SCH4U U4 Solubility and Equilibrium
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1. When is chemical equilibrium achieved?
a. | when both the forward and reverse reactions stop |
b. | when all of the reactants are used up |
c. | when the concentration of products and reactants become equal |
d. | when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal |
e. | all of the above |
d. | when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal |
2. In the equilibrium constant expression below, what do the exponents represent?
Keq= [C]c[D]d / [A]a[B]b
a. | the concentrations of reactants and products |
b. | the equilibrium constant |
c. | the rates of the forward and reverse reactions |
d. | the stoichiometric coefficients from the balanced equation |
e. | none of these |
d. | the stoichiometric coefficients from the balanced equation |
3. A system has reached chemical equilibrium. Which is true of the system?
a. | there is no net change in the concentration of reactants or products |
b. | the molecules have stopped combining and decomposing |
c. | the system is open |
d. | there is no change taking place |
e. | All of the above are true |
a. | there is no net change in the concentration of reactants or products |
4. Which of the following systems would be considered to be at equilibrium:
I. an open flask with 2.0 mL of perfume
II. a closed flask with 10 mL of water
III. an open flask with 10 mL of water
IV. closed flask with ice cube and 10 mL of water
a. | I | c. | II & IV | e. | III |
b. | I & II | d. | II |
d. | II |
II. a closed flask with 10 mL of water
5. When a catalyst is added to a chemical system involving a reversible reaction, the catalyst __________.
a. | increases the rate of reaction in both directions |
b. | increases the rate of reaction in the forward direction only |
c. | increases the rate of reaction in the reverse direction only |
d. | has no effect on the rate of reaction in either direction |
e. | shifts equilibrium in one direction |
a. | increases the rate of reaction in both directions |
6. A very large value of Keq indicates that _____________.
a. | the reaction reaches equilibrium quickly |
b. | the reaction doesn’t reach equilibrium quickly |
c. | the reaction makes a lot of product |
d. | the reaction does not make a lot of product |
e. | the reaction is irreversible |
c. | the reaction makes a lot of product |
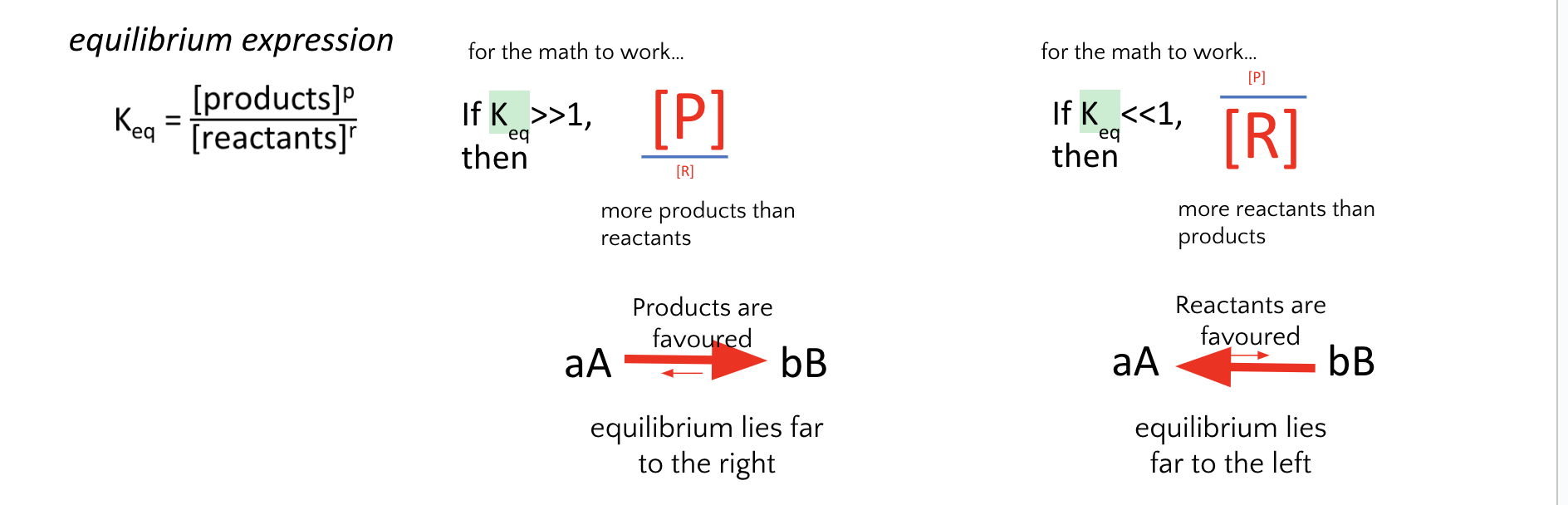
7. What does it mean if Keq < 1, at equilibrium?
a. | The concentration of reactants is greater than the concentration of products. |
b. | The concentration of products is greater than the concentration of reactants. |
c. | The rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the reverse reaction. |
d. | The rate of the reverse reaction is greater than the rate of the forward reaction. |
e. | The concentration of products and reactants are about the same. |
a. | The concentration of reactants is greater than the concentration of products. |
8. A catalyst is added to a system involving a reversible reaction. Which do you expect to occur?
a. | the catalyst is consumed |
b. | the equilibrium shifts in one direction |
c. | the temperature of the system increases |
d. | the system reaches equilibrium more quickly |
e. | all of the above |
d. | the system reaches equilibrium more quickly |
9. For the equilibrium system below, which of the following would result in an increase in the quantity of Cl2(g)?
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) <-> PCl5(g) + 45 kJ
a. | adding some PCl3(g) |
b. | removing some PCl5(g) |
c. | decreasing temperature |
d. | increasing the volume of the container |
e. | injecting some He gas |
d. | increasing the volume of the container |
Increasing volume decreases pressure.
The reaction has 2 moles of gas on the left and 1 mole on the right.
So the system will shift toward the side with more moles (left) to increase pressure.
This shift to the left produces more Cl₂.
10. If Qeq > Keq, then ______.
a. | the system is at equilibrium |
b. | the ratio of products to reactants is less than |
c. | the ratio of products to reactants is > |
d. | the reaction shifts toward product formation |
e. | more reactants must be consumed to reach equilibrium |
c. | the ratio of products to reactants is > |
This means there are more products (or fewer reactants) than there would be at equilibrium.
So, to reach equilibrium, the reaction must shift left, toward the reactants, to reduce the amount of products and increase reactants.
This directly reflects Q > K.
2.4 mol of PCl5(g) are injected into a 2.0 L container and the following equilibrium becomes established.
PCl5(g) <-> PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
If at equilibrium 1.0 mol of PCl5(g) is still in the container the Ke must be which of the following?
a. | 2.0 | c. | 0.71 | e. | 1.02 |
b. | 1.4 | d. | 0.98 |
d. | 0.98 |
We’re given:
2.4 mol of PCl₅ in a 2.0 L container
At equilibrium, 1.0 mol of PCl₅ remains
Reaction: PCl₅ ⇌ PCl₃ + Cl₂
Step 1: Determine change in moles
Initial PCl₅ = 2.4 mol
At equilibrium = 1.0 mol
So 1.4 mol of PCl₅ dissociated, producing:
1.4 mol of PCl₃
1.4 mol of Cl₂
Step 2: Find equilibrium concentrations (using volume = 2.0 L):
[PCl₅] = 1.0 mol ÷ 2.0 L = 0.50 mol/L
[PCl₃] = 1.4 mol ÷ 2.0 L = 0.70 mol/L
[Cl₂] = 1.4 mol ÷ 2.0 L = 0.70 mol/L
Step 3: Write the Ke expression
Ke = [PCl₃][Cl₂] ÷ [PCl₅]
Ke = (0.70)(0.70) ÷ 0.50 = 0.49 ÷ 0.50 = 0.98
12. 6.0 mol of ammonia gas is injected into a 3.0 L container. At equilibrium 1.5 mol of hydrogen gas is found in the container. The number of moles of ammonia gas left in the container must be which of the following?
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇌ 2NH3(g) + 94 kJ
a.2.0 | c.4.0 | e.4.5 | |
b.3. | d.5.0 |
d.5.0
We’re given:
Initial moles of NH₃ = 6.0 mol
Volume = 3.0 L
At equilibrium, 1.5 mol of H₂ is present
Reaction:
N₂ + 3H₂ ⇌ 2NH₃
Step 1: Use stoichiometry
Let’s track changes in mol, not concentrations, since all are in the same container (3.0 L).
