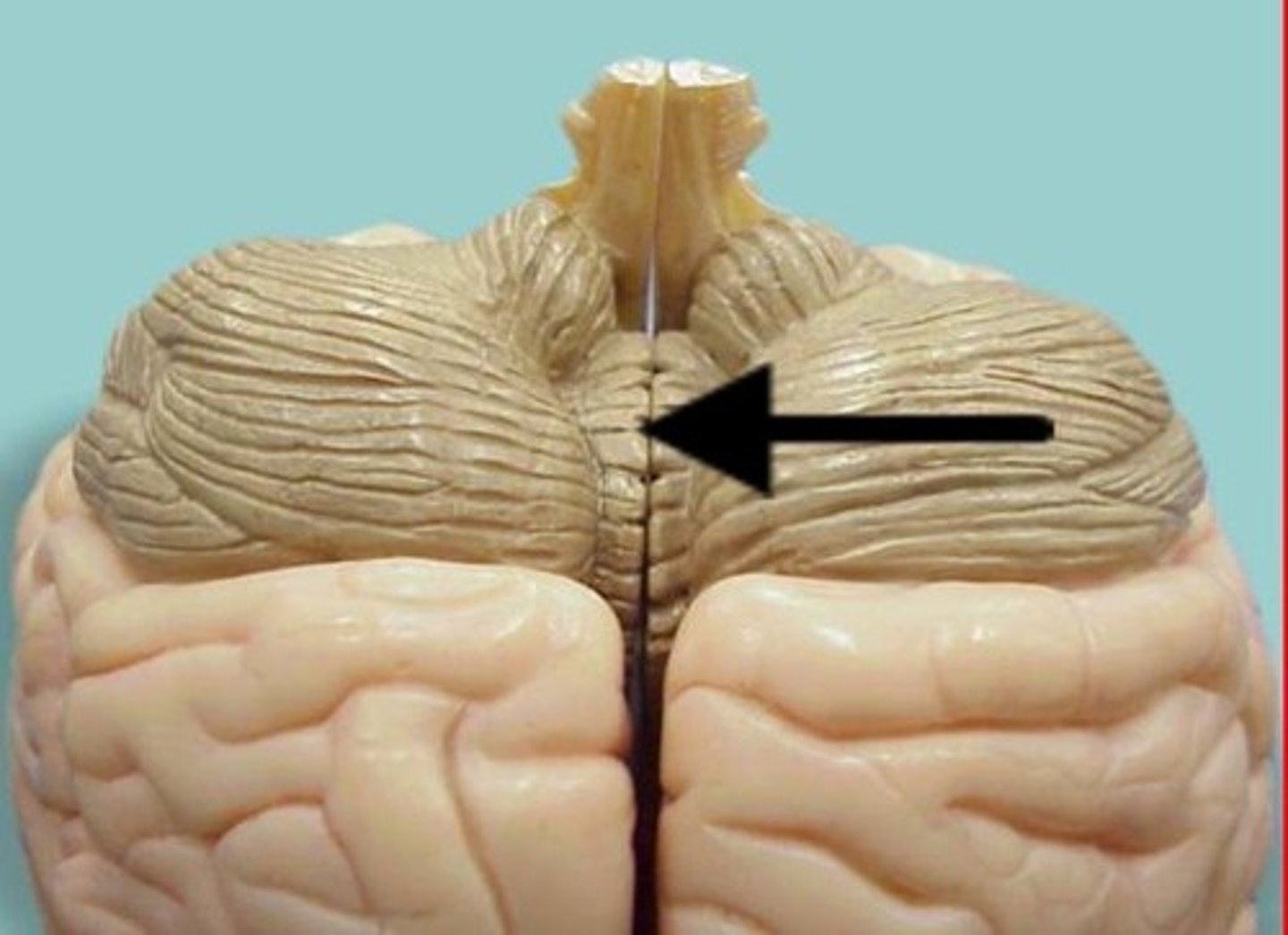
Functions of the cerebellum
Balance and coordination
What is the arbor vitae of the cerebellum?
tree like pattern of white matter
components of diencephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
Thalamus function
sensory relay station
Hypothalamus function
homeostasis
What are nociceptors stimulated by?
