BE 345: Chapter 10
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
Nervous System
Detects changes, makes decisions, stimulates muscles and glands to respond, and maintains homeostasis
What cell types are in the neural tissue?
• Neurons – transmit impulses
• Neuroglial cells – many other functions
What are the divisions of the nervous system?
• Central Nervous System (CNS)
• Brain
• Spinal cord
• Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
• Cranial nerves
• Spinal nerves
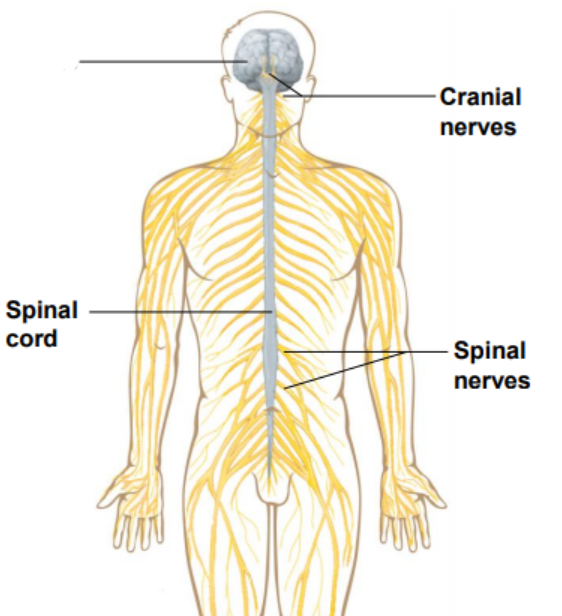
Label the diagram
Brain
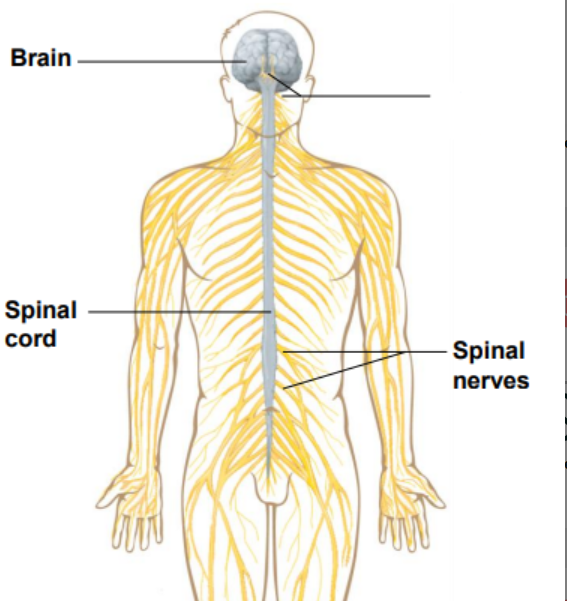
Label the diagram
Cranial nerves
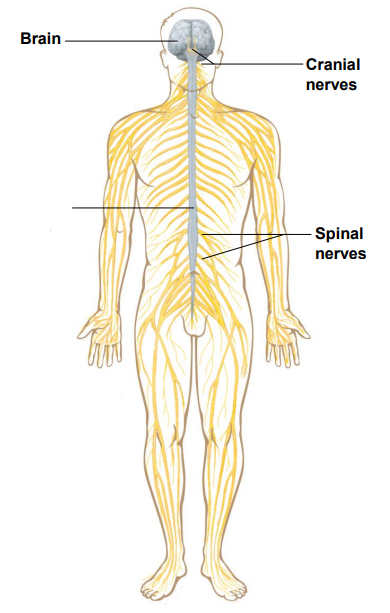
Label the diagram
Spinal cord
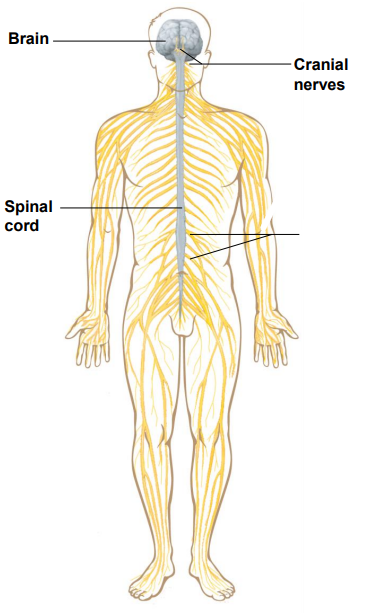
Label the diagram
Spinal nerves
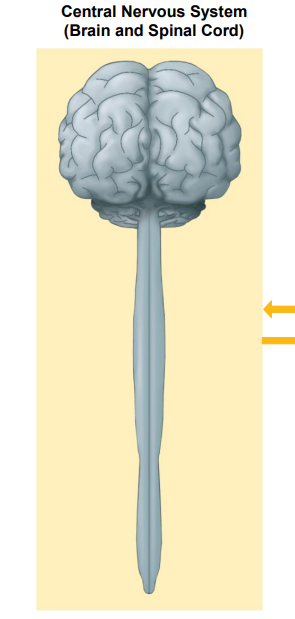
Identify the diagram
Central Nervous System (Brain and Spinal Cord)
The Peripheral Nervous System contains what nerves?
Cranial and Spinal nerves
What does the Peripheral Nervous System control?
Sensory division and Motor division
Sensory receptors are in tact with what division?
Sensory division
The Motor division is broken up into what two nervous systems?
Somatic and Autonomic
What does the Somatic Nervous System control?
Skeletal Muscle
What does the Autonomic Nervous System control?
Smooth muscle, Cardiac muscle, Glands
Neurons vary in what?
Size, shape, length and size of axons and dendrites
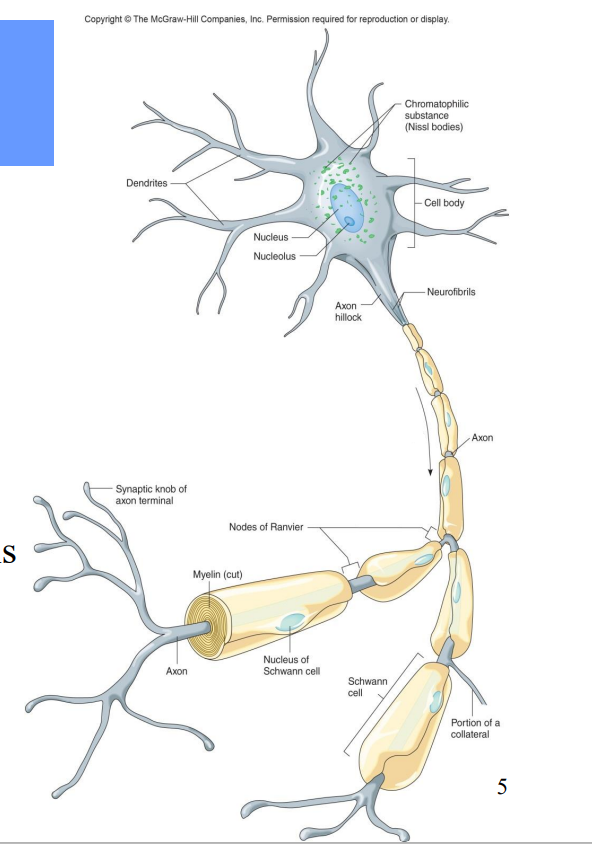
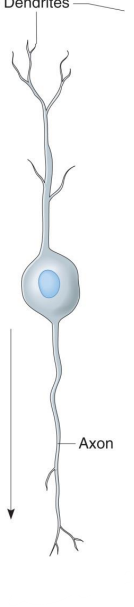
All neurons contain what?
