Microbiolgy: Chapter four
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Prokaryotes
One circular chromosome, not in a membrane.
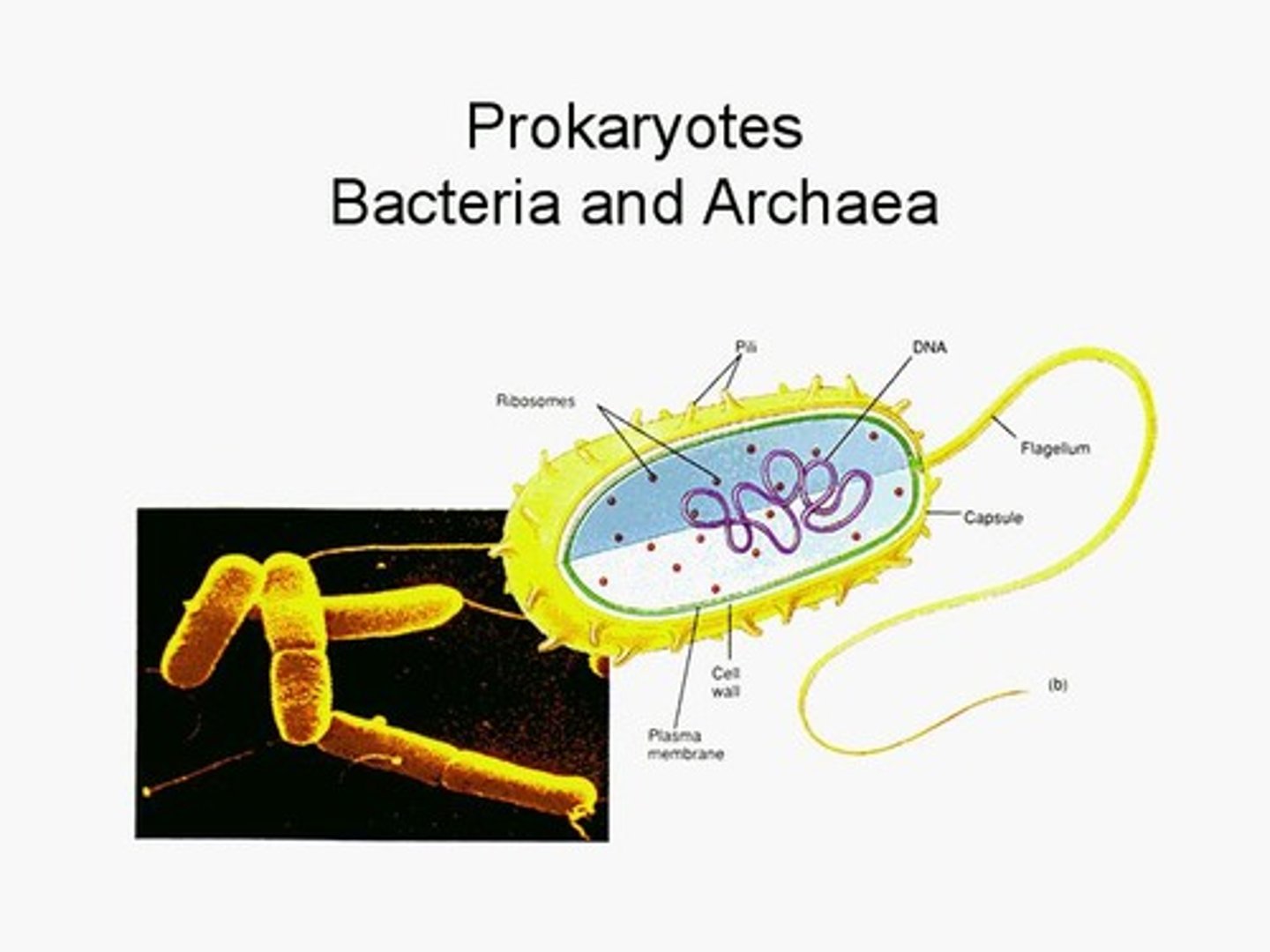
Distinguishing Characteristics of Prokaryotes
Peptidoglycan in their cell walls, no sterols in their plasma membrane, reproduce by binary fission.