-thermal means: extreme temperatures
-chemical: acids or chemicals produced by body (bradykinin, histamine, prostaglandin)
-physical: pressure
What are thermoreceptors?
This is a type of receptor responds to changes in temperature.
What are chemoreceptors?
A receptor that responds to a change in the chemical composition (PaCo2 and pH) of the fluid around it.
What are the 3 types of mechanoreceptors
tactile, baroreceptors, (pressure) proprioceptors (monitor body positioning important in movement and locomotion)
What are the general senses?
temperature, pain, touch, pressure, vibration, proprioception
An overview of the sensory pathways and the somatic nervous system
Arriving stim→ action potential gen-> propagation→ CN processing(sensation)(2 pathways→ immediate involuntary response perception
What are somatic sensory pathways
Carry sensory information from the skin and musculature of the body wall, head, neck, and limbs
What are the 3 major somatic sensory pathways
1. spinothalamic pathway
2. posterior column pathway
3. spinocerebellar pathway
What is the spinothalamic pathway?
carries info mainly about pain, itch, temp and crude (non-discriminative touch and pressure)
What is the posterior column pathway
Carries sensations of highly localized ("fine") touch, pressure, vibration, and proprioception
What is the spinocerebellar pathway
Cerebellum receives proprioceptive information about position of:
Skeletal muscles
Tendons
Joints
What is decussation?
crossing of the midline that occurs in many tracts so that brain senses and controls contralateral side of body
Motor Pathways & Descending Tracts: Corticospinal (voluntary)
Descending: Corticospinal Pathway: focus on the pathway=pyramidal system= involves at least two motor neurons
First- vs. Second- vs. Third-order sensory neurons
The body of the first-order neuron, within the ganglia, projects its axons to the posterior gray horn of the spinal cord. Here, it synapses with second-order neurons that ascend along the spinal cord and project onto third-order neurons which are found in the subcortical structures of the brain, such as the thalamus.
Upper Motor neurons vs. Lower Motor neurons
The upper motor neurons originate in the cerebral cortex and travel down to the brain stem or spinal cord, while the lower motor neurons begin in the spinal cord and go on to innervate muscles and glands throughout the body
What is the sensory homunculus
Functional map of the primary sensory cortex
What is the motor homunculus?
the body map on the motor cortex
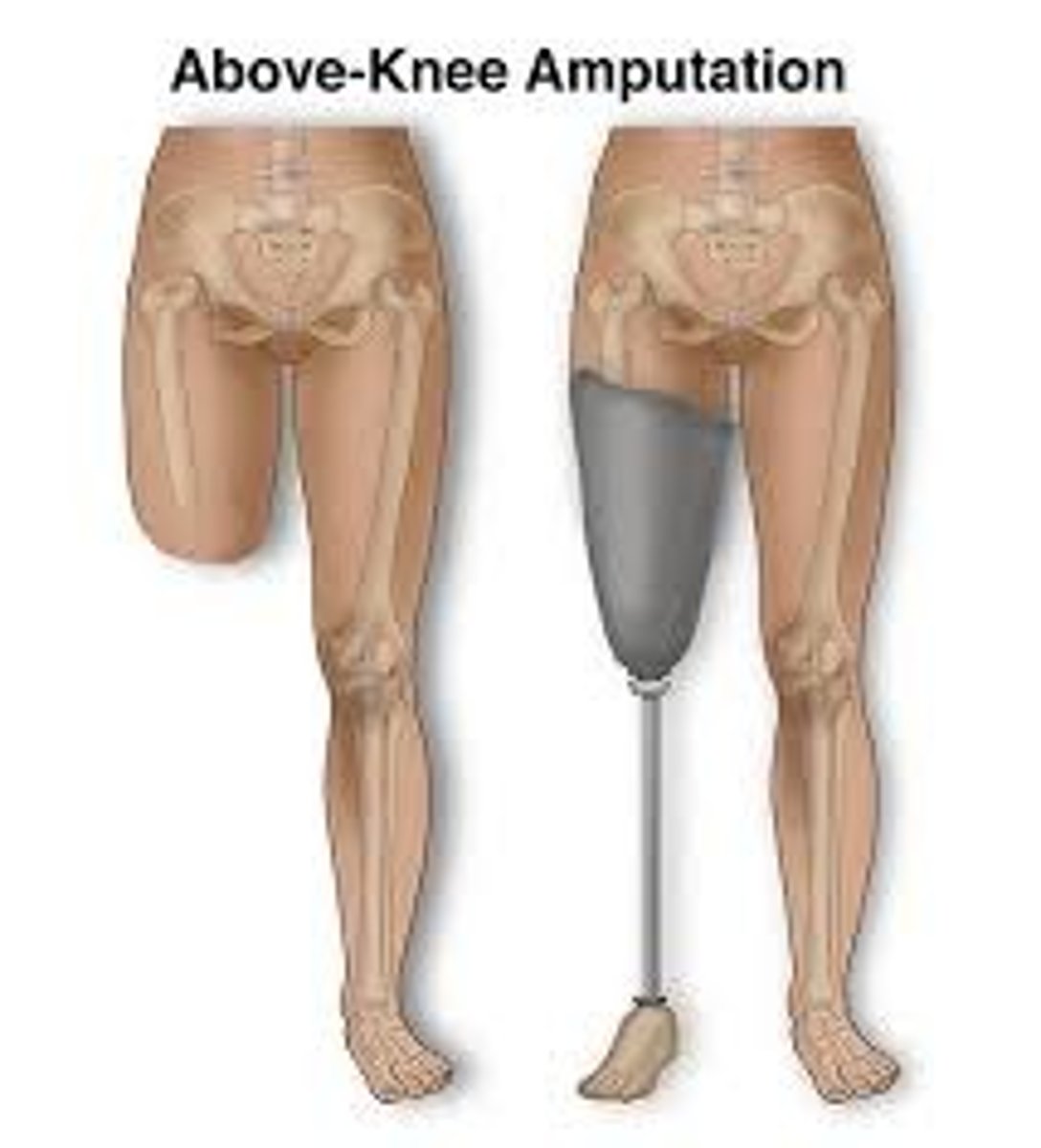