Dendrites – receiving ends
• A cell body (soma)– contains nucleus
• An axon – transmits impulses and releases neurotransmitters to another neuron or effector
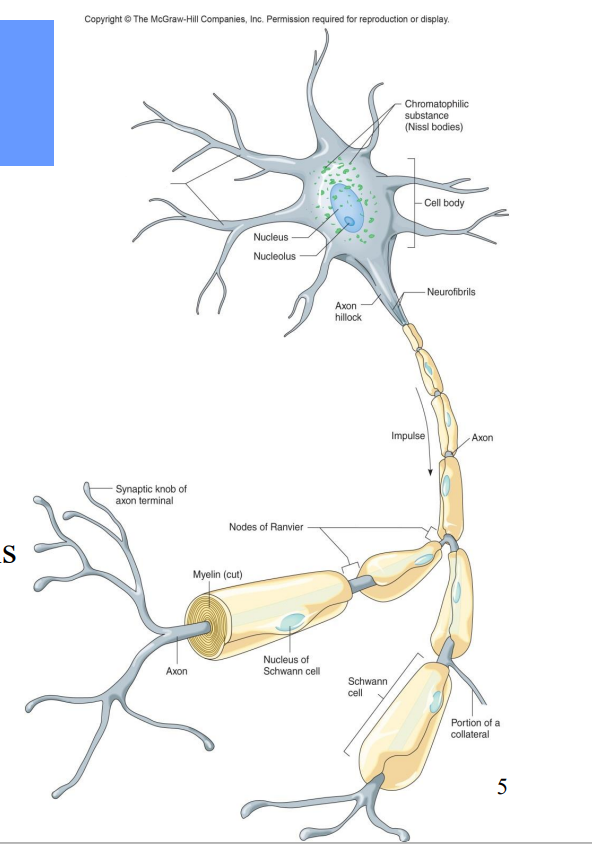
Label the diagram
Dendrites
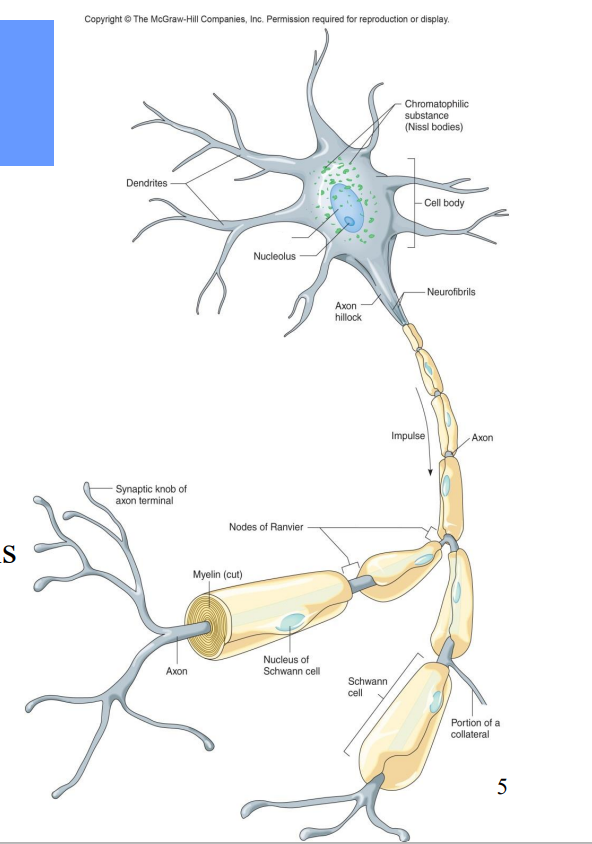
Label the diagram
Nucleus
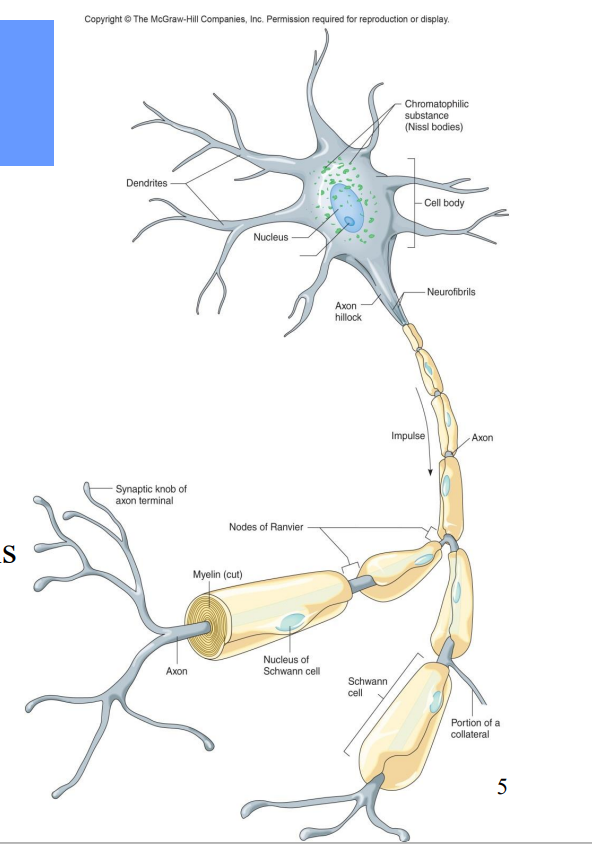
Label the diagram
Nucleolus
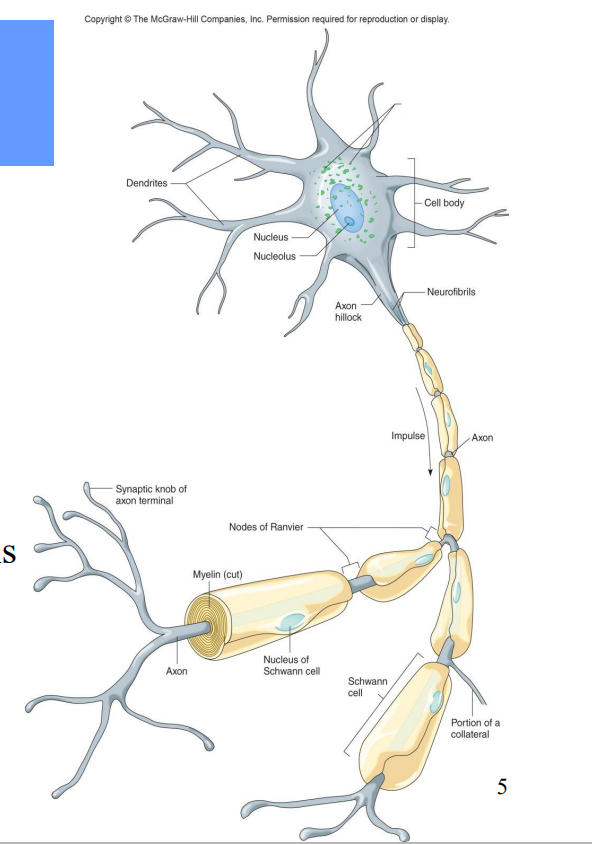
Label the diagram
Chromatophilic Substance
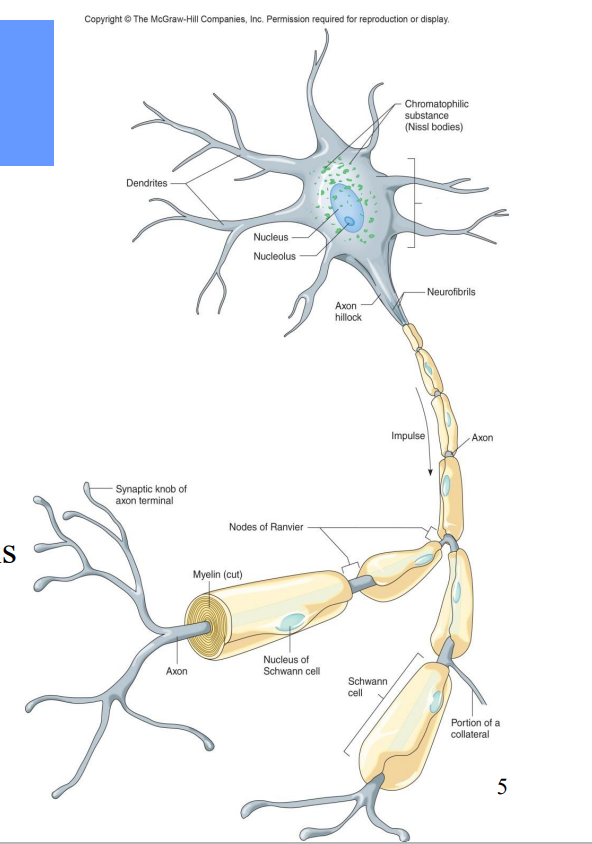
Label the diagram
Cell bodies
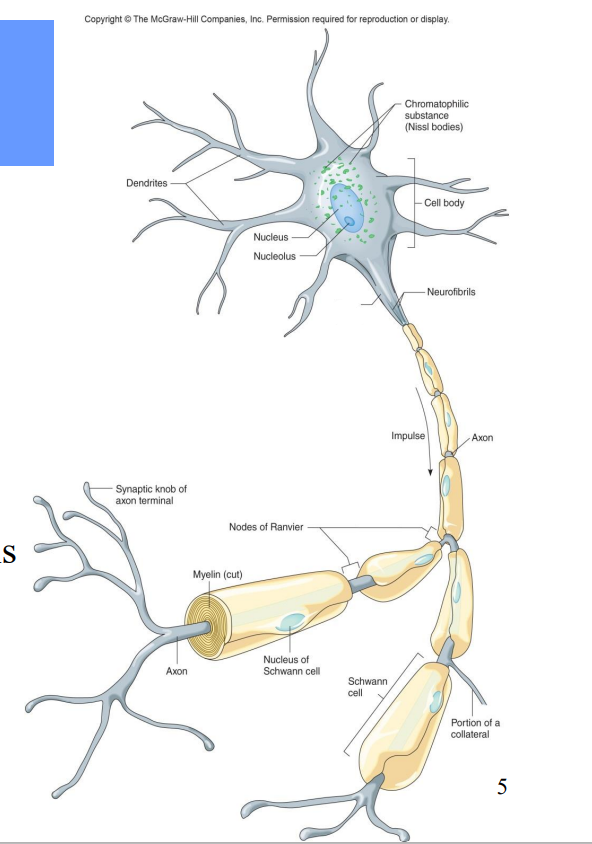
Label the diagram
Axon hillock
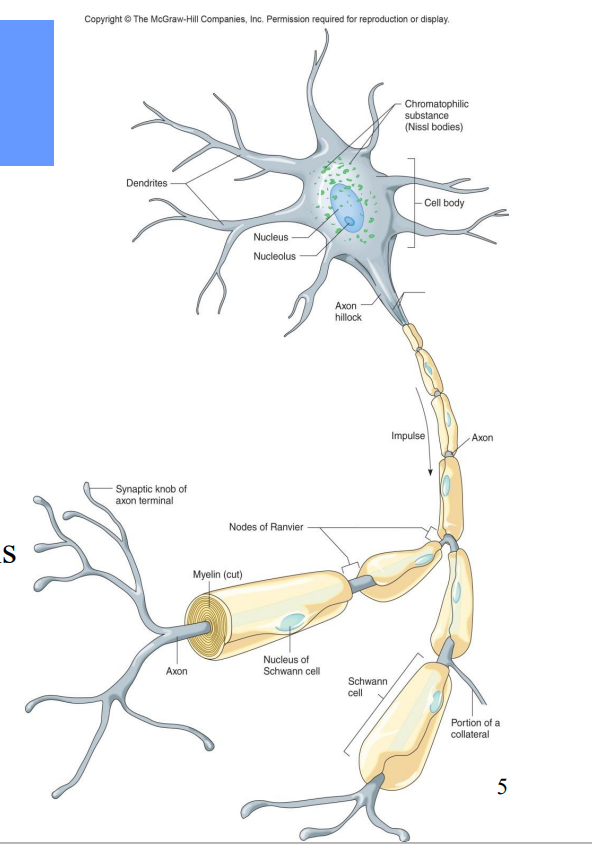
