Ch12 Learning and Memory
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
fixed action pattern
species-specific evolved pattern of complex behavior as a reponse to a specific stimulus
habituation
occurs when an organism reduces its behavioral response to an unchanging, harmless stimuli
sensitization
occurs when repeated exposure to a strong stimulus increases response to other similar environmental stimuli
delay conditioning
type of classical conditioning when the CS overlaps with the UCS
trace conditioning
type of classical conditioning when the CS and UCS do not overlap in training, requires conscious declarative processes
extinction
in classical conditioning when exposure to the CS without the UCS reduces CRs (does not generalize outside of the training situation)
long-term habituation
fewer presynaptic terminals of sensory neurons (signal does not get sensed as often)
long-term sensitization
more presynaptic terminals of sensory neurons, more dendrites on motor neurons (sends signals more frequently)
biochemical correlates of sensitization
serotonin at axo-axonic synapse between interneuron and sensory neuron activates the enzyme adenyl cyclase
adenyl cyclase converts ATP into messenger cAMP
cAMP activates protein kinase A (PKA)
PKA decreases K+ current, prolongs action potential, signals vesicles to move into release zone, and opens more CA2+ channels
all leads to enhanceed glutamate release from sensory neurons
cAMP-PKA-MAPK-CREB pathway
leads to long-term changes in behavior and structural changes in sensory neurons
amygdala in learning and memory
threat conditioning
cerebellar circuits in classical conditioning
cerebellar granule cells provide info about the CS
climbing fibers from the medulla synapse on Purkinje cells, provide info about the UCS
Purkinje cells synapse on cells in interpositus nucleus
*learning occurs when climbing fibers(UCS) and parallel fibers (CS) synapse onto a Purkinje cell and fire at the same time*
stages of memory
encoding → storage → retrieval
atkinson-shiffrin multistore model of memory
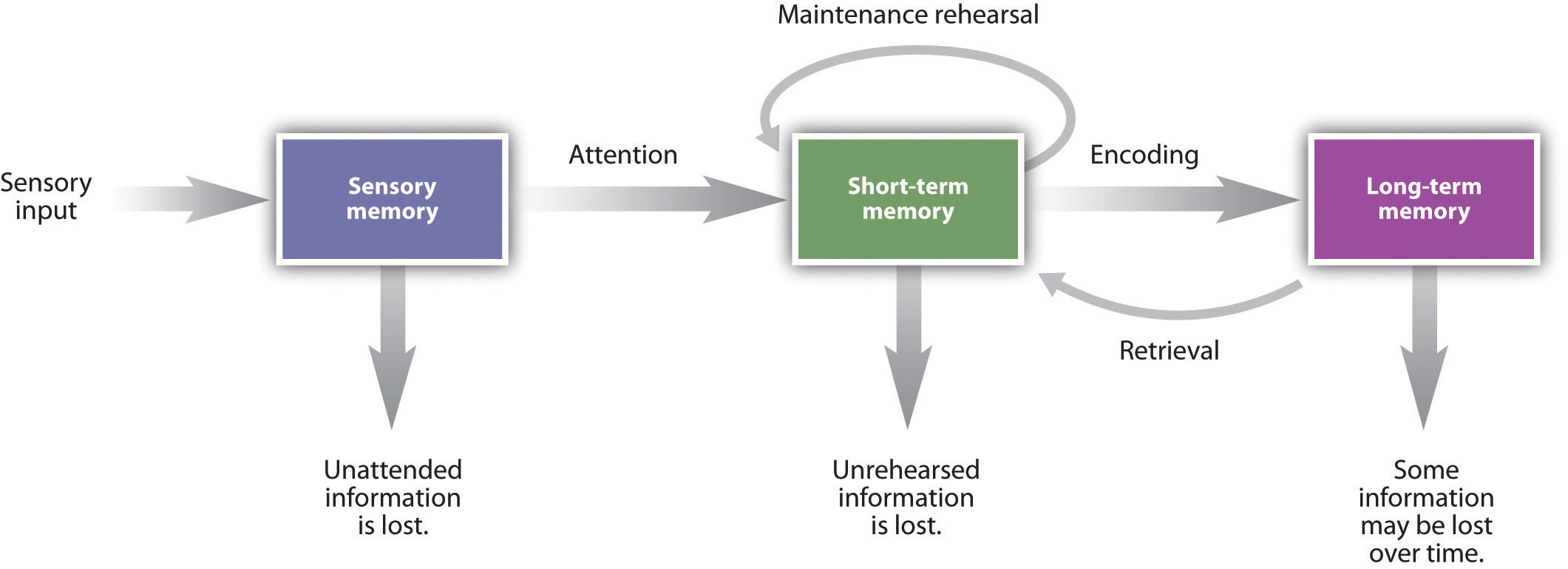
types of declarative memory
episodic (events) and semantic (facts)
types of non-declarative memory
procedural, perceptual representation, classical conditioning, and nonassociative learning
episodic memory in the brain
hippocampus
semantic memory in the brain
cortex
procedural memory in the brain
basal ganglia
perceptual representation in the brain
sensory systems
classical conditioning in the brain
cerebellum
nonassociative learning in the brain
reflex pathways
anterograde amnesia
inability to encode new memories
retrograde amnesia
loss of past memories
Hebb’s Law basics
neurons that fire together wire together
long-term potentiation
??
associative long-term potentiation (LTP) rules
cooperativity: inputs must be active at the same time
associativity: weak inputs are potentiated when fired with strong ones
specificity: only the stimulated synapse shows potentiation
spacial mapping paradigms
hippocampus (dependent on): place cells, where am I?
subiculum: direction cells, where am I going?
entorhinal cortex: grid cells, what’s my environment?
*Morris water maze
semantic memory networks
anterior temporal lobe is the “hub” of semantic cognition (part of language area)
ventral ATL: connects with core semantic areas
dorsal ATL: connects with language and auditory processing areas
what does the striatum do
helps form procedural memory
basal ganglia in memory
involved with memories of motor patterns
nucleus accumbens in memory
emotional and reward correlates of procedures
short term memory involves what area
frontal cortex, think object permanence in toddlers
reactivation and reconsolidation
synapses are weakened when info is retrieved, retrieval stimulates same consolidation processes as the original learning.
reconsolidation updates memory to sometimes include ongoing current information at the time of retrieval, sometiems false info
stress and memory
stress as alertnesswith learning immproves memory
stress produces a refractory period, causing a delay between stress and learning, which might impair memory