Lec 3: WBC
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What are the 5 types of WBCs?
Neutrophils, eosinophils basophils, lymphocytes, monocytes
What is the main function of WBCs?
Identify and react to foreign substances (immunity) and damage (inflammation) in/to the body
Which WBCs are classified as Granulocytes?
Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
Which WBCs are classified as Agranulocytes?
Lymphocytes and monocytes
Non specific, physical and chemical barriers, inflammation
Innate immunity
Specific, humoral (fluid) response, cell mediated response
Acquired immunity
What are examples of physical barriers for innate immunity?
Intact skin, mm
What are examples of chemical barriers for innate immunity?
Tears, saliva, HCl in the stomach
What characterized inflammation?
Pain, swelling, heat, redness, and loss of function
APCs present antigen to B lymphocytes which stimulates antibody production
Humoral (fluid) response
APCs present antigen to T lymphocytes which are stimulates and produce a variety of specific cells
Cell mediated response
What are two types of responses in acquired (specific) immunity?
Humoral (fluid) response and cell mediated response
What are the cellular components of innate immunity?
Neutrophils, NK cells, Interferon, monocytes/macrophages
What are the cellular components of acquired immunity?
B lymphocytes (plasma cells, memory B cells), T lymphocytes (memory T cells, helper T cells, killer T cells suppressor T cells, mediator T cells), monocytes/macrophages
First responders which phagocytize foreign matter and organisms
Neutrophils
Clean up what the neutrophils cannot control.
Phagocytosis of viruses, protozoa, fungi, and other microorganisms
Recognize, process, and present antogen to lymphocytes for removal
Monocytes/macropahges
Direct cell-to-cell contact and lysis of invading of foreign materials
Destroy some tumor cell types
NK cells
Interferon
Released by healthy cells in response to viral invasion to protect against viral entry
Which major cell component of acquired immunity (B lymphocytes or T lymphocytes) contains plasma cells and memory B cells?
B lymphocytes
Which major cell component of acquired immunity contain memory T cells, helper T cells, killer T cells, suppressor T cells, and mediator T cells?
T lymphocytes
Produce specific antibodies to particular antigen
Plasma cells
Survive for months to years and can respond to antigen at a later time and faster
Memory B cells
Assist B lymphocytes in antigen recognition and antibody production
Helper T cells
Control and limit the immune response of all T cells
Suppressor T cells
Which cellular component is in both innate and acquired immunity?
Monocytes/macrophages
How long does it take to upregulate the immune response?
2-3 days
At what point does the immune response peak before declining?
1-2 weeks
What are immunoglobulins?
Antibodies the are considered “gamma” globulins (4 types)
what are the 4 types of antibodies found in animals?
IgG, IgM, IgE, IgA
Most common, comprises 75% of antibodies in the body, found int he blood vessels and tissues
IgG
Large molecule confined to the vasculature, 5% of the total
IgM
Normally 1% of total but usually increases in presence of allergies or parasites
IgE
Normally found on body surfaces, secretions of the skin , the digestive tract, and the respiratory tract, comprised 20% of the total
IgA
Overall picture of the status of the WBCs in the body
Leukogram
Cells being formed in the bone marrow
Proliferation
Mature cells stores in the spleen and bone marrow
Storage
Freely moving in the vessels from where the sample is taken
Circulating
Stuck to or rolling along the vessel walls
Marginal
Various areas of the body where WBCs perform basic functions
Tissue
Increase in the number of WBCs above the normal reference range
Leukocytosis
Abnormally low number of WBCs below the normal reference range
Leukopenia/leukocytopenia
Presence of abnormal WBCs in the circulating blood: usually seen when neoplasia (cancer) is also present
Leukemia
Presence of abnormal WBCs in the circulating blood in the absence of neoplasia
Leukemoid response
What can cause normal physiological changes in the Leukogram?