Label the diagram
Neurofibrils
Label the diagram
Impulse
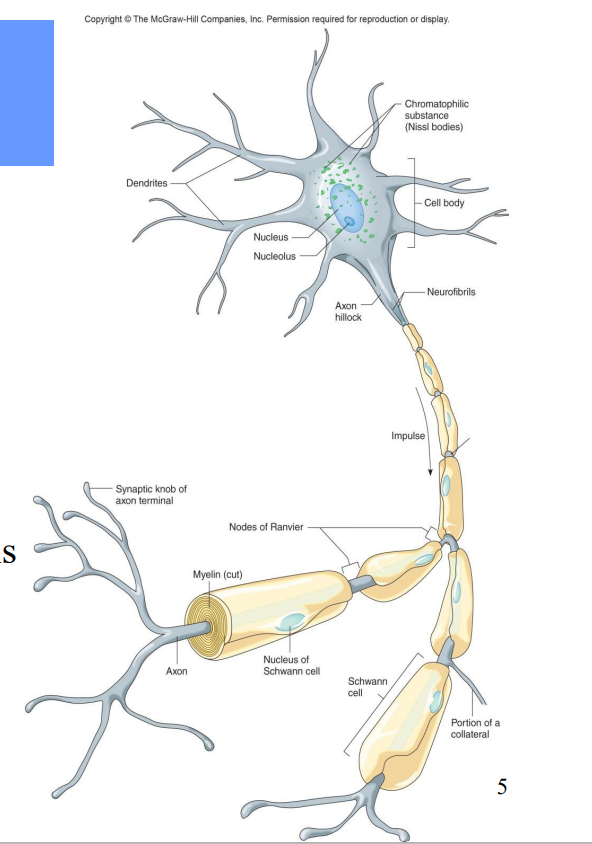
Label the diagram
Axon
Label the diagram
Nodes of Ranvier
Label the diagram
Myelin
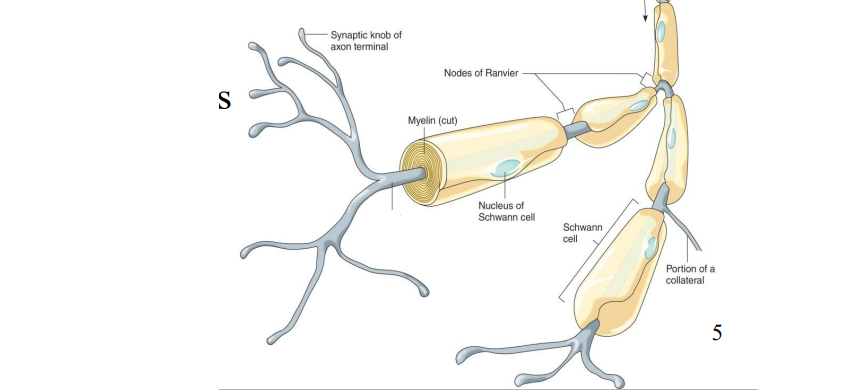
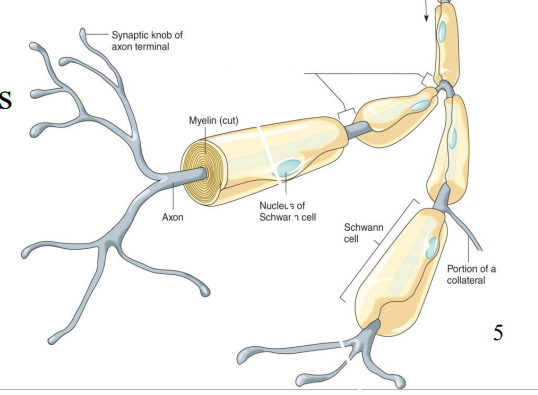
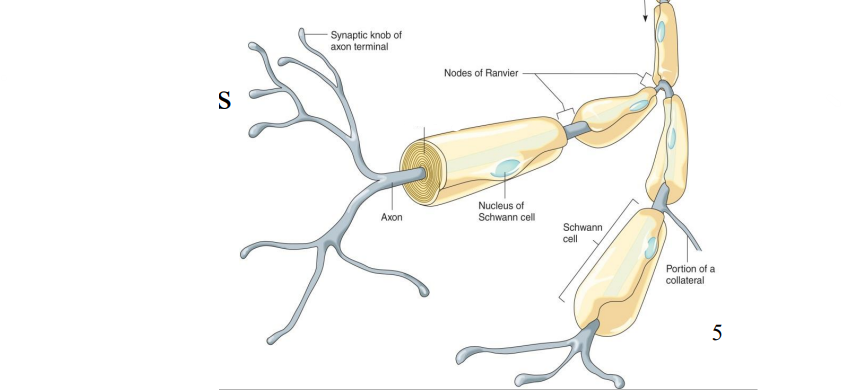
Label the diagram
Axon
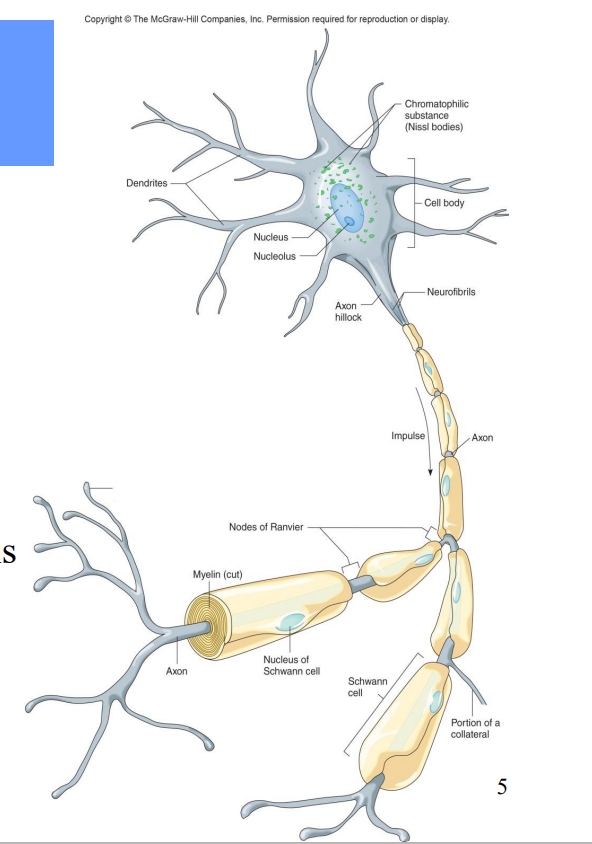
Label the diagram
Synaptic knob of axon terminal
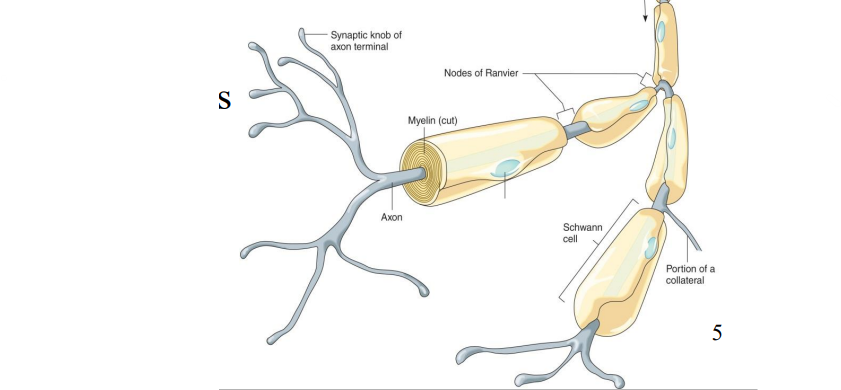
Label the diagram
Nucleus of Schwann Cell
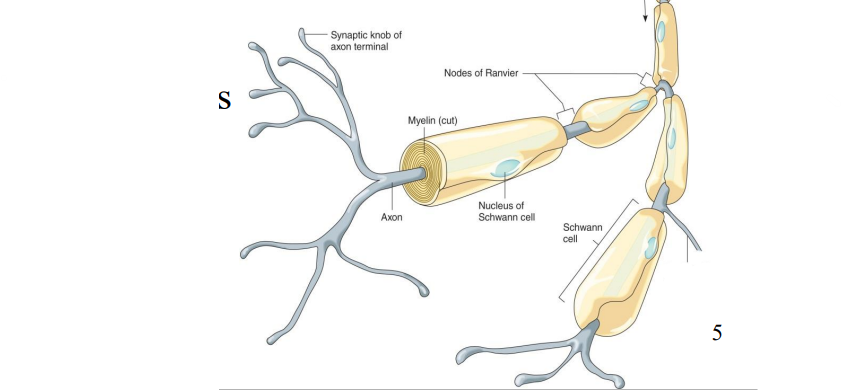
Label the diagram
Portion of a Collateral
What does Myelinated mean?
