Health Priorities in Aus
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/120
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
1
New cards
What are the benefits of measuring health status?
Measuring health status:
- identifies priority health issues
- monitors progress
- re-evaluates health promotions
- identifies priority health issues
- monitors progress
- re-evaluates health promotions
2
New cards
Define epidemiology.
epidemiology - study of patterns of disease within a population over a period of time
3
New cards
What is the role of epidemiology and what does it provide?
- collection of data from hospitals, GPs, practitioners (physios etc), surveys + CENSUS
- provides picture of health status in terms of quantifiable measures of ill health
- identifies patterns of health and disease + analyses how health services + facilities are used
- provides info on ethnic, socioeconomic, age + gender groups
- provides picture of health status in terms of quantifiable measures of ill health
- identifies patterns of health and disease + analyses how health services + facilities are used
- provides info on ethnic, socioeconomic, age + gender groups
4
New cards
What are does epidemiology consider?
Considers:
- prevalence - n. cases (proportion of cases e.g. 1 in 4)
- incidence - n. new cases
- distribution - extent
- apparent causes - determinants + indicators
- prevalence - n. cases (proportion of cases e.g. 1 in 4)
- incidence - n. new cases
- distribution - extent
- apparent causes - determinants + indicators
5
New cards
Identify common epidemiology statistics used.
Commonly used statistics: births, deaths, hospitilisations, lost work days, injury incidence
6
New cards
Who uses epidemiology statistics?
Used by: researchers, gov, health departments, medical practitioners
7
New cards
What do epidemiological observations show and how are they used?
Epidemiological observations:
- describe + compare patterns of health
- identifies health needs + allocates resources accordingly
- evaluates health behaviours + promotes healthy ones
- describe + compare patterns of health
- identifies health needs + allocates resources accordingly
- evaluates health behaviours + promotes healthy ones
8
New cards
Identify the three major purposes of epidemiology.
Three major purposes: disease management, vaccine development, gov policy making
9
New cards
What are limitations of epidemiology?
Limitations of epidemiology:
- cannot survey everyone
- doesn’t show severity (accurately demonstrate quality of life) e.g. Stage 1 v Stage 4 cancer
- doesn't include all areas of health e.g. spiritual
- doesn’t account for determinants i.e. why
- doesn’t always show variations e.g. rural v remote
- statistics can be manipulated + open to bias
- tends to focus on negatives not positives e.g. wellbeing
- reliability depends on source of info
- cannot survey everyone
- doesn’t show severity (accurately demonstrate quality of life) e.g. Stage 1 v Stage 4 cancer
- doesn't include all areas of health e.g. spiritual
- doesn’t account for determinants i.e. why
- doesn’t always show variations e.g. rural v remote
- statistics can be manipulated + open to bias
- tends to focus on negatives not positives e.g. wellbeing
- reliability depends on source of info
10
New cards
What are the measures of epidemiology?
Life expectancy - expected n. years to live.
Mortality - death rates of a health condition/age group over a given period of time.
Morbidity - injury + disease rates.
Infant mortality - deaths rates of 0-1yrs per 1000 live births.
Mortality - death rates of a health condition/age group over a given period of time.
Morbidity - injury + disease rates.
Infant mortality - deaths rates of 0-1yrs per 1000 live births.
11
New cards
Why has life expectancy increased over the years?
Life expectancy increased over the years due to:
- improved health care accessibility e.g. defibrillators
- health promotion campaigns through education
- improved medical technology
- improved health care accessibility e.g. defibrillators
- health promotion campaigns through education
- improved medical technology
12
New cards
Why do females generally have a higher life expectancy than males?