Phantom Limb Syndrome
the perception of sensations, including pain, in a limb that has been amputated
What is a preganglionic neuron?
The first neuron of the ANS; its cell body is in the nucleus of brainstem or spinal cord
what is the postganglionic neuron
The nerve opposite the preganglionic neuron on the other side of the ganglionic synapse that receives the impluse.
What is Adrenergic?
activated by epinephrine (adrenaline)
What is the Cholinergic
acetylcholine releasing neurons
Nonrepinephrine and Epinephrine
neurotransmitter: alertness and arousal (adrenaline)
autonomic ganglion
the collection of synapses between the pre- and post-ganglionic nerve fibers
collateral ganglion
sympathetic ganglion independent of the sympathetic chain
What are the Cranial Nerves
12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain
what are the spinal nerves
The bundles of sensory and motor neurons that are bringing information to the CNS and activating skeletal or other types of muscles.
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
"Rest and digest" Blood pressure/heart rate decrease, digestive increases.
What is the sympathetic nervous system
"Fight or flight" Blood pressure/heart rate increase, digestive slowing.
Describe the main eye structures through which light passes before it is converted into a nervoussignal and then trace the visual pathways to their destinations in the brain (know the sequentialsteps from light stimulus to interpretation of signal by the CNS)
Cornea: The transparent front part of the eye that allows light to enter
Pupil: Controls how much light passes through
Lens: The clear inner part of the eye that works with the cornea to focus light onto the retina
Vitreous humor: The clear, jelly-like substance in the center of the eye that helps keep the eye round
Retina: The light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye that contains photoreceptors that convert light into electrical signals
Optic nerve: Carries the signals from the retina to the visual cortex of the brain
Visual cortex: Turns the signals into images
What is the optic nerve?
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
What is the Vestibulocochlear nerve
hearing and balance
functional differences between the roles of the cerebrum (visual cortex vs. association)
The primary visual cortex is retino-topically organized, so each part the visual field is processed by a specific part of the cortex. visual association areas, where visual signals are further interpretated and given additional meaning
midbrain (colliculi or pineal gland) structures.
