L17 Manipulation of the Immune System for Clinical Purposes
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Layers of the immune system
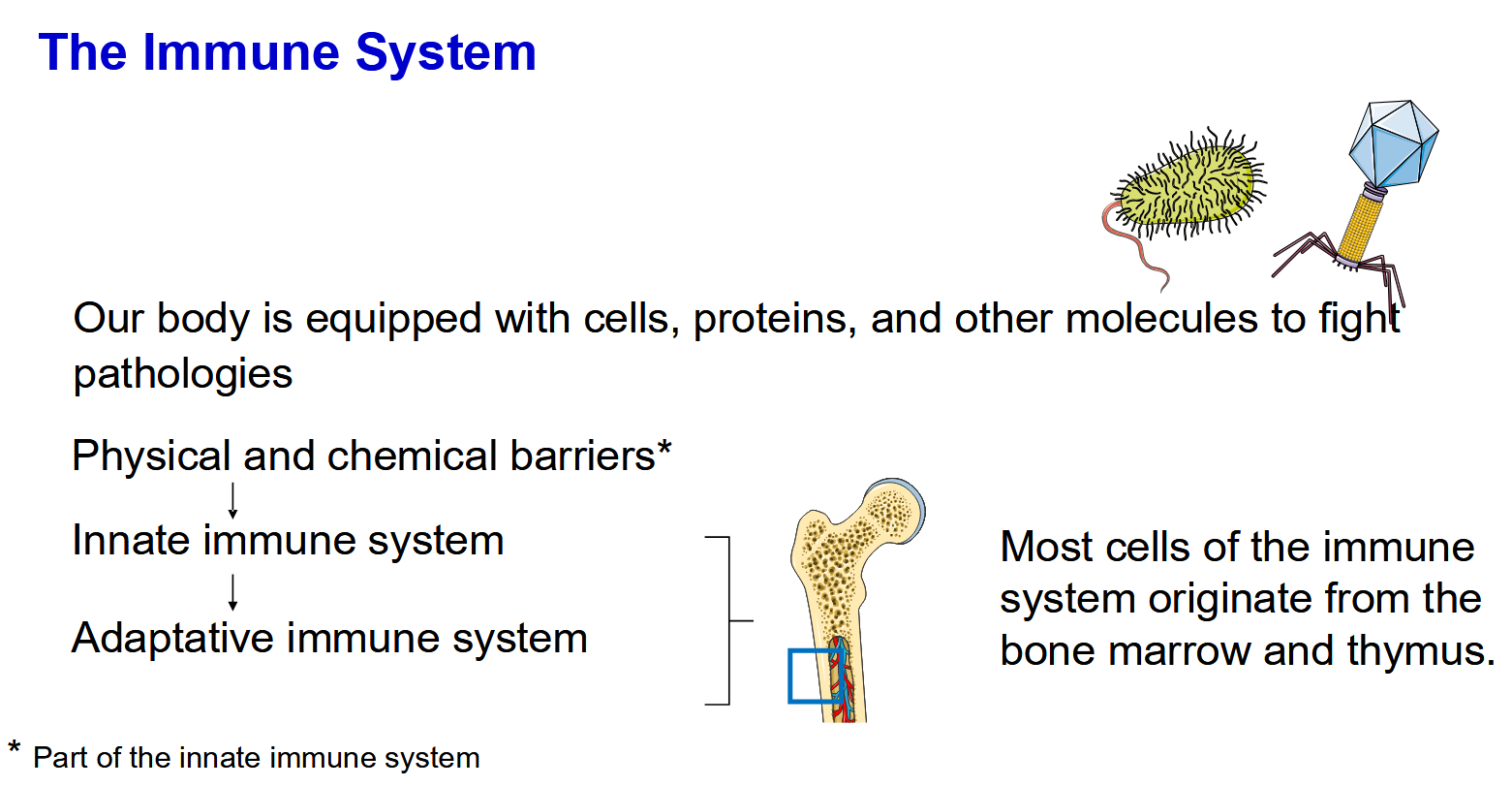
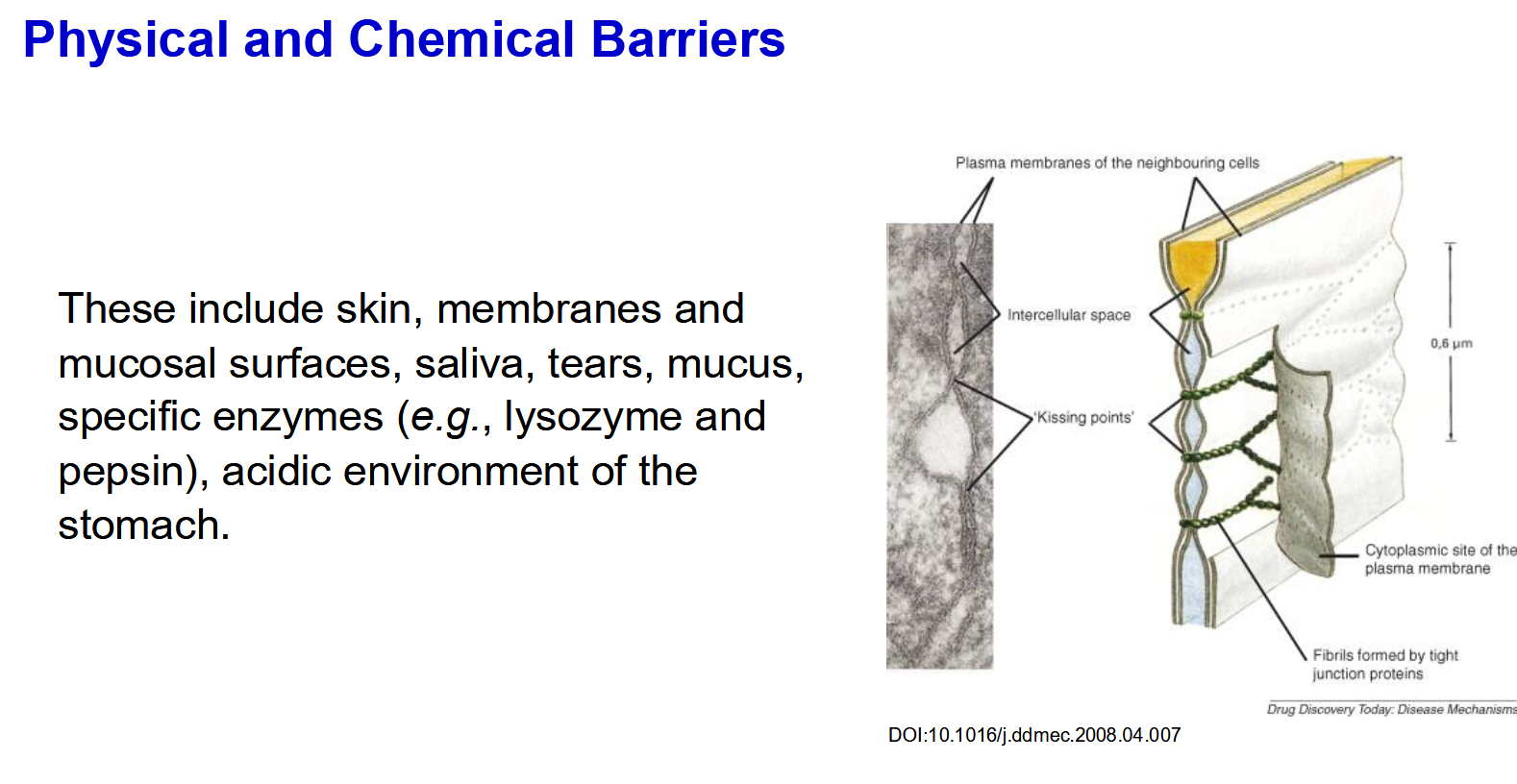
