Construction 1 Midterm Final Review
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Zoning Ordinances
-Governs the types of activities that may take place on a given piece of land,
-how much of the land may be covered by buildings
-how far buildings must be set back from adjacent property lines
-parking,
-floor area and height
Building Codes
Protect Public health and safety
- sets minimum standards regarding: structural integrity, livability, quality of construction, accessibility, durability,
especially fire safety
IBC (International Building Code)
predominant building code in the United States
Sprinklers, Firewalls, more than 1/4 perimeter faces public ways or open spaces
3 ways to modify (expand) Building Code limitations
Answer:
Sprinklers, Firewalls, more than 1/4 perimeter faces public ways or open spaces
Americans with Disabilities Act
What does ADA stand for?
- It makes accessibility to buildings a civil right of all Americans
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
What does OSHA stand for?
- controls the design of workplaces to minimize hazards to the health and safety of workers.
- sets safety standards under which a building must be constructed.
American Society for Testing and Materials
What does ASTM stand for?
- establishes standard specifications for commonly used materials and construction.
- provides shorthand designations for the quality of material that is required. (for example: C150 is code for "Portland Cement")
Construction Specifications Institute
What does CSI stand for?
- it is the national association that creates standards to improve construction documents and project delivery.
Masterformat
What is the standard outline created by the Construction Specifications Institute (CSI) that is used to organize information?
Joists
floors
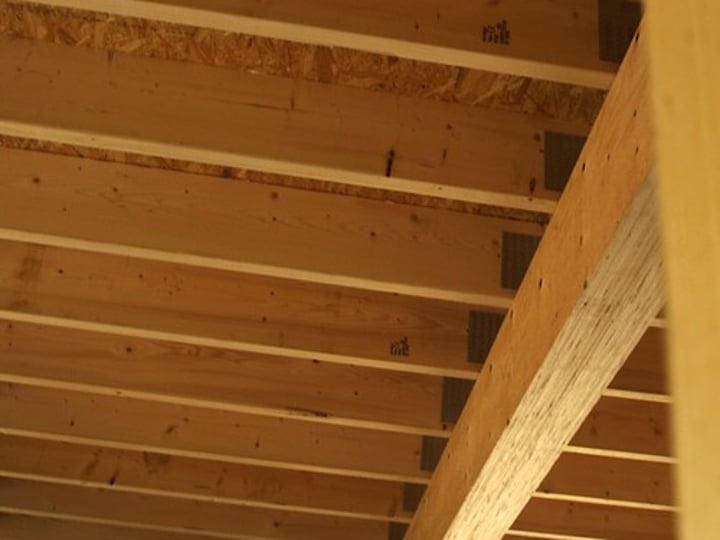

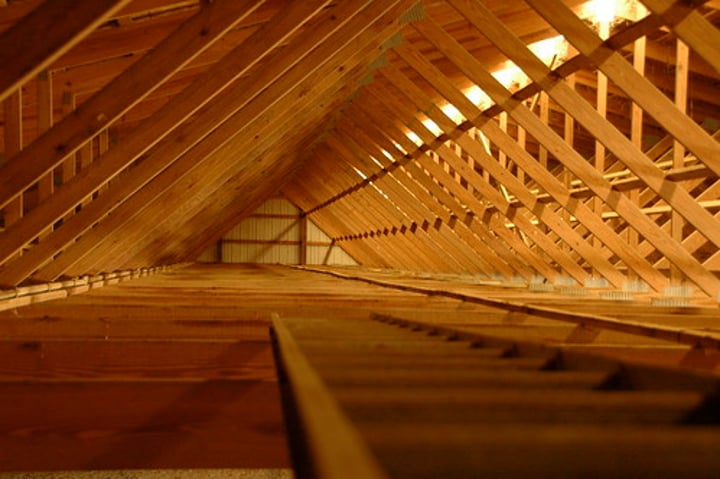
Rafters
sloping roofs

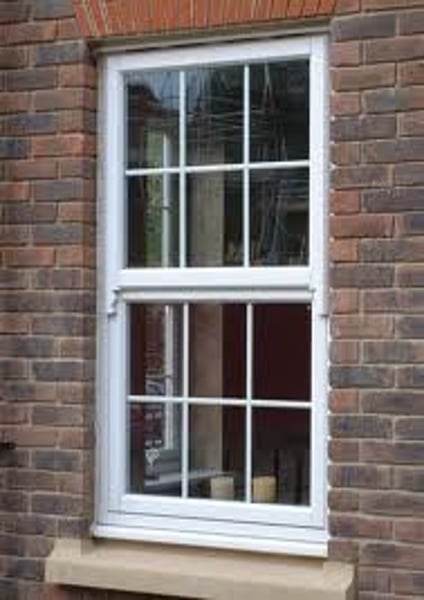
sill
the horizontal bottom portion of a window or door.

studs
walls
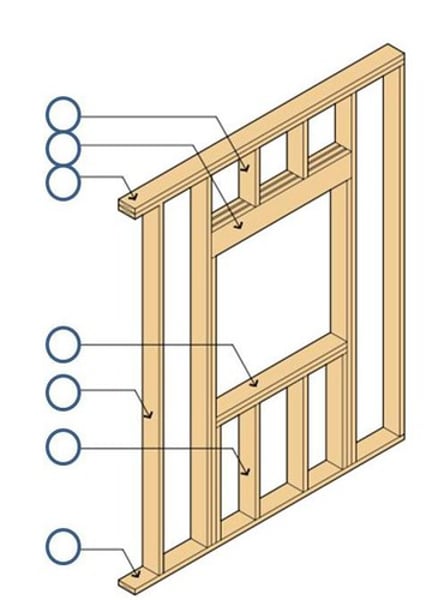
sheathing
a key component that joins and stabilizes the frame.
- 4x8 panels that are nailed to the studs
-becomes the surface for interior and exterior finishes
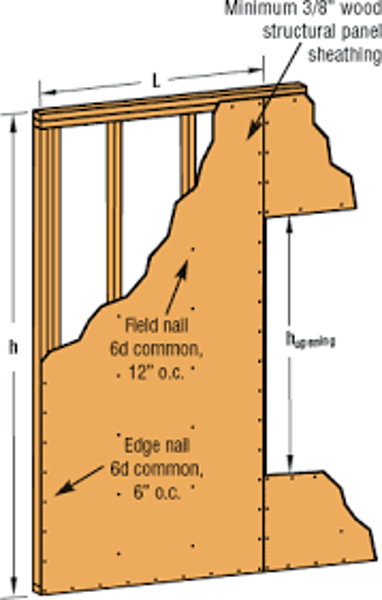
increments of 4"
What is the typical spacing of framing elements?
- this is due to the 4x8 panels that are produced only in those dimensions, therefore the spacing must match the panels.
housewrap
a synthetic sheet material with water-resistive and air-resistive properties used to provide a protective layer in an exterior wall assembly

