Employment Law Essentials (not finished)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Governing Agencies for Labor Law
US Department of Labor (DOL)
US Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (OEEOC)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
US Citizenship Immigration Service (USCIS)
Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
Office for Civil Rights (USDHHS)
What is OEEOC responsible for?
Discrimination (age, equal pay, disability, national origin, race, color, religious)
Sexual harassment
What is OSHA responsible for?
Workplace safety laws enforcement
What is USCIS responsible for?
I9 and authorization to work in US
What is IRS responsible for?
Taxation as it relates to independent contractor vs employees
Withholding
Remote workers
What is USDHHS responsible for?
HIPAA Privacy and Security
Gender Affirming Care and Privacy
Online tracking technologies
Civil rights as related to unlawful discrimination in health and human services
Conscience and religious freedom
Employment laws treat _____ and _____ differently
employees, independent contractors
Under common law rules, the relationship between worker and employer must be examined and the _____ the worker is able to exert must be assessed
degree of independence and control
Three factors are analyzed to determine whether and individual is an employee or independent contractor:
Degree of behavioral control
Degree of financial control
Relationship between the parties
Courts have determine that employees are those who are:
Paid salary or wages
Under some form of supervision
Independent contractors
Receive a sum of money for the performance of discrete services or completion of projects
May decide (without direct supervision) how work is performed
If an independent contractor is treated as an employee, then all protections afforded other employees will be available to that individual