Physical and chemical barriers
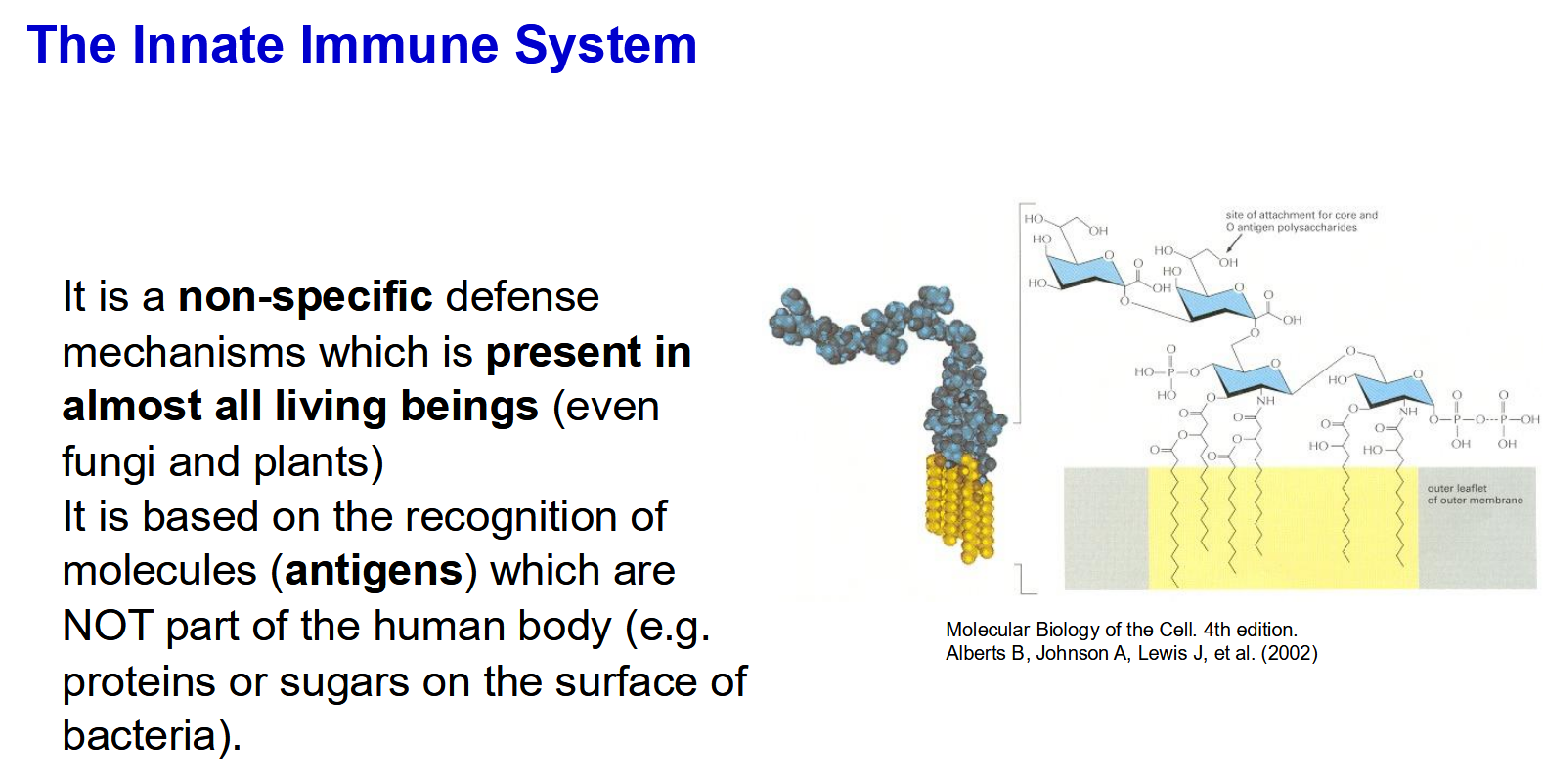
Innate Immune System
Pattern Recognition Receptors recognise the foregin molecules
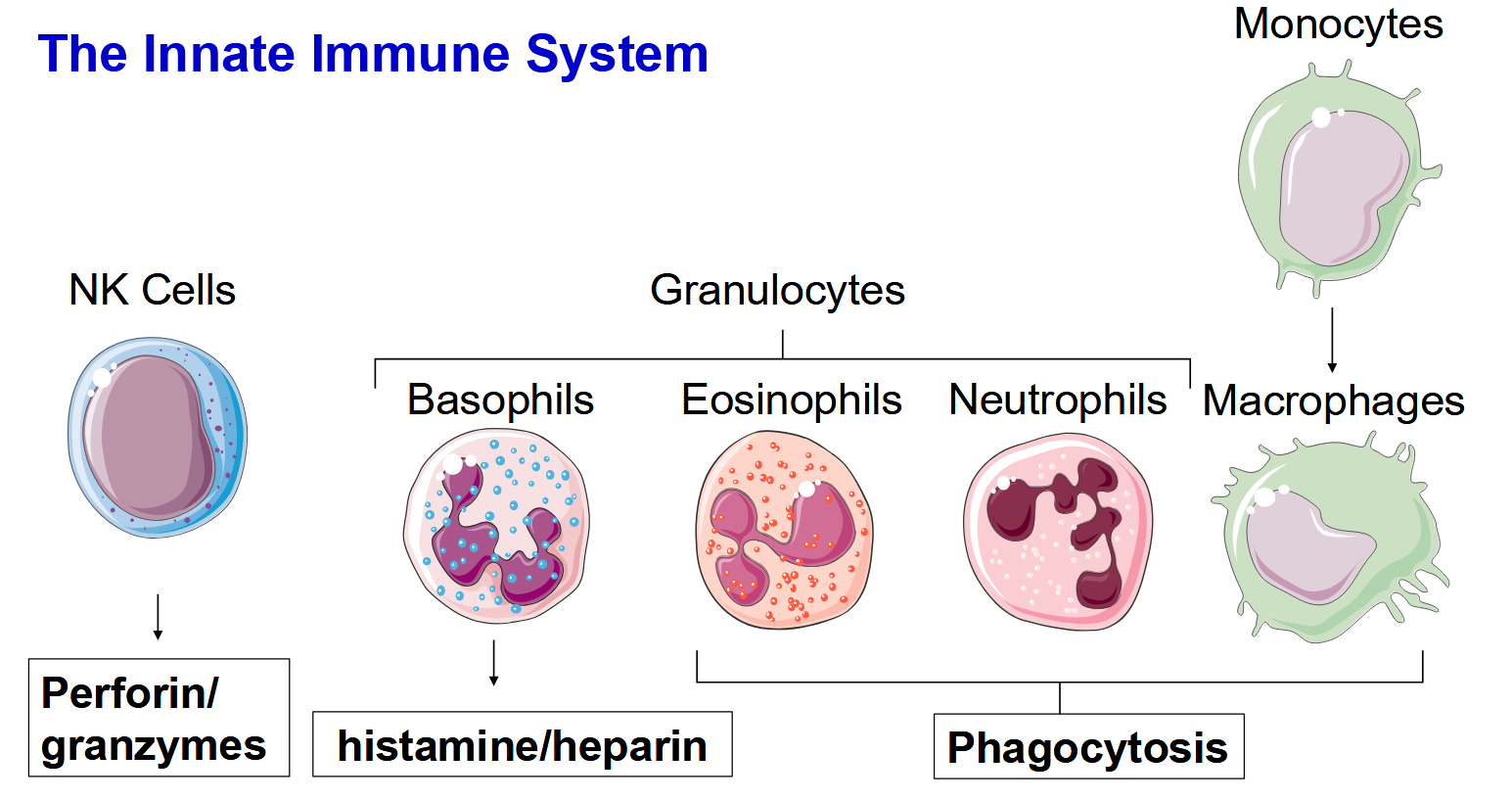
Members of the innate immune system