From the balanced equation:
2 mol NH₃ ⇌ 1 mol N₂ + 3 mol H₂
So, for every 2 mol of NH₃ broken down, 3 mol of H₂ is produced.
We’re told 1.5 mol of H₂ is present at equilibrium.
From the ratio:
3 mol H₂ comes from 2 mol NH₃
So 1.5 mol H₂ comes from (2/3) × 1.5 = 1.0 mol of NH₃ that dissociated.
Step 2: Subtract the NH₃ that dissociated
Initial NH₃ = 6.0 mol
Dissociated NH₃ = 1.0 mol
So NH₃ remaining = 6.0 – 1.0 = 5.0 mol
13. Which equilibrium shows a decrease in [products] when the volume increases?
I. 2H2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2H2O(g)
II. Cl2(g) + PCl3(g) ⇌ PCl5 (g)
III. H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
IV. 2NH3(g) ⇌ N2 + 3H2(g)
a. | I | c. | IV | e. | II |
b. | I and II | d. | III and IV |
b. | I and II |
I. 2H2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2H2O(g)
II. Cl2(g) + PCl3(g) ⇌ PCl5 (g)
Increasing the volume = decreasing pressure
The system will shift toward the side with more moles of gas to increase pressure again.
If the reaction shifts toward reactants, the concentration of products decreases.
14. Consider this equilibrium
4HCl(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2H2O(g) + 2Cl2(g)
The equilibrium law expression for the balanced chemical equation would be
a. | [HCl][O2] / [H2O][Cl2] |
b. | [H2O]2[Cl2]2/ [HCl]4[O2] |
c. | 2[H2O][Cl2]/ 4[HCl][O2] |
d. | [HCl]4[O2] / [H2O]2[Cl2]2 |
e. | [H2O][Cl2]/HCl][O2] |
b. | [H2O]2[Cl2]2/ [HCl]4[O2] |
15. In a saturated solution of aluminum hydroxide, the concentration of aluminum ion is 2.4 x 10-8 mol/L. The Ksp of aluminum hydroxide would be which of the following?
a. | 1.7 x 10-15 | c. | 1.0 x 10-30 | e. | none of these |
b. | 4.2 x 10-23 | d. | 9.0 x 10-30 |
D.
d. | 9.0 x 10-30 |
Given:
Al³⁺ = 2.4 × 10⁻⁸ mol/L
Solid: Al(OH)₃
Step 1: Write the dissociation equation
Al(OH)₃(s) ⇌ Al³⁺(aq) + 3OH⁻(aq)
Let the solubility s = Al3+ = 2.4 × 10⁻⁸
Then:
OH− = 3s = 3 × 2.4 × 10⁻⁸ = 7.2 × 10⁻⁸
Step 2: Write the Ksp expression
Ksp = Al³⁺x(OH⁻)3
Substitute the values:
Ksp = (2.4 × 10⁻⁸) × (7.2 × 10⁻⁸)³
First, cube the OH−OH⁻OH− concentration:
(7.2 × 10⁻⁸)³ = 373.248 × 10⁻²⁴ ≈ 3.73 × 10⁻²²
Now multiply:
Ksp = (2.4 × 10⁻⁸) × (3.73 × 10⁻²²) = 8.95 × 10⁻³⁰
16. In a saturated solution of lead(II) chloride, the concentration of chloride ion is 6.2 x 10-4 mol/L. The Ksp of lead(II) chloride would be which of the following?
a. | 1.9 x 10-7 | c. | 1.2 x 10-10 | e. | none of these |
b. | 6.0 x 10-11 | d. | 2.3 x 10-17 |
c. | 1.2 x 10-10 |
on paper

17. If the equilibrium shown below is cooled at a constant pressure.
H2(g) + I2(g) <-> 2HI(g) + 65 kJ
What is most likely to happen?
a. | Keq decreases |
b. | Keq increases |
c. | [HI] increases |
d. | both a and c |
e. | both b and c |
e. | both b and c |
b. | Keq increases |
c. | [HI] increases |
If the system is cooled, that means heat is being removed.
According to Le Châtelier’s Principle, the system will shift to produce more heat, so it shifts right (toward products).
Effects of cooling:
[HI] increases ✅
Reaction shifts right, so Keq increases (for exothermic reactions) ✅
![<p></p><table style="min-width: 50px"><colgroup><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"></colgroup><tbody><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p class="p1">e.</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p class="p1">both b and c</p></td></tr></tbody></table><p></p><table style="min-width: 50px"><colgroup><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"></colgroup><tbody><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p class="p1">b.</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p class="p1">Keq increases</p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p class="p1">c.</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p class="p1">[HI] increases</p></td></tr></tbody></table><p>If the system is <strong>cooled</strong>, that means heat is being <strong>removed</strong>.</p><p class="">According to <strong>Le Châtelier’s Principle</strong>, the system will shift to <strong>produce more heat</strong>, so it shifts <strong>right (toward products)</strong>.</p><p>Effects of cooling:</p><ul><li><p class=""><strong>[HI] increases</strong> <span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span></p></li><li><p class="">Reaction shifts right, so <strong>Keq increases</strong> (for exothermic reactions) <span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span></p></li></ul><p></p><p class="placeholder"></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a668c1c4-b118-43a5-bfea-6ee360c0a768.png)
18. If the equilibrium constant for an equilibrium system is increased by a decrease in temperature then
a. | [reactants] and [products] decreases |
b. | [reactants] and [products] increases |
c. | [reactants] increases and [products] decreases |
d. | [reactants] decreases and [products] increases |
e. | none of the above |
d. | [reactants] decreases and [products] increases |
19. Consider the equilibrium reaction where carbon monoxide reacts with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide. The equilibrium position occurs far to the right. This means that once equilibrium has been established,
a. | very little product remains |
b. | the reaction vessel would contain equal amounts of product and reactant |
c. | very little reactant remains |
d. | the reaction vessel contains high concentrations of reactant |
c. | very little reactant remains |
20. The equilibrium constant for a given reaction will be the same, regardless of the initial concentrations, but only if the environmental conditions remain the same. Why?
a. | The order of the reaction remains constant. |
b. | The number of collisions remains constant, regardless of concentration. |
c. | The reaction rate is constant. |
d. | The product concentration will be similarly affected by increases or decreases in reactant concentration. |
d. | The product concentration will be similarly affected by increases or decreases in reactant concentration. |
21. The equilibrium constant for the production of ammonia gas was 1.02 x 10–5 at 300 °C. The equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction would be
a. | 980 | c. | 9.8 X 10–5 | e. | none of these |
b. | 9.8 X 104 | d. |
b. | 9.8 X 104 |
Key concept:
To find the equilibrium constant of the reverse reaction, take the reciprocal of the forward reaction's K.
So:
K (reverse) = 1 ÷ (1.02 × 10⁻⁵) ≈ 9.8 × 10⁴
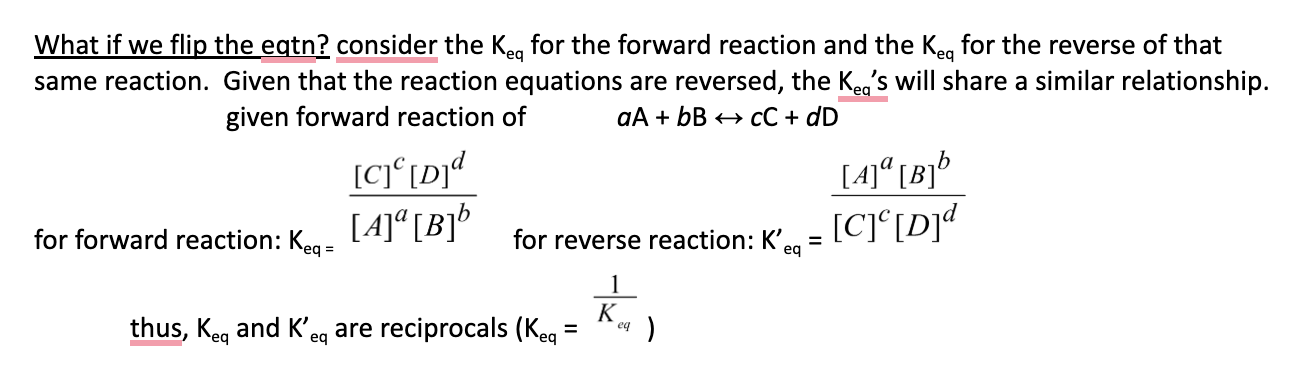
22. Suppose the equilibrium constant for the production of ammonia gas is 4.26 x 108 at 25 °C. This reaction’s equilibrium position is
a. | to the left | c. | to the right |
b. | near the centre | d. | undetermined |
c. | to the right |
keq » 1 so product have to be bigger keq = p / r
23. Pure substances can be elements or compounds. What effect do solid and liquid pure substances have on the equilibrium position when a gas is also involved?
a. | They are denser than gases, and so shift the equilibrium away from their position as product or reactant. |
b. | They are more concentrated and so shift the equilibrium away from their position in a balanced equation. |
c. | They have no effect on the equilibrium. |
d. | They have a profound effect in determining equilibrium position, but this effect is dependent on their bond energies. |
c. | They have no effect on the equilibrium. |
24. A homogeneous equilibrium involves chemicals that are
a. | in the same state, solid, liquid, or gas |
b. | gases, liquids, or aqueous solutions |
c. | gases or aqueous solutions |
d. | gases only. |
c. | gases or aqueous solutions |
25. Methanol is a useful substrate for the production of esters, aldehydes, and other industrial chemicals. Carbon dioxide is reacted with hydrogen to produce methanol.