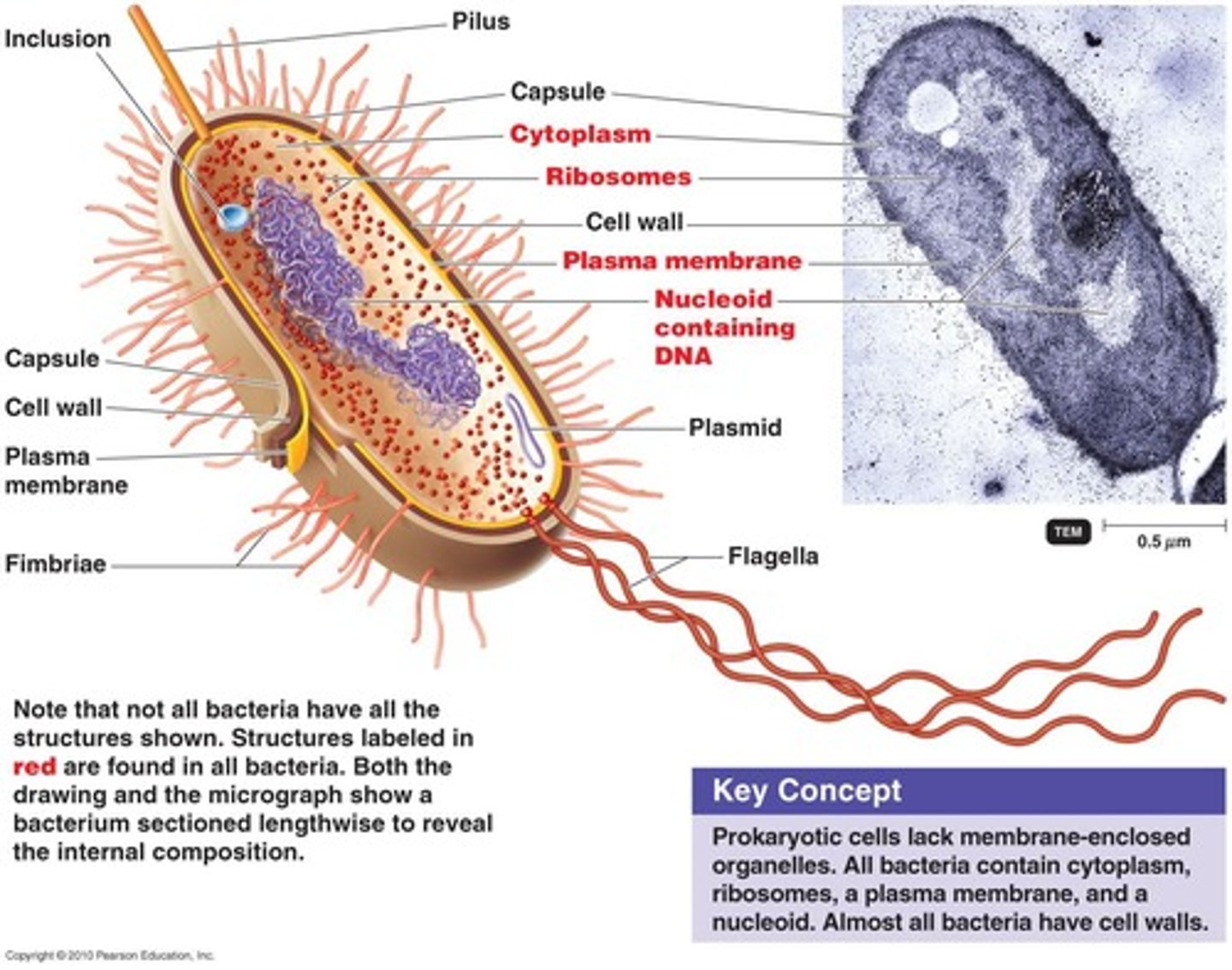
Bacterial Shapes
Cocci, Bacilli, and Spiral.