The innate immune system acts on a large range of pathogens with similar molecules present on their surface
The adaptive (humoral) immune system

T and B lymphocytes
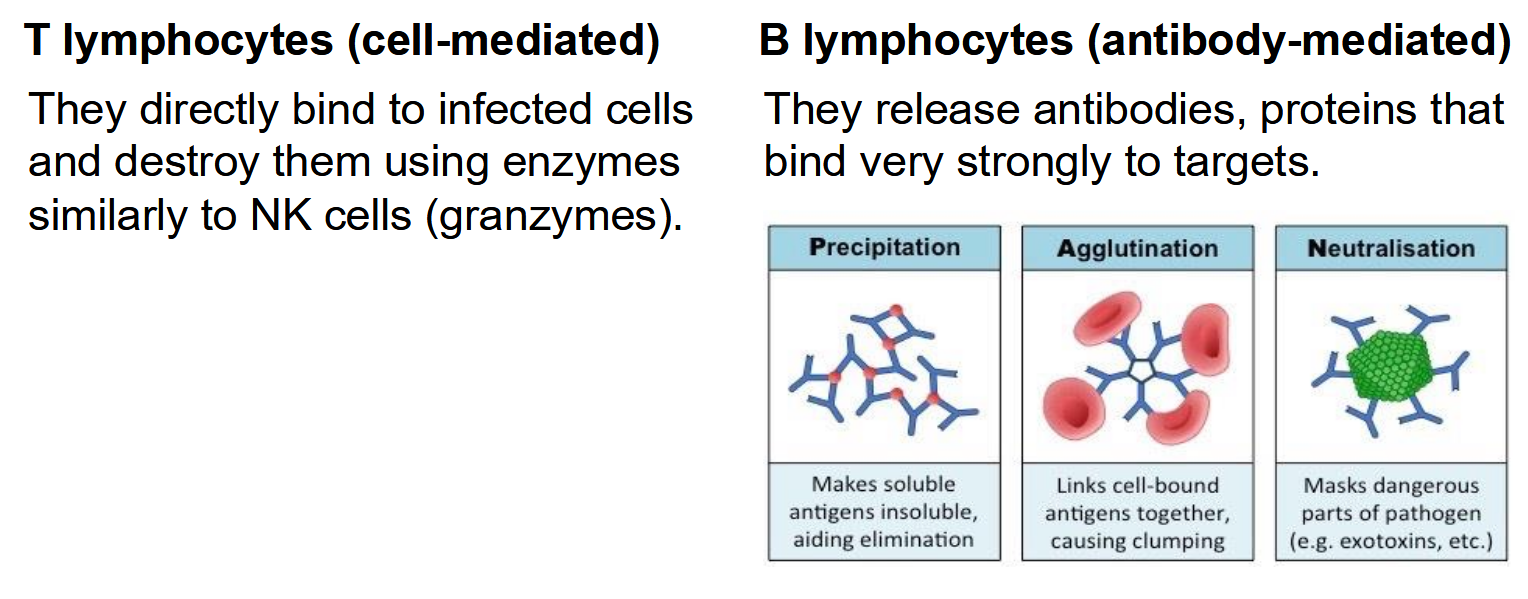