H = –238.7 kJ/mol. Low temperatures will
a. | have no effect on the equilibrium |
b. | favour the production of carbon dioxide and hydrogen |
c. | prevent the reaction from occurring |
d. | favour the production of methanol |
d. | favour the production of methanol |
According to Le Châtelier’s Principle:
Lowering temperature removes heat.
So the equilibrium will shift to produce more heat — that is, toward the products (forward direction) in an exothermic reaction.
Therefore, low temperatures will:
✅ Favour the production of methanol
26. Consider the reaction in which water (steam) reacts with carbon monoxide (gas) to produce hydrogen (gas) and carbon dioxide (gas). A decrease in the volume of the reaction vessel will
a. | have no effect on the equilibrium position |
b. | create an equilibrium shift to the left |
c. | create an equilibrium shift to the right |
d. | prevent the reaction from occurring |
a. | have no effect on the equilibrium position |
Decrease Pressure | Shifts to side with more gas molecules | System increases pressure by increasing gas moles |
equal mols on both sides so no effect
27. How does an increase in temperature affect the equilibrium of an endothermic reaction?
a. | The equilibrium will shift to the right. |
b. | The equilibrium will not change. |
c. | The equilibrium will shift to the centre. |
d. | The equilibrium will shift to the left. |
a. | The equilibrium will shift to the right. |
28. Where is the equilibrium position for K = 3 x 102?
a. | to the right | c. | in the centre |
b. | not possible to tell | d. | to the left |
a. | to the right |
29. Sulfuric acid is an important industrial chemical. It is used for fertilizers, detergents, dyes, and medicine. The equilibrium equation for the first step in the contact process is as follows:
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2SO3(g), H = –196 kJ/mol
What would you do to increase the production of SO3?
a. | Raise the temperature considerably to shift the equilibrium to the right. |
b. | Raise the temperature to shift the equilibrium to the right and increase the rate of formation (collision theory). |
c. | Lower the temperature considerably to shift the equilibrium to the right. |
d. | Lower the temperature moderately to shift the equilibrium right while maintaining the rate of formation (collision theory). |
d. | Lower the temperature moderately to shift the equilibrium right while maintaining the rate of formation (collision theory). |
30. What will the magnitude of the equilibrium constant indicate?
a. | how concentrated the initial reactants were |
b. | the rate of the reaction |
c. | how concentrated final equilibrium products were |
d. | the extent of the reaction |
d. | the extent of the reaction |
31. The Ksp for an ionic substance is taken into consideration when studying
a. | thermal energy |
b. | the release of anions and cations |
c. | the dissolving and forming of precipitates |
d. | the release of acidic and basic ions |
c. | the dissolving and forming of precipitates |
32. The trial ion product, Q, when compared to the Solubility Product Constant, Ksp, will indicate if the final products will be insoluble. The equilibrium will shift left if Q is
a. | equal to Ksp |
b. | less than Ksp |
c. | 100 times less than the value of Ksp |
d. | greater than Ksp |
d. | greater than Ksp |
Q < Ksp → The solution is unsaturated → More solid can dissolve → No precipitate.
Q = Ksp → The solution is saturated → At equilibrium → No change.
Q > Ksp → The solution is supersaturated → A precipitate forms → Reaction shifts left to form more solid.
So if Q is greater than Ksp, the solution has too many ions, and the excess will form a solid (precipitate), shifting the equilibrium left.
33. What will happen to the following equilibrium if silver ions are added to the solution?
AgNO3(s) ↔ Ag(aq) + NO3(aq)
a. | There will be no change. |
b. | The equilibrium will shift to the right. |
c. | The equilibrium will shift to the left. |
d. | The equilibrium will shift to the centre. |
c. | The equilibrium will shift to the left. |
Apply Le Châtelier’s Principle:
Adding Ag⁺ increases the concentration of a product.
The system will try to reduce this added product by shifting the equilibrium to the left (toward the solid AgNO₃).
Final answer: c. The equilibrium will shift to the left. ✅
34. Nitrogen dioxide (brown) and dinitrogen tetroxide (colourless) are placed in a syringe. The syringe is depressed to half its volume. What happens to the pressure in the syringe?
2 NO2(g) ↔ N2O4(g)
a. | It will initially double, then decrease as the equilibrium shifts left (brown). |
b. | It will double, driving the reaction to the right (clear). |
c. | It will double, driving the reaction to the left (brown). |
d. | It will initially double, then decrease slightly as the equilibrium shifts right (clear). |
d. | It will initially double, then decrease slightly as the equilibrium shifts right (clear). |
35. Consider the equilibrium where iron (III) ions (yellow) are mixed with thiocyanate ions (clear) to produce iron thiocyanate ions (red). This reaction is exothermic. When the equilibrium position is shifted to the right, the solution is red. When the position is shifted left, the solution is yellow. Predict the colour change when the test tube containing these solutions is cooled to 5°C.
a. | yellow: removing thermal energy will overcompensate, driving the reaction to the extreme left |
b. | darker red: removing thermal energy will drive the reaction past the initial equilibrium position |
c. | clear: removing energy will balance the energy generated, shifting the equilibrium left |
d. | red: removing thermal energy drives the reaction to generate thermal energy |
b. | darker red: removing thermal energy will drive the reaction past the initial equilibrium position |
According to Le Chatelier’s Principle, when a system at equilibrium experiences a change (like removing heat), the system will shift to counteract that change.
If thermal energy is removed, the reaction will shift in the exothermic direction — the direction that releases heat — in order to generate more thermal energy and restore balance.
So, removing thermal energy drives the reaction to generate thermal energy, which is option d (red).
36. Carbonic acid, H2CO3(aq), is a chemical substance which plays an important role in controlling the pH of body fluids. In aqueous solution it produces HCO3–(aq) and CO32–(aq) as shown below.
H2CO3(aq) + H2O( ) → H3O+(aq) + HCO3–(aq)
HCO3–(aq) + H2O( ) → H3O+(aq) + CO32–(aq)
The overall reaction can be written as the sum of the two reactions:
H2CO3 (aq) + 2H2O( ) → 2H3O+(aq) + CO32-(aq)
The concentration of the following substances involved in the reaction are:
[H3O+(aq)] = a mol/L [CO32–(aq)] = b mol/L [H2CO3(aq)] = c mol/L
The equilibrium constant for the overall reaction is:
a. | ab/c | c. a2bc |
b. | a²b/c | d. ab²/c |
b. | a²b/c |
ll happen to the following equilibrium if the pressure is decreased.
2NH3(g) ⇔ N2(g) + 3H2(g)
a. | The system will not change. |
b. | Equilibrium will shift toward the products. |
c. | Equilibrium will shift toward the reactants. |
d. | The concentration of N2 will decrease. |
e. | The concentration of NH3 will increase. |
b. | Equilibrium will shift toward the products. |
*1. Which of these is NOT an example of heterogeneous equilibrium?
a. H₂O(l) ⇌ H₂O(g)
b. C(s) + CO₂(g) ⇌ 2CO(g)
c. N2O4(G) ⇌ 2NO2(G)
d. C₂H₅OH(l) ⇌ C₂H₅OH(g)
e. CaCO3(s) ⇌ CaO(s) + CO2(G)
c. N2O4(G) ⇌ 2NO2(G)
3. Two substances are mixed together in a flask. They undergo a reaction and reach chemical equilibrium. Which statement is true?
a. The flask now contains only the products in the reaction.
b. The flask now contains only the reactants in the reaction.
c. The flask now contains both the reactants and the products.
d. The flask now contains neither the reactants nor the products.
e. The contents of the flask cannot be determined.
c. The flask now contains both the reactants and the products.