Gable
Type of roof

Hip
Type of Roof

Gambrel
Type of Roof
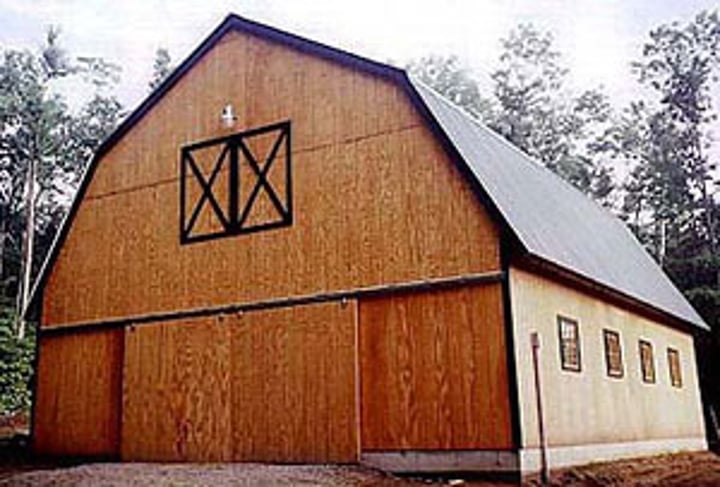

Stepped Gable
Type of roof
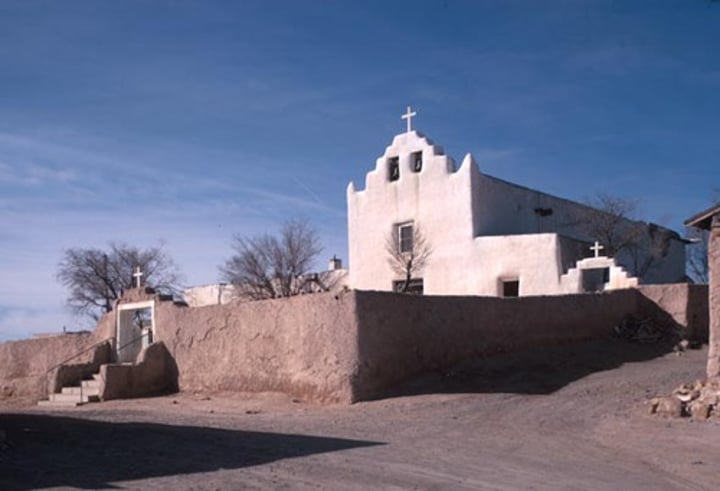

Half-hip (chamfered)
Type of Roof
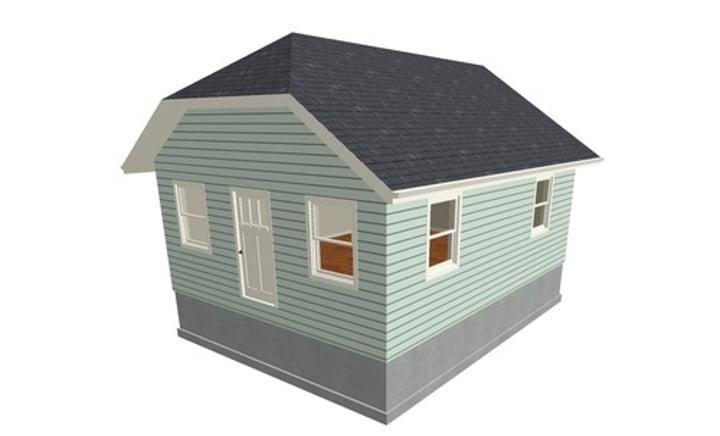

Mansard roof
Type of Roof
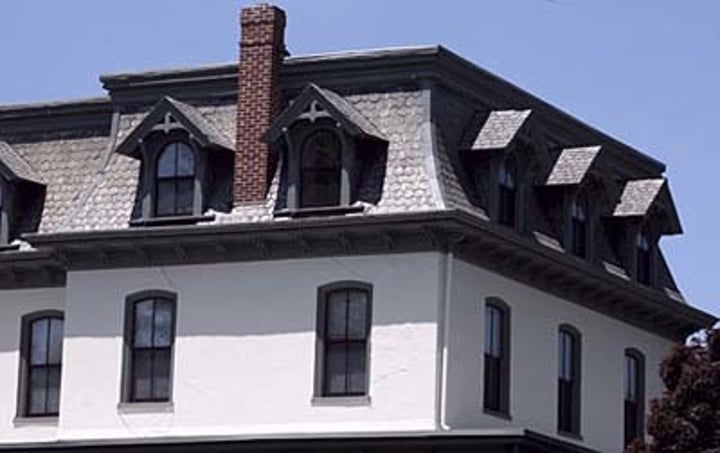

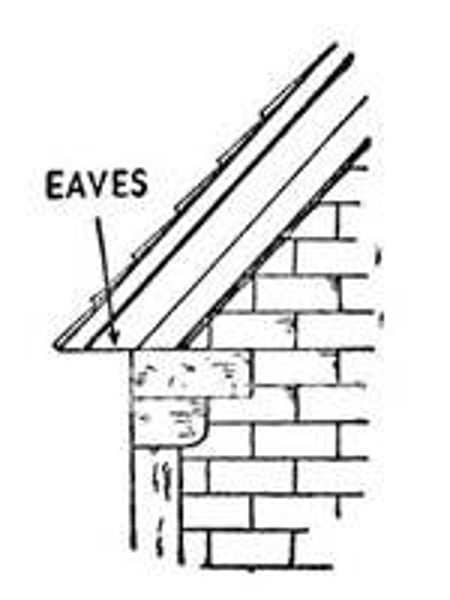
Eaves
roof edges that run parallel to the ground
rakes
roof edge that goes from the eaves upward along the gable ends.
ridge
top edge of the roof where the rafters rest
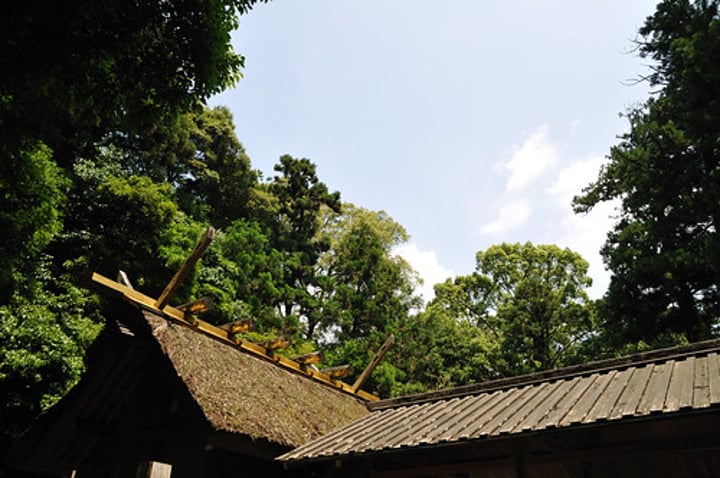

