NUCL320 Exam 2 - Deformation and Annealing
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(3/3)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
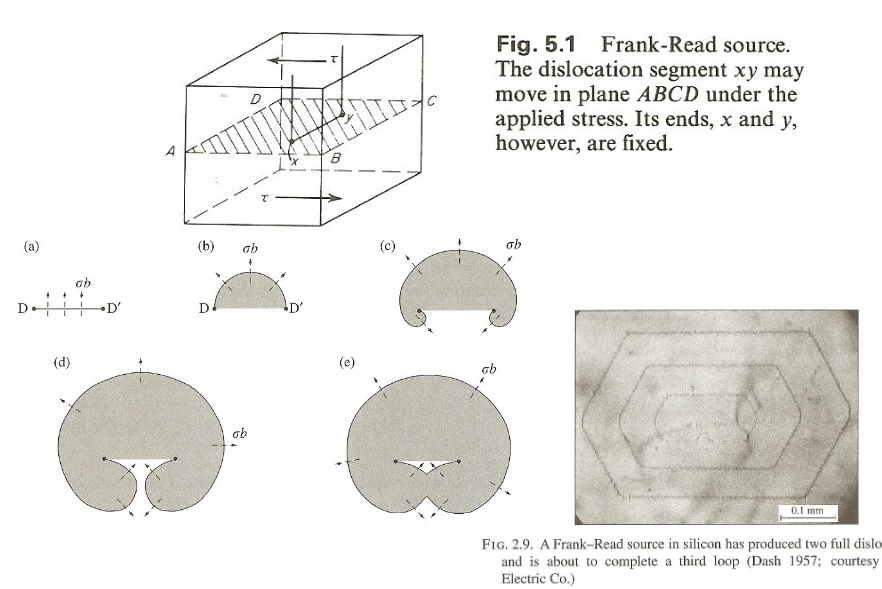
What is a Frank-Read source?
a way in which dislocations are generated in a crystal where a pinned segment of a segment of an existing dislocation bows out under stress, eventually looping around to form a new dislocation
What is the preferred slip system (plane, direction) for BCC structures?
There are no close packed planes in the BCC structure, only close packed directions. The preferred combination is: {110}<111>
Slightly less preferred are: {112}<111> and {123}<111>
What is the preferred slip system (plane, direction) for FCC structures?
{111} <110>
What is the preferred slip system (plane, direction) for HCP structures?
For atoms for which c/a=1.633 or greater, basal planes of HCP structures are close packed planes with close packed directions: {0001} <11-20>
As atoms where c/a<1.633, a prism plane can become preferred: {10-10} <11-20>
What is the equation for resolved shear stress and what are its variables?
TRSS - resolved shear stress
fn - force in the vertical direction
phi - angle between the vertical and the slip direction
Asp - area of an angled slip plane
theta - angle between vertical and normal vector to slip plane
sigman - normal stress
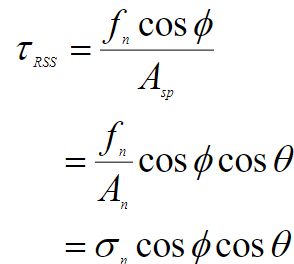
What is the schmid factor equation, what are its variables, and what does it indicate?
m - schmid factor
phi - angle between vertical and the slip direction
theta - angle between vertical and normal vector to slip plane
The schmid factor indicates the effectiveness of an applied shear stress in causing slip in a specific plane and direction. It also highlights the orientation-dependent relationship between applied stress and resolved shear stress in a slip system.
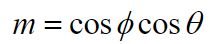
What is the equation for slip plane area and what are its variables?
Asp - area of angled slip plane
An - area of normal plane of the space occupied by the angled slip plane
theta - angle between vertical and normal vector to slip plane
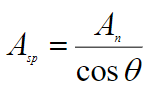
What is the definition of CRITICAL resolved shear stress?
the minimum stress needed for slip to begin
What is the condition for dislocation motion?
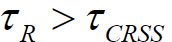
What is stage I of tensile testing in single crystals?
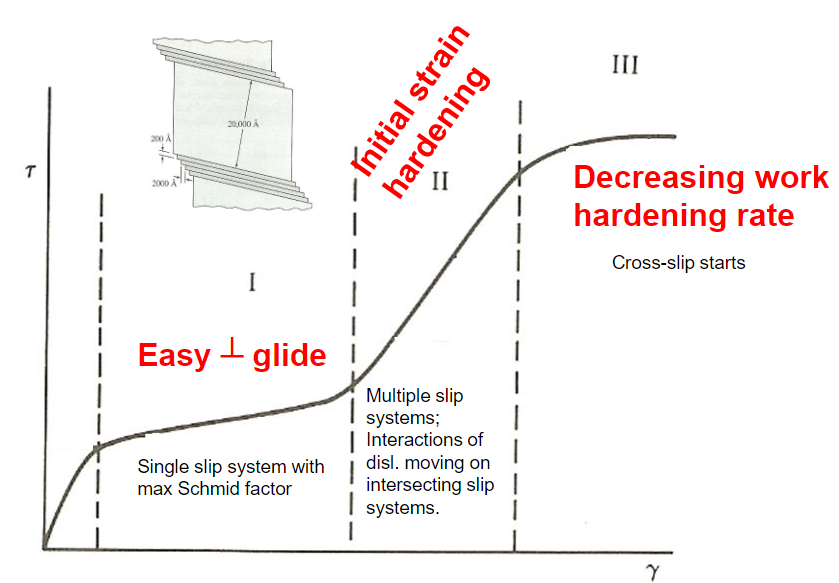
What is stage II of tensile testing in single crystals?