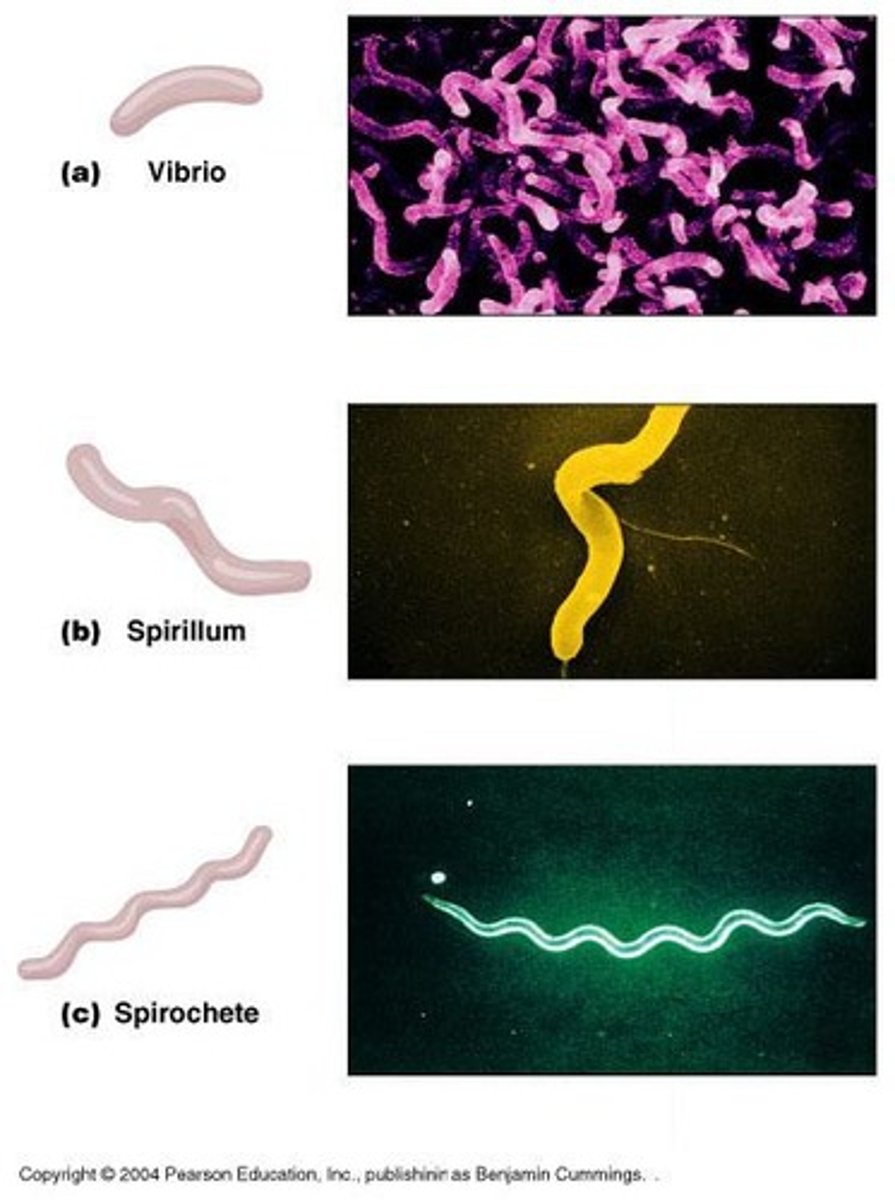
Glycocalyx
Viscous and gelatinous, made of polysaccharide and/or protein, slime layer, capsule
EX: streptococcus pneumoniae
Functions of Glycocalyx
Adherence, antiphagocytic, contributes to biofilm formation.