4. The equilibrium system shown below was analyzed and the concentrations of HI(g), H₂(g), and I₂(g) were found, in mol/L, to be 4.4, 3.2, 1.5 respectively. The equilibrium constant must be which of the following?
H₂(g) + I₂(g) ⇌ 2HI(g) + 65 kJ
a. 4.0
b. 0.25
c. 0.92
d. 1.1
e. 0.16
a. 4.0
We are given:
[HI] = 4.4 mol/L
[H₂] = 3.2 mol/L
[I₂] = 1.5 mol/L
Reaction: H₂(g) + I₂(g) ⇌ 2HI(g)
Step 1: Write the equilibrium expression
K = [HI]² / ([H₂][I₂])
Step 2: Plug in the values
K = (4.4)² / (3.2 × 1.5)
K = 19.36 / 4.8
K ≈ 4.0
Which of the following equilibrium constant values best represents a reaction where the concentration of products is almost equal to the concentration of reactants?
a, 3.4 × 106
b. 2.9 × 10-6
c. 9.8 × 10-1
d. 1.5 × 10-1
c. 9.8 × 10-1
To determine which equilibrium constant (K) represents a reaction where products ≈ reactants, we look for a K value that is close to 1.
c. 9.8 × 10-1 = 0.98
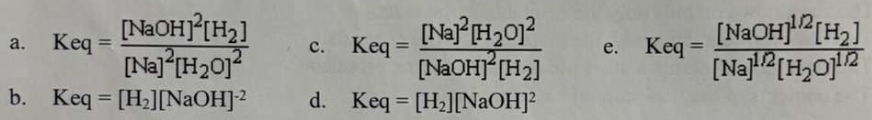
Which of the following is the correct equilibrium exprression for the following reaction: 2 Na(s) + 2 H2O(l) ⇌ 2 NaOH (aq) + H2(g)
D.
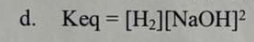
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
a. When Keq » 1 the forward reaction is favored and essentially goes to completion.
b. When Keq << 1, the reverse reaction is favored and the forward reaction does not proceed to a great extent.
c. When Keq ≈ 1, neither the forward or reverse reaction is strongly favored, and about the same amount of reactants and products exist at equilibrium.
d. Keq >> 1 implies that the reaction is very fast at producing products.
e. None of the above
d. Keq >> 1 implies that the reaction is very fast at producing products.
If Qeq > Keq, then _____.
a. the system is at equilibrium
b. the ratio of products of reactants is les than Keq
c. the ratio of products of reactants is greater than Keq
d. the reaction shifts toward product formation
e. more reactants must be consumed to reach equilibrium
c. the ratio of products of reactants is greater than Keq
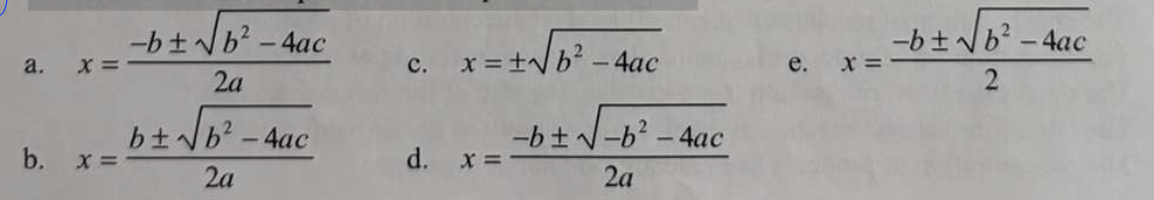
Which is the correct equation for the quadratic formula?
a.
14. For the equilibrium system below, which of the following would result in an increase in the quantity of CO(g)?
2H₂(g) + CO(g) ⇌ CH₃OH(g) + 92 kJ
i. decreasing temperature
ii. decreasing the volume of the container
iii. adding some CH₃OH
iv. decreasing the pressure in the container
v. removing some H₂
a. i and ii only
b. i and iii only
c. ii, iii, and v only
d. iii, iv, and v only
e. all of i, ii, iii, iv, and v
d. iii, iv, and v only
iii. adding some CH₃OH
iv. decreasing the pressure in the container
v. removing some H₂
15. If the equilibrium shown below is heated at a constant pressure:
2HI(g) + 65 kJ ⇌ H₂(g) + I₂(g)
Which of the following is (are) most likely to happen?
i. K_eq gets larger
ii. K_eq gets smaller
iii. [I₂] increases
iv. [I₂] decreases
a. i only
b. ii only
c. both i and iii
d. both ii and iv
e. both i and iv
c. both i and iii
i. K_eq gets larger
iii. [I₂] increases
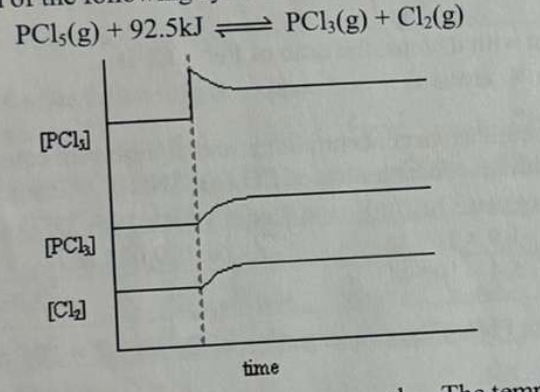
What interpretation is correct for the following graph, which shows the reaction to some change imposed on the equilibrium of the following system:
PCl₅(g) + 92.5 kJ ⇌ PCl₃(g) + Cl₂(g)a. Some PCl₅(g) was injected.
b. Some PCl₃(g) was removed.
c. The temperature was increased.
d. The temperature was decreased.
e. The pressure was increased.
a. Some PCl₅(g) was injected.
A catalyst is added to a system involving a reversible reaction. Which do you expect to occur?
a. The catalyst is consumed.
b. The equilibrium shifts in one direction.
c. The temperature of the system increases.
d. The system reaches equilibrium more quickly.
e. All of the above.
d. The system reaches equilibrium more quickly.
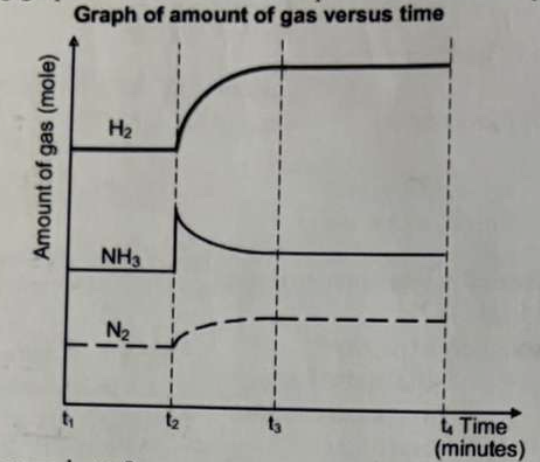
The following graph is for the reaction to produce ammonia from its elements:
What event occurred at t3?
a. Some NH₃(g) was removed.
b. The pressure was changed.
c. The temperature was increased.
d. The temperature was decreased.
e. A catalyst was added.
e. A catalyst was added.
When solid FeCl₃ is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of Fe³⁺:Cl⁻ is:
a. 1:1
b. 2:1
c. 1:2
d. 1:3
e. 3:1
d. 1:3
20, Consider the following reaction, equilibrium concentrations, and equilibrium constant at a particular temperature. Determine the equilibrium concentration of CO2(g). [NH₃]eq = 2.9 × 10⁻³ M
NH2COONH₄(s) ⇌ 2 NH₃(g) + CO2(g)
Keq = 1.58 × 10-8
a. 0.053 M
b. 4.6 × 10⁻¹¹ M
c. 1.9 × 10⁻³ M
d. 5.4 × 10-6 M
e. 0.022 M
c. 1.9 × 10⁻³ M
Given:
Reaction:
NH₂COONH₄(s) ⇌ 2 NH₃(g) + CO₂(g)
[NH₃] = 2.9 × 10⁻³ M
Kₑq = 1.58 × 10⁻⁸
Step 1: Write the equilibrium expression
Kₑq = [NH₃]² × [CO₂]
Step 2: Substitute values
1.58 × 10⁻⁸ = (2.9 × 10⁻³)² × [CO₂]
1.58 × 10⁻⁸ = 8.41 × 10⁻⁶ × [CO₂]
Step 3: Solve for [CO₂]
[CO₂] = (1.58 × 10⁻⁸) ÷ (8.41 × 10⁻⁶)
[CO₂] ≈ 1.88 × 10⁻³ M
Final Answer:
c. 1.9 × 10⁻³ M
In a saturated solution prepared from PbBr₂, the concentration of Br⁻ is 8.2 × 10-2 mol/L. The [Pb²⁺] in mol/L is which of the following?
a. 8.2 × 10⁻²
b. 4.1 × 10⁻²
c. 0.16
d. 0.24
b. 4.1 × 10⁻²
Reaction:
PbBr₂(s) ⇌ Pb²⁺(aq) + 2Br⁻(aq)
Given:
[Br⁻] = 8.2 × 10⁻² mol/L
We want: [Pb²⁺] = ?