Females live longer due to:
- men more likely to engage in risk behaviours
- social stigma in regards to men receiving help
- men more likely to drinks + smoke
- men more likely to engage in risk behaviours
- social stigma in regards to men receiving help
- men more likely to drinks + smoke
13
New cards
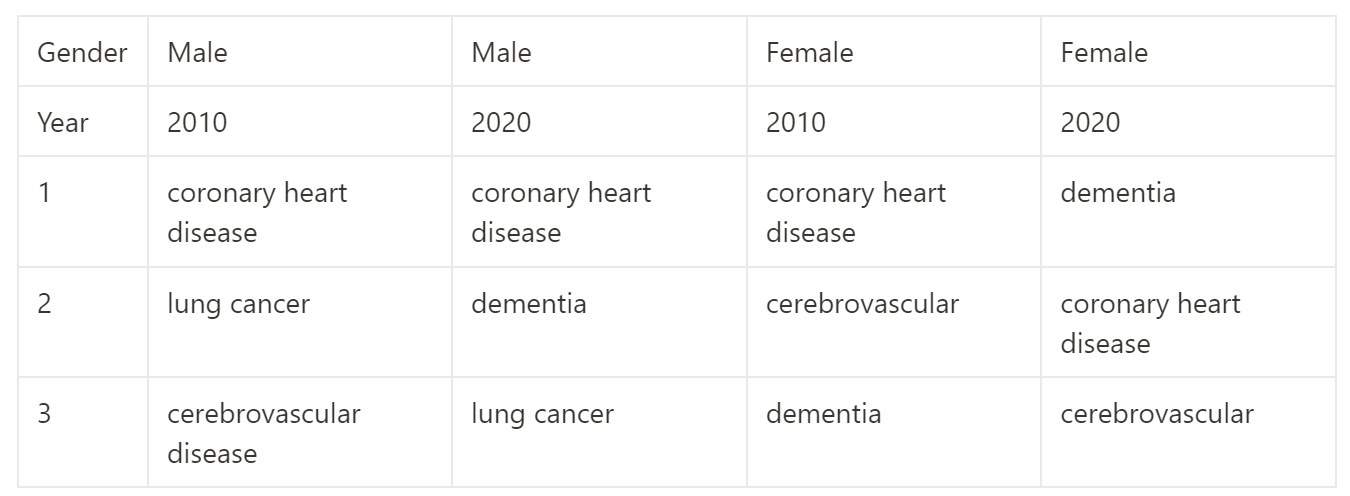
Compare the leading causes of deaths for males and females between 2010-20.
14
New cards
What are the leading causes for cancer mortality for males and females?
Leading cancer deaths:
F-lung, breast, colorectal.
M-lung, prostate, colorectal.
F-lung, breast, colorectal.
M-lung, prostate, colorectal.
15
New cards
Compare life expectancy for males and females between 2000 to 2020.
Life expectancy 2000: F-82 M-77.
Life expectancy 2020: F-85 M-81.
Life expectancy 2020: F-85 M-81.
16
New cards
What is the leading cause of death for young people?
N.1 cause of death for 15-24 is suicide.
17
New cards
What is the trend in infant mortality and why is it important?
Infant mortality:
Neonatal (28 days) + post-neonatal have declines steadily. 5.7 in 1999 to 3.1 in 2020.
*infant mortality is the most influential indicator of health status
** ATSI 2x rates higher
Neonatal (28 days) + post-neonatal have declines steadily. 5.7 in 1999 to 3.1 in 2020.
*infant mortality is the most influential indicator of health status
** ATSI 2x rates higher
18
New cards
Compare the leading causes of morbidity for those young and old.
Morbidity:
Young - asthma, self-harm, mental illness.
Older - dementia, heart disease.
Young - asthma, self-harm, mental illness.
Older - dementia, heart disease.
19
New cards
What are the most commonly diagnosed cancers for both males and females?
2021 most commonly diagnosed cancers:
M - prostate, melanoma, colorectal.
F - breast, colorectal, melanoma.
M - prostate, melanoma, colorectal.
F - breast, colorectal, melanoma.
20
New cards
In what population groups is the rates of morbidity the highest?
ATSI + rural
21
New cards
What has contributed to increases in incidence of morbidity?
increases in incidence due to aging population + better technologies to identify + diagnose disease
22
New cards
What are the trends in ATSI life expectancy?
- ATSI life expectancy increasing (still gap) due to reduced bronchitis + emphysema
- health promotion initiatives aligned w/ education
- reduced infant mortality
- health promotion initiatives aligned w/ education
- reduced infant mortality
23
New cards
What are the trends in overall life expectancy?
LE overall increasing:
- decreased mortality + infant mortality
- decline in death rates from CVD, cancer + traffic accidents
- live longer due to medical knowledge + technologies
- morbidity remains steady as health problems still exist
- decreased mortality + infant mortality
- decline in death rates from CVD, cancer + traffic accidents
- live longer due to medical knowledge + technologies
- morbidity remains steady as health problems still exist
24
New cards
What are indicators of morbidity?
Prevalence + incidence
25
New cards
How do the social justice principles influence identifying priority health issues?