Flagella
Made of chains of flagellin, anchored to the wall and membrane by the basal body.
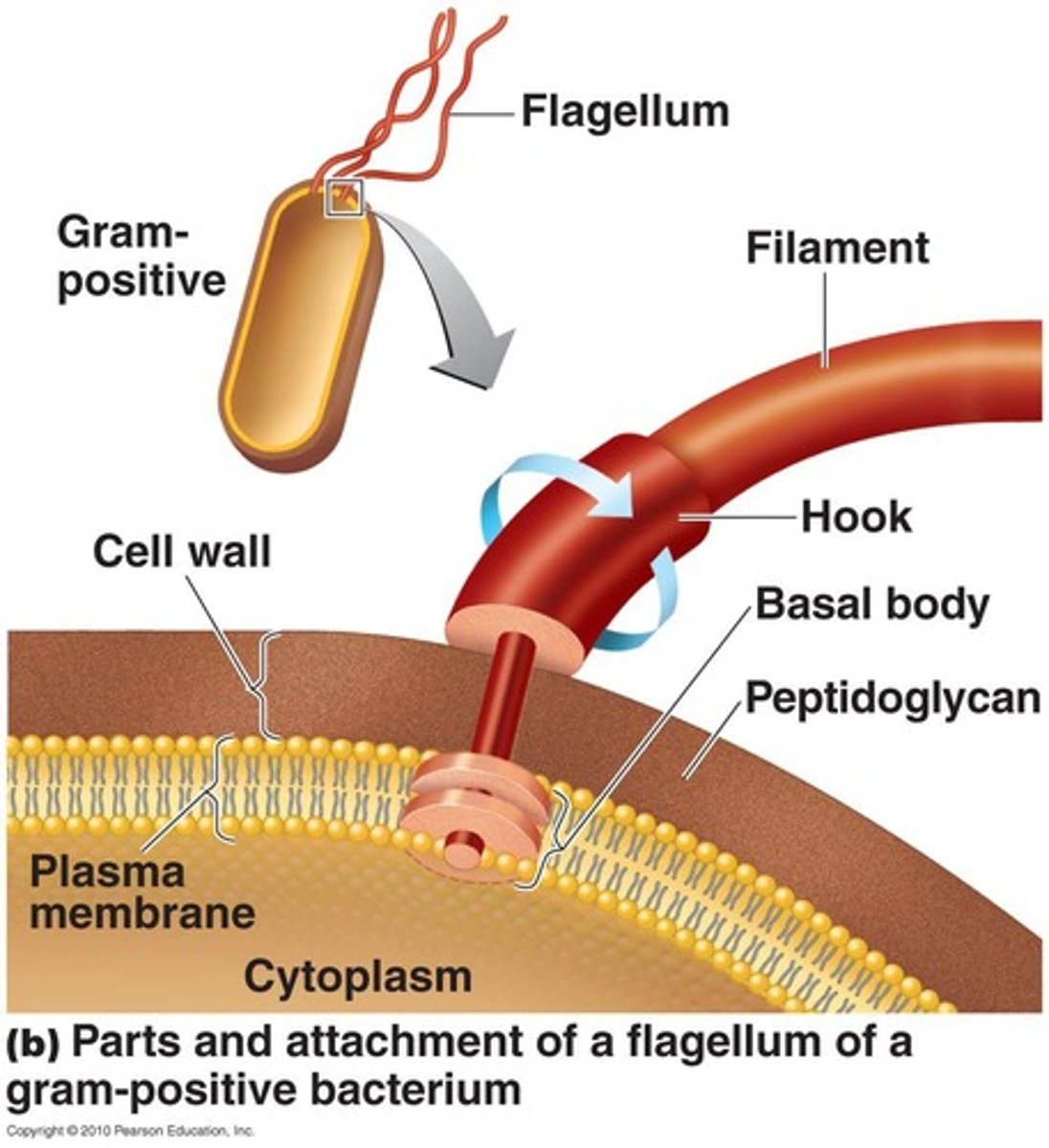
Motile Cells (functions of flagella)
Move toward or away from stimuli (taxis).