Excitement, fear, apprehension, or pain, muscular exertion or exercise, stress, digestion, pregnancy, estrus, age, species, post immunization
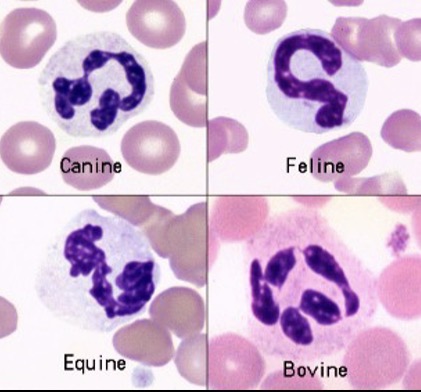
Mature within the bone marrow in 3-10 days
Migrate to tissues from circulation within 6-7 hours of release form storage pools
Remain in the tissues as needed for 2-3 days
May only last a few hours within tissues in the presence of a disease process
Neutrophils
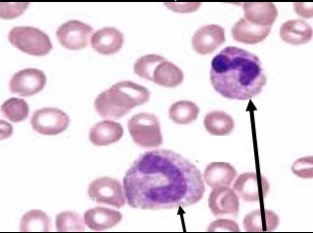
Immature form, nucleus has no lobes or segments
“Band” or “stab” neutrophil
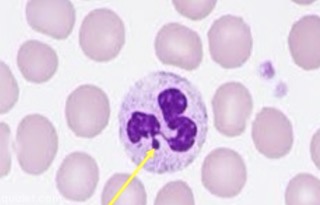
Drumstick or club-like appendage of the nucleus
Only seen in females
Remnant of an inactivated X chromosome
Barr body
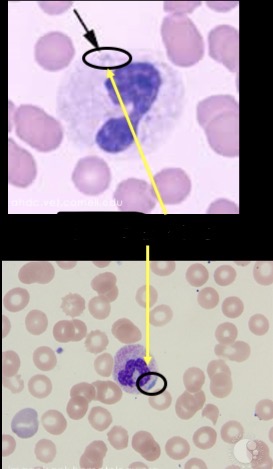
Bluish staining inclusions in the cytoplasm
Remnants of rough ER
Dohle bodies
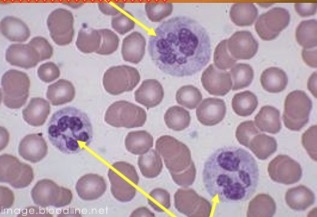
Nucleus contains more than 5 lobes or segments
Indicates cell has been in circulation for awhile
Hypersegmented neutrophil
Small particles are engulfed and broken down by enzymes in the cytoplasmic granules
Larger particles are broken down via release of enzymatic granules from the cell
Inflammation and phagocytosis
Increased numbers of circulating neutrophils; infection, inflammation (trauma), neoplasia, toxins, physiologic or iatrogenic corticosteroids or epinephrine (stress)
Neutrophilia
Decreased numbers of circulating neutrophils; bone marrow suppression, massive infection, shock
Neutropenia
When rapid loss and increased demand for neutrophils leads to increased production by the bone marrow to keep up with demand in the body
A greater percentage of immature forms is released as a result
Left shift in the leukogram
What is the order of the degree of left shift from slight to extreme?
(Slight 1) bands only
(Moderate 2) metamyelocytes
(Marked 3) myelocytes and promyelocytes
(Extreme 4) myeloblasts
Neutrophilic leukocytosis is present
Immature forms are =/< mature adult forms (segmented neutrophils)
Indicates adequate bone marrow response
Good prognosis
Regenerative left shift
Neutropenic leukopenia
Immature forms>mature adult forms
Bone marrow has not had time or cannot meet demand
Poor prognosis
Degenerative left shift
Morphological changes that occur in neutrophils when demand is very high and maturation time is shortened in the marrow
Toxic change
What is the earliest sign of toxic change?
Dohle bodies
How does cytoplasmic basophilia appear?
Streaky, diffuse blue appearance
What are the features of toxic change?
Dohle bodies, cytoplasmic basophilia, presence of vacuoles, giantism, toxic granulation
True or False: Toxic changes often accompany a degenerative “left shift” and are a negative prognostic indicator
True
Maturation and circulation times in the blood and tissues are similar to that for neutrophils
The greyhound is unique because the eosinophils contain vacuoles in the cytoplasm making it easy to confuse with monocytes
Eosinophils
What do eosinophils play a role in regulating and controlling?
Parasitic infections, allergic reactions, inflammation, coagulation and fibrinolysis
Increases numbers of circulating eosinophils
Parasitic infections and allergic reactions
Eosinophilia
Decreased numbers of circulating eosinophils
Stress or treatment with corticosteroids
Difficult to detect in most animals
Eosinopenia
Little is known about maturation and circulation or function since they are so rarely appreciated in circulation of most common domestic species
More commonly seen in horses and ruminants
Usually last for a total of 10-12 days from the time of production to entry into tissues from circulation
Basophils
Similar in structure and function to the mast cell
Stimulated by dust, molds viruses and other proteins
Release enzymatic granules composed of histamine and other enzymes
Initiate acute inflammatory reactions
Specific functions of basophils
Increases numbers of circulating basophils
Often seen with eosinophils in allergic reactions and parasitic infections
Often seen with mast tumor cells
Basophilia
Decreased numbers of circulating basophils
Of no clinical significance
Basopenia
Where are lymphocytes produced?
Bone marrow and lymphoid tissues (lymph nodes, spleen, thymus (fetus and neonate), GALT, tonsils, appendix)
Life span varies depending on intended function:
lymphocytes last____
Memory cells last for____
days
Years to a lifetime
_____produce antibodies in the humoral immune system
B lymphocytes
_____are part of the cell mediated immune response
T lymphocytes
Increased numbers of circulating lymphocytes
excitement, fear, anxiety, pain (stress), very young animals (age related), muscular exertion/exercise
Stimulation by viruses, blood parasites, and immunizations (acquired immunity)
Lymphocytosis
Maturation and circulation times are similar to those for other WBCs
Can last for months in the tissues as macrophages
Monocytes
Engulf fungi, protozoa, intracellular organisms, and bacteria
Remove debris and damaged cells following trauma
Process antigen for presentation to B and T lymphocytes
Phagocytosis
Chronic infection or inflammatory response
Necrosis
Conditions which initiate a granulomatous response
Fear, anxiety, excitement, pain (stress)
Monocytosis
Of no clinical significance
Monocytopenia