Unit 5 Electricity
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is electric current?
The rate of flow of charge
What is potential difference?
Work done per unit charge
What is resistance?
Voltage/current
What is Ohm’s law?
It states that in an ohmic conductor current is directly proportional to the potential difference across it given that physical conditions (temperature) are kept constant
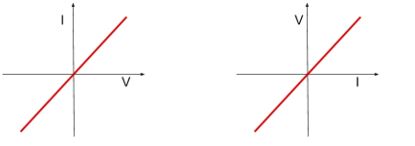
Which component has this graph?
Ohmic conductor
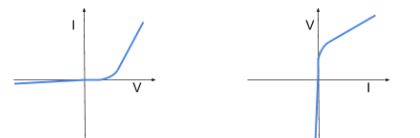
Which component has this graph?
Semiconductor diode
How do semiconductor diodes work?
They have a forward bias of a diode which is in the direction in which it will allow current to flow easily past the threshold voltage. In the direction of the reverse bias the resistance of the diode is extremely high meaning that only a very small current can flow
What is the threshold voltage?
The smallest voltage needed to allow current to flow
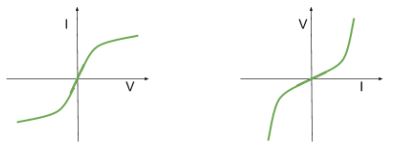
Which component has this graph?
Filament lamp
How do filament lamps work?
It contains a length of metal wire which heats up as current increases therefore the resistance increases as current increases. At low currents the metal wire will not heat up significantly therefore for very low currents Ohm’s law is obeyed
Unless otherwise indicated how much resistance does an ammeter have?
0
Unless otherwise indicated how much resistance does a voltmeter have?
Infinite
What is resistivity?
A measure of how easily a material conducts electricity
What is the equation for resistivity?
Resistance*cross-sectional area / length
What happens when the temperature of a metal conductor increases and why?
Its resistance will increase because the atoms of the metal gain kinetic energy and move more which causes the electrons to collide with the atoms more frequently causing them to slow down therefore current decreases and so resistance increases
How do thermistors work?
As the temperature of a thermistor increases its resistance decreases because the temperature of a thermistor causes electrons to be emitted from atoms therefore the current increases causing resistance to decrease
What is an application of a thermistor in circuits?
As a temperature sensor which can trigger an event to occur once the temperature drops or reaches a certain value
What is a superconductor?
A material which below the critical temperature has zero resistivity
What are the uses of superconductors?
Power cables which would reduce energy loss through heating to zero during transmission
Strong magnetic fields which would not require a constant power source. These could be used in maglev trains where there would be no friction between the train and the rail
What is the equation for adding resistance in series?
RT = R1 + R2
What is the equation for adding resistance in parallel?
1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2
What is power?
The rate of energy transfer
What are some equations for power?
P = VI
P = V² /R
P = I²R
What are the rules for a series circuit?
The current is the same everywhere in the circuit
The EMF is shared across all elements in the circuit therefore the total sum of the voltages across all elements is equal to the EMF
What are the rules for a parallel circuit?
The sum of the currents in each parallel set of branches is equal to the total current
The potential difference across each branch is the same
What is Kirchoff’s first law?
The total current flowing into a junction is equal to the current flowing out of that junction. Conservation of charge
What is Kirchoff’s second law?
The sum of all the voltages in a series circuit is equal to the EMF. Conservation of energy
What is a potential divider?
A circuit with several resistors in series connected across a voltage source used to provide a required fraction of the EMF which remains constant
How can a potential divider be used to supply a variable potential difference?
By using a variable resistor as one of the resistors in series therefore by varying the resistance across it the potential difference output can be varied
What is a light dependent resistor?
A resistor where as light intensity increases resistance decreases
What causes the internal resistance in batteries?
Electrons colliding with atoms inside the battery and is represented as a small resistor inside the battery
What is electromotive force (EMF)?
The energy transferred by a cell per coulomb of charge that passes through it
What is the equation for EMF in terms of current and resistance?
E = IR + Ir
What is terminal p.d?
The p.d across the resistor R
What are lost volts?
The p.d across the resistor r because this value is equal to the energy wasted by the cell per coulomb of charge