Flagella proteins
H antigens (e.g., E. coli O157:H7).
Axial Filaments and functions
In spirochetes, anchored at one end of a cell, corkscrew rotation causes cell to move.
Fimbriae and functions:
Hair-like appendages. (outside of cell wall)
Functions: adherence to host or surfaces, contributing to colonization
Pili (Sex) and function:
Short appendages made of pilin, function in DNA transfer between bacteria (conjugation).
Cell Wall structure and function:
Functions: protection from changes of osmotic pressure, maintains: shape, structure, or cell. Identification of bacteria (gram stain and acid-fast stain), cell wall = site of action of certain antibodies
Structure: Made of peptidoglycan (in bacteria).
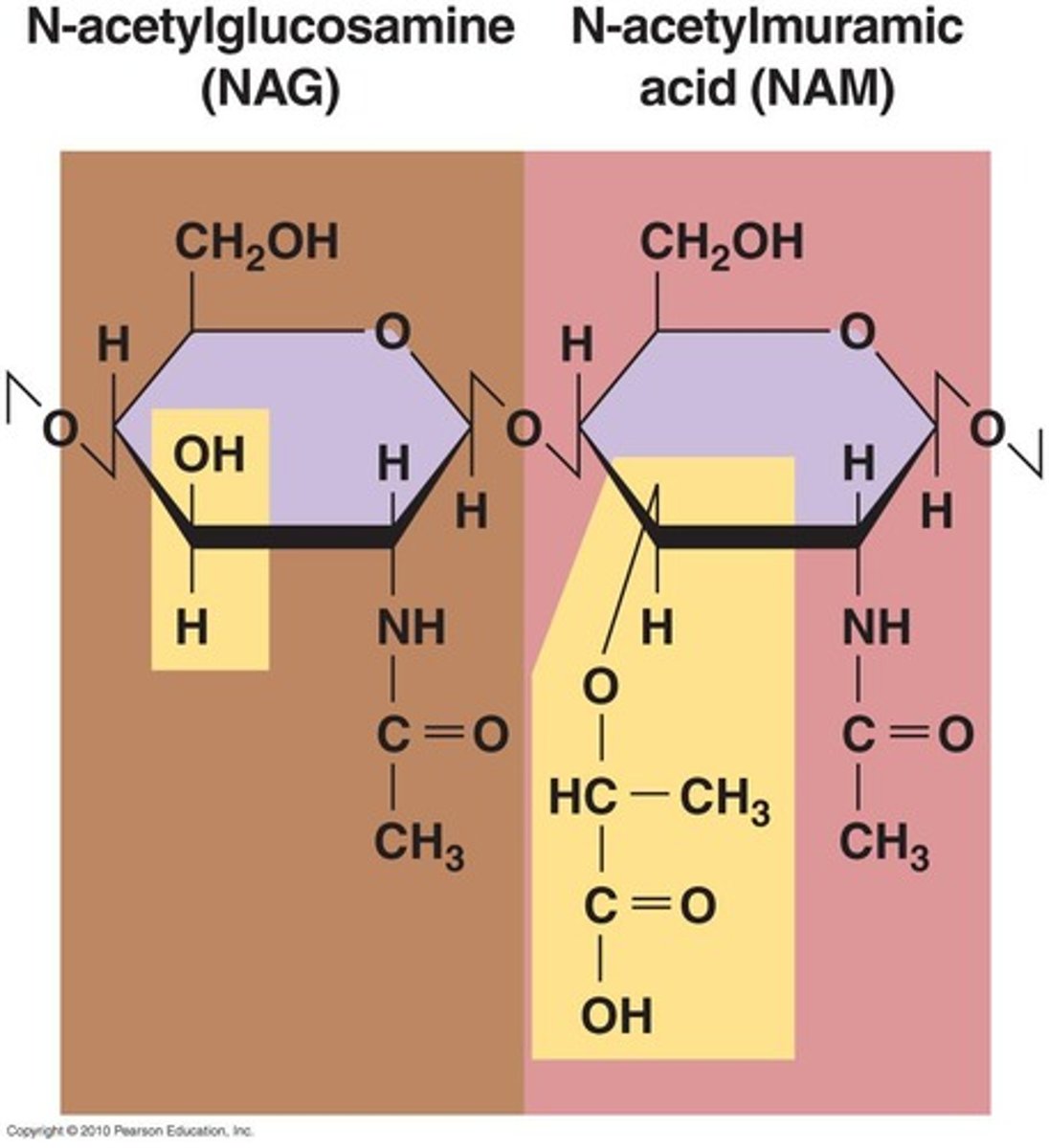
Peptidoglycan
Polymer of repeating disaccharide of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) & N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM), linked by polypeptides.