Axons which are tightly wrapped by neuroglial cells
What does white matter contain?
• Contains myelinated axons
• Considered fiber tracts
What does Grey matter contain?
• Contains unmyelinated structures
• Cell bodies, dendrites
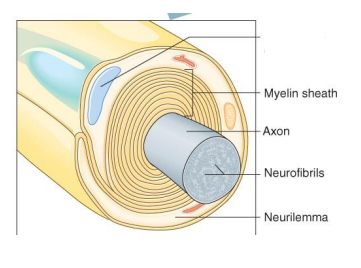
Label the diagram
Schwann Cell Nucleus
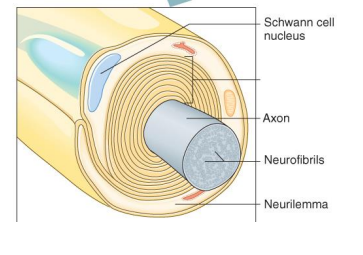
Label the diagram
Myelin Sheath
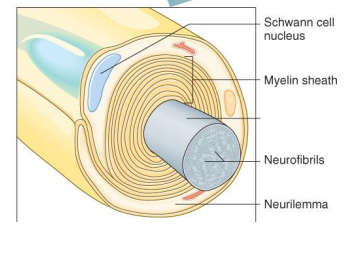
Label the diagram
Axon
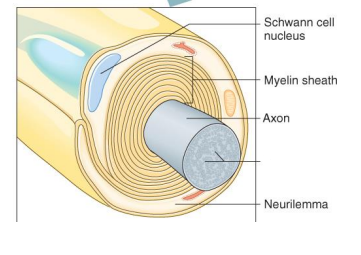
Label the diagram
Neurofibrils
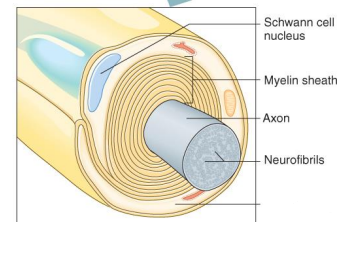
Label the diagram
Neurilemma
Multipolar neurons do what?
• 99% of neurons
• Many processes
• Most neurons of CNS
Bipolar neurons do what?
• Two processes
• Eyes, ears, nose
Unipolar neurons do what?
• One process
• Ganglia of PNS
• Sensory
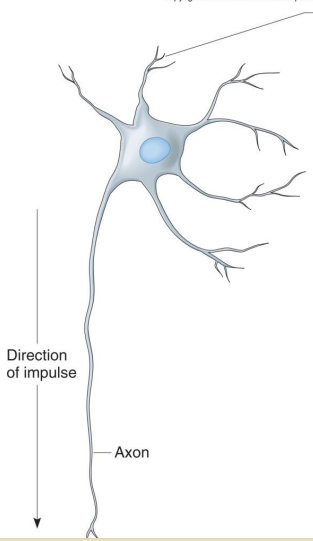
Label the diagram
Multipolar neuron
Label the diagram
Bipolar neuron
Label the diagram
Unipolar neuron
What do Sensory neurons do?
• Afferent
• Carry impulse to CNS
• Most are unipolar
• Some are bipolar
What do Interneurons do?
• Link neurons
• Multipolar
• Located in CNS
What do Motor neurons do?
• Multipolar
