Kingdom Fungi
It is a unique kingdom of heterotrophic organisms.
- They show a @@great diversity@@ in morphology and habitat.
- Fungi are cosmopolitan and occur in ==air, water, soil, and on animals and plants.==
- They prefer to grow in warm and humid places.
- Fungi are %%filamentous (Except Yeast).%%
- Their bodies consist of long, slender thread-like structures called @@hyphae and their network@@ @@is known as@@ @@mycelium.@@
- Some hyphae are continuous tubes filled with ^^multinucleated cytoplasm^^ ^^known as^^ ^^coenocytic hyphae.^^
- The cell walls of fungi are composed of chitin and polysaccharides.
Examples:
- The common %%mushroom%% %%and%% %%toadstools.%%
- ==White spots seen on mustard leaves== are due to a parasitic fungus.
- ^^Yeast is used to make bread and beer. (unicellular fungi)^^
- %%Puccinia causes rusting in wheat.%%
- ==Penicillin== is a source of ==antibiotics.==
Saprophytes:
Most fungi are %%heterotrophic and absorb soluble organic matter%% from dead substrates.
Parasites:
- The fungi are heterotrophic and depend on living plants and animals.
- They can also live as ^^symbionts^^ – in association with %%algae as lichens%% and with roots of higher plants as mycorrhiza.
Reproduction:
- Vegetative means – fragmentation, fission, and budding.
- Asexual reproduction is by spores called ==conidia or sporangiospores or zoospores.==
- Sexual reproduction is by %%oospores, ascospores, and basidiospores%%****.
- The various spores are produced in distinct structures called ^^fruiting bodies.^^
- %%The fusion of protoplasms%% between two motile or non-motile gametes is called ^^plasmogamy.^^
- Fusion of two nuclei called %%karyogamy.%%
- ^^Meiosis^^ in zygotes results in ^^haploid spores.^^
- When a fungus reproduces sexually, two haploid hyphae of compatible mating types come together and fuse.
@@Exception:@@ @@In@@ @@Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes@@, an intervening dikaryotic stage (two nuclei per cell) occurs which is called a @@dikaryon and the phase is called dikaryophase of fungus.@@
Phycomycetes: \n 
- Members of Phycomycetes are found %%in aquatic habitats and on decaying wood in moist and damp places%% or as obligate parasites on plants.
- The mycelium is ^^aseptate and coenocytic.^^
- Asexual reproduction takes place by zoospores (motile) or by aplanospores (non-motile).
- These spores are endogenously produced in sporangium.
- A zygospore is formed by the fusion of two gametes.
- These gametes are ==similar in morphology (isogamous) or dissimilar (anisogamous or oogamous).==
Examples: Mucor, Rhizopus (the bread mold), and ==Albugo== (the parasitic fungi on mustard).
Ascomycetes:
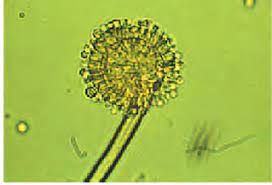
- They are mostly ==multicellular. (Exception:== ==yeast or Saccharomyces)==
- They are %%saprophytic, decomposers, parasitic or coprophilous.%%
- Mycelium is ^^branched and septate.^^
- The asexual spores are conidia produced exogenously on the special mycelium called ==conidiophores.==
- ==Conidia on== ==germination== ==produce== ==mycelium.==
- Sexual spores are called ascospores which are produced endogenously in sac-like asci.
- These asci are arranged in different types of @@fruiting bodies called ascocarps.@@
Examples: ^^Aspergillus, Claviceps, and Neurospora.^^
Note: Many members like ==morels and truffles are edible and are considered delicacies.==
Basidiomycetes:

- They grow in soil, on logs and tree stumps, and in living plant bodies as parasites.
- The mycelium is branched and septate.
- The asexual spores are generally not found, but vegetative reproduction by fragmentation is common.
- The ==sex organs are absent,== but plasmogamy is brought about by the fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells of different strains or genotypes.
- The resultant structure is ==dikaryotic== which ultimately gives rise to %%basidium.%%
- Karyogamy and meiosis take place in the basidium producing @@four basidiospores.@@
- The basidiospores are exogenously produced on the basidium.
- The basidia are arranged in fruiting bodies called basidiocarps.
Examples: %%Agaricus (mushroom), Ustilago (smut), and Puccinia (rust fungus).%%
Deuteromycetes:
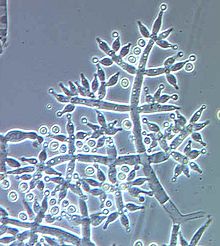
- They are commonly known as imperfect fungi because only the asexual or vegetative phases of these fungi are found.
- Once perfect (sexual) stages of members of Deuteromycetes were discovered they were often moved to ascomycetes and basidiomycetes.
- The Deuteromycetes reproduce only by @@asexual spores known as conidia.@@
- The mycelium is ^^septate and branched.^^
- Some members are saprophytes or parasites while a large number of them are decomposers of litter and help in mineral cycling.
Examples: %%Alternaria, Colletotrichum, and Trichoderma%%.