The structure of an antibody - what are CDRs and how many per antibody
What are paratopes and epitopes
What does the FC region do
CDR = complementarity determining region. There are 12 per antibody
Paratopes are the binding sequences on the antibody that bind to the epitopes - the target sequence on the foreign particle
The FC region is reponsible for encouraging processes like agglutination. The FC region is diffeent in different animals and is what allows the immune system to recognise your own antibodies
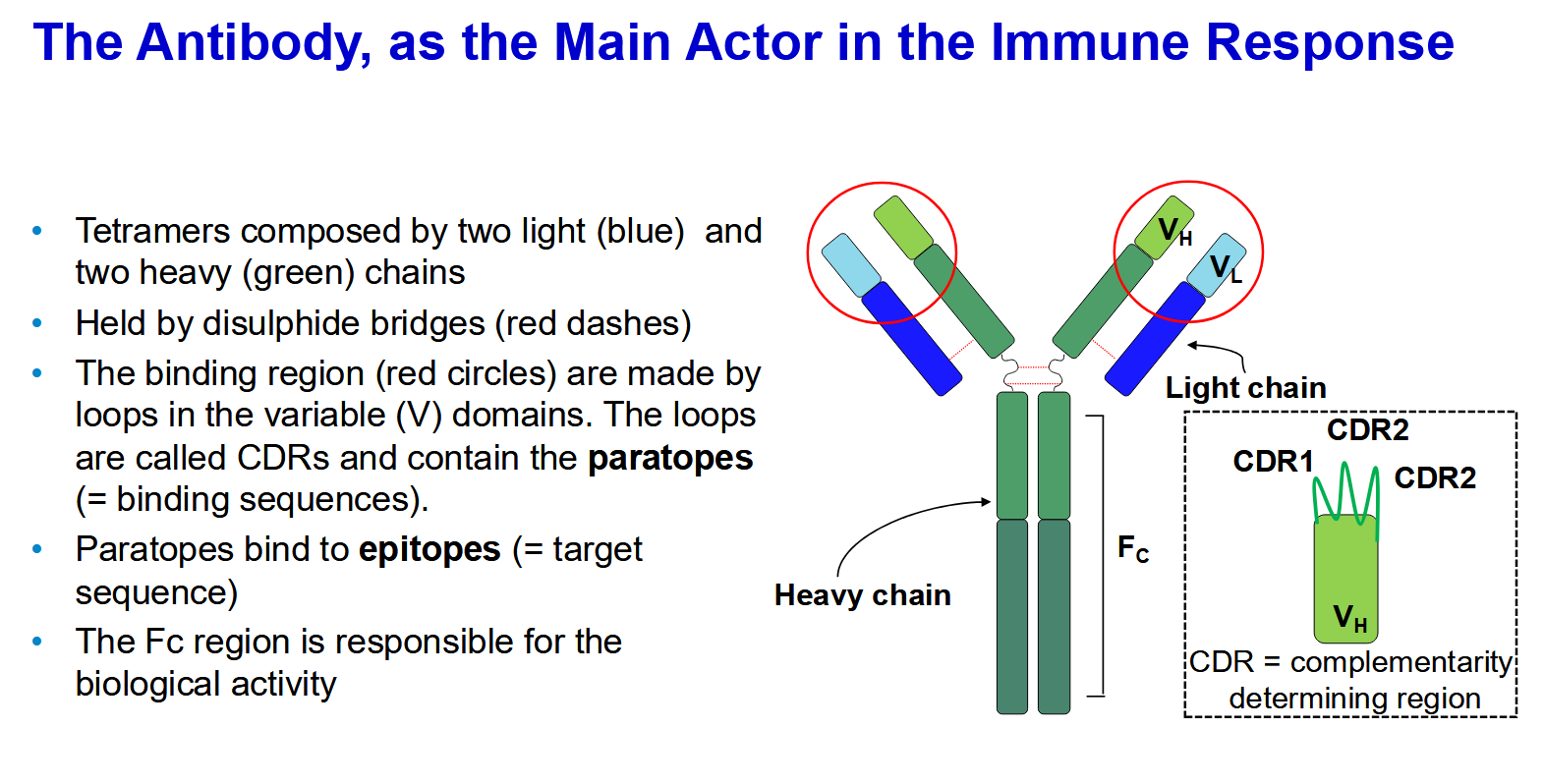
The 5 types of antibodies in humans
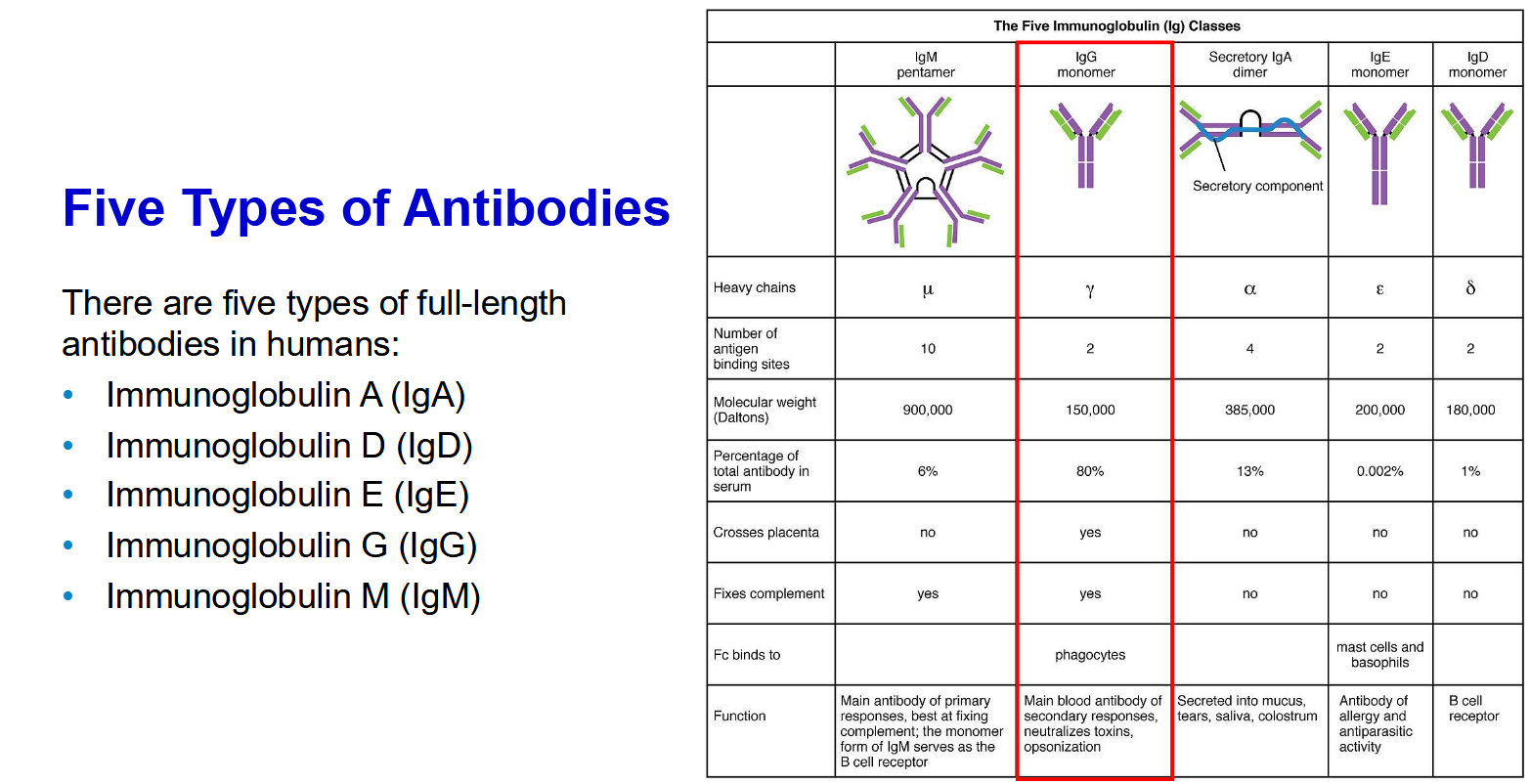
The Process of Lymphocyte Activation and “Memory” - Initial
