Thermal adaptations
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Impacts of Abioitc variables
depend on climate (temp and ppt) which vary with latitude and altitude. Plants and animals have adaptations that enable them to live in certain conditions.
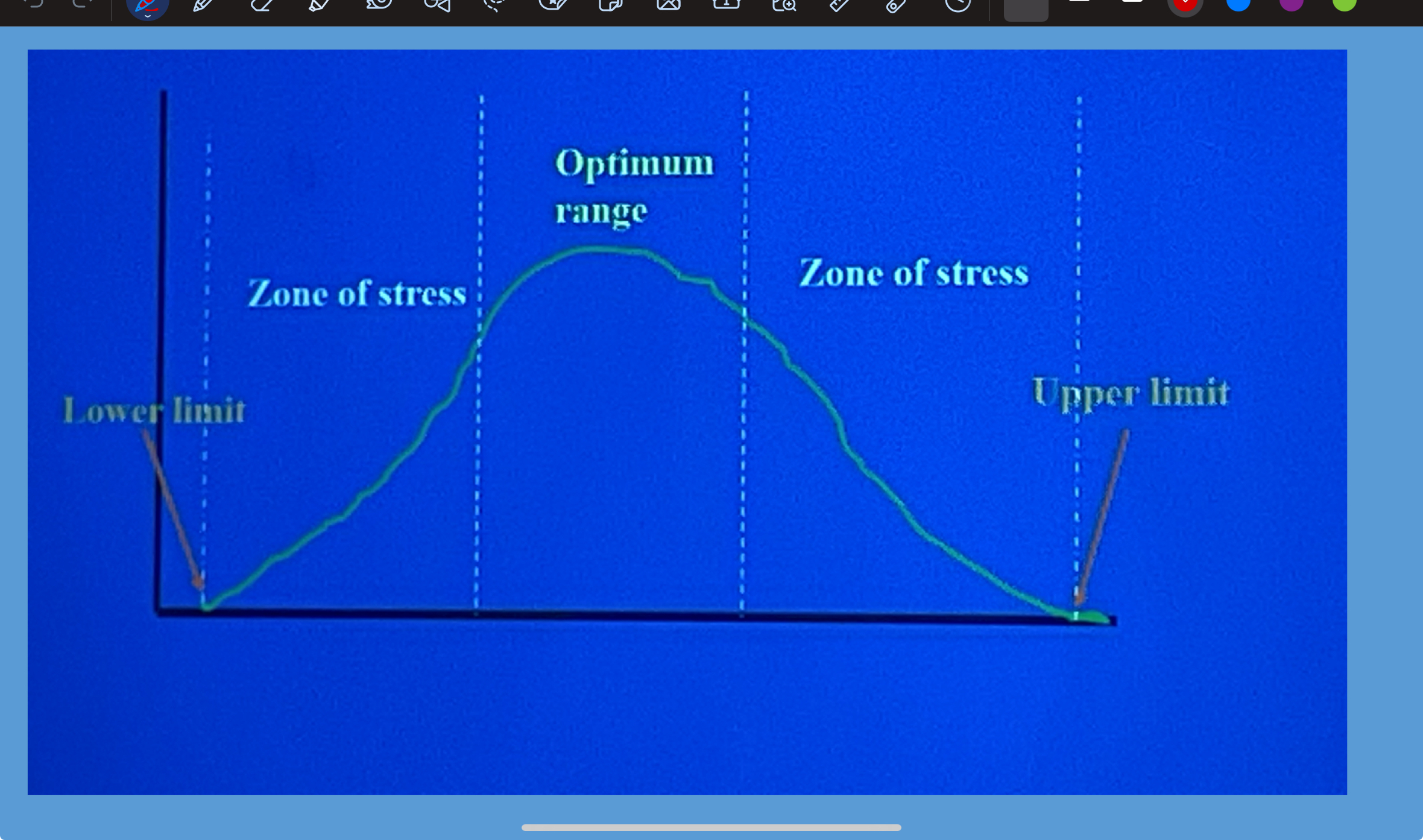
optimum level of abiotic variable
each species has an optimum level ( or zone) for each variable.