• Carry impulses away from CNS
• Carry impulses to effectors
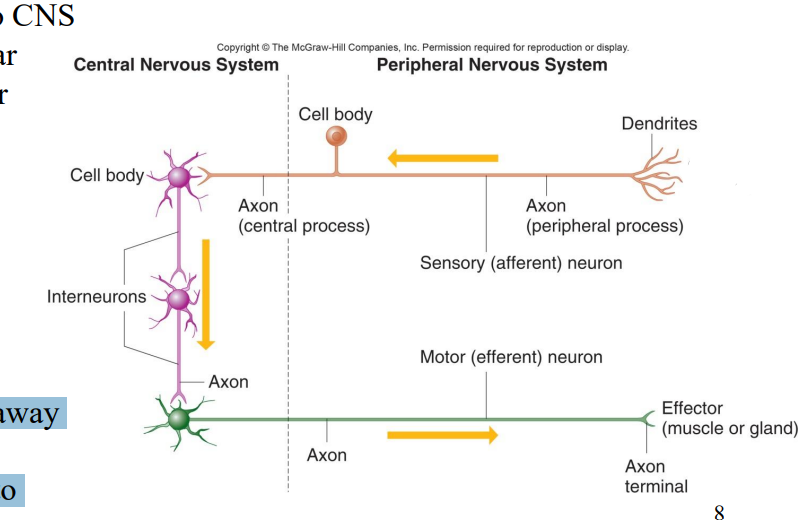
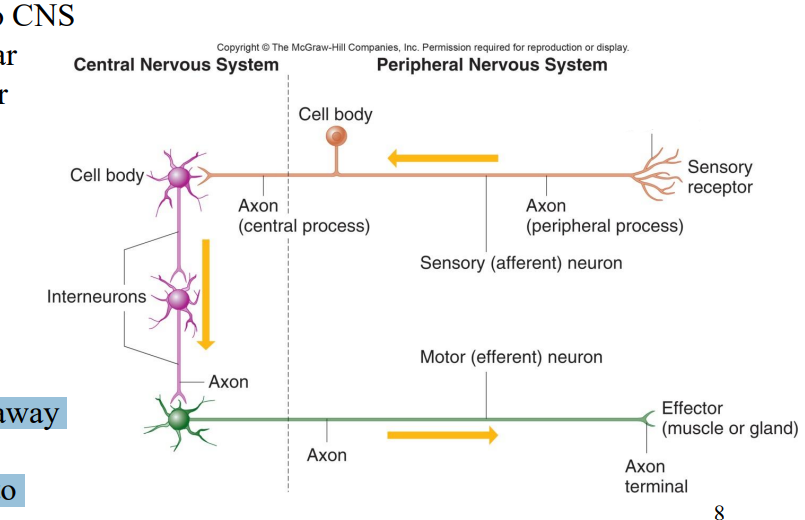
Label the diagram
Sensory receptor
Label the diagram
Dendrites
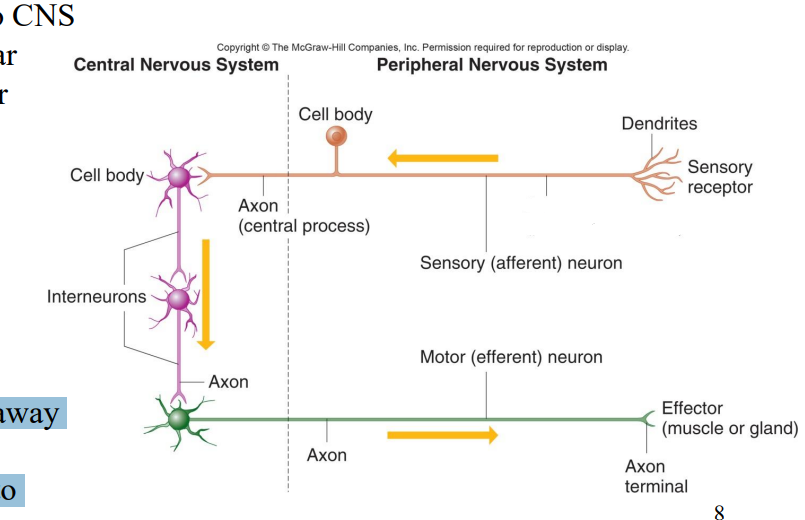
Label the diagram
Axon (Peripheral Process)
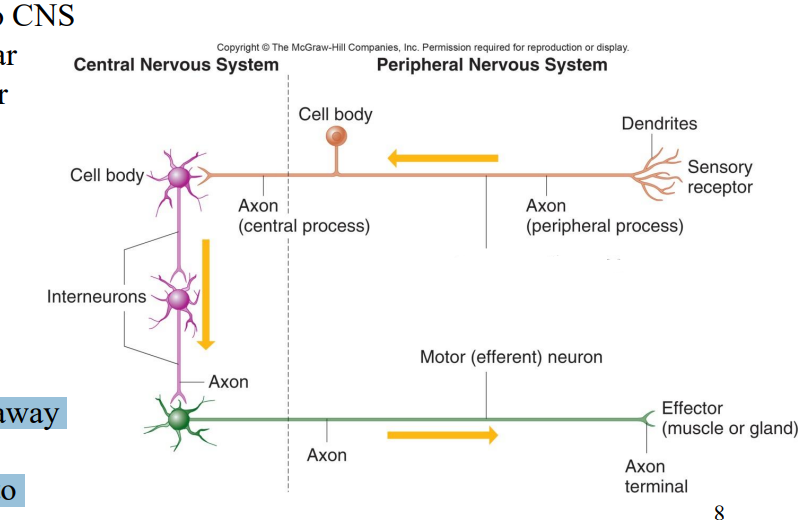
Label the diagram
Sensory afferent neuron
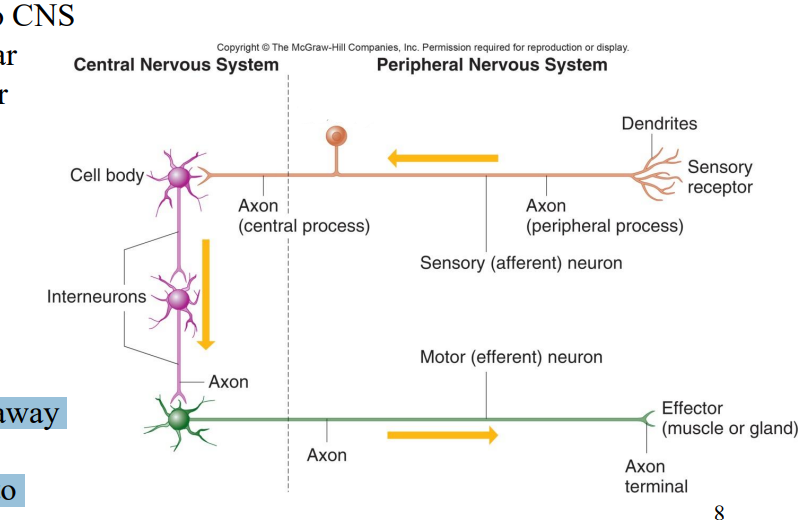
Label the diagram
Cell body
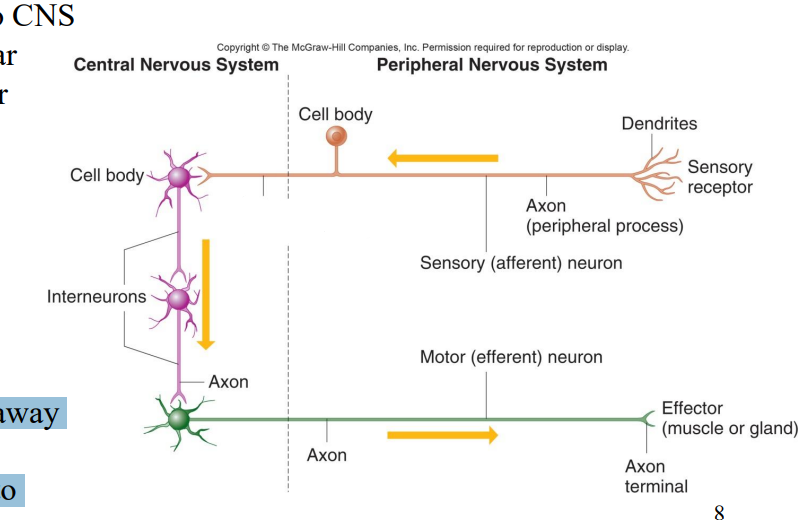
Label the diagram
Axon (Central process)
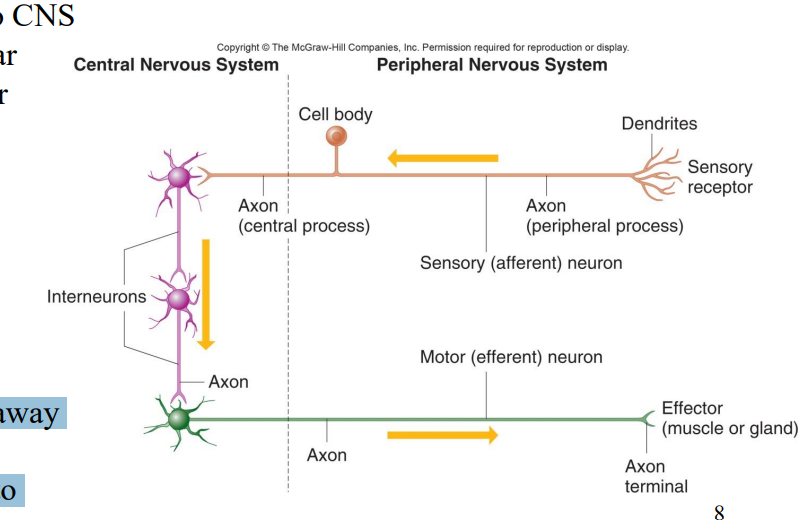
Label the diagram
Cell body
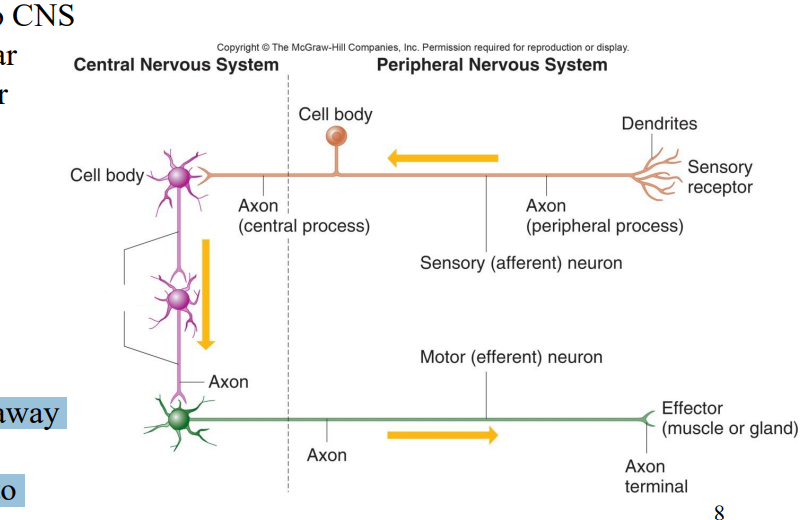
Label the diagram
Interneurons
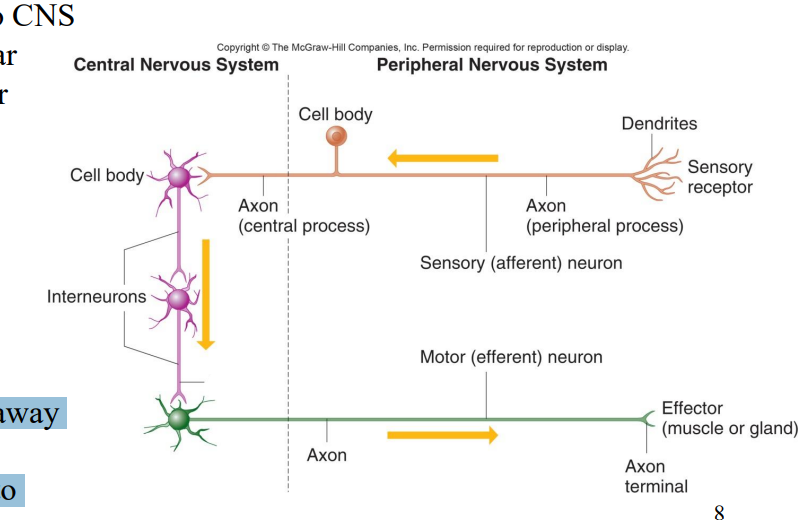
Label the diagram
Axon
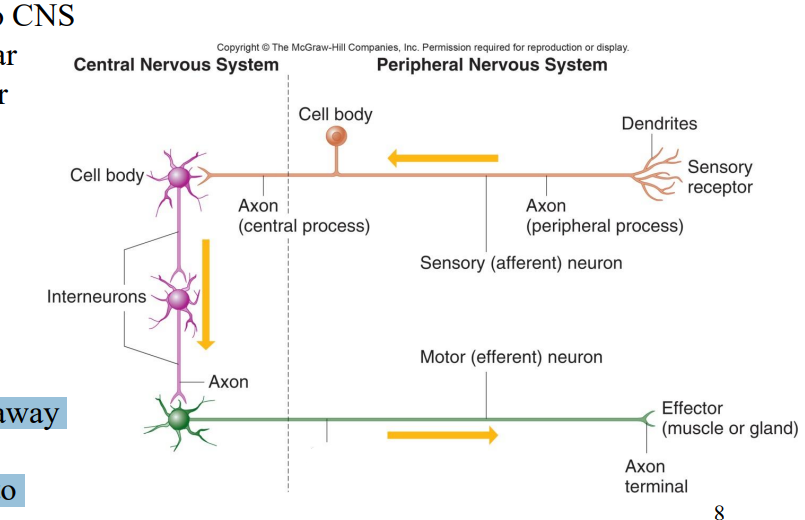
Label the diagram
Axons
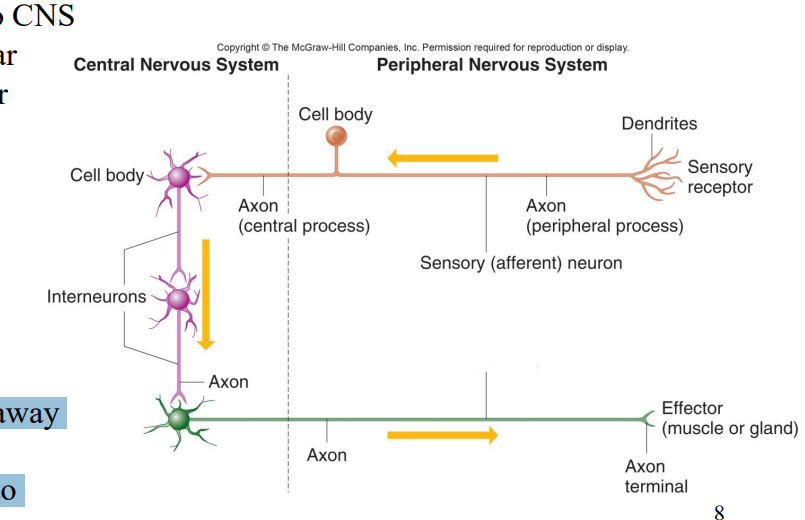
Label the diagram
Motor (efferent) neuron
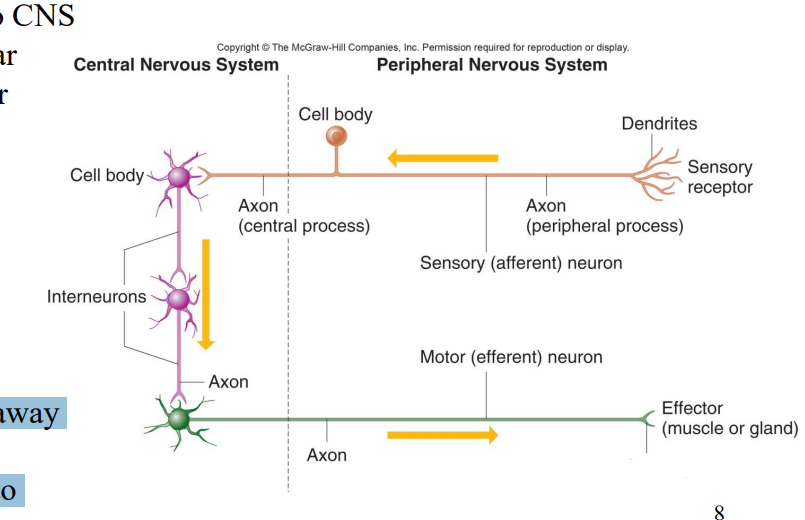
Label the diagram
Axon terminal
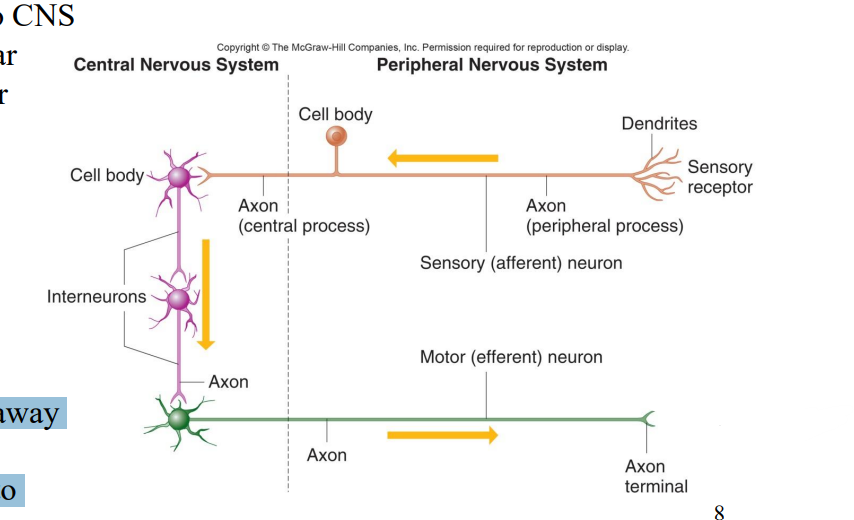
Label the diagram
Effector (muscle or gland)
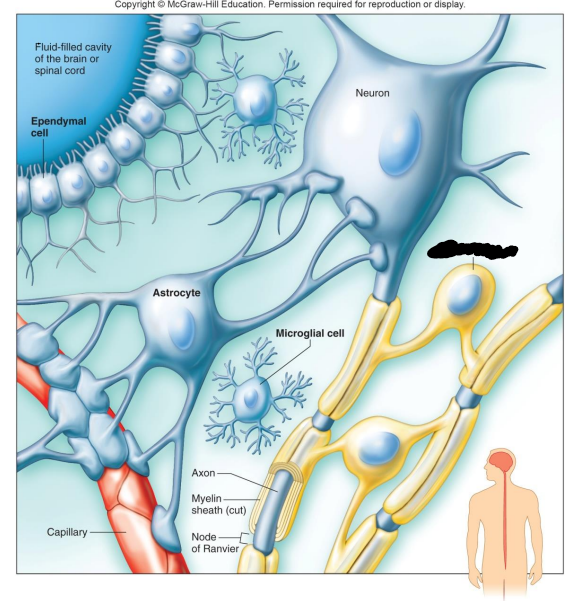
What do Astrocytes do?
•Scar tissue
• Aid metabolism of certain substances
