Agriculture and Transportation Revolution
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
agriculture
The deliberate effort to modify a portion of Earth's surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance or economic gain.
Agricultural Revolution
A time when new inventions such as the seed drill and the steel plow made farming easier and faster. The production of food rose dramatically.
enclosure
the process of taking over and consolidating land formerly shared by peasant farmers
commons
land or resources belonging to or affecting the whole of a community.
graze
to feed on growing grass
broadcast
to sow seeds by throwing them over a field by hand
manure
animal dung used for fertilizing land
fodder
food, especially dried hay or feed, for cattle and other livestock.
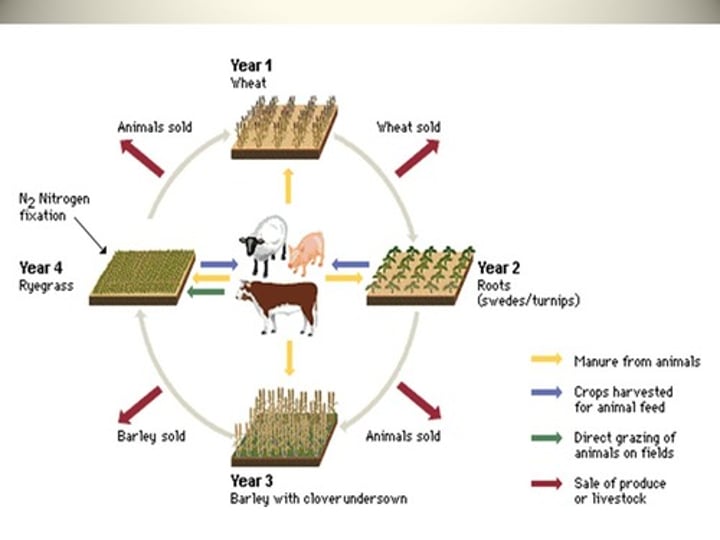
crop rotation
The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year, to avoid exhausting the soil.
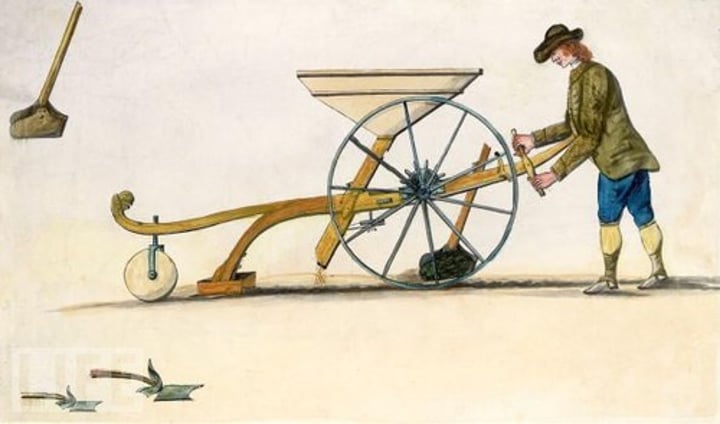
seed drill
created by Jethro Tull, it allowed farmers to sow seeds in well-spaced rows at specific depths; this boosted crop yields
breed
a group of animals distinguished by a particular characteristic. Animals got hardier during the agricultural revolution.
industry
all the businesses that make one kind of product or provide one kind of service
capitalist economy
an economic system in which the market determines production, distribution, and price decisions, and property is privately owned
cast iron
A rigid, strong construction material made by adding carbon to iron

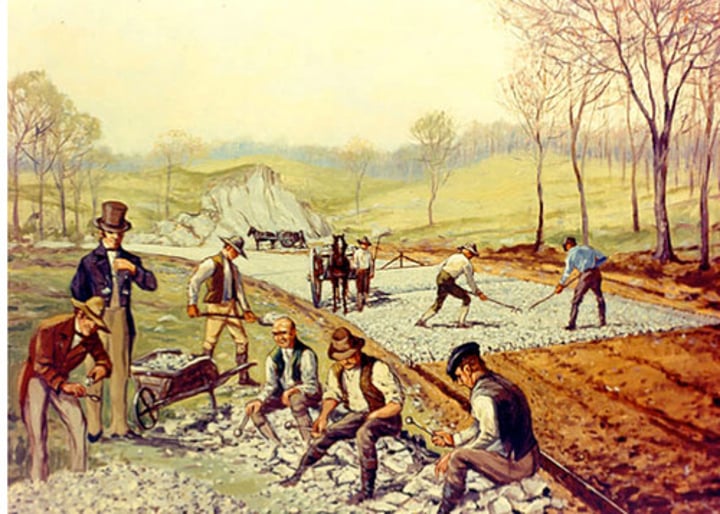
McAdam Roads
The building of new roads that made it an easier safer and faster travel conditions started by John McAdam . In the roads smaller stones topped the bigger set of stones theses roads would be a model for engineers later on.