hip
formed by the meeting of two sloping roof surfaces going upward
valley
a trough formed by the intersection of two roof slopes
Pitch
the slope of the roof specified as rise to run.
- a 5:!2 slope means that for every 12" of run, there is 5" of rise.
True (because of their greater ability to absorb heat)
True or False.
Large timbers catch fire and burn more slowly than smaller pieces of wood.
1 hour
How long is the fire resistance rating of heavy timber?
along with steel, concrete, or masonry
True
True or False.
Heavy timber can continue to support loads longer than unprotected steel.
Anchorage
3 problems to be solved when timbers join concrete or masonry:
1. Protect beam from decay caused by moisture seeping through the wall - leave a ventilating airspace of at least 1/2 inch between masonry & all sides of the beam except the bottom
2. Under use, wood pulls away from wall - the wall must be anchored securely
3. Wood can pry the wall apart if it collapses- must be able to rotate freely by using a ledger board to attach the wood
Answer: Anchorage
(pg. 147)
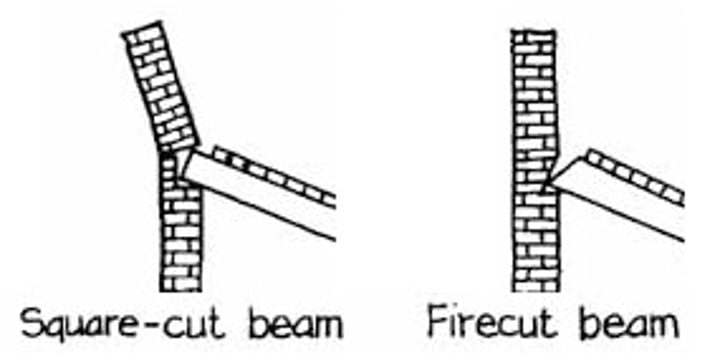
firecut beam
allows wood to move freely without breaking the wall in the event of a fire.
cruck
curved timbers extending from the ground in the roof framework of a medieval type house

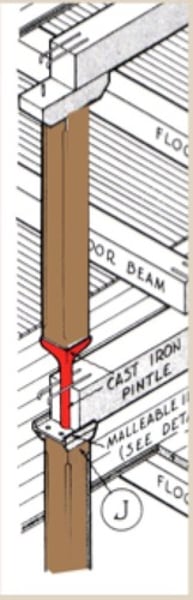
pintle
a metal device used to transmit compressive forces between superimposed columns in Mill construction
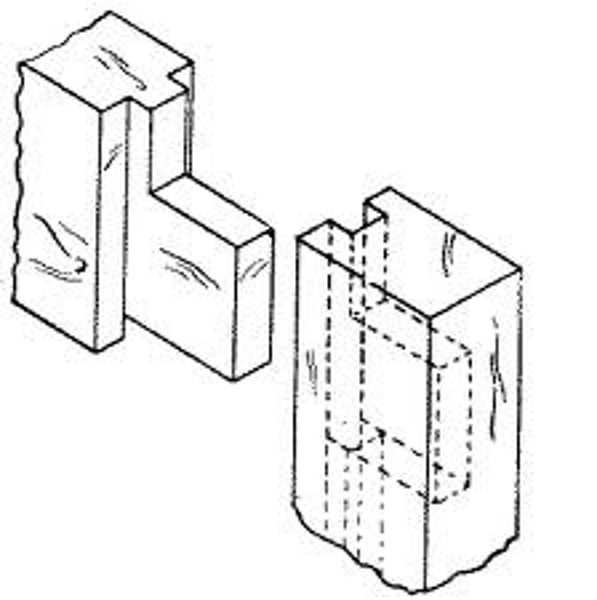
mortise
A hole cut into a piece of wood that creates joinery and locks the parts together
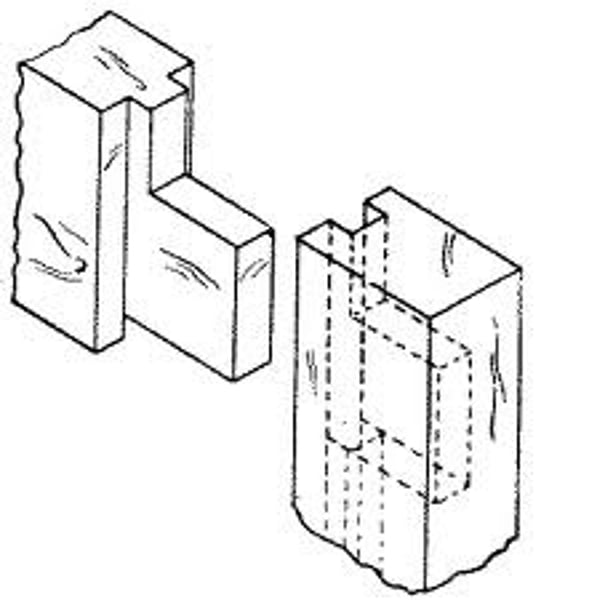
Tenon
A projecting piece of wood that locks in place in the cavity of another
bent
each plane of columns, beams, rafters, and braces that is laid out on the floor and raised to position.
(pg. 151)
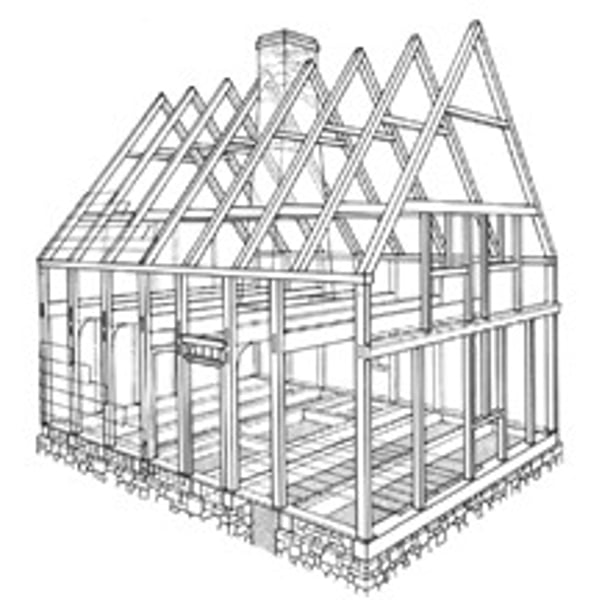
peg
holds the mortise and tenon joinery together
Hardwoods
Type of wood that comes from Deciduous trees.
- larger cell-structure
-interesting patterns
- used for flooring, paneling furniture, and interior trim
Deciduous means fruit bearing/ flowering trees
Soft woods
Type of wood that comes from Coniferous trees
- very uniform
- no grain patterns
- used for general construction
-plentiful and inexpensive
Lumber
lengths of wood that are square, for use in construction
Board
Cut wood that is less than 2 inches in nominal thickness is known as a _____________.
Dimensional lumber
pieces of wood ranging from 2-4 inches in nominal thickness.
sold in 2 in. increments
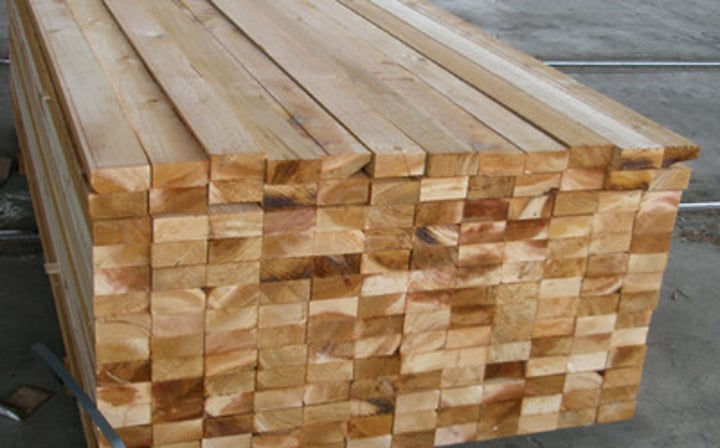