• Induce synapse formation
• Connect neurons to blood vessels- part of Blood Brain Barrier
What are Oligodendrocytes?
Myelinating Cell
What are Microglia?
Myelinating Cell
What are Ependymal Cells?
•Ciliated
• Line central canal of spinal cord
• Line ventricles of brain
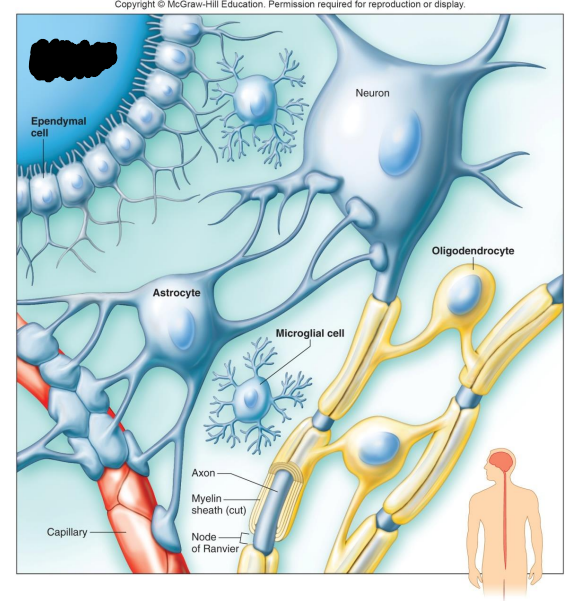
Label the diagram
Fluid-filled cavity of the brain or spinal cord
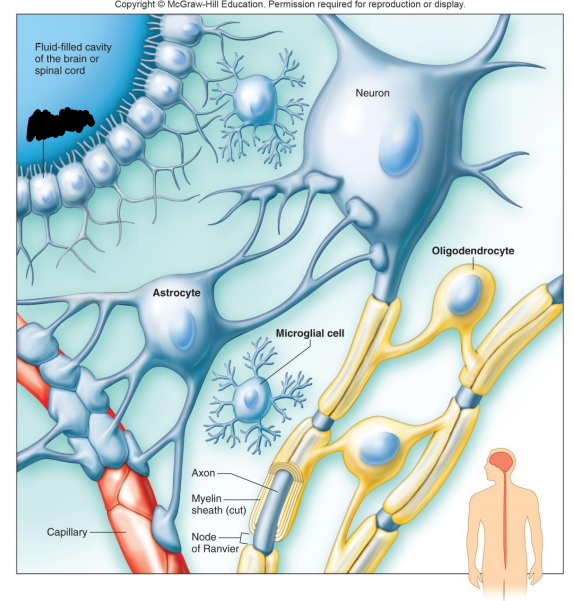
Label the diagram
Ependymal Cell
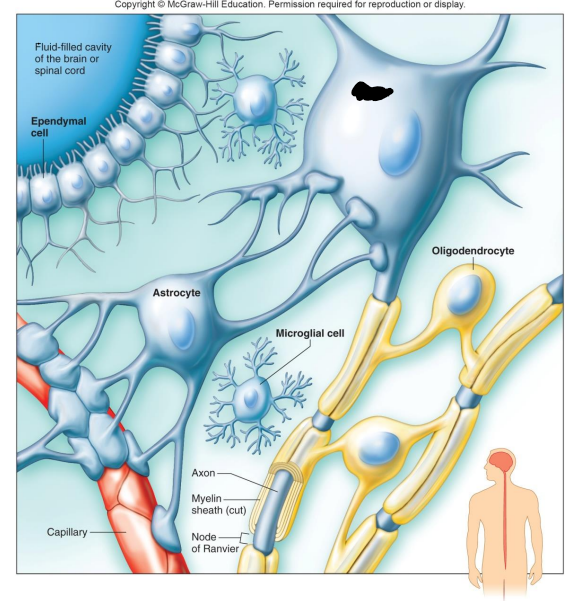
Label the diagram
Neuron
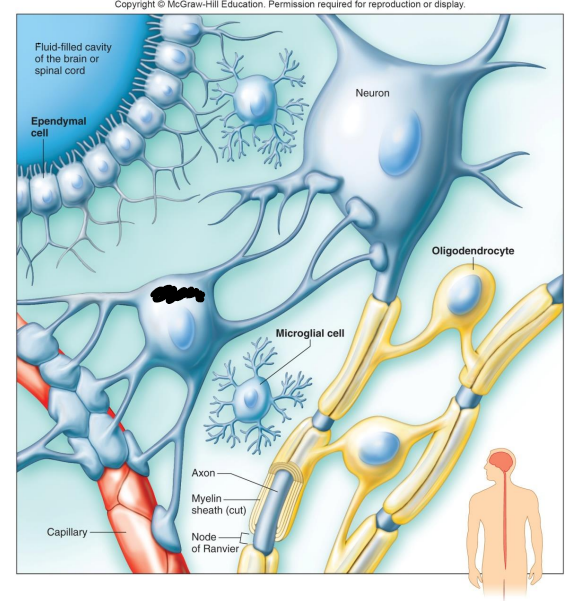
Label the diagram
Astrocyte
Label the diagram
Oligodendrocyte
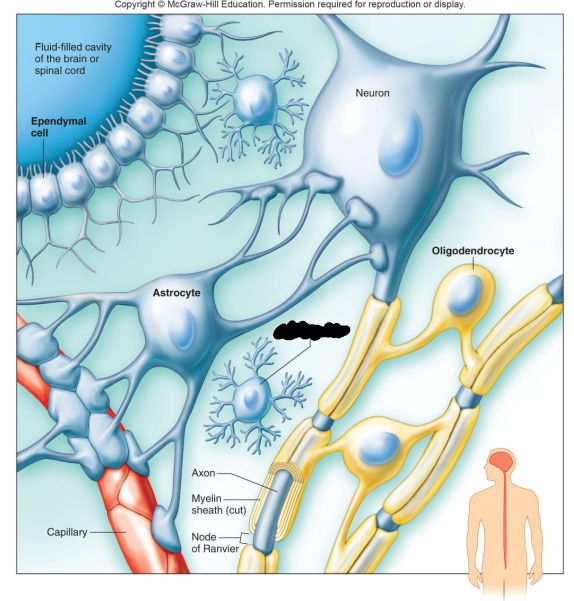
Label the diagram
Microglial Cell
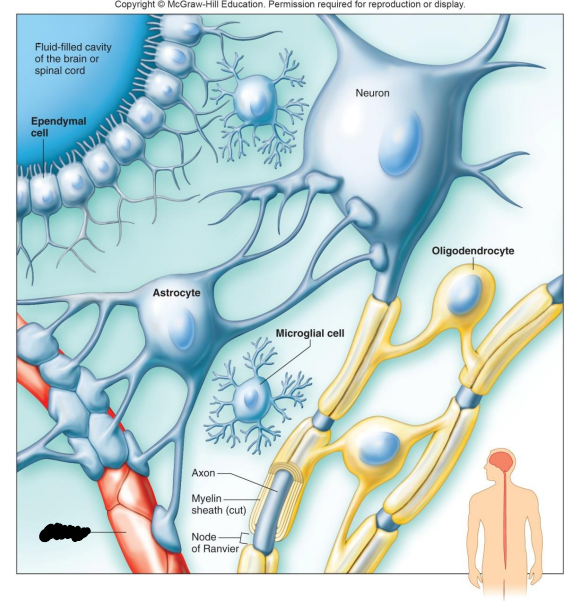
Label the diagram
Capillary
What are the different types of Neuroglial Cells in the PNS?
Schwann Cells, Satellite Cells
Schwann Cells do what?
• Produce myelin found on peripheral myelinated neurons
• Speed up neurotransmission
Satellite Cells do what?
• Support clusters of neuron c
Cell Membrane Potential
• A cell membrane is usually electrically charged, or polarized, so that the inside of the membrane is negatively charged with respect to the outside of the membrane.