From the balanced equation:
1 mol of PbBr₂ → 1 mol of Pb²⁺ and 2 mol of Br⁻
So the mole ratio is:
[Pb²⁺] / [Br⁻] = 1 / 2
Step-by-step calculation with units:
[Pb²⁺] = (1 mol Pb²⁺ / 2 mol Br⁻) × (8.2 × 10⁻² mol Br⁻ / L)
= (0.5) × (8.2 × 10⁻² mol/L)
= 4.1 × 10⁻² mol/L
After completing an ICE table for a reaction with a K_eq = 1 × 10⁹, the following equilibrium expression was obtained:
K_eq = x(2 – x)² / 2 + x
The value of x isa. 1 × 10-9
b. 5 × 10-10
c. 0
d. 2
e. not solvable with this information
b. 5 × 10-10
When a solid is dissolved in water, it separates into its constituent ions. If a new compound with an identical anion is dissolved in the same solution, this will drive the equilibrium to the left. This process is known as
a. the common ion effect.
b. Le Châtelier’s principle.
c. collision theory.
d. Dalton’s law of partial pressures.
a. the common ion effect.
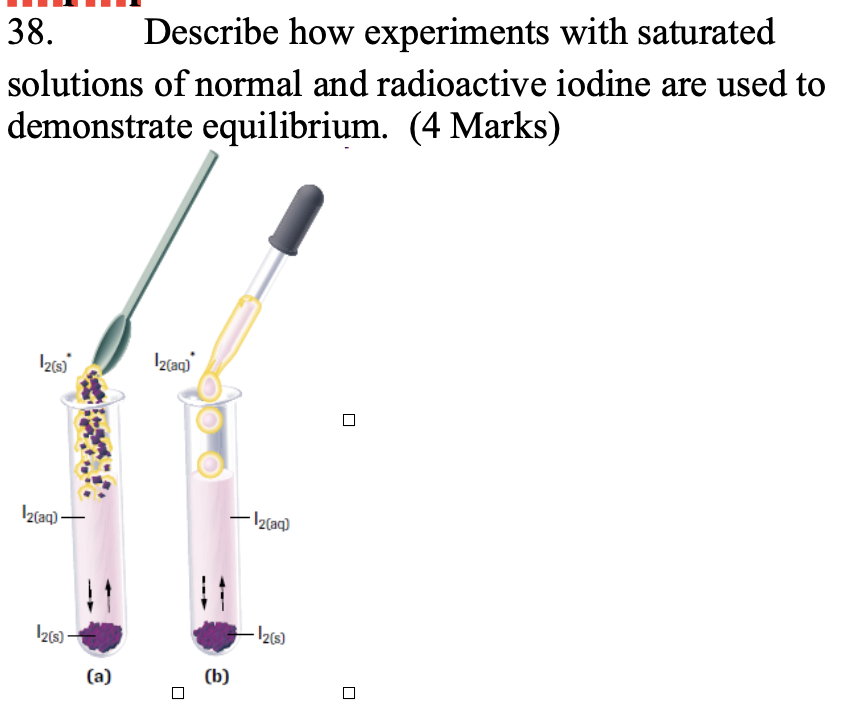
Describe how experiments with saturated solutions of normal and radioactive iodine are used to demonstrate equilibrium. (4 Marks)
To demonstrate dynamic equilibrium, two experiments are done with saturated iodine (I₂) solutions, where solid I₂ is in equilibrium with dissolved I₂(aq). In experiment (a), radioactive solid iodine (I₂*) is added; in (b), radioactive aqueous iodine (I₂*(aq)) is added. At first, radioactivity is only in the phase it was added to, but after several hours, it appears in both phases in both experiments.
This shows that even in a saturated solution, I₂(s) continues to dissolve while I₂(aq) crystallizes at the same rate. The total amounts stay constant, but the movement of radiolabeled iodine proves the system is dynamic—particles are constantly exchanged even though concentrations don’t change.
8.0 moles of pure ammonia gas were injected into a 2.0-L flask and allowed to reach equilibrium according to the equation shown below. If the equilibrium mixture was analyzed and found to contain 2.0 moles of nitrogen gas, calculate the value of the equilibrium constant.
2NH3(g) ↔ N2(g) + 3H2(g)
39. Keq = (3.0)3(1.0) / (2.0)2 = 6.8
2NH₃(g) ⇌ N₂(g) + 3H₂(g)
Given:
8.0 mol NH₃ in 2.0 L → [NH₃] = 4.0 M
No N₂ or H₂ initially
At equilibrium: 2.0 mol of N₂ in 2.0 L → [N₂] = 1.0 M
Let’s set up the ICE table.
Step 1: ICE Table
Species | Initial (M) | Change (M) | Equilibrium (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
NH₃ | 4.0 | –2x | 4.0 – 2x |
N₂ | 0 | +x | x |
H₂ | 0 | +3x | 3x |
From given info:
[N₂] = x = 1.0 M → x = 1.0
Now plug back in:
[NH₃] = 4.0 – 2(1.0) = 2.0 M
[H₂] = 3(1.0) = 3.0 M
Step 2: Write the expression for K_eq
K = [N₂][H₂]³ / [NH₃]²
Now plug in:
K = (1.0)(3.0)³ / (2.0)²
= 1 × 27 / 4 = 6.8
![<p><em>39</em>. Keq = (3.0)<sup>3</sup>(1.0) / (2.0)<sup>2 </sup>= 6.8 </p><p></p><p><strong>2NH₃(g) ⇌ N₂(g) + 3H₂(g)</strong></p><p><strong>Given:</strong></p><ul><li><p>8.0 mol NH₃ in 2.0 L → <strong>[NH₃] = 4.0 M</strong></p></li><li><p>No N₂ or H₂ initially</p></li><li><p>At equilibrium: <strong>2.0 mol of N₂</strong> in 2.0 L → <strong>[N₂] = 1.0 M</strong></p></li></ul><p>Let’s set up the ICE table.</p><p><strong>Step 1: ICE Table</strong></p><table style="min-width: 100px"><colgroup><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"></colgroup><tbody><tr><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Species</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Initial (M)</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Change (M)</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Equilibrium (M)</p></th></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>NH₃</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>4.0</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>–2x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>4.0 – 2x</p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>N₂</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>+x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>x</p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>H₂</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>+3x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>3x</p></td></tr></tbody></table><p>From given info:<br><strong>[N₂] = x = 1.0 M → x = 1.0</strong></p><p>Now plug back in:</p><ul><li><p>[NH₃] = 4.0 – 2(1.0) = 2.0 M</p></li><li><p>[H₂] = 3(1.0) = 3.0 M</p></li></ul><p><strong>Step 2: Write the expression for K_eq</strong></p><p><strong>K = [N₂][H₂]³ / [NH₃]²</strong></p><p></p><p>Now plug in:</p><p><strong>K = (1.0)(3.0)³ / (2.0)²</strong><br>= <strong>1 × 27 / 4 = 6.8</strong></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/89d9ad08-ba24-4e84-9dbf-f1fad9683c90.jpg)
The Keq for the equilibrium shown below is 50. Some methane and hydrogen sulfide are added to a container and at equilibrium the concentrations of methane and hydrogen sulfide are found to be 0.24 mol/L and 0.36 mol/L respectively. What are the equilibrium concentrations of carbon disulfide and hydrogen gas?
CH4(g) + 2H2S(g) ↔ CS2(g) + 4H2(g).