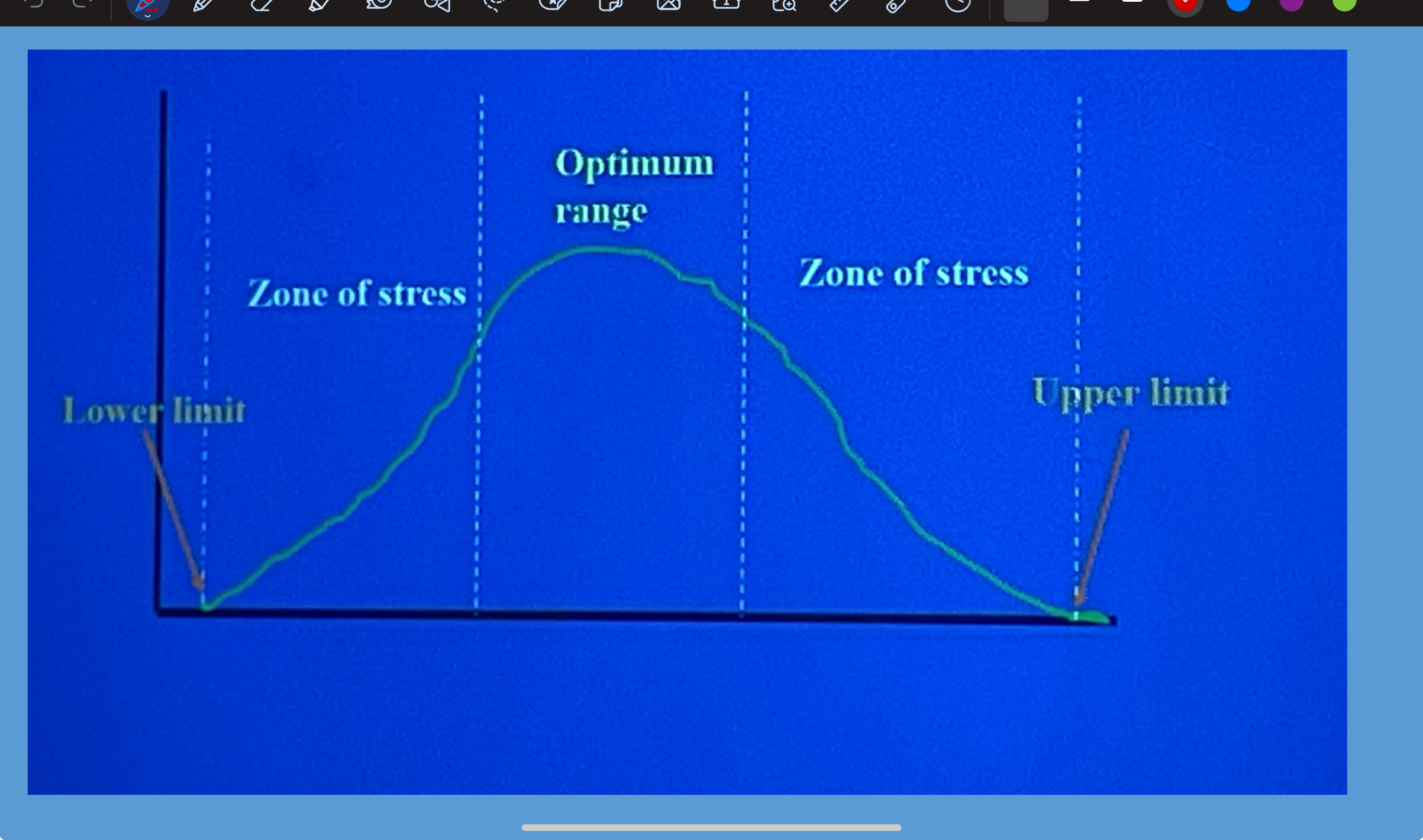
range of tolerance
the entire range over which a species can survive is its..