• This is as a result of unequal distribution of ions on the inside and the outside of the membrane.
What are Potassium K+ ions?
major intracellular positive ions (cations).
What are Sodium Na+ ions?
major extracellular positive ions (cations).
What are Ion Channels?
formed by membrane proteins, help regulate passage of specific ions into or out of the cell
•Many chemical & electrical factors affect opening & closing of gated channels
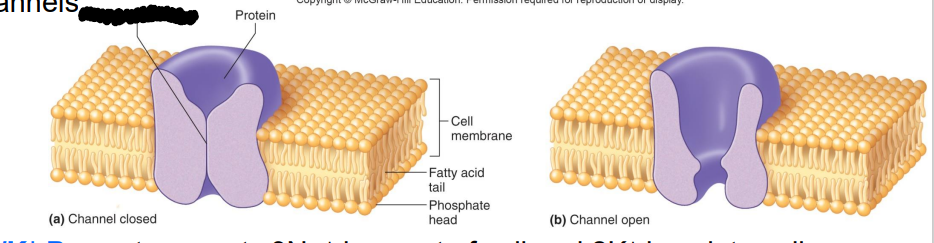
Label the diagram
Gate-like mechanism
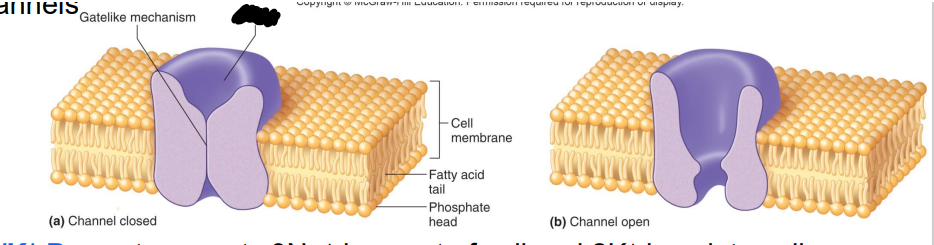
Label the diagram
Protein
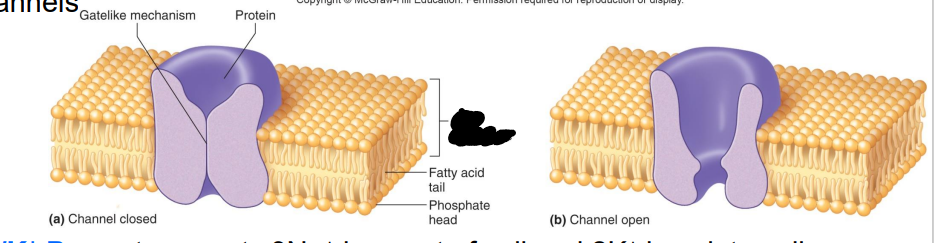
Label the diagram
Cell membrane
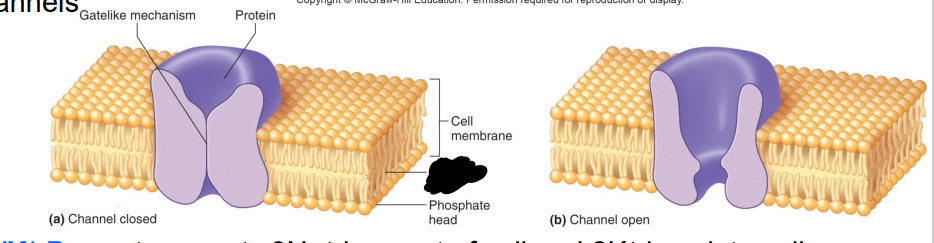
Label the diagram
Fatty acid tail
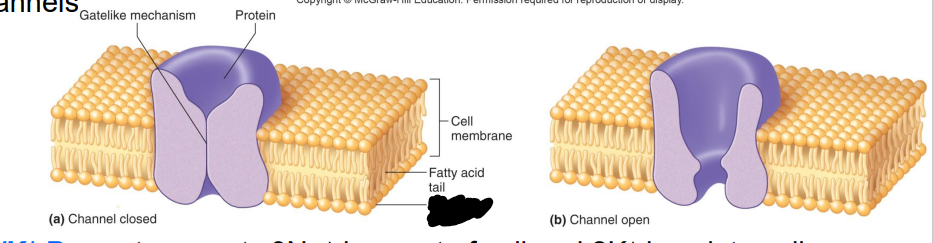
Label the diagram
Phosphate head
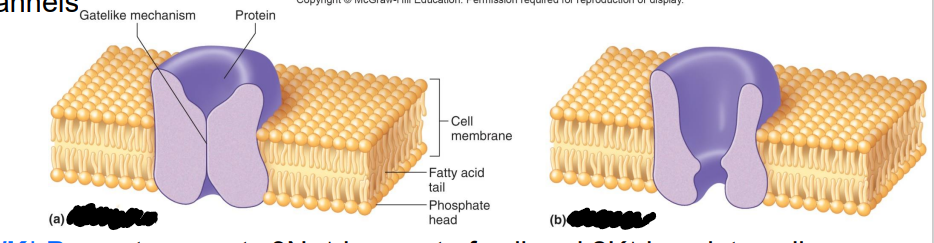
Label the diagram
a. Channel closed
b. Channel open
What is a Na+/K+ pump?
transports 3Na+ ions out of cell and 2K+ ions into cell
•The ion distribution is largely created by the Sodium/Potassium Pump (Na+/K+ pump) but also by ion channels in the cell membrane.