Gram-Positive Cell Wall
Thick peptidoglycan, teichoic acids, regulate movements of cations
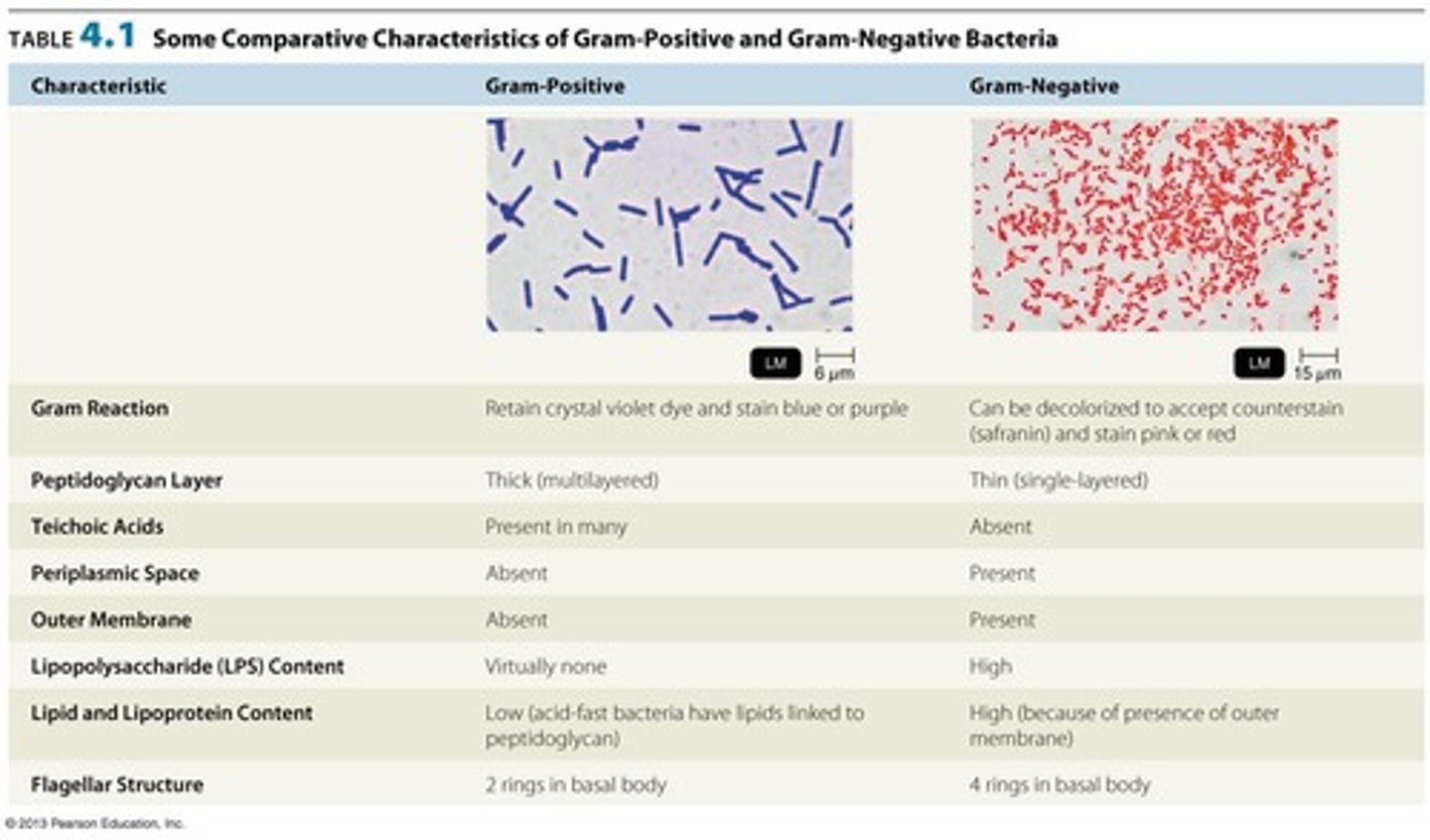
Gram-Negative Cell Wall
Thin peptidoglycan, outer membrane, porin proteins, and has a periplasmic space.
Gram-Negative Outer Membrane
O polysaccharide antigen, e.g., E. coli O157:H7; Lipopolysaccharide (Lipid A) is an endotoxin; Porins (proteins) form channels through membrane.
Gram Stain Mechanism
Based upon differences in cell wall structure.
Cell walls and the gram stain mechanism:
1. the crystal violet-iodine complex combines with peptidoglycan
2. the decoloizer (alcohol or acetone) dissolves the lipid outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria and washes out the crystal violet-idoine complex
3. Gram negative bacteria are decolorized after alcohol wash and safranin stains the cells pink
Atypical cell walls
Like gram-positive, waxy lipid (mycolic acid) bound to peptidoglycan, Archaea lack peptidoglycan
Damage to Cell Walls
Lysozyme digests peptidoglycan; Antibotics like Penicillin inhibits/ inferes with cell wall synthesis
Plasma Membrane: structure and function
Function: Selective permeability, enzymes for ATP production, and photosynthetic pigments, lyzosome digests peptidoglycan
Structure: transports substances in and out of the cell.
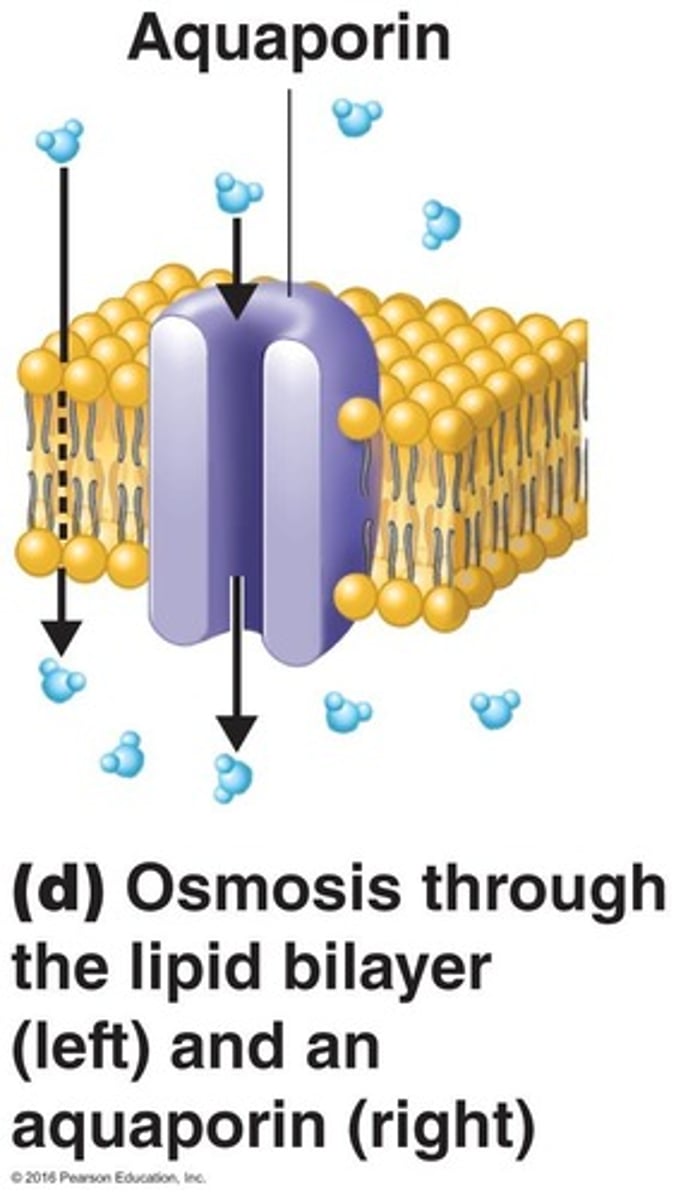
Passive Transport