Employer is then obligated to withhold and contribute to appropriate federal, state, and local taxes
Certain federal protections (e.g., number of work hours) will also apply to the individual
Hiring/Selection practices are significantly affected by the following federal laws:
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act
Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA)
American with Disabilities Act Amendments Act (ADAAA)
Fair Labors Standards Act (FLSA)
Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
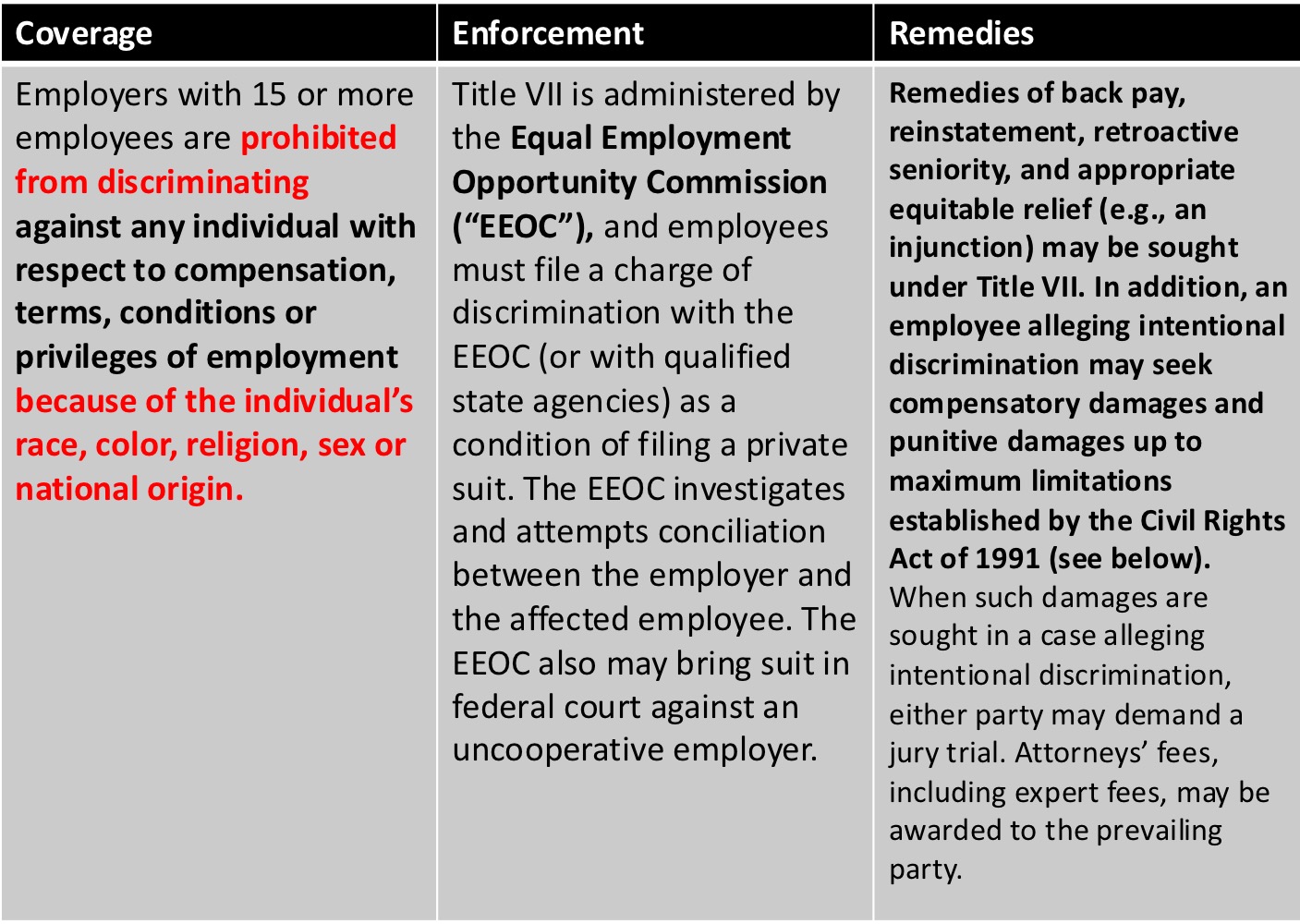
Civil Rights Act of 1964 Title VII - Equal Employment Opportunity
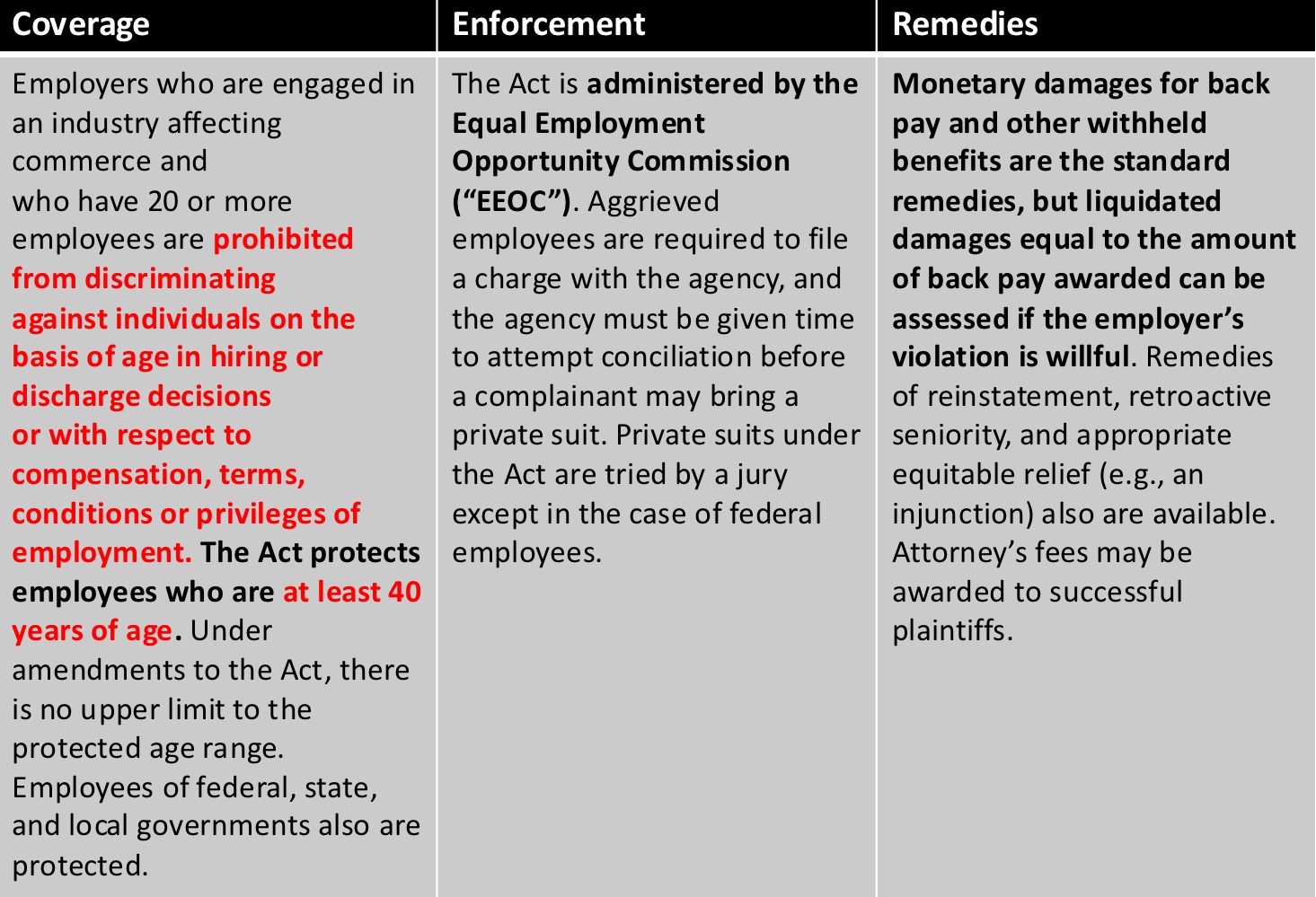
Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967
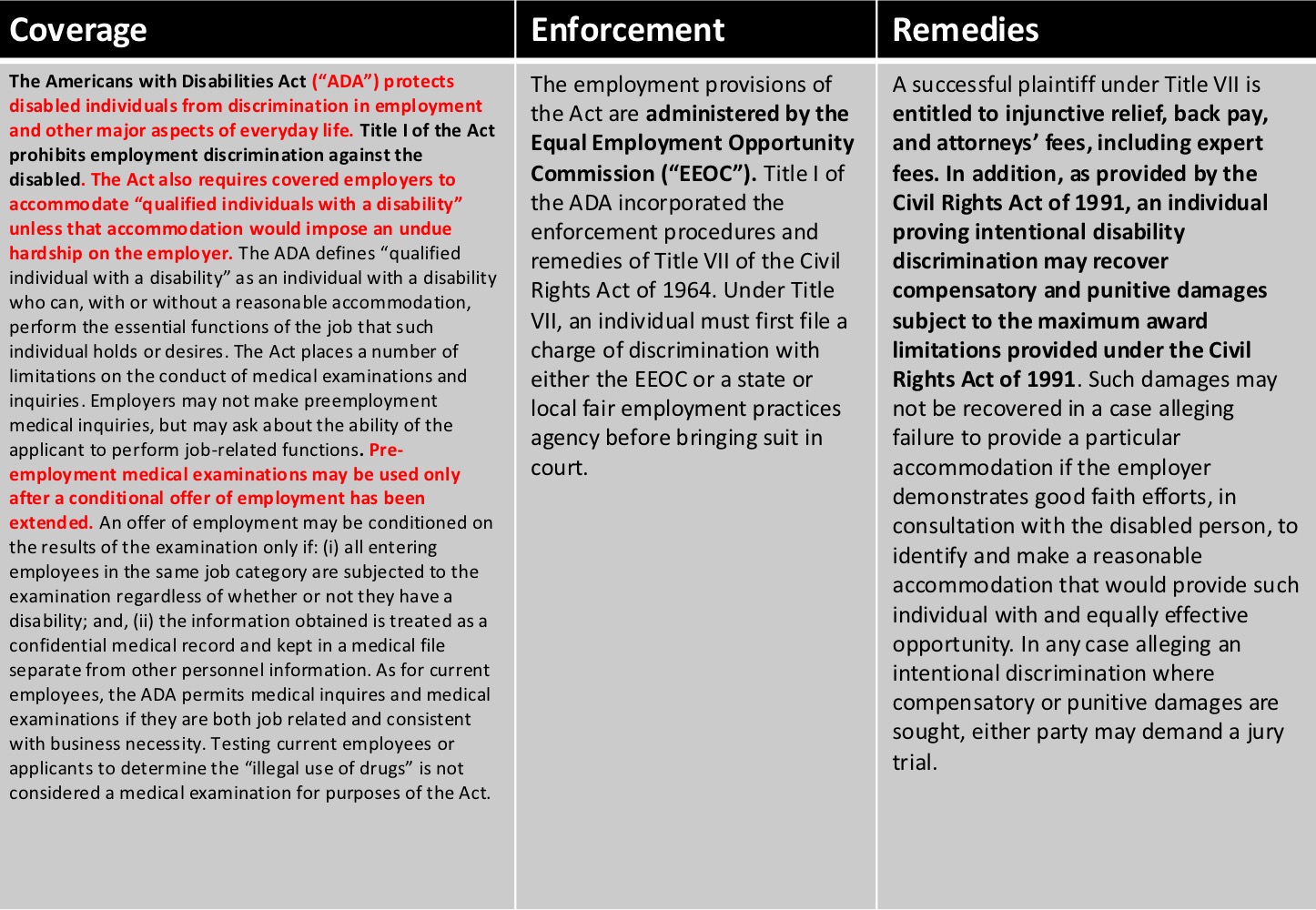
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990
Equal Pay Act of 1963

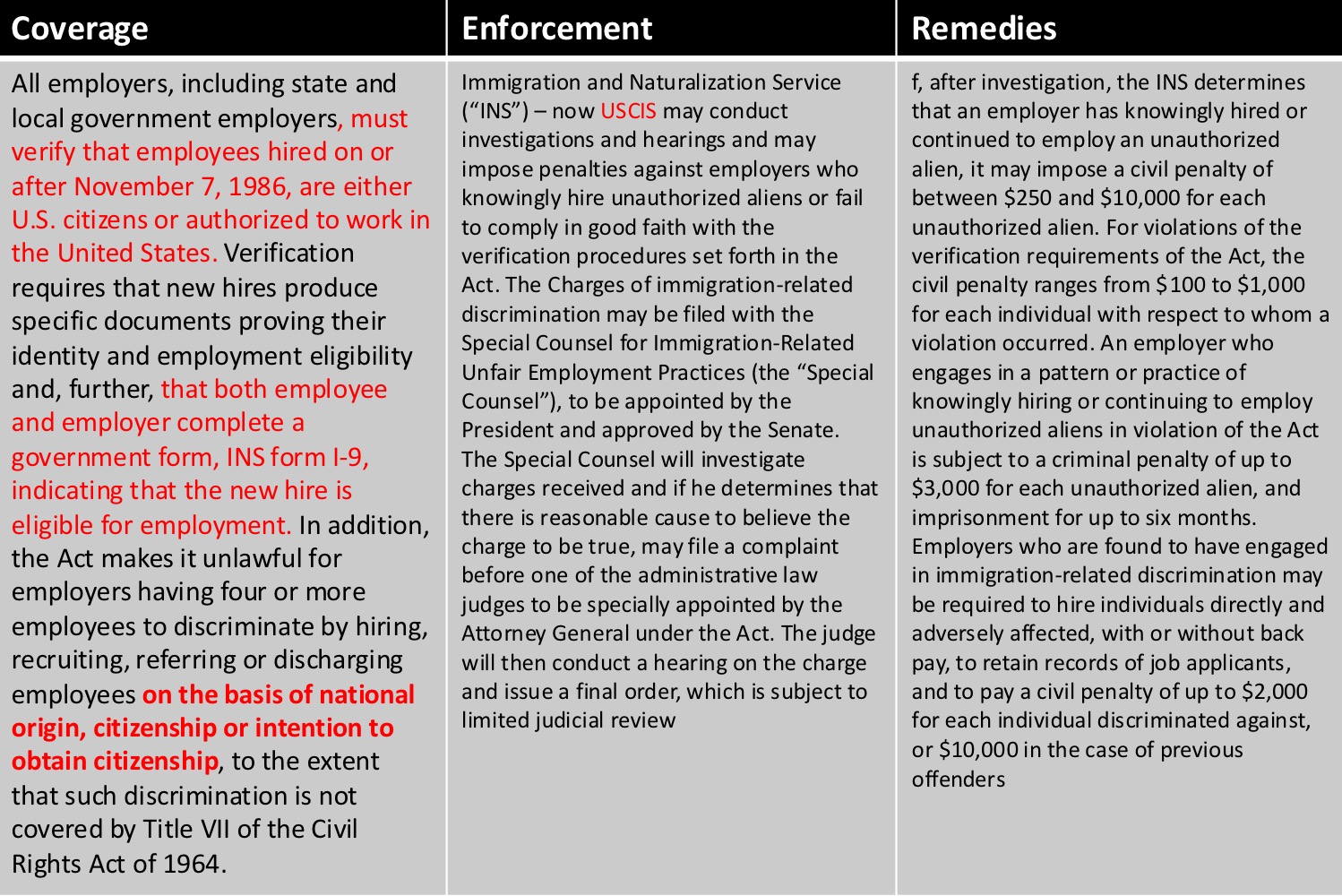
Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986
During the interview process, curiosity about an applicant’s personal life can lead to _____
lawsuits (child care, pregnancy)
When interviewing, it is generally best to avoid any questions that relate to:
Gender (sex), Age, Religion, National origin, Disabilities, Marital status, Sexual orientation, Ethnicity, Parental status/intended parental status
Most pharmacist managers use _____ to review the backgrounds of employment finalists before extending an offer of employment
due diligence
Due diligence may include:
Reference checks with current or former employers
Educational degree verifications
Criminal records checks
Drug tests
_____ can reveal potential employees’ shortcomings including dishonesty and performance issues, which can prevent future problems
Preemployment screenings
Screenings must comply with state and federal laws related to fair credit reporting and privacy, as background checks are covered by the _____
Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
Federal consumer protection statute that regulates the screening process
The FCRA is a perfect vehicle for _____ — a successful claim can recover statutory damages between $100 and $1000 per violation, attorney’s fees, punitive damages and costs as well as actual damages
class action litigation
One of the fundamental requirements of the FCRA is to have _____ from a job applicant or employee prior to conducting an employment background check. The authorization and disclosure must stand alone, and should not be combined with other forms or hidden within the job application
written authorization and disclosure
Adverse action notification
Two-step process that must be followed strictly by the book, and many employers get tripped up by skipping one or even both steps
Step 1: Pre-adverse action notice
This is sent to the applicant prior to making a not to hire decision based on the background check. You have to provide the applicant with a notice, send them a copy of the report, and attach a Summary of Rights under the FCRA
Step 2: Adverse action notice
This is sent after the final decision has been made and must contain information on how to dispute the background check
Criminal background checks may be conducted as follows:
A manager may check public records
An outside company or investigator may conduct an intensive records interview
Organizations may require prospective employees to submit to fingerprinting to use federal and state databases to match criminal records
Criminal backgrounds of prospective employees
Managers must decide whether the nature, timing, and seriousness of an offense is job-related and would preclude individual from employment
Should consider whether hiring someone with a criminal record would adversely affect the workplace, patient safety, or how employee performs assigned duties