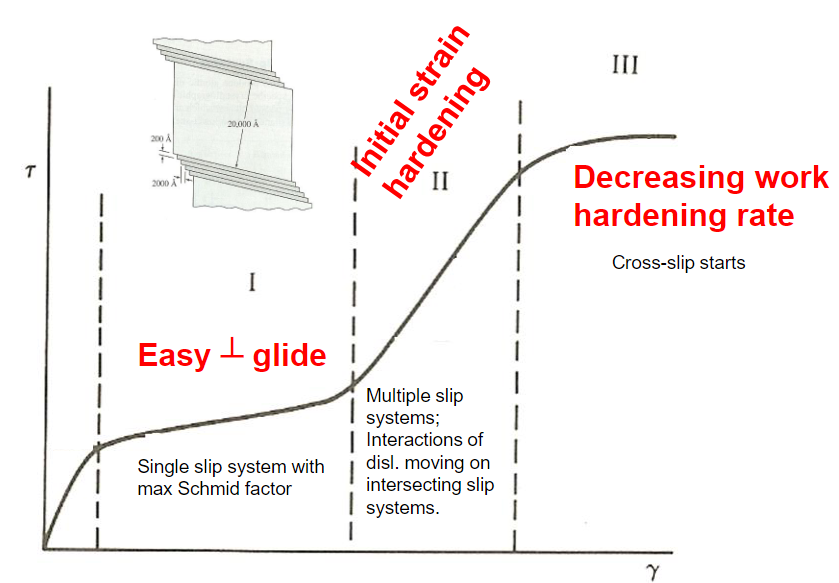
What is stage III of tensile testing in single crystals?
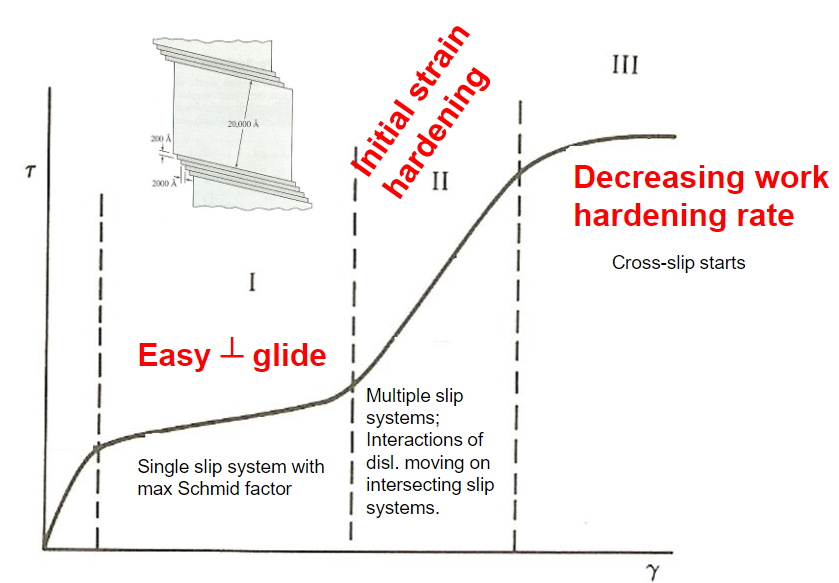
How does temperature effect the stages of tensile testing in single crystals?
Increasing temperature creates a decrease in the extent of stage I and stage II. For stage I, this is because the initiation of secondary slip systems is easier at higher temperatures. For stage II, this is because cross slip is easier at higher temperatures.
A decrease in the SFE causes a decrease in cross slip which increases the stress needed for the transition from stage II to stage III.
How does the orientation of stress effect stress vs strain?
The orientation of the stress axis controls the number of slip systems that will be activated. More slip systems result in harder materials.
Why does no stage I exist when multiple slip systems co-exist?
Stage I (easy glide) doesn't occur when multiple slip systems are active because dislocations on different planes interact and block each other, causing strain hardening right from the start, preventing the smooth, easy movement of dislocations.