40. x = 4.1 mol/L so [CS2]=4.1M; [H2] = 16.4M
![<p> <em>40</em>. x = 4.1 mol/L so [CS<sub>2</sub>]=4.1M; [H<sub>2</sub>] = 16.4M</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/121493f1-8368-4de4-acfc-527fa60dff9d.jpg)
Consider the following reaction:
CH4(g) + 2 H2S(g) ↔ CS2(g) + 4 H2(g)
A reaction mixture initially contains 0.50 M CH4 and 0.75 M H2S. If the equilibrium concentration of H2 is 0.44 M, find the equilibrium constant (Keq) for the reaction. (5 marks)
. Keq=0.038
We are given the balanced equation:
CH₄(g) + 2 H₂S(g) ⇌ CS₂(g) + 4 H₂(g)
Initial concentrations:
[CH₄] = 0.50 M
[H₂S] = 0.75 M
[CS₂] = 0 M
[H₂] = 0 M
Equilibrium concentration of H₂: 0.44 M
Step 1: ICE Table
Species | CH₄ | H₂S | CS₂ | H₂ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
I | 0.50 | 0.75 | 0 | 0 |
C | -x | -2x | +x | +4x |
E | 0.50−x | 0.75−2x | x | 4x = 0.44 |
From the equilibrium concentration of H₂:
4x = 0.44 → x = 0.11
Step 2: Solve for equilibrium concentrations
[CH₄] = 0.50 − x = 0.50 − 0.11 = 0.39 M
[H₂S] = 0.75 − 2x = 0.75 − 0.22 = 0.53 M
[CS₂] = x = 0.11 M
[H₂] = 0.44 M (given)
Step 3: Write the expression for Keq
Keq = ([CS₂] × [H₂]⁴) / ([CH₄] × [H₂S]²)
Now plug in the equilibrium concentrations:
Keq = (0.11 × (0.44)⁴) / (0.39 × (0.53)²)
First, calculate:
(0.44)⁴ = 0.0375 (approx)
(0.53)² = 0.2809
So:
Keq = (0.11 × 0.0375) / (0.39 × 0.2809)
Keq = 0.004125 / 0.109551 ≈ 0.038
![<ol start="41"><li><p>. Keq=0.038 </p></li></ol><p>We are given the balanced equation:</p><p><strong>CH₄(g) + 2 H₂S(g) ⇌ CS₂(g) + 4 H₂(g)</strong></p><p>Initial concentrations:</p><ul><li><p>[CH₄] = 0.50 M</p></li><li><p>[H₂S] = 0.75 M</p></li><li><p>[CS₂] = 0 M</p></li><li><p>[H₂] = 0 M</p></li></ul><p>Equilibrium concentration of H₂: 0.44 M</p><p>Step 1: ICE Table</p><table style="min-width: 125px"><colgroup><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"></colgroup><tbody><tr><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Species</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>CH₄</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>H₂S</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>CS₂</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>H₂</p></th></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>I</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0.50</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0.75</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0</p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>C</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>-x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>-2x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>+x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>+4x</p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>E</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0.50−x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0.75−2x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>4x = 0.44</p></td></tr></tbody></table><p>From the equilibrium concentration of H₂:</p><p><strong>4x = 0.44 → x = 0.11</strong></p><p>Step 2: Solve for equilibrium concentrations</p><ul><li><p>[CH₄] = 0.50 − x = 0.50 − 0.11 = <strong>0.39 M</strong></p></li><li><p>[H₂S] = 0.75 − 2x = 0.75 − 0.22 = <strong>0.53 M</strong></p></li><li><p>[CS₂] = x = <strong>0.11 M</strong></p></li><li><p>[H₂] = <strong>0.44 M</strong> (given)</p></li></ul><p>Step 3: Write the expression for <strong>Keq</strong></p><p>Keq = ([CS₂] × [H₂]⁴) / ([CH₄] × [H₂S]²)</p><p>Now plug in the equilibrium concentrations:</p><p>Keq = (0.11 × (0.44)⁴) / (0.39 × (0.53)²)</p><p>First, calculate:</p><ul><li><p>(0.44)⁴ = 0.0375 (approx)</p></li><li><p>(0.53)² = 0.2809</p></li></ul><p>So:</p><p>Keq = (0.11 × 0.0375) / (0.39 × 0.2809)<br>Keq = 0.004125 / 0.109551 ≈ <strong>0.038</strong></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f20ded47-5057-4eb6-a178-18c1b56da650.jpg)
Gaseous NOCl decomposes to form the gases NO and Cl2. At 35oC, the Keq=1.6x10-5. In an experiment in which 1.0 mol NOCl is placed in a 2.0 L flask, what are the equilibrium concentrations?
2NOCl(g) ↔ 2NO(g) + Cl2(g)
42.[NOCl] = 0.50 – 2x ≈ 0.50 M [NO] = 2x = 2(1.0x10-2 M) = 2.0x10-2 [Cl2] = x =1.0x10-2 M
![<p> <em>42</em>.[NOCl] = 0.50 – 2x ≈ 0.50 M [NO] = 2x = 2(1.0x10<sup>-2</sup> M) = 2.0x10<sup>-2</sup> [Cl<sub>2</sub>] = x =1.0x10<sup>-2</sup> M</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/06e2473f-78f1-4ca7-aacf-331935a0a643.jpg)
If solutions of calcium fluoride and potassium carbonate were mixed and a precipitate formed, the precipitate would be what compound?
43. calcium carbonate
To find the precipitate, we’ll do a double displacement reaction between:
Calcium fluoride → CaF₂
Potassium carbonate → K₂CO₃
Step 1: Write the formulas of the compounds
CaF₂ (calcium fluoride)
K₂CO₃ (potassium carbonate)
Step 2: Predict the double displacement reaction
Swap the cations:
CaF₂ + K₂CO₃ → CaCO₃ + 2 KF
Step 3: Determine if a precipitate forms
CaCO₃ (calcium carbonate) is insoluble in water → forms a precipitate
KF (potassium fluoride) is soluble → stays in solution
If solutions of copper(II) nitrate and sodium carbonate were mixed and a precipitate formed, the equilibrium equation for the precipitate would be __________.
44. CuCO3(s) <===> Cu2+(aq) + CO32-(aq)
When solid magnesium carbonate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of Mg2+ ion to CO32- is _____.
45. 1:1
When magnesium carbonate (MgCO₃) is in equilibrium with its ions in water, the dissociation equation is:
MgCO₃(s) ⇌ Mg²⁺(aq) + CO₃²⁻(aq)
From the balanced equation, 1 mole of MgCO₃ dissolves to produce:
1 mole of Mg²⁺
1 mole of CO₃²⁻
✅ Final Answer:
The ratio of Mg²⁺ to CO₃²⁻ is 1:1.