Movement of substance from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration across a selectively permeable membrane. No energy or ATP required.
Explain simple diffusion
- Passive transport
- Random movement of molecules
- Substances move from higher concentration to lower concentration
Explain facilitated diffusion
- passive movements
- movement down gradient through channel proteins
Explain osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
Explain osmosis types:
1. isotonic: 0.85% NaCl
Effect on cell: no change
2. Hypotonic solutions: less then <0.85% NaCl
Effect on cell: cell will burst - "osmotic lysis"
3. Hypertonic solutions: greater then >0.85% NaCl
Effect on cell: cell will shrink - plasmolysis or crenation
Active Transport
Requires a transporter protein and ATP.
Group translocation
Involves chemical changes in a substance as it is being transported.
Cytoplasm of Prokaryotes
The substance inside the plasma membrane, consisting of liquid aqueous material, nuclear area, ribosomes, and inclusions.
Nuclear Area (Nucleoid)
DNA is a single, circular chromosome that lacks histones and has no nuclear membrane or nucleoli.
Plasmids
Closed circular, extrachromosomal DNA molecules that are self-replicating and encode enzymes and R factors (antibiotic resistance genes).
Ribosomes
Function for protein synthesis and are the site of action of antibiotics.
Size of ribosomes = 70S
Inclusions
Metachromatic granules (volutin) ---> important for storage of substances (reserve deposits)
ex: polysaccharide granules, lipid inclusions, sulfur granules, carboxysomes, gas vacuoles, and magnetosomes.
Endospores
Resting or inactive, dormant cells that are resistant to desiccation (The removal of moisture from something.), heat, and chemicals, usually produced by Gram-positive bacteria.
Sporulation or sporogenesis
Endospore formation.
Endospore Germination
The return of an endospore to its vegetative (active) state.
and endotoxins are then released
Eukaryotic Cells
Distinguished by paired linear chromosomes, a nuclear membrane, histones associated with DNA, and many organelles.
Distinguishing Characteristics of Eukaryotes
Polysaccharide cell walls, sterols present in their plasma membrane, and the presence of a mitotic spindle.
Cilia and Flagella
Composed of microtubules arranged in 9 pairs + 2.
Cell Wall
Found in plants, algae, and fungi, composed of carbohydrates such as cellulose and chitin.
Glycocalyx
Carbohydrates extending from the animal plasma membrane.
Endocytosis
Includes phagocytosis and pinocytosis.
Size of Ribosomes
80S ribosomes are membrane-bound and attached to ER, while 70S ribosomes are found in chloroplasts and mitochondria.
Endosymbiotic Theory
Model of origin of eukaryotes supported by various evidence.