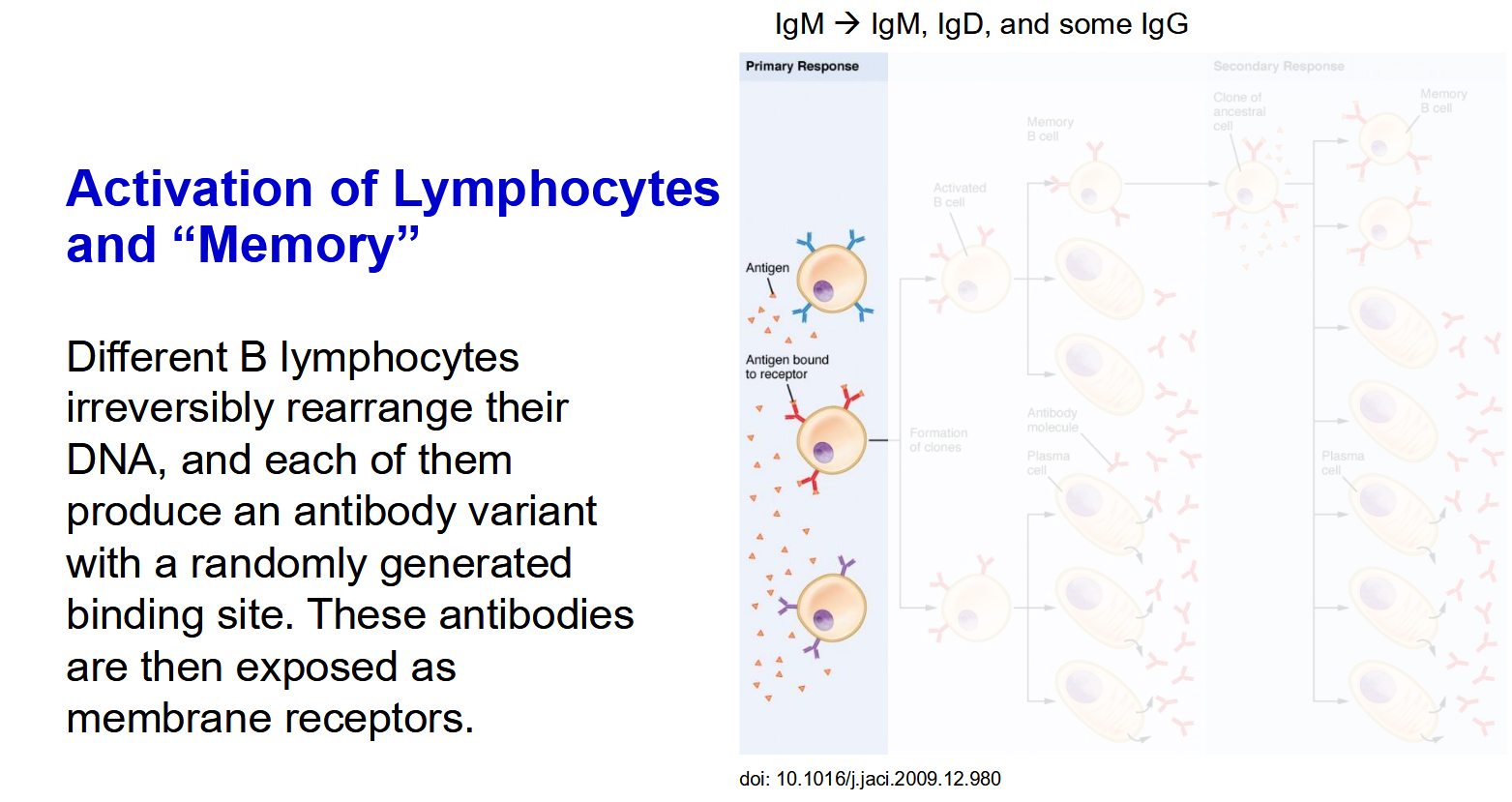
The Process of Lymphocyte Activation and “Memory” - First contact with pathogen
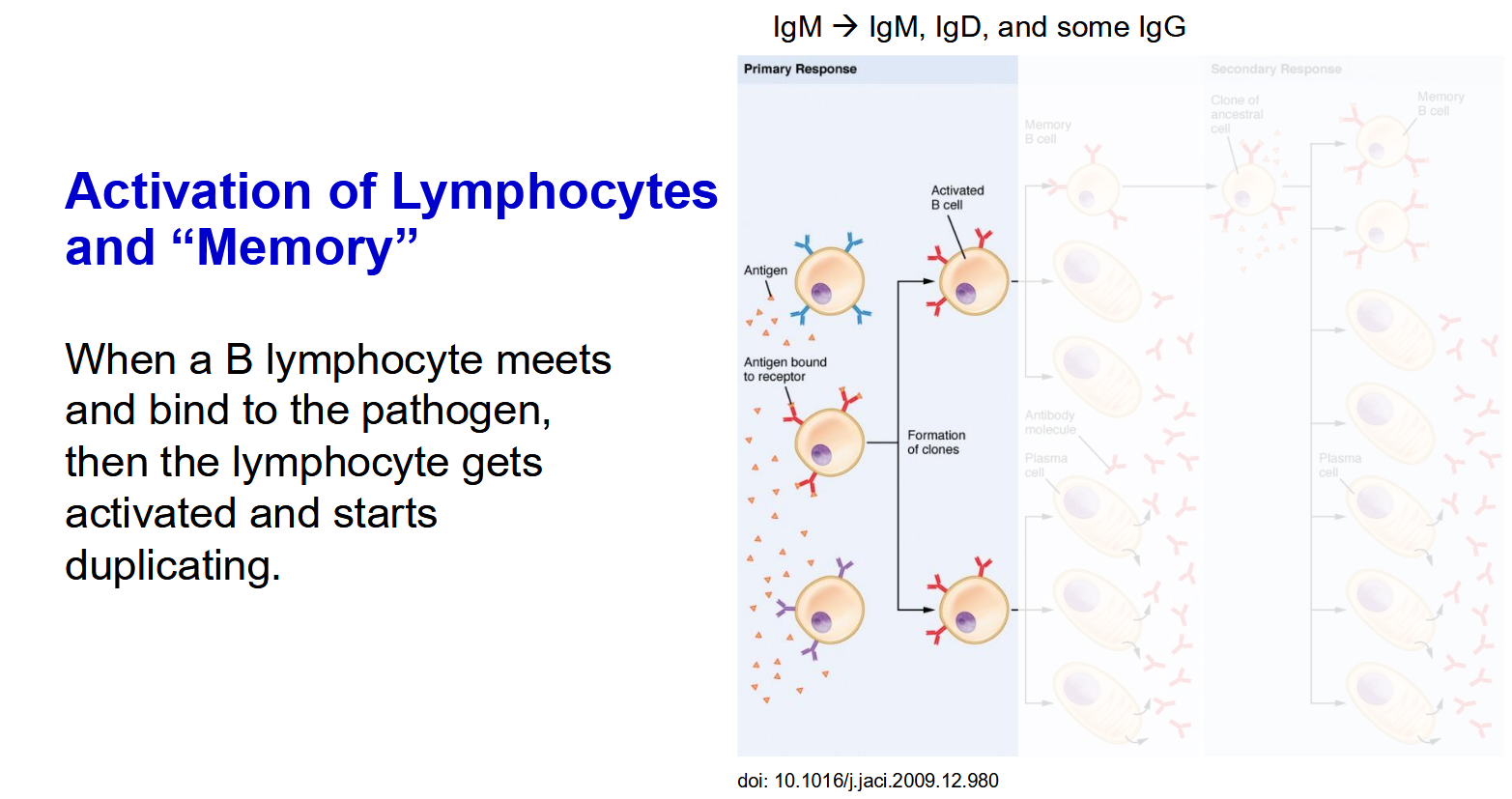
The Process of Lymphocyte Activation and “Memory” - Post replication