Timber
wood that is 5 inches or more in nominal thickness
given in actual sizes

Glulam
Glue Laminated Wood
used for large structural members
produced by joining together many small trips of wood with glue
- more stable than solid lumber
- more efficient use of wood

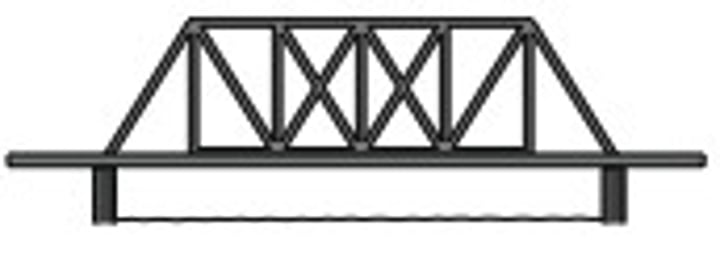
Trusses
structure that supports both roof and floor construction
I-joists
-more efficient use of wood
- can span farther
- lighter in weight
- lengths up to 40 ft.

Scarf joints
diagonal joints used on glue-laminated woods

finger joints
zigzag joints used on glue-laminated woods
4' x 8'
What is the typical wood panel size?
common, box, casing, finish, brad
5 most common nail types
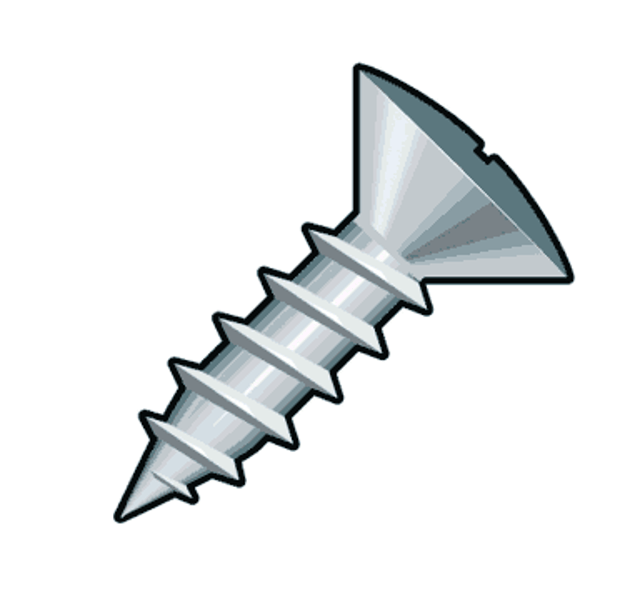
Screws
spiral-threaded fasteners installed by turning action

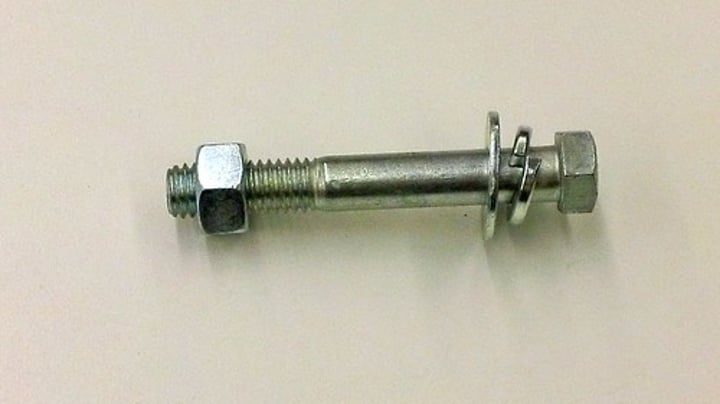
Bolts
used with washers and nuts for major structural connections

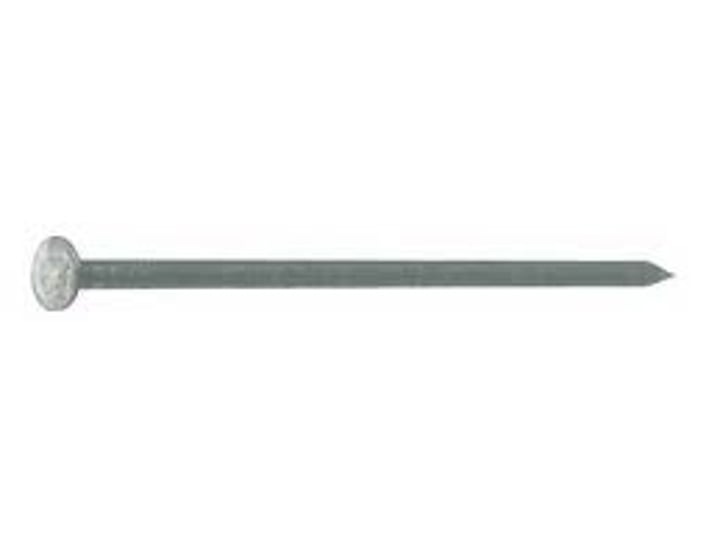
Common (box) nail
thinner nails used as structural connections in light frame construction

toothed plates
connectors used for lightweight roof and floor trusses

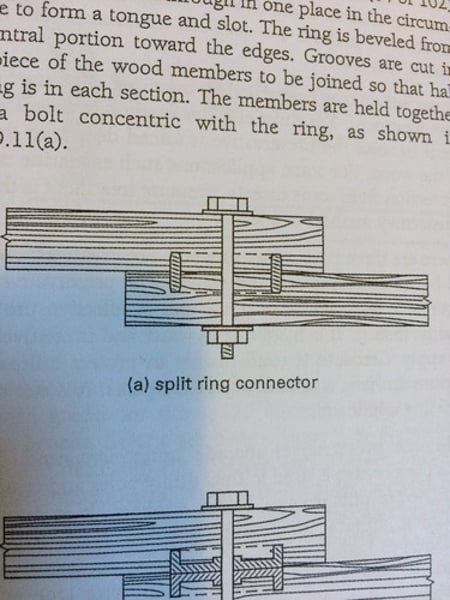
split ring connectors
connectors used often in heavy timber construction
timber rivet connectors
connectors made up of large plates fastened to timber with spike-like rivets
Plain-sawn
Sawing method that produces a variety of grain patters, wears unevenly, tends to have raised grain, shrinks and swells more in width,
most economical