26
New cards
How do priority population groups influence identifying priority health groups?
Receive more funding + focus of health campaigns to address health gaps e.g. ATSI, elderly.
E.g. 10yr gap health gap, higher death rates in remote areas.
*Royal Flying Doctor Service improving access to health in remote areas
E.g. 10yr gap health gap, higher death rates in remote areas.
*Royal Flying Doctor Service improving access to health in remote areas
27
New cards
How does prevalence influence identifying priority health groups? Provide examples.

28
New cards
How does potential for change and early intervention influence identifying priority health issues? Which diseases can be prevented or require early intervention?
Disease places high economic + health burden on indvs + communities.
Early intervention + preventative measures decreases incidence + increases survival rates.
Which diseases can be prevented?
- Type 2 diabetes
- skin cancer
- CVD
Which require early intervention?
- prostate cancer
- breast cancer
Early intervention + preventative measures decreases incidence + increases survival rates.
Which diseases can be prevented?
- Type 2 diabetes
- skin cancer
- CVD
Which require early intervention?
- prostate cancer
- breast cancer
29
New cards
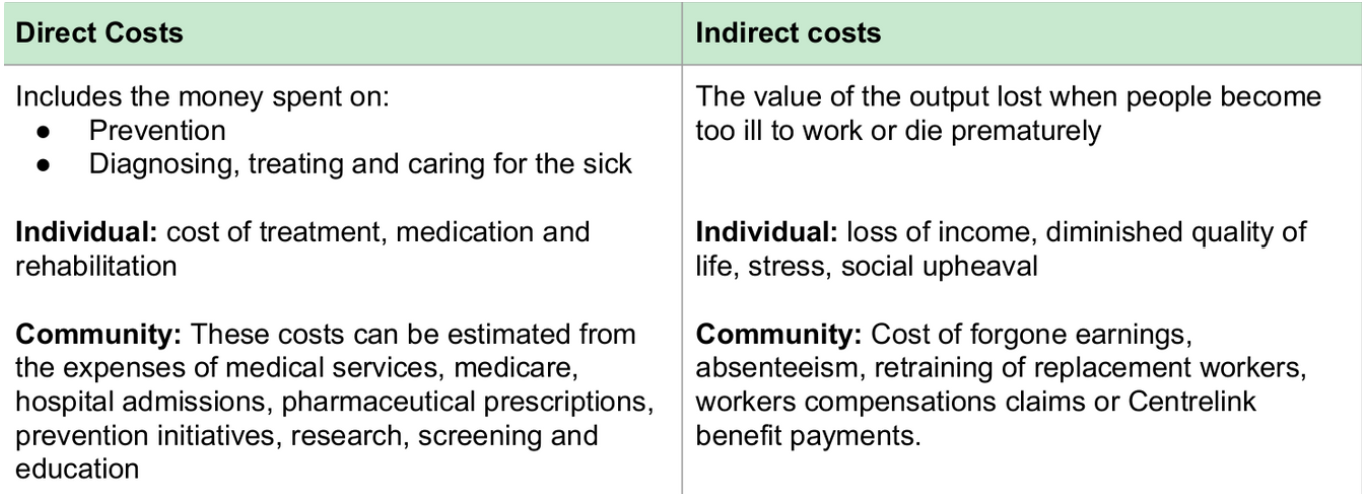
How does costs towards individuals and communities influence identifying population group. Give examples of costs.
Financial loss (i.e. cost of treatment), time, loss of productivity/ability to work, diminished quality of life and emotional stress.
Cost of CVD to gov + cancer respectively is approx $12 billion annually + increasing each year.
Cost of CVD to gov + cancer respectively is approx $12 billion annually + increasing each year.
30
New cards
Discuss why dementia has been identified as a priority health issue using the 5 indicators.
- prevalence increasing
- N.1 cause of death for women 65+
- brain stimulation activities e.g. crosswords may prevent early onset
- increased research into effects of concussions (contact sports)
- does not discriminate
- N.1 cause of death for women 65+
- brain stimulation activities e.g. crosswords may prevent early onset
- increased research into effects of concussions (contact sports)
- does not discriminate
31
New cards
Why is it important to prioritise?
- meets needs of the dis
- creates supportive environments
- lowers prevalent issues
- empowers indvs
- fair allocation of resources
- creates supportive environments
- lowers prevalent issues
- empowers indvs
- fair allocation of resources
32
New cards
What percentage of the Australian population account for ATSI?