Healthcare providers are often subjected to check through the:
National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDP)
Healthcare Integrity and Protection Data Bank
Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA)
These organizations maintain information related to whether the applicant holds and appropriate health care license or the applicant has been convicted of a crime or has pending civil judgements against him/her
The Americans With Disabilities Act Amendments (ADAA) places limitations on medical screenings
Must be job related
Must be required of all employees
Only permitted after an employer makes a “real” employment offer and conducts all other forms of preemployment screening
Some employers search the internet for information about job candidates
May return unreliable information
May violate equal opportunity mandates
Should be used with caution
To constitute a valid employment contract, agreement must occur between the offeror (employer) and offeree (potential employee)
To achieve this, one party makes an offer, and the other party accepts
If the other party makes a counter-offer, then no contract exists until the parties agree on all terms of the contract
When both parties agree on employment terms, the final agreement should be put in writing
Employment agreements may be made for an established time period or for “at will” employments
Most employment contracts are at will: may be terminated by either party at any time for any reason that does not violate public policy
Type of employment contract determined by
Terms of the agreement
Policy manual governing the employment relationship
State law
Public policy considerations
For contracts that extend beyond one year, many states’ statutes of fraud require the agreement to be _____
in writing
Agreements often contain noncompete clauses or restrictive covenants
Used to prevent an employee from opening a competing practice nearby for a specified period of time
Courts do not look favorably on such clauses and require them to be reasonable in duration and geographic location
May not unnecessarily impede departing employee’s ability to earn a living
An employer must provide adequate consideration (compensation) to the employee
Many organizations are substituting liquidated damages provisions for noncompete clauses
Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) — “The Overtime Law”
Establishes minimal wage, overtime pay, recordkeeping, and youth employment standards affecting employees in the private sector and in Federal, State, and local governments
Unless specifically exempted, employees covered by the Act must receive overtime pay for hours in excess of 40 in a workweek at a rate not less than time and one-half their regular rates of pay. There is no limit in the Act on the number of hours employees aged 16 and older may work in any workweek. The Act does not require overtime pay for work on Saturdays, Sundays, holidays, or regular days of rest, as such
Regular pay cannot be less than minimum wage
Overtime pay may not be waived in agreement
Final rule in effect July 1, 2024
Unlawful Harassment
Includes harassment on the basis of race, religion, color, creed, age, national origin/ancestry, sex, marital status, veteran status, physical/mental disability, sexual orientation, pregnancy, or any other basis made unlawful by law, regulation, or ordinance
Unlawful harassment, such as sexual harassment, is a form of employment discrimination
Two kinds of sexual harassment
Quid pro quo harassment — “something for something”
Hostile environment harassment
A plantiff does have to prove psychological injury to prove hostile environment harassment
Depends on the totality of the circumstances