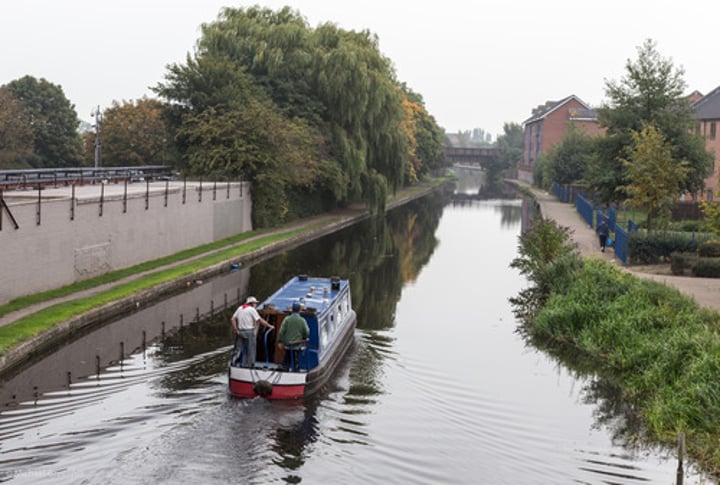
Canals
human-made waterways

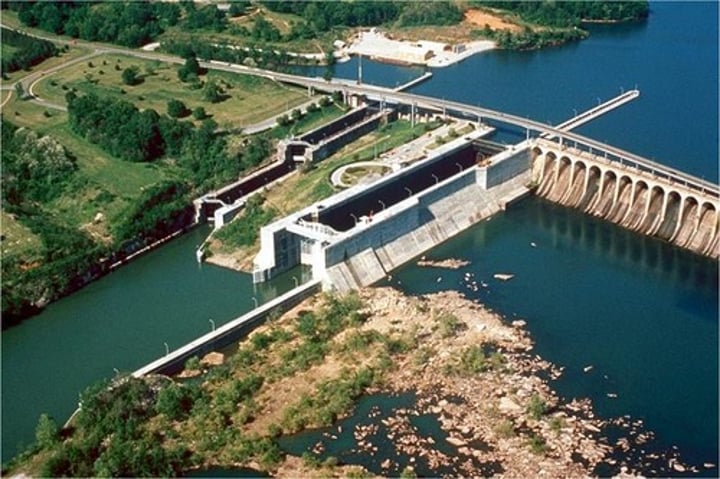
Locks
an enclosure with gates built in a canal or river so that ships can be raised or lowered by changing the water level

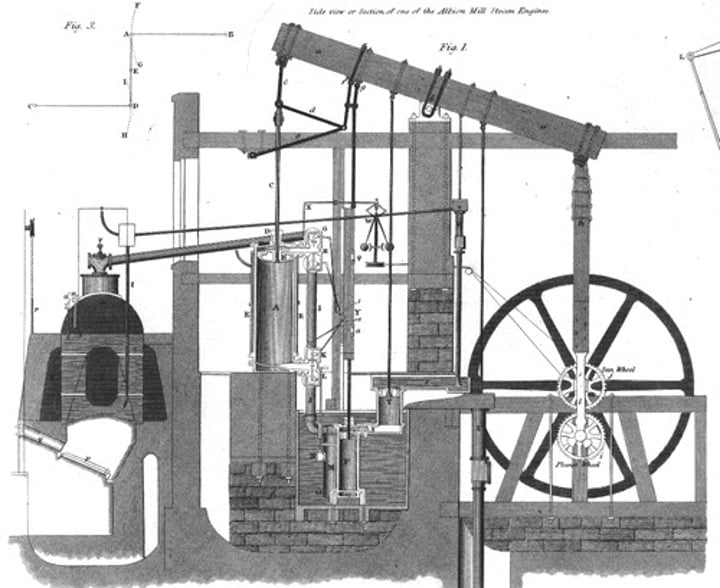
Steam Engine (James Watt)
A machine that turns the energy released by burning fuel into motion. Thomas Newcomen built the first crude but workable steam engine in 1712. James Watt vastly improved his device in the 1760s and 1770s. Steam power was then applied to machinery.
locomotive
a powered rail vehicle used for pulling trains

coal
A fossil fuel that forms underground from partially decomposed plant material
Lassez-faire economics
economic system where government should not interfere in the marketplace