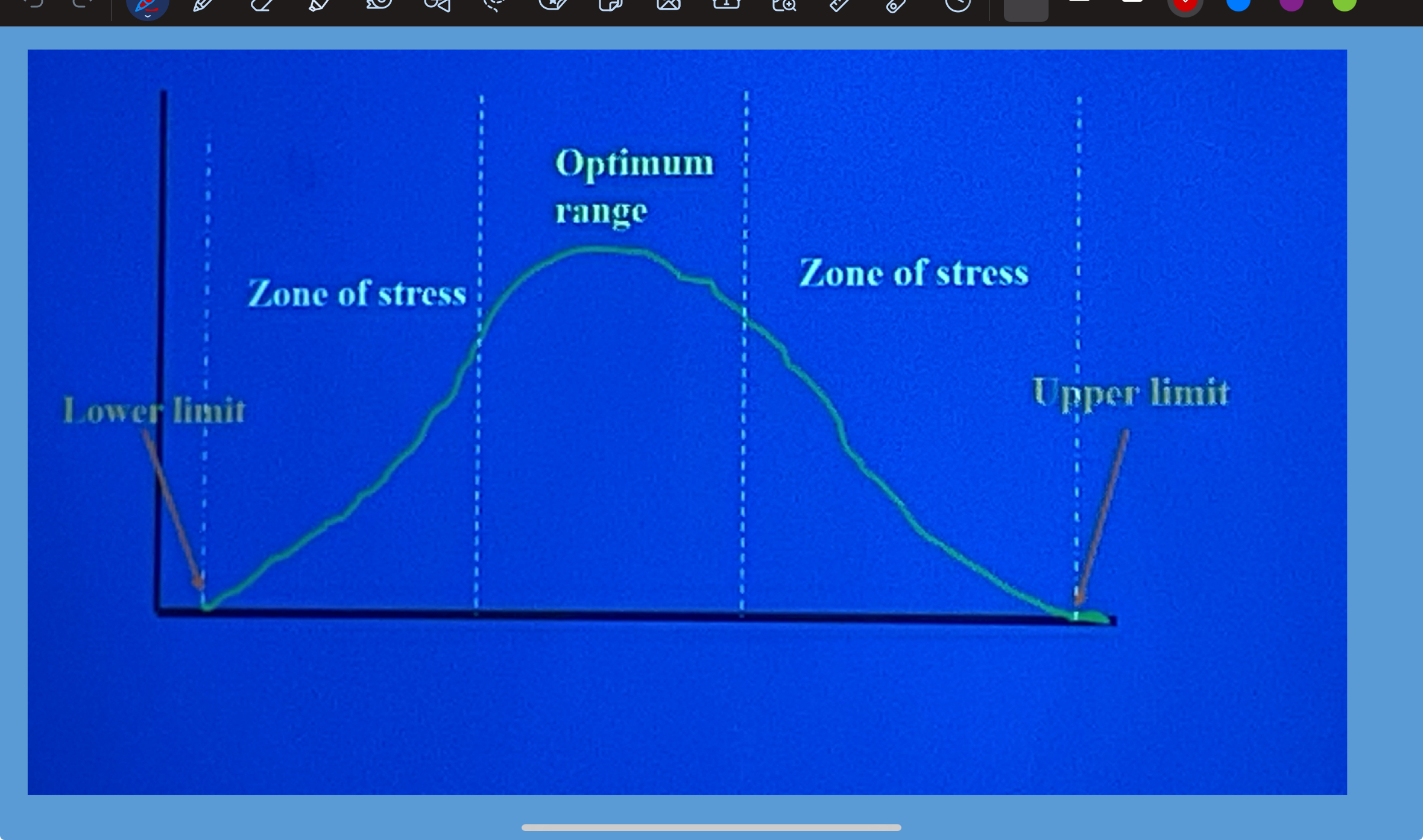
zones of stress
high and low extremes are the limits of tolerance and between the limits and the optimum are..
limiting factors
a resource that is scarce relative to its demand. Living organisms must become better at “mining” the resource, or not be present in that location.
indicator species
organisms with narrow ranges of tolerance. organisms whose presence, absence, or abundance reflects the health of their environment
synergistic effects
limiting factors have an addition of heat and humidity. can alter tolerances through acclimation. But there are limits to abilities to acclimate like isozymes and heat shock proteins
The threshold effect
a point where a relatively small change in an environmental factor triggers a rapid and often irreversible shift in an ecosystem's structure, function, or composition. May also escape variables. Evolve only a long-term solution. Adaptations compare with acclimation.
size and scaling
allometry (the study of how the relative size of body parts changes in proportion to the overall size of an organism) Surface area/ volume ratio is important. adaptations are important.
principle of allocation
all organism must distribute their limited resources to one of lifes functions. evolutionary tradeoffs. therefore most organisms perform best under a limited range of conditions (including thermal. recall optimum zones.
animals need for energy and nutrients.
herbivory vs carnivory vs omnivore. gut specialization. hindgut/foregut fermentation coprophagy. (Hindgut fermentation occurs in the large intestine (colon) or cecum, while foregut fermentation happens in specialized stomach compartments (like the rumen in ruminants). Coprophagy, the re-ingestion of feces, is a strategy used by some hindgut fermenters to access nutrients produced by gut microbe) Mineral needs especially in the spring for herbivores.