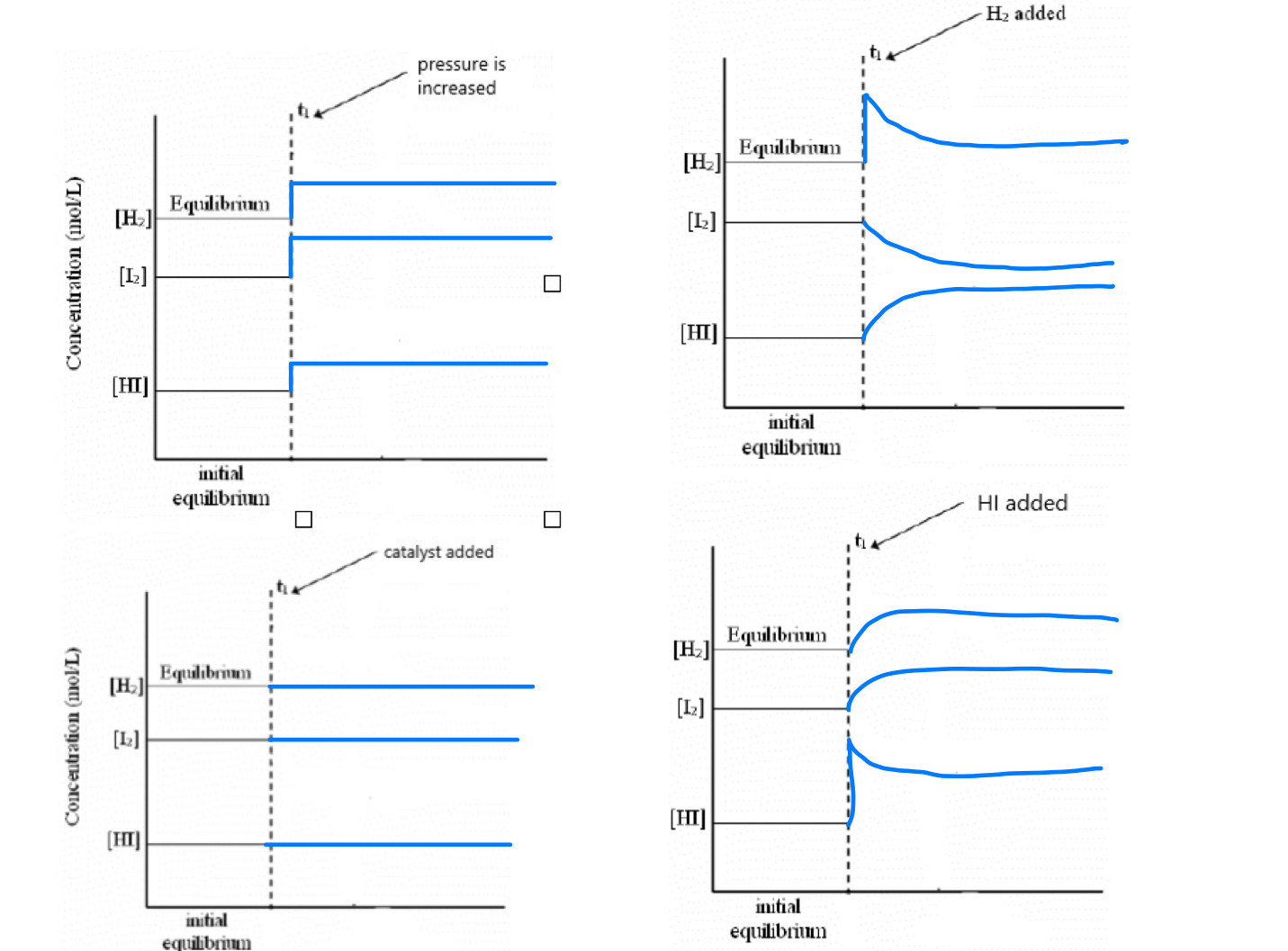
46. Hydrogen iodide is a colourless gas that can be prepared by the following equilibrium reaction: H2(g) + I2(g) ⇔ 2HI(g)
Represent graphically (use the graphs here or other side) the effect each change will have on the above reaction.
Graph 1 – Pressure Increased
Increasing pressure compresses all gases, slightly increasing their concentrations.
But because there are equal numbers of gas molecules on both sides (2 mol ⇌ 2 mol), there is no shift in equilibrium.
The concentrations of H₂, I₂, and HI may all slightly jump up, then stay constant.
Result:
All lines show a small upward step at the pressure change, then remain flat.Graph 2 – H₂ Added
Adding H₂ increases its concentration suddenly.
The system shifts right, toward products, to reduce the disturbance.
I₂ is used up (decreases), and more HI is formed (increases).
H₂ drops slightly after the jump as it reacts.
Result:
H₂ jumps up, then gradually falls.
I₂ decreases slowly.
HI increases gradually.Graph 3 – Catalyst Added
A catalyst speeds up both the forward and reverse reactions.
It does not change concentrations or shift the equilibrium.
The system just reaches equilibrium faster — not something shown on these graphs.
Result:
All concentrations stay exactly the same — flat lines.Graph 4 – HI Added
Adding HI increases its concentration suddenly.
The system shifts left, toward reactants, to reduce the added product.
Some HI breaks down to form more H₂ and I₂.
Result:
HI jumps up, then slightly decreases.
H₂ and I₂ both increase slowly.
47. If the solubility of Mg(OH)2 is 1.3 ◊ 10-4 mol/L, what is its Ksp?
47. Ksp = (1.3 ◊ 10-4 )( 2 * 1.3 ◊ 10-4)2 = 8.8 ◊ 10-12
ICE Table
Mg(OH)₂ (s) | Mg²⁺ (aq) | OH⁻ (aq) | |
|---|---|---|---|
I | — | 0 | 0 |
C | — | +1.3 × 10⁻⁴ | +2(1.3 × 10⁻⁴) = 2.6 × 10⁻⁴ |
E | — | 1.3 × 10⁻⁴ | 2.6 × 10⁻⁴ |
(Note: The solid Mg(OH)₂ doesn't appear in the Ksp expression, so we mark it with a dash.)
Now Calculate Ksp:
Ksp = [Mg²⁺][OH⁻]²
= (1.3 × 10⁻⁴) × (2.6 × 10⁻⁴)²
= (1.3 × 10⁻⁴) × (6.76 × 10⁻⁸)
= 8.79 × 10⁻¹²
✅ Final answer: Ksp = 8.8 × 10⁻¹²
![<p><em>47</em>. Ksp = (1.3 ◊ 10<sup>-4 </sup>)( 2 * 1.3 ◊ 10<sup>-4</sup>)<sup>2</sup> = 8.8 ◊ 10<sup>-12</sup> </p><p></p><p><strong>ICE Table</strong></p><table style="min-width: 100px"><colgroup><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"></colgroup><tbody><tr><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p></p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Mg(OH)₂ (s)</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Mg²⁺ (aq)</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>OH⁻ (aq)</p></th></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p><strong>I</strong></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>—</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0</p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p><strong>C</strong></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>—</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>+1.3 × 10⁻⁴</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>+2(1.3 × 10⁻⁴) = 2.6 × 10⁻⁴</p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p><strong>E</strong></p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>—</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>1.3 × 10⁻⁴</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>2.6 × 10⁻⁴</p></td></tr></tbody></table><p></p><p>(Note: The solid Mg(OH)₂ doesn't appear in the Ksp expression, so we mark it with a dash.)</p><p><strong>Now Calculate Ksp:</strong></p><p><strong>Ksp = [Mg²⁺][OH⁻]²</strong><br>= (1.3 × 10⁻⁴) × (2.6 × 10⁻⁴)²<br>= (1.3 × 10⁻⁴) × (6.76 × 10⁻⁸)<br>= <strong>8.79 × 10⁻¹²</strong></p><p></p><p><span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span> Final answer: <strong>Ksp = 8.8 × 10⁻¹²</strong></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/78bf1add-08b4-455e-bbaf-a8283da95f19.jpg)
If the concentration of Pb2+ is found to be 2.3 ◊ 10-9 mol/L in a saturated solution of Pb3(PO4)2, what is the Ksp of Pb3(PO4)2 ?