Quarter-sawn
Sawing method that produces more even grain patterns, less warping, wears evenly, shrinks and swells more in thickness.
creates more waste and is more expensive
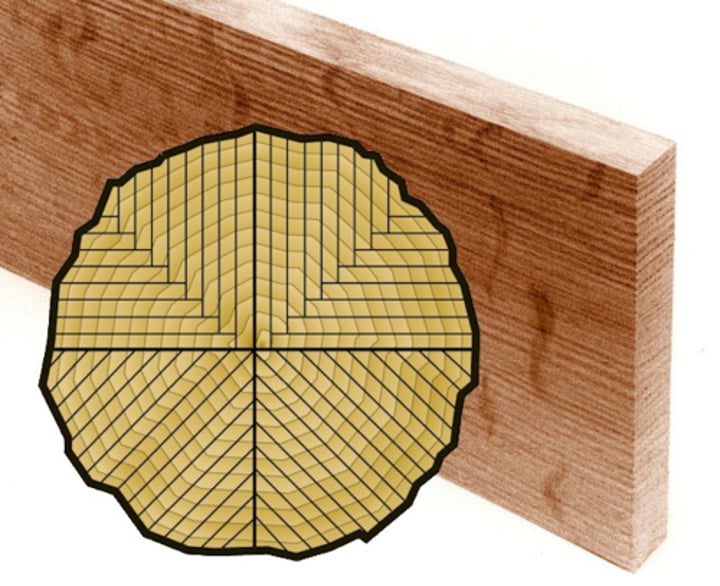
Nominal Dimensions
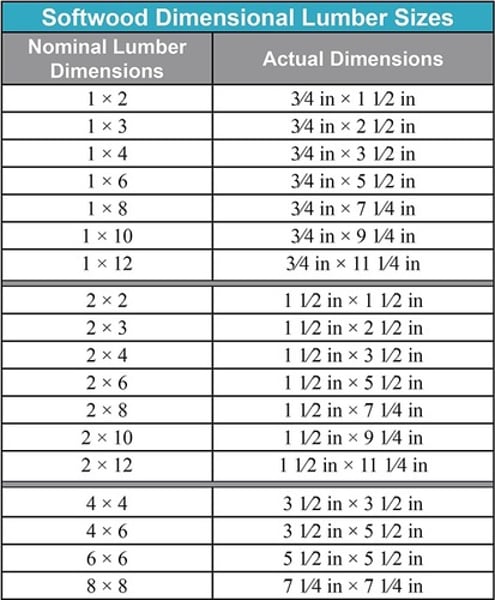
cross-laminated timber
Wood Products
- structural panels laminated from solid lumber
they may be used for floors, walls & roofs
ADVANTAGES
- produced in sizes not otherwise available
- lightweight and efficient
- rapid on-site assembly

structural composite lumber
also called Engineered Lumber
- made by compacting layers of veneers or strands of wood

Wood Plastic Composite
Made from wood or plastics
- used for exterior decking, railing, and trim (interior and exterior)

Advantages and Disadvantages of plastic lumber over wood lumber
Answer: Advantages and Disadvantages of plastic lumber over wood lumber:
ADVANTAGES
- Resists sun, water, insects
- no coatings needed (maintenance free)
- durable
- non toxic
- good alternative to pressure treated lumber
DISADVANTAGES
- more flexible
- expands/ contracts more with temp change.
span rating
the distance a building panel spans between supports
for example:
- 32/16 means that the panel may be used as roof sheathing over rafters spaced 32" o.c. and as subflooring over joists spaced 16".
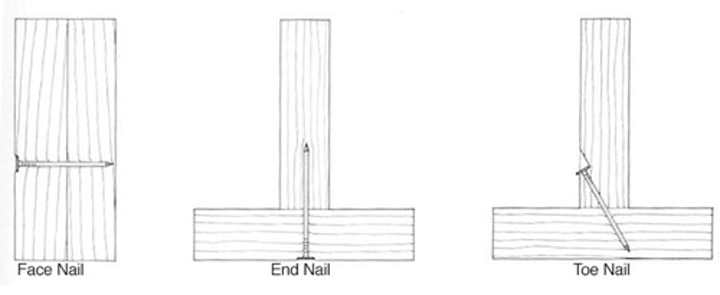
face nail, end nail, toe nail
3 methods of fastening nails
Dead load
the combined weight of the building itself and the foundation, including the permanent equipment
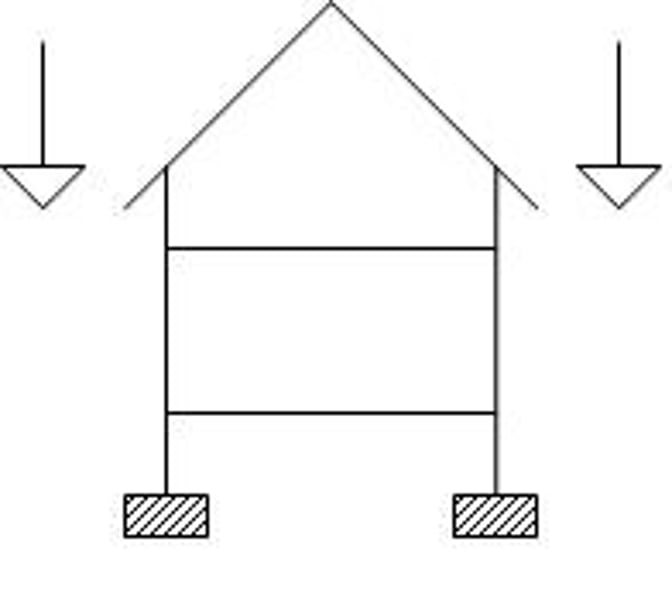
Live load
nonpermanent loads caused by the weights of the buildings occupants, furnishings and movable equipment
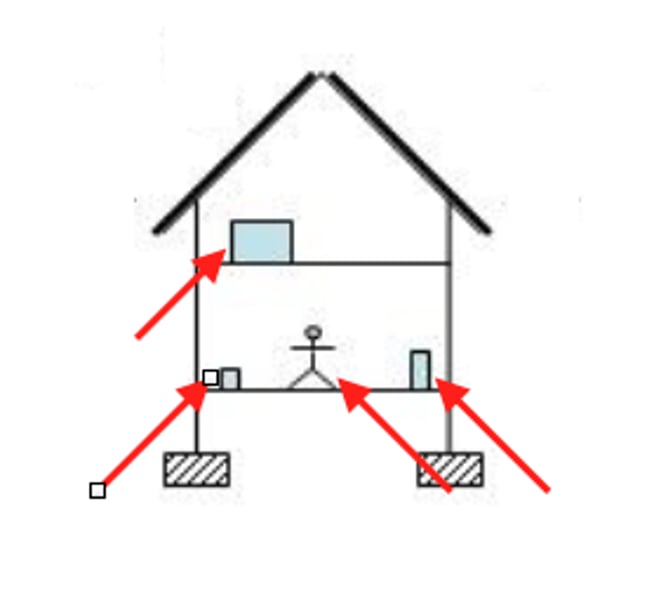
Rain and Snow Load
type of load that acts primarily downward on building roofs.
Wind Load
type of load which can act laterally (sideways), downward, or upward on a building.
Seismic Load
highly dynamic horizontal and vertical forces caused by the motion of the ground relative to the building during an earthquake.
below frost line
Where should foundations be built in relationship to the Frost Line?
Shallow and Deep
2 types of foundations
Shallow Frost-Protected Foundations
footings placed closer to the ground surface but insulated in such a way that the ground underneath them cannot freeze. (pg. 52)
- continuous layers of insulation board are placed around the perimeter of the building in such a way that heat flowing into the soil in winter from the interior of the building maintains the soil beneath the footings at a temperature above freezing.
frictional or cohensionless
Soils that rely primarily on internal friction for strength are called ________________________________ or __________________________________
- coarse-grained soil like sand or gravel
cohesive
clay soils that tend to stick together are characterized as ____________________ rather than frictional.
(sticks together)
rock, gravel, sand
3 Examples of Good Soil types to build on
silt, clay
2 Examples of Poor Soil types to build on
sloped excavation
if the construction site is sufficiently larger than the area to be covered by the building the edges of the excavation can be sloped back at a low enough angle that the soil will not slide back into the hole.
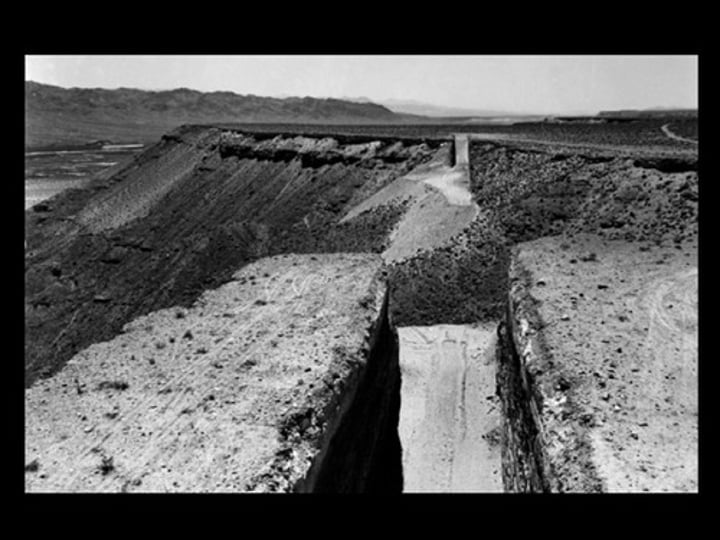