It is attached by a stalk to the posterior wall of third ventricle. In close proximity to the gland are the superior colliculi of the midbrain
what is the lens
focuses light into the retina
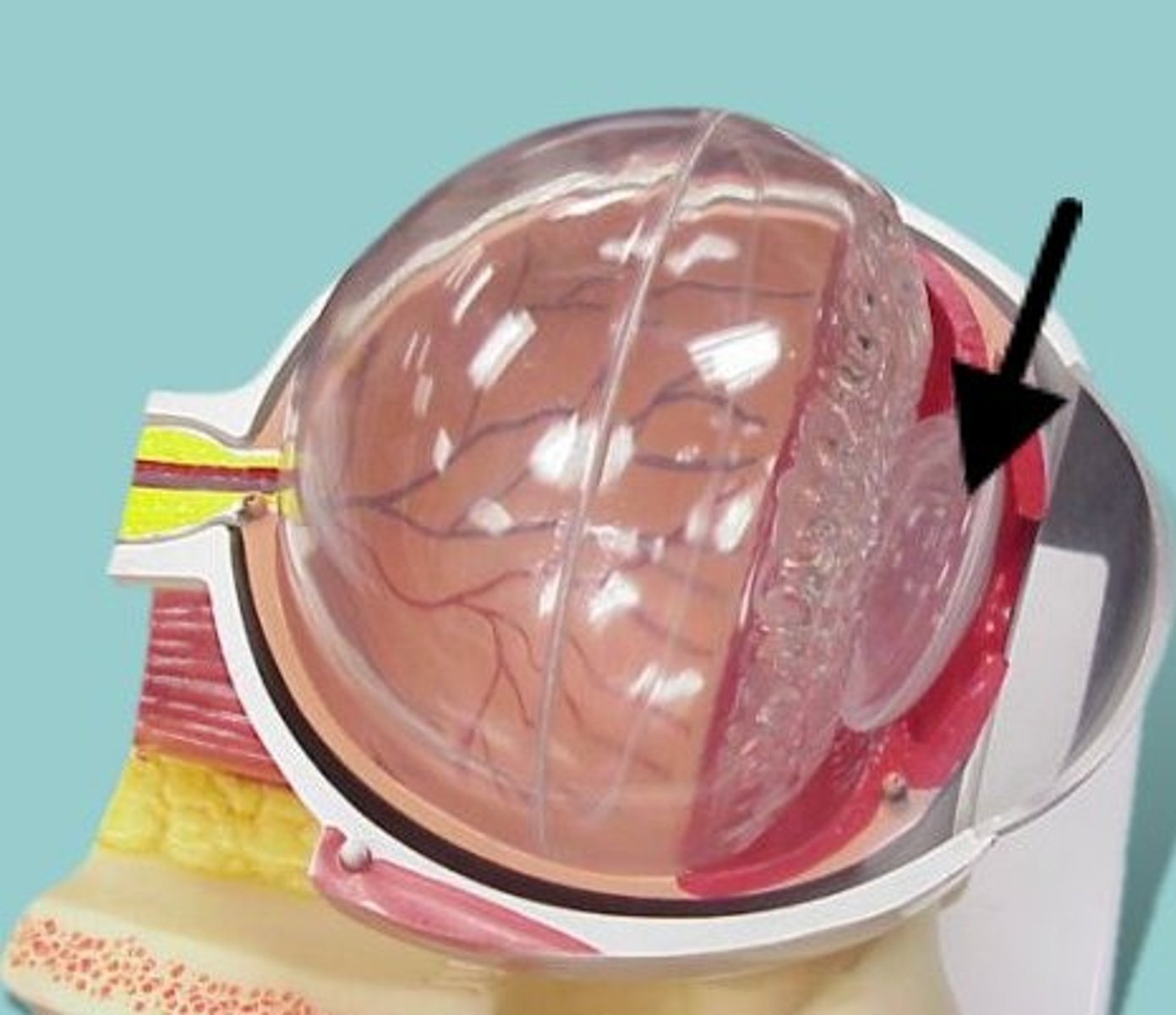
What is the retina
the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
difference between lens and retina
The retina is at the back of your eye. It's opposite the lens and pupil. The lens focuses light that enters your eye to hit your retina and its photoreceptor cells.
What are rods and cones?
Rods and cones are photoreceptors present in the retina. Rods are specialized for night vision; cones are specialized for daylight vision, fine visual acuity, and color.