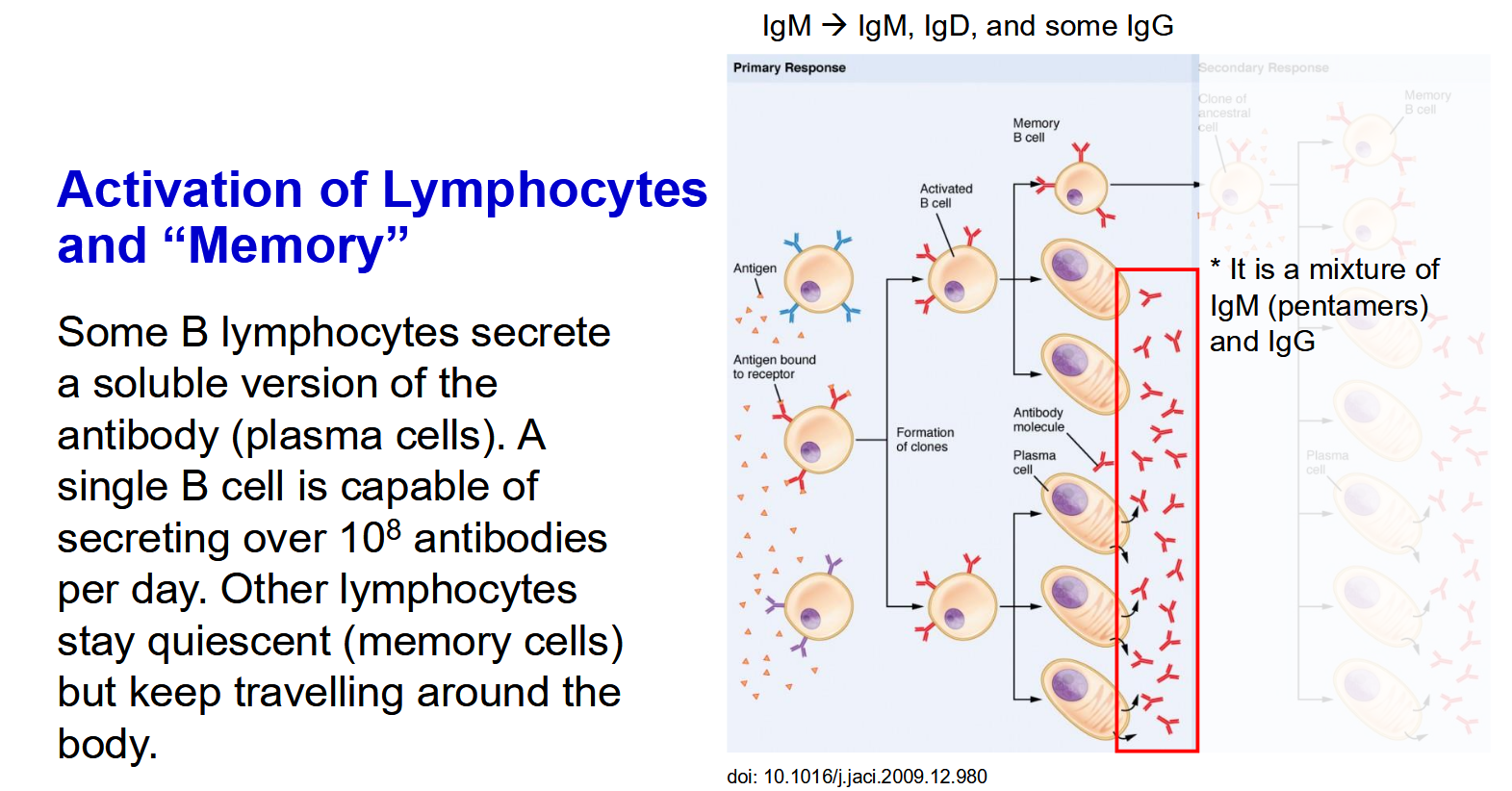
The Process of Lymphocyte Activation and “Memory” - Memory cells
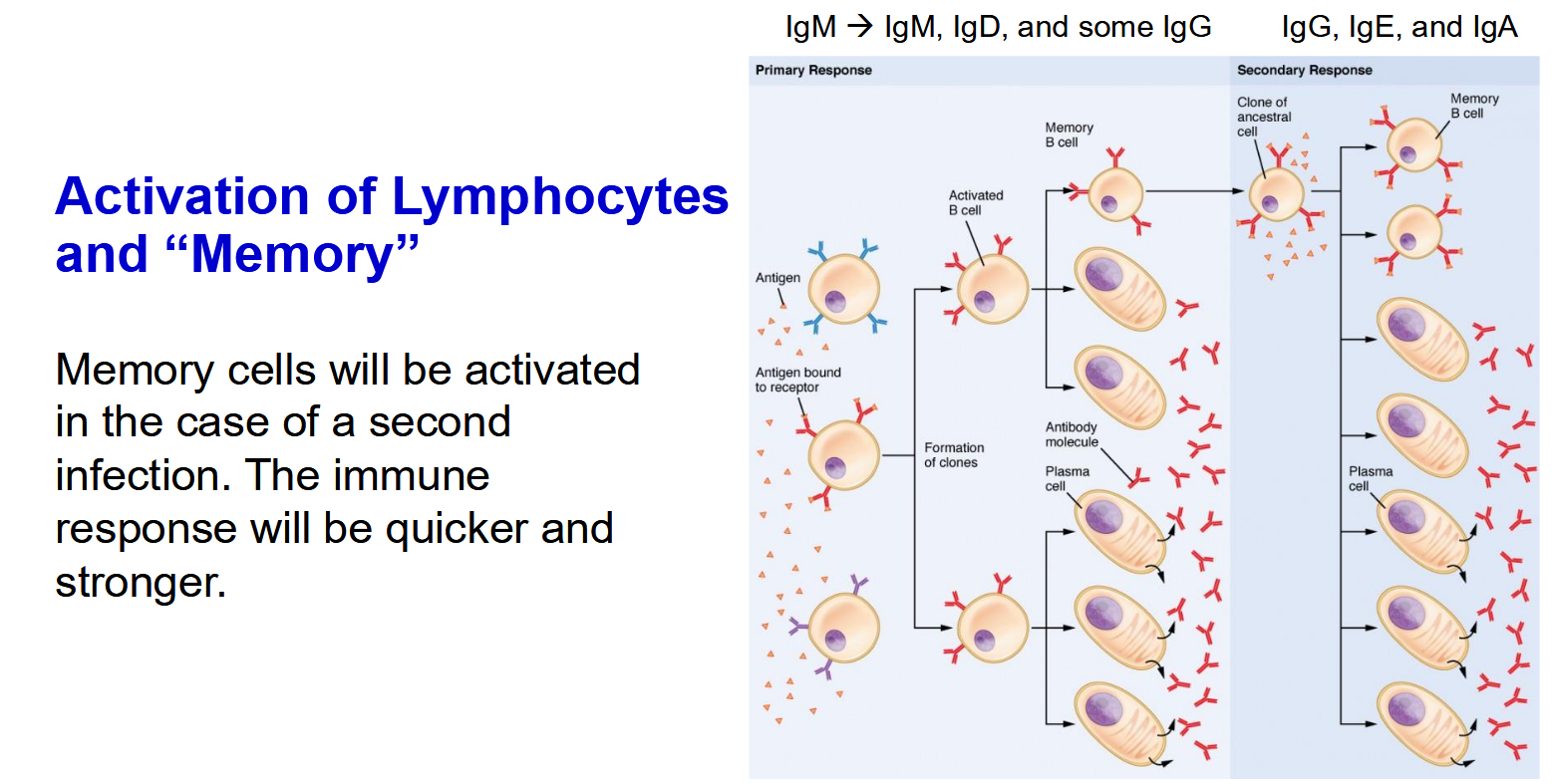
Vaccines description

Activation, Suppressive and Passive immunotherapy