3%
33
New cards
What is the life expectancy gap between ATSI and non-ATSI?
10yrs
34
New cards
How many times more likely are ATSI to get diabetes?
3x
35
New cards
What percentage of ATSI receive a HSC or higher?
50%
36
New cards
What is the trend in ATSI child and infant mortality rates?
Child mortality rates decreasing.
Infant mortality significantly decreasing - contributes to higher life expectancy.
Infant mortality significantly decreasing - contributes to higher life expectancy.
37
New cards
What are the leading causes of death for ATSI?
Circulatory diseases (CVD) + neoplasms (irregular cells causing cancer) leading causes of death.
38
New cards
What are the leading causes of morbidity for ATSI?
Hyperopia (long-sighted) + asthma leading causes of morbidity.
39
New cards
What are ATSI unwilling to adopt?
Westernised medical practices.
40
New cards
How many times more likely are ATSI to have kidney disease?
7x
41
New cards
How many times more likely are ATSI to have cancer?
1.5x
42
New cards
How many times more likely are ATSI to commit suicide?
6x more female suicide rates + 4x males.
43
New cards
How do the socioeconomic, sociocultural and environmental determinants contribute to ATSI health inequalities?

44
New cards
What percentage of ATSI homes are in the lowest income bracket?
50%
45
New cards
What is the trend for ATSI median income?
median income 55% of non-ATSI
46
New cards
How many times higher is the ATSI unemployment rate?
3x
47
New cards
What percentage of ATSI are blue collar workers?
25%
48
New cards
How many times higher is the ATSI homelessness rate?
4x
49
New cards
What are the trends in motor vehicle ownership between ATSI and non-ATSI?
50% own motor vehicle compared to 85% non-ATSI
50
New cards
How many times more likely are ATSI to be raised by a single parent and what are the connotations?
2x more likely to be raised by single parent (low SES assoc)
51
New cards
Give examples of non-measurable inequities that ATSI experience?
non-measurable inequities e.g. loss of identity, lack of ATSI role models
52
New cards
What is the role of individuals, groups and the government in addressing inequities in ATSI health?

53
New cards
How has the NRL addressed ATSI health inequities?
E.g. NRL ‘Indigenous All Stars v NRL All Stars’ + ‘Indigenous Round’.
Respects, acknowledges + celebrates on a national stage.
Develops identity + pride.
Showcase to celebrate role models e.g. Johnathan Thurston.
Respects, acknowledges + celebrates on a national stage.
Develops identity + pride.
Showcase to celebrate role models e.g. Johnathan Thurston.
54
New cards
What areas in 'Close the Gap' (2016) are on track?
On track: infant mortality rates, numeracy + literacy, Yr12 attainment.
55
New cards
What areas in 'Close the Gap' (2016) are not on track?
Not on track: early childhood education, school attendance, mortality rates.
56
New cards
What are solutions to 'Closing the Gap'?
Solutions: acknowledging culture, nurturing optimism for change, strengthening community action (Ottawa Charter).
57
New cards
What percent of Aus lives in rural or remote areas?
30%
58
New cards
How many times higher are rural and remote death rates?
1.5x
59
New cards
Give examples of what rural and remote experiences higher rates of.
Higher disability, cancer, diabetes, transport accidents, suicide, stroke rates.
Higher rates of obesity, smoking, inactivity, risky alcohol consumption, cholesterol levels, preventable hospitalisations + poorer access to aged care.
More likely to defer treatment e.g. dental work.
Higher rates of obesity, smoking, inactivity, risky alcohol consumption, cholesterol levels, preventable hospitalisations + poorer access to aged care.
More likely to defer treatment e.g. dental work.
60
New cards
How do the socioeconomic, sociocultural and environmental determinants contribute to rural and remote health inequalities?