What is Resting Membrane Potential (RMP)
•70 mV difference from inside to outside of cell • It is a polarized membrane
• Inside of cell is negative relative to the outside of the cell
• RMP = -70 mV
• Due to distribution of ions inside vs. outside
• Na+ /K+ pump
RMP
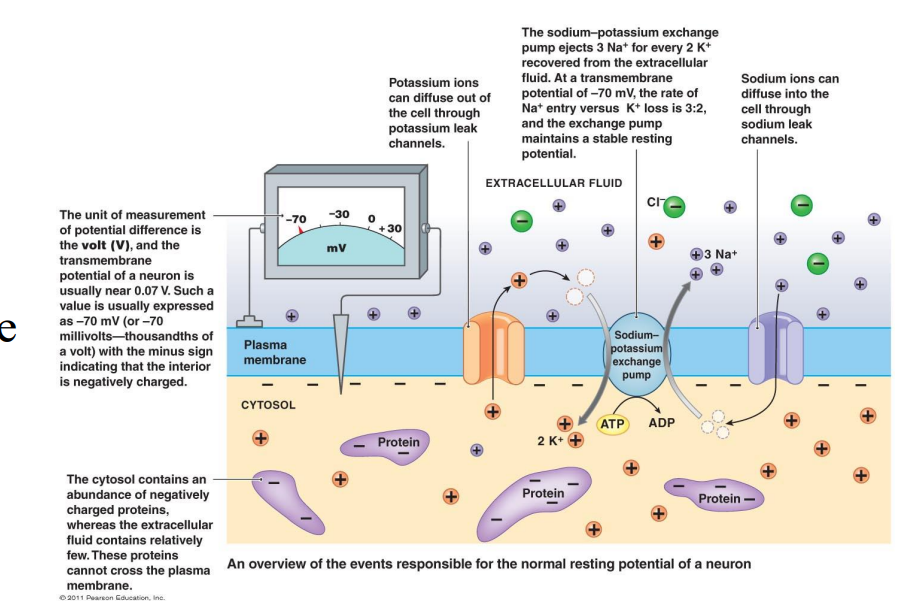
Environmental changes can cause what to open?
Gated ion channels
What happens as ions flow through the membrane what happens?
The membrane potential changes
If the membrane potential becomes more negative than the resting potential it is?
Hyperpolarized
If the membrane potential becomes less negative than the resting potential it is?
Depolarized
Local potential changes are graded
the greater the stimulus intensity, the greater the potential change
If degree of depolarization reaches threshold potential of -55 mV what happens?
an action potential results
If degree of depolarization does not reach threshold potential what will happen?
an action potential will not occur
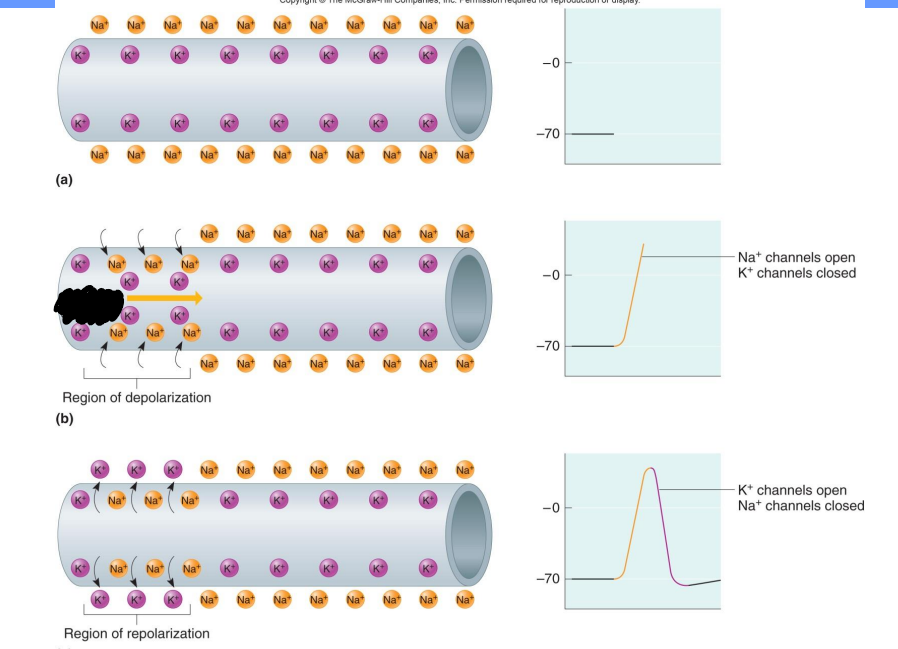
Label the diagram
Threshold stimulus
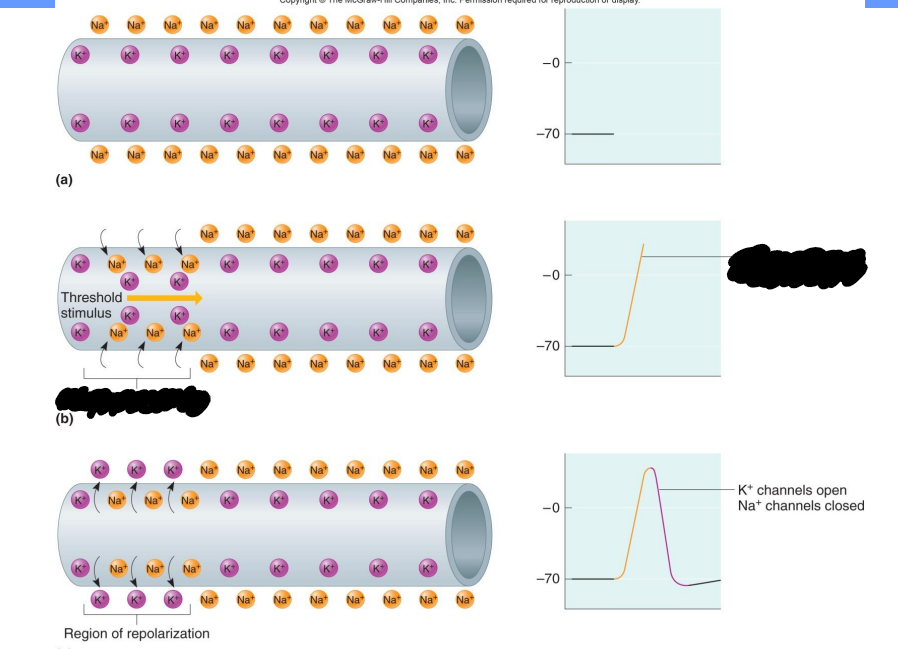
Label the diagram
Region of depolarization, Na+ channels open, K+ channels closed
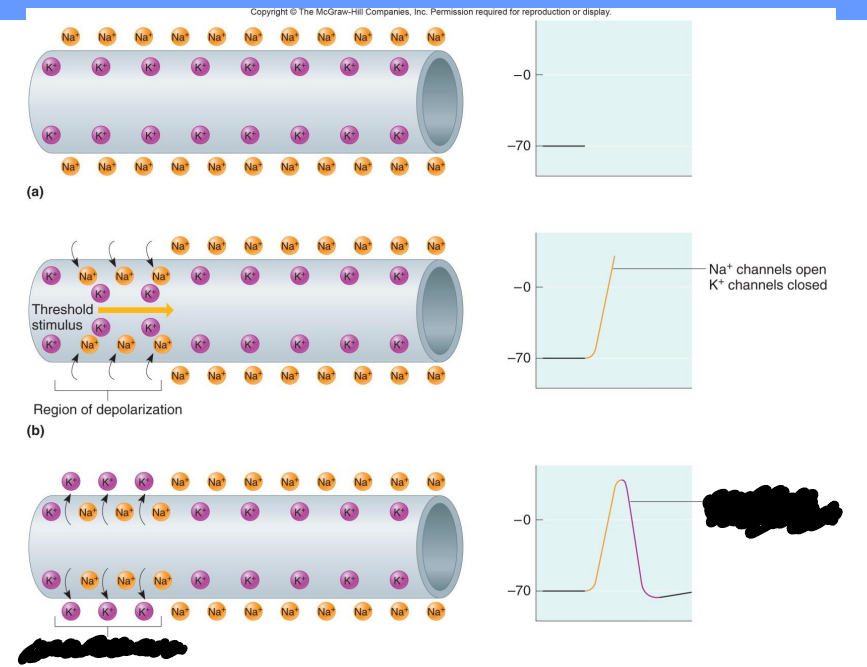
Label the diagram
Region of repolarization, K+ channels open, Na+ channels closed
What does the trigger zone at the first end of the axon contain?
many voltage gated sodium channels (axon hillock)
What is the first sequence of events in an action potential?
Voltage gated Na+ channels open in response to threshold