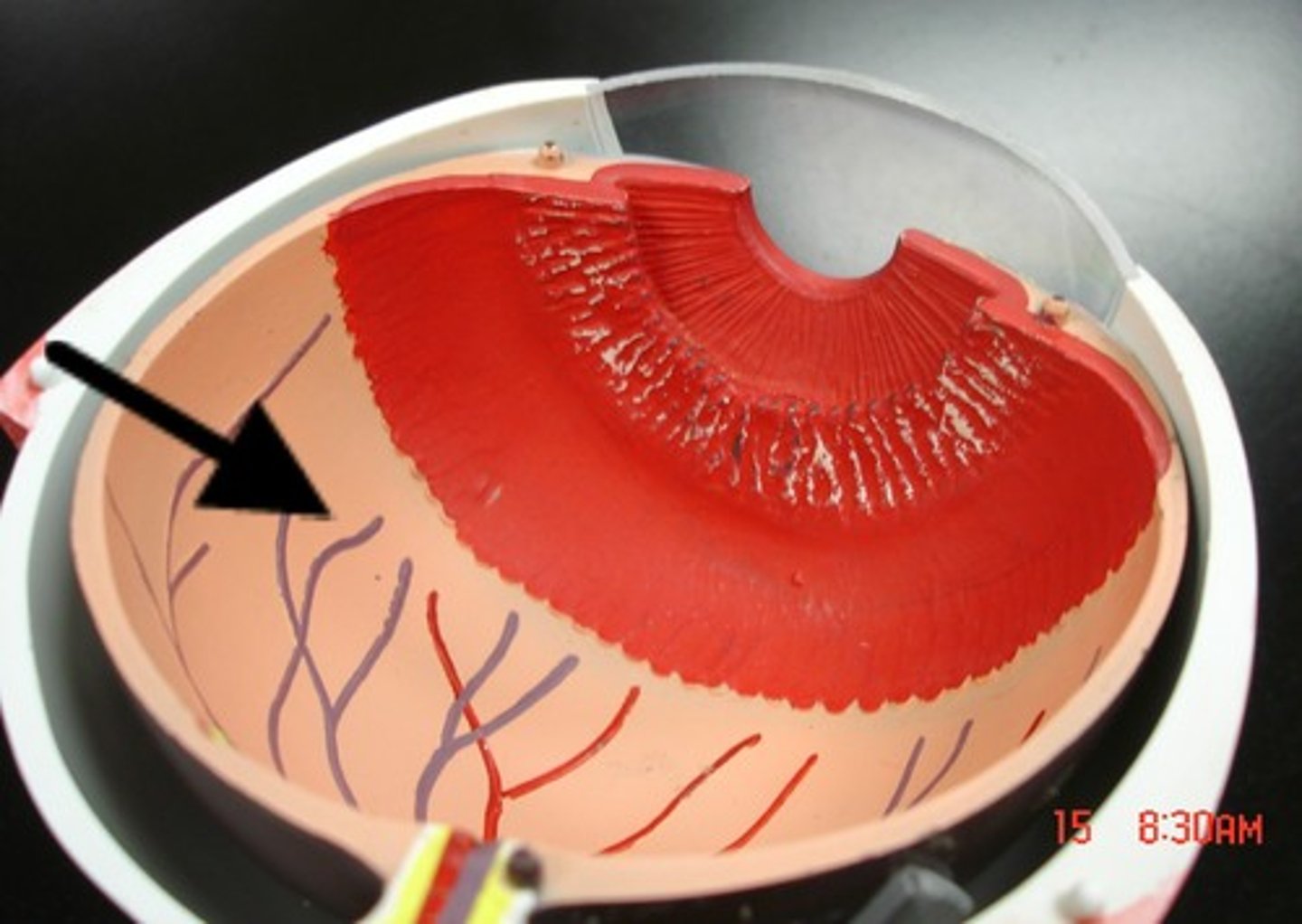
What is the fovea centralis & why is it important?
A small pit in the retinal layer that contains cones only is located lateral to the optic disk in each eye. Anything that must be viewed (discriminative vision) is focused on the fovea bcuz its the area of greatest visual acuity.
What is macula
area of retina with high cone density
What is the optic disc?
The site where the optic nerve attaches to the eye - no vision (photoreceptor cells) here.