61
New cards
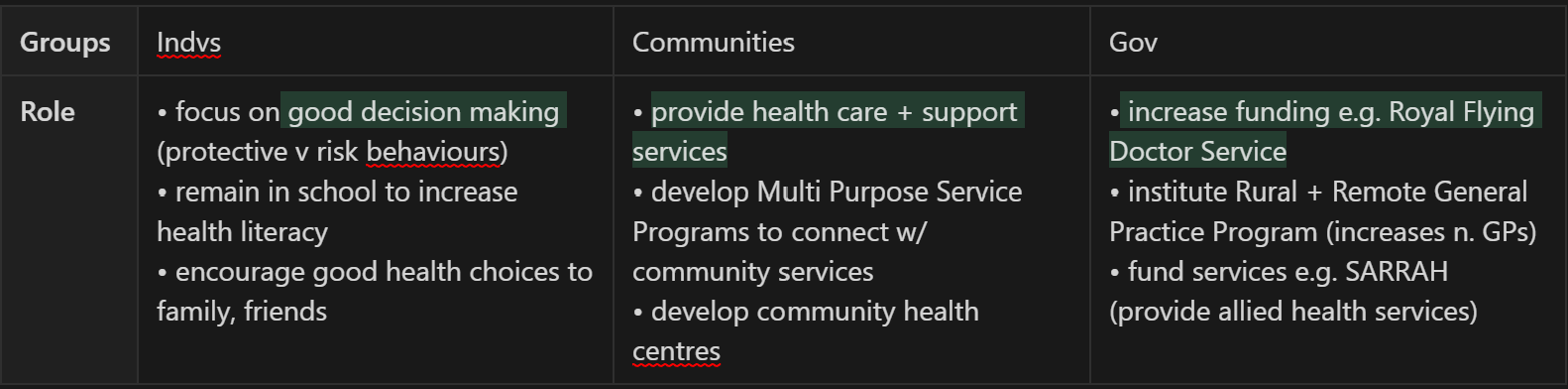
What is the role of individuals, groups and the government in addressing inequities in rural and remote health?
62
New cards
How much has Aus population increased?
Aus popultion has doubled from 12 million in 1968 to 24 in 2022.
63
New cards
How does WHO define 'healthy ageing?'
process of developing + maintaining the functional ability that enables wellbeing in older age
64
New cards
What are the benefits of engaging in healthy ageing?
Engaging in healthy ageing:
- reduces burden on health services e.g. nursing homes
- reduces burdens of families e.g. carers
- increase contribution to workforce + environment
- increase chance of living in own home
- reduces burden on health services e.g. nursing homes
- reduces burdens of families e.g. carers
- increase contribution to workforce + environment
- increase chance of living in own home
65
New cards
What does healthy ageing include?
Includes: nutritious diet, light exercise e.g. lawn bowls, socialising, mental e.g. crosswords.
66
New cards
Why will there be an increased population living with chronic disease and disability?
Increases in n. people surviving heart attacks, strokes + cancer > increases in n. Aus living w/ chronic disease/disability.
Likelihood of developing increases w/ age.
Aged population will double by 2055 (better diagnostic + access to health services).
Likelihood of developing increases w/ age.
Aged population will double by 2055 (better diagnostic + access to health services).
67
New cards
How large is the demand for health services and why are there workforce shortages.
Poor enrolment into health profession due to: insufficient pay, challenging work hours > reduced workforce.
N. elderly requiring daily medical assistance doubled in past few years.
N. elderly requiring daily medical assistance doubled in past few years.
68
New cards
What percentage of carers and volunteers are family members or spouses?
80%
69
New cards
What organisations/systems provide care for the elderly?
Org providing care: state-run hospitals, nursing homes (need more funding), Meals on Wheels, community nurses + transport.
70
New cards
Give examples of what carers of the elderly are responsible for and why there are workforce shortages?
Responsible for wide range of needs e.g. shopping, cleaning, bathing, administering medication.
Poor/limited pay + lack of societal respect > reduced numbers.
Poor/limited pay + lack of societal respect > reduced numbers.
71
New cards
What do health care facilities provide?
Hc facilities provide range range of services for prevention, treatment + management of injuries + illness > more holistic view of health (dimensions + determinants).
72
New cards
What are the four types of Australian health facilities and services?
1. Public health services
2. Primary care + community health care services
3. Specialised health services
4. Hospitals
2. Primary care + community health care services
3. Specialised health services
4. Hospitals
73
New cards
What are public health services?
• key focus - prevention, promotion + protection
• services target broad pop.
• include education + awareness programs, infection control, promoting positive legislation
• e.g. hp, cancer screening, immunisation
• services target broad pop.
• include education + awareness programs, infection control, promoting positive legislation
• e.g. hp, cancer screening, immunisation
74
New cards
What are primary care and community health care services?