shoring
construction used to support the sides of an excavation and prevent its collapse.
For large excavations the most common types of shoring are soldier beams and lagging, and sheet piling.
pg. 40
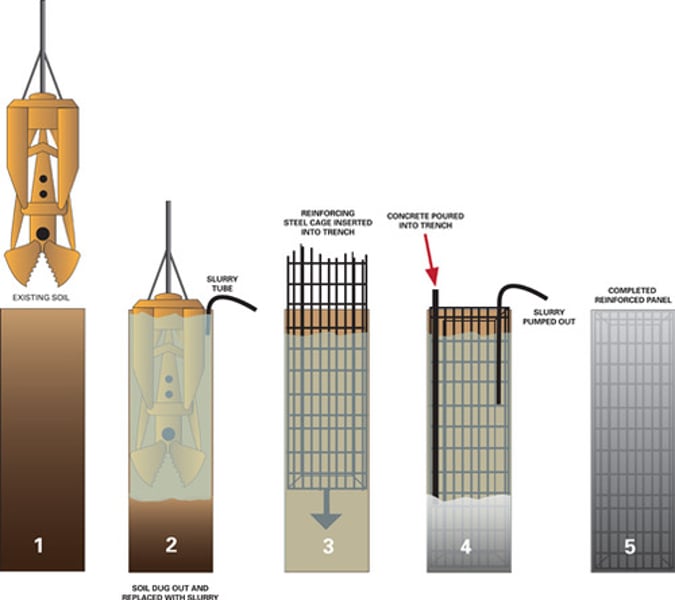
slurry wall
a complex method of constructing a complete steel-reinforced, concrete wall in the ground before excavation takes place.
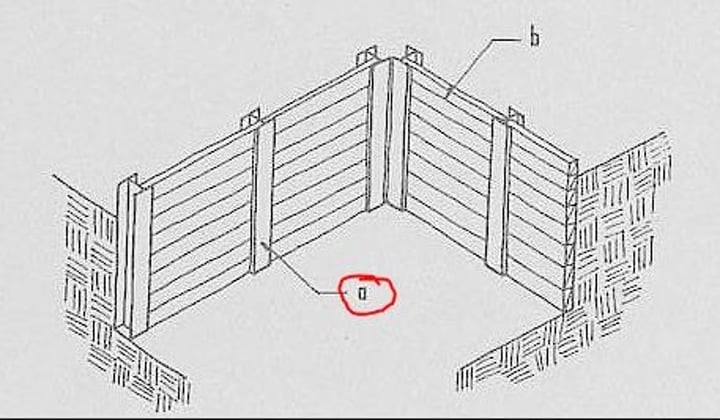
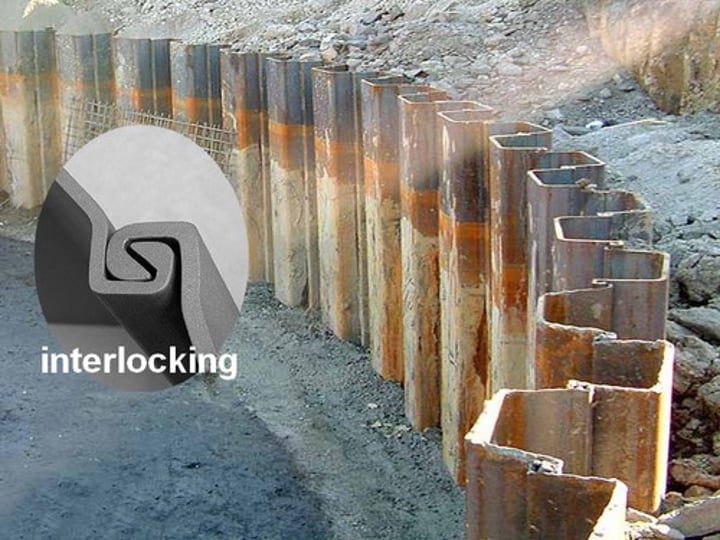
soldier beams and lagging
Type of shoring that uses steel columns driven vertically into the earth at close intervals around an excavation site before digging begins.
As earth is removed heavy wooden planks are placed against the flanges of the columns to retain the soil outside the excavation.

Sheeting (or sheet piling)
Type of shoring that consists of vertical sheets of various materials that are aligned tightly against one another edge-to-edge and driven into the earth to form a solid wall before excavation begins
- usually steel sheets but might be wood, aluminum, PVC plastic, composite polymers or precast concrete.