How does dislocation motion happen in polycrystal systems? (4 things)
slip planes and directions change from one crystal to another
resolved stress value varies between each crystal
the crystal with the highest resolved stress value will yield first
others that are less favorable oriented will yield later on
How does heating brass alloy after cold working (strain hardening) it effect the material?
This process (called annealing) decreases tensile strength as it increases ductility (percent elongation). Heating it reverses the effects of cold working it.
What is the definition of annealing?
A heat treatment process that involves heating a material to a specific temperature and then slowly cooling it to reduce internal stresses, increase ductility, and improve its microstructure by allowing the rearrangement and elimination of defects like dislocations.
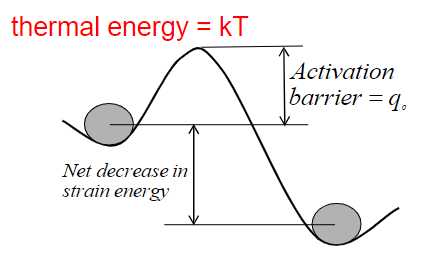
How can dislocation glide reduce (recover) strain energy?
Opposite dislocations can move towards one another, combining and cancel each other, thereby reducing strain energy in the crystal.
How can dislocation climb reduce (recover) strain energy?
Dislocation climb reduces strain energy by allowing an edge dislocation to move out of its original slip plane, bypassing obstacles that block its glide. This movement helps relieve built-up stress by rearranging atoms through diffusion, reducing the overall energy in the crystal.
How does the formation of tilt boundaries reduce (recover) stain energy?
If dislocations cannot eliminate one another due too large of separation distances, rough vertical alignment occurs, reducing the strain energy in the crystal, lowering electrical resistivity, and slightly reducing strength.
What happens to climb distance and climb time with an increase in temperature?
climb distances increase
climb times decrease
What can low angle grain boundaries be mistaken for, and under what circumstances?
they can appear as dislocation cells, when viewed from above
What is the recovery process? (5 stages)
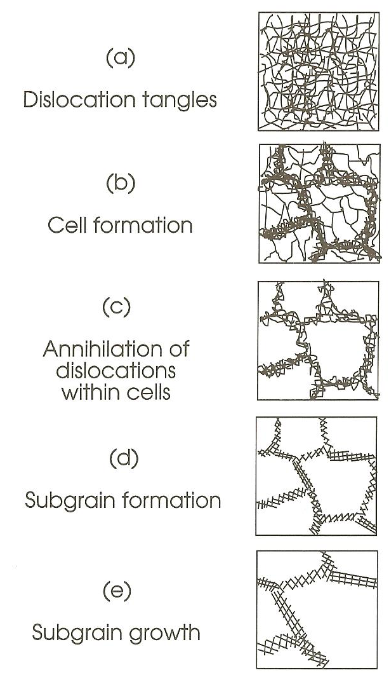
What is recrystallization temperature?
the temperature at which a deformed material undergoes recrystallization, forming new, strain-free grains without changing its phase, also restoring the material’s ductility and reducing internal stresses
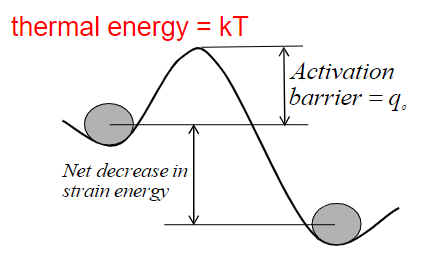
What is the arrhenius model of thermal activation? What is its equation and what are its variables?
the rate of thermally activated processes increase exponentially with temperature
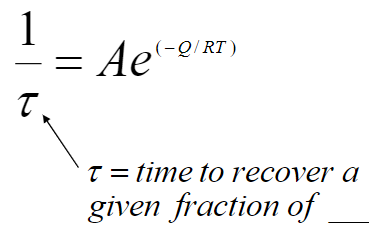
What is the linearized version of the arrhenius equation and what are its y=mx+b variables?
y - ln(1/tau)
m - -Q/R
x - 1/T
b - ln(A)
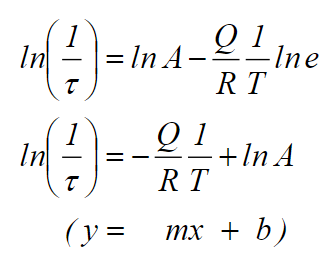
What is the equation for the non-linearized arrhenius equation and what are its variables?
tau - time of recovery [s]
Q - activation energy [J/mol]
R - 8.314 J/molK or 1.987 BTU/lbmolR
T - absolute temperature [K, R]
A - pre-exponential factor
![<p>tau - time of recovery [s]</p><p>Q - activation energy [J/mol]</p><p>R - 8.314 J/molK or 1.987 BTU/lbmolR</p><p>T - absolute temperature [K, R]</p><p>A - pre-exponential factor</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/651e0ab0-af86-47b3-97bb-0796000cf08c.png)