• most first points of contact w/ GP
• 2016/17 150 million claims made totaling $11 billion through PBS
• community services e.g. antenatal/postnatal support, dieticians, physiotherapists
• 2016/17 150 million claims made totaling $11 billion through PBS
• community services e.g. antenatal/postnatal support, dieticians, physiotherapists
75
New cards
How much do hospitals account for in health care expenditure, and what are the two types?
• account for 40% hc expenditure
• public hospitals funded by gov + accessed through Medicare
• private hospitals run as private entities + accessed through private health insurance
• public hospitals funded by gov + accessed through Medicare
• private hospitals run as private entities + accessed through private health insurance
76
New cards
What are specialised health services?
• target particular conditions e.g. mental illness, drug + alcohol reliance, IVF
• use of service increasing esp. mental health
• use of service increasing esp. mental health
77
New cards
Has health care funding increased or decreased in the past decade?
- spending on health increased 50% in past decade
- $110 billion (2006/07) > $200 billion (2019/20)
- compares with 17% pop. growth
- $110 billion (2006/07) > $200 billion (2019/20)
- compares with 17% pop. growth
78
New cards
How much do Governments contribute to health care compared to NGOs?
- gov funds 2/3 of all spending
- non-gov 1/3 (indvs contribute 1/2)
- non-gov 1/3 (indvs contribute 1/2)
79
New cards
Separate the responsibilities of the three levels of government and the private sector in health care?
80
New cards
Why does equity exist in health care?
Equity exists so that all hc facilities/services are evenly + fairly distributed so that all of Aus has equal opportunity to maximise their health.
81
New cards
How do Medicare and PBS help achieve equity in health care?
Medicare: provides free/minimal cost for health treatments/checkups.
Bulk billing:
- feature of Medicare that removes cost as a a barrier
- health practitioners directly bill Medicare
- promotes equity for low SES
PBS: Aus Gov subsidises common prescriptions making it more affordable.
- new medicines added consistently
Bulk billing:
- feature of Medicare that removes cost as a a barrier
- health practitioners directly bill Medicare
- promotes equity for low SES
PBS: Aus Gov subsidises common prescriptions making it more affordable.
- new medicines added consistently
82
New cards
What is the Medicare levy surcharge and what is its aim?
- standard levy 2%
- earning above $90k/part of family $180k must pay surcharge (extra 1-1.5%)
- acts as incentive to take out private insurance (don’t pay surcharge)
- earning above $90k/part of family $180k must pay surcharge (extra 1-1.5%)
- acts as incentive to take out private insurance (don’t pay surcharge)
83
New cards
How does the Royal Flying Doctor service and Mobile Dental services promote equity in access?
Royal Flying Doctor Service: provides 24hr, 365 day aeromedical emergency + hc services to remote areas
- emergency evacuation, hc clinics, telephone + radio consultations
- receives grants from gov + relies on donated funds
Mobile dental services: free for ATSI (’Close the Gap’), wheelchair accessible (elderly)
- emergency evacuation, hc clinics, telephone + radio consultations
- receives grants from gov + relies on donated funds
Mobile dental services: free for ATSI (’Close the Gap’), wheelchair accessible (elderly)
84
New cards
How much is spent on curative compared to preventative services?
90% treatment + curative services.
2% preventative + early intervention initiatives i.e. $4/200 billion
2% preventative + early intervention initiatives i.e. $4/200 billion
85
New cards
What are the benefits of preventative services and health promotion?
- reduced mortality + morbidity
- increased life expectancy
- enhanced quality of life
- reduced impact on carers, family + friends
- increased life expectancy
- enhanced quality of life
- reduced impact on carers, family + friends
86
New cards
What is the main benefit of early intervention and give examples for how it is achieved?
Early intervention: increased survival rates (likelihood of recovery) e.g. screening - mammograms, pap smears, skin cancer checks.
- healthy canteens - gov schools sell food meeting clearly defined criteria
- workplace health checkups - periodical checks subsidised/free
- legislation for safe workplaces - no smoking in pubs + clubs
- RMS - cycling lanes on new major roads
- healthy canteens - gov schools sell food meeting clearly defined criteria
- workplace health checkups - periodical checks subsidised/free
- legislation for safe workplaces - no smoking in pubs + clubs
- RMS - cycling lanes on new major roads
87
New cards
Why is it easier for the government to spend money on curative rather than preventative services?