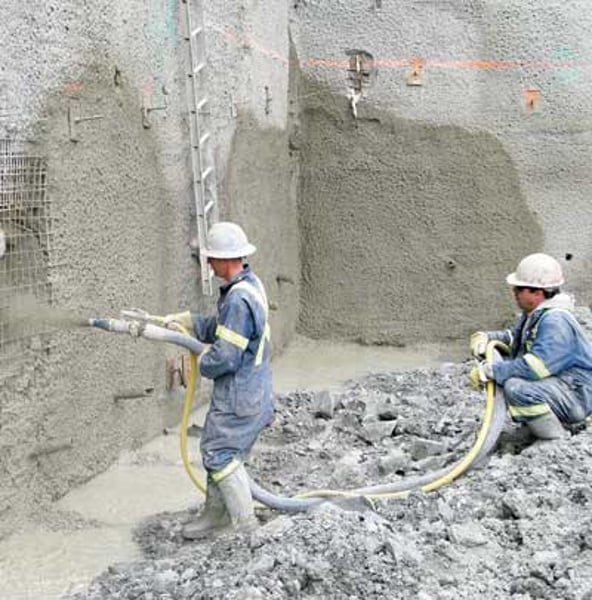
shotcrete
Stiff concrete mixture that is sprayed directly from a hose onto the soil shortly after the soil is excavated.
- the hardened concrete reinforces the slope and protects against erosion.