- must wait to see results - curative shown through epidemiology
- cannot control indv behaviours e.g. smoking, wearing spf
- cannot control indv behaviours e.g. smoking, wearing spf
88
New cards
What is the impact of emerging technologies and treatments on health care?
- improves early detection > earlier treatment > increased chance of survival
- improves treatment + prevention > increased quality of life
- increases in ageing pop. + n. living w/ chronic disease
- high costs > increased need for hc expenditure > if not funded through Medicare > dis low SES
- poorer access in rural areas due to cost
- improves treatment + prevention > increased quality of life
- increases in ageing pop. + n. living w/ chronic disease
- high costs > increased need for hc expenditure > if not funded through Medicare > dis low SES
- poorer access in rural areas due to cost
89
New cards
Describe apps and the impact they have on health care?

90
New cards
Describe an MRI and the impact it has on health care?

91
New cards
Describe key hole surgery and the impact it has on health care?

92
New cards
What does Medicare cover?
- free hospital care
- free/subsidised GP treatment, specialists + optometrists
- prescription medicine
- free/subsidised GP treatment, specialists + optometrists
- prescription medicine
93
New cards
How does Medicare address the social justice principles?
Equity - free/low cost allowing for low SES access
Diversity - for all
SE - improved access to hc services
Diversity - for all
SE - improved access to hc services
94
New cards
How is Medicare funded?
Funded by tax system through Medicare levy (2% taxable income).
95
New cards
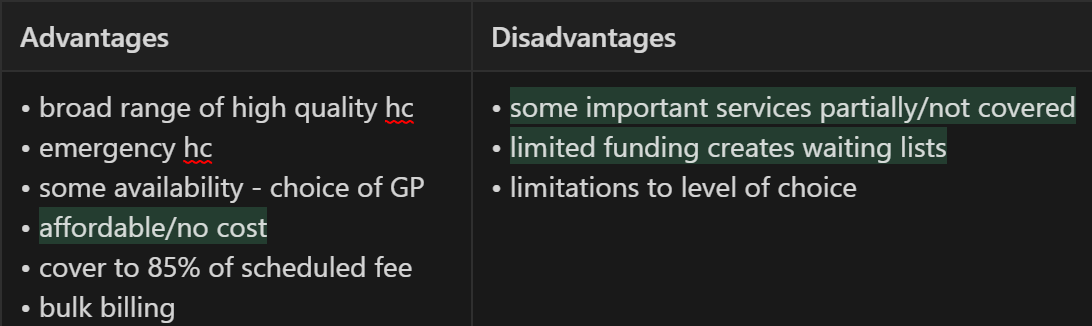
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Medicare?
96
New cards
What are the advantages and disadvantages of private health insurance?

97
New cards
Why might a private patient choose to be treated as a public patient?
Private patient may choose to be treated as public if bad experience + some private hospitals small (less services).
98
New cards
Differentiate between complementary and alternate health care.
Complementary - used together with western medicine
Alternative - used instead of western medicine
Alternative - used instead of western medicine
99
New cards
Give examples of complimentary and alternate health care.
- natural medicines (herbs, nutrition, homeopathy, Chinese medicine)
- supplementation (vitamins, minerals, oils, protein, vegetable powders)
- physiological treatment (physiotherapy, osteotherapy, remedial massage, occupational therapists, acupuncture )
- energy based treatments (crystals, some forms of massage, acupuncture)
- supplementation (vitamins, minerals, oils, protein, vegetable powders)
- physiological treatment (physiotherapy, osteotherapy, remedial massage, occupational therapists, acupuncture )
- energy based treatments (crystals, some forms of massage, acupuncture)
100
New cards
Account for reasons for growth of the alternate and complementary health care industry.
- $2 billion industry
- 50% pop. uses non medically prescribed medicine once a year
- 82% visit one complementary therapist a year
Reasons:
- formal qualifications - enhances credibility (professional assoc w/ guidelines)
- changes in demographic mix - multicultural society (Asia), ageing society (more health problems = looking for alternate methods)
- persuasive marketing campaigns - ‘feel good’, use of organic + natural products
- 50% pop. uses non medically prescribed medicine once a year
- 82% visit one complementary therapist a year
Reasons:
- formal qualifications - enhances credibility (professional assoc w/ guidelines)
- changes in demographic mix - multicultural society (Asia), ageing society (more health problems = looking for alternate methods)
- persuasive marketing campaigns - ‘feel good’, use of organic + natural products