deep, shallow
2 types of foundations
Shallow
Type of foundation that transfers load to the earth at the base of a building's columns/walls
- must be built on undisturbed soil and below the frost line
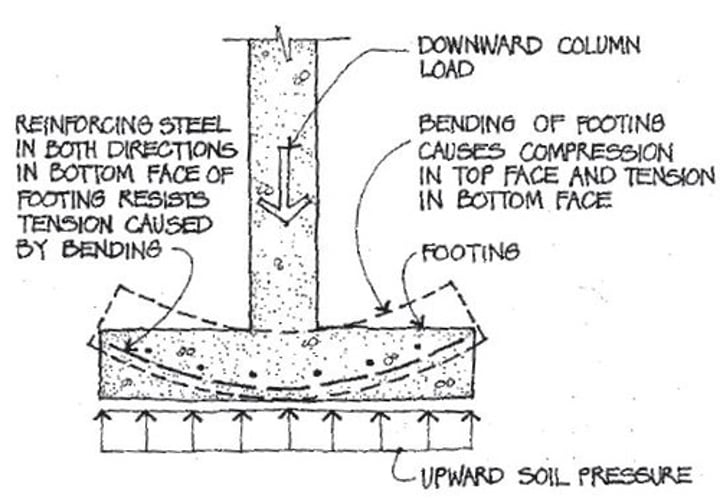
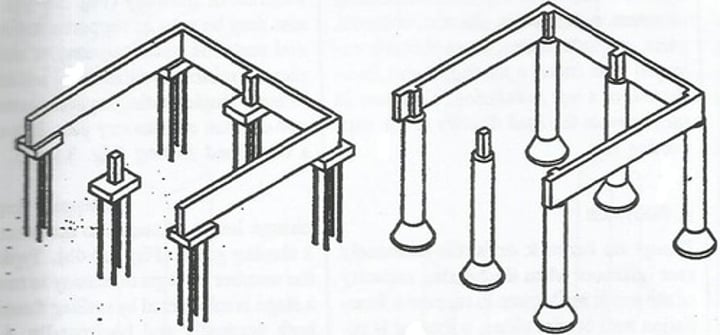
Spread footing
A type of shallow foundation that takes concentrated loads and spreads them out over a large area of soil.
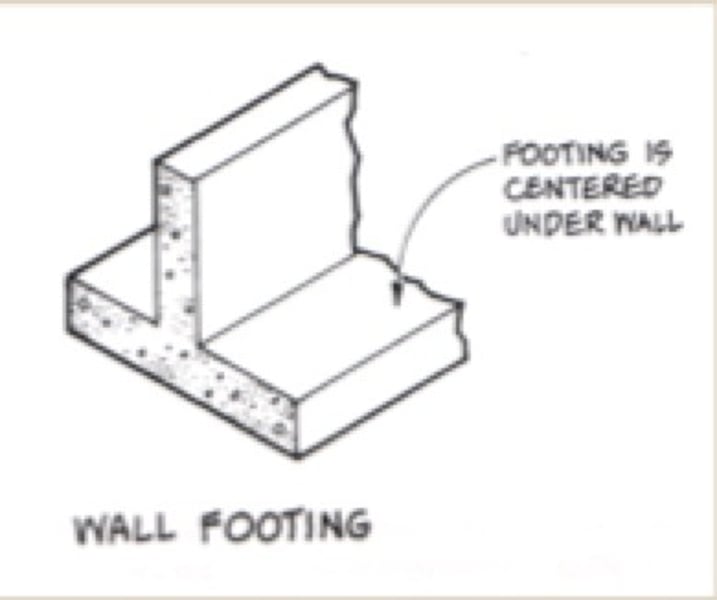
Wall Footing (or strip footing)
Type of Shallow foundation(spread footing) that is a continuous strip of concrete that spreads the load to a larger area
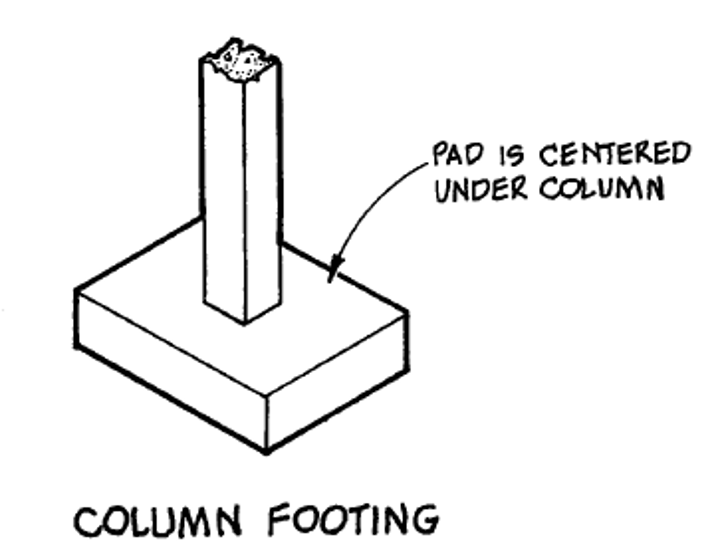
Column footing
Type of Shallow foundation (spread footing) that transfers load from building column to soil area large enough to support it.
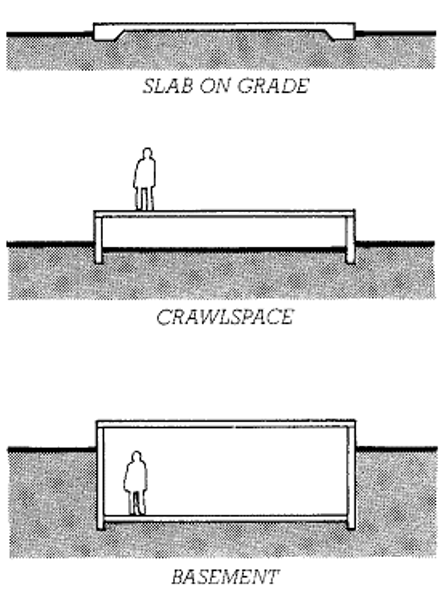
Slab on Grade
Least expensive type of shallow foundation with thickened edges.
- used for 1-2 story high buildings
- used when there is a high water table and for climates with little to no frost.
Crawl space (basement)
Type of shallow foundation supported by strip footings when the floor is raised above the ground.
-allows better access to piping and wiring.
stepped footing
Example of shallow foundation used when buildings are on a slope
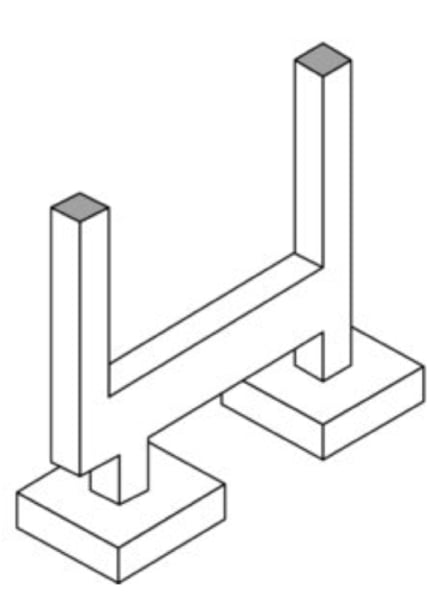
combined footings and cantilevered footings
Foundations cannot extend beyond property lines. In these cases ___________________________________ and _______________________________ are used to balance the footing design.
(pg. 53 F.2.33)
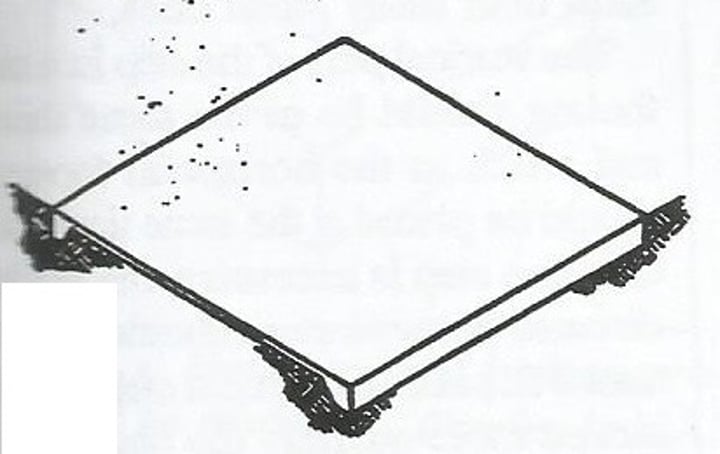
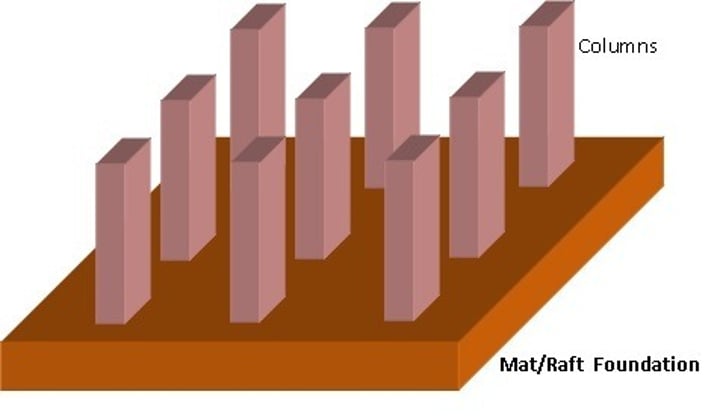
Mat/Raft foundation
where bearing capacity of the soil is low it is more economical to merge column footings into a single mat that supports the entire building.
Deep foundation
type of foundation that extends below poor soil to more competent soils or rock
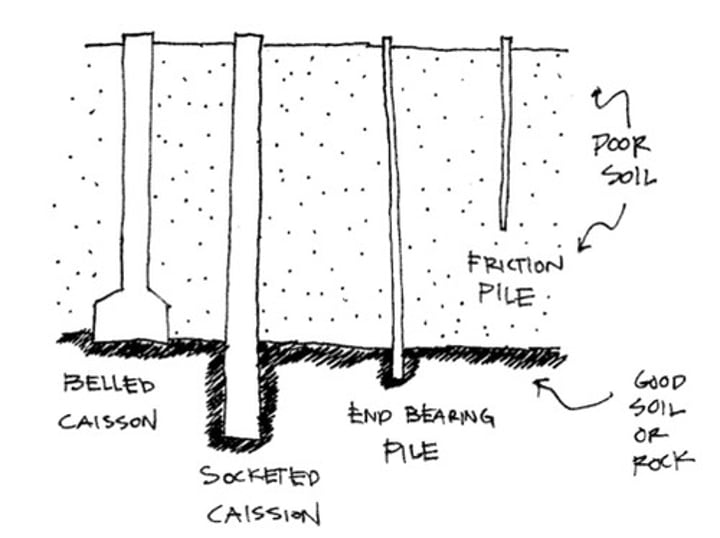
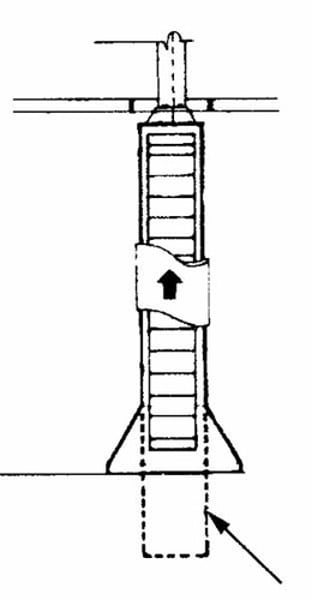
Caisson
Also known as a "drilled pier"
- it is similar to column footing but reaches through poor soil to acceptable soil.
Socketed Caisson
a type of caisson that is drilled into the rock rather than belled at the bottom.
Pile
similar to caissons, but driven into soil rather than drilled or poured.
- might be made of timber (more economical for lightly loaded foundations) or made of steel.
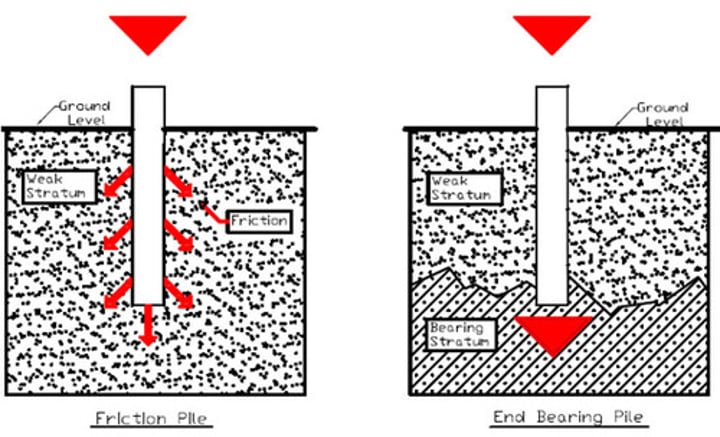
design thresholds
1. Building below the water table
2. Building Close to an existing structure
3. Building a heavier load beyond what the soil can support
These are 3 _______________________________ to take into account when designing a foundation.
- the make foundations more expensive and difficult to construct.