48.Ksp = (2.3 x 10-9 )3 ( 2/3 x 2.3 x 10-9 )2 = 2.86 ◊ 10-44
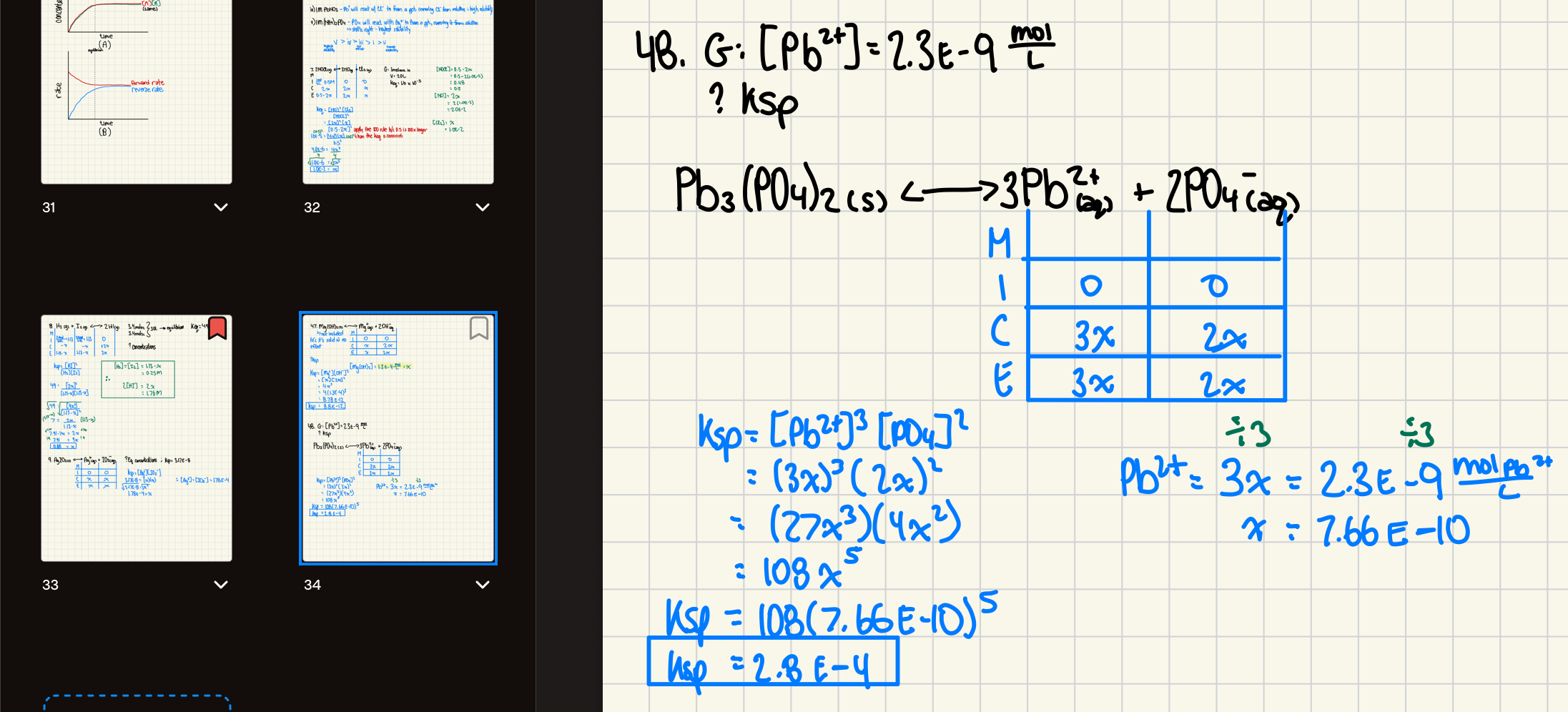
49. If 1.7 L of a saturated solution of AgC2H3O2 is found to contain 14.1 g of AgC2H3O2, what is the Ksp of AgC2H3O2.
49. Ksp = 2.4 x 10-3
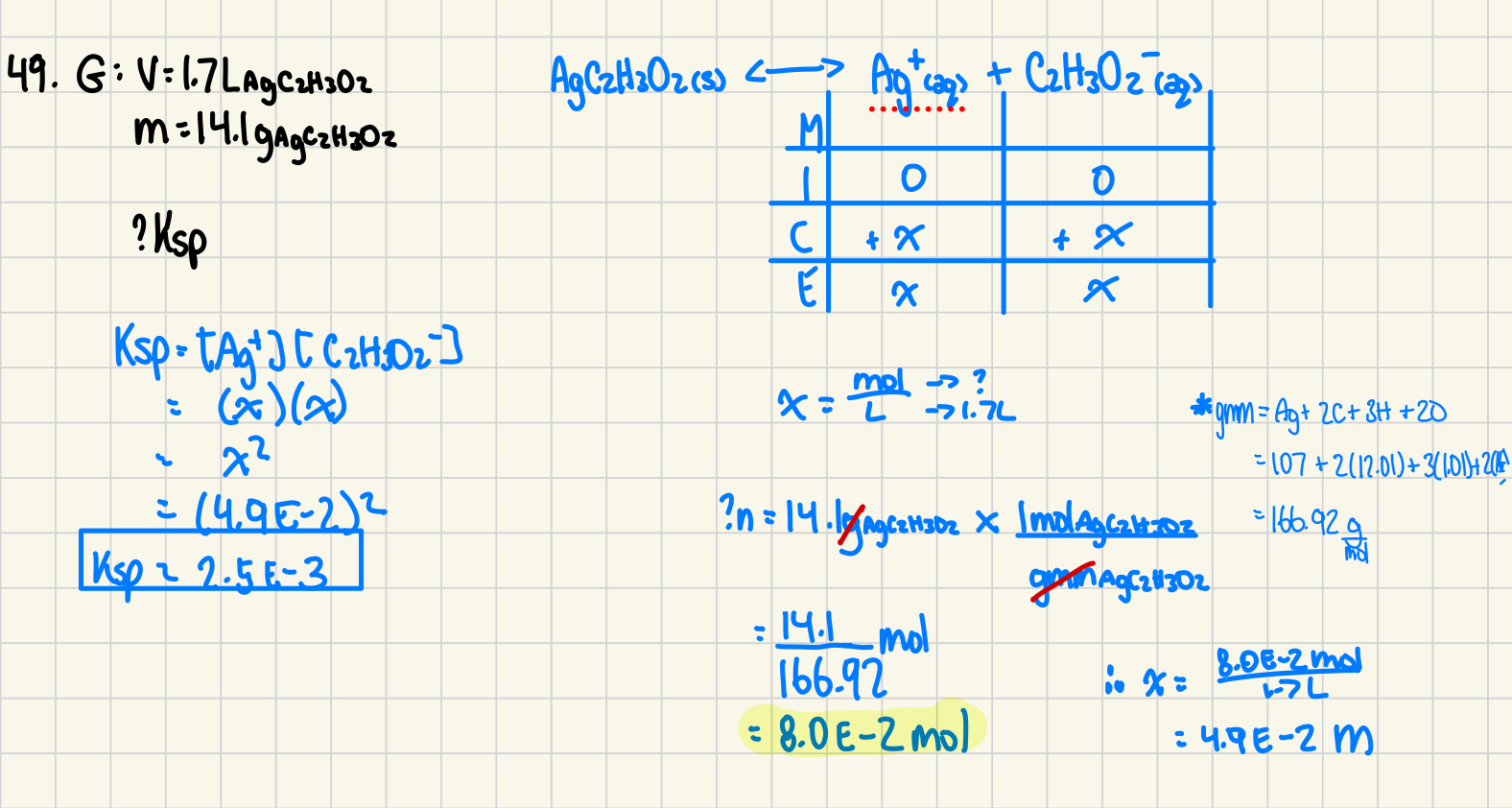
If 76 L of a saturated solution of Mg(OH)2 is found to contain 0.58 g of Mg(OH)2, what is the Ksp of Mg(OH)2.
50. Ksp = (0.58 g / 58.32 g/mol / 76 L )(2 ◊ 0.58 g / 58.32 g/mol / 76 L )2 = 9.0 ◊ 10-12
done on paper
51. What mass of Ag2CO3 would be found in 1.4 L of a saturated solution if the Ksp of Ag2CO3 is 8.2 ◊ 10-12?
51. mAg2CO3 = (1.27 ◊ 10-2 mol/L)(1.4 L)(331.73 g/mol) = 4.9 ◊ 10-2 g
⚛ Step 1: Dissociation equation
Ag₂CO₃ (s) ⇌ 2 Ag⁺ (aq) + CO₃²⁻ (aq)
Let solubility = x mol/L of Ag₂CO₃
Then:
[Ag⁺] = 2x
[CO₃²⁻] = x
🧮 Step 2: Write Ksp expression
Ksp = [Ag⁺]² × [CO₃²⁻]
Substitute:
Ksp = (2x)² × (x) = 4x³
We are told:
Ksp = 8.2 × 10⁻¹²
So:
4x³ = 8.2 × 10⁻¹²
→ x³ = (8.2 × 10⁻¹²) ÷ 4 = 2.05 × 10⁻¹²
→ x = ∛(2.05 × 10⁻¹²) ≈ 1.27 × 10⁻⁴ mol/L
🧪 Step 3: Find moles in 1.4 L
mol = (1.27 × 10⁻⁴ mol/L) × (1.4 L) = 1.78 × 10⁻⁴ mol
⚖ Step 4: Convert moles to grams
Molar mass of Ag₂CO₃:
Ag = 107.87 × 2 = 215.74
C = 12.01
O = 16.00 × 3 = 48.00
→ Total = 215.74 + 12.01 + 48.00 = 275.75 g/mol
Mass = mol × molar mass
= (1.78 × 10⁻⁴ mol) × (275.75 g/mol)
≈ 0.0491 g
≈ 4.9 × 10⁻² g
✅ Final Answer:
Mass of Ag₂CO₃ = 4.9 × 10⁻² g ✅
![<p><em>51</em>. mAg<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub> = (1.27 ◊ 10<sup>-2</sup> mol/L)(1.4 L)(331.73 g/mol) = 4.9 ◊ 10<sup>-2</sup> g <br><br><span data-name="atom" data-type="emoji">⚛</span> Step 1: Dissociation equation</p><p><strong>Ag₂CO₃ (s) ⇌ 2 Ag⁺ (aq) + CO₃²⁻ (aq)</strong></p><p></p><p>Let solubility = <strong>x mol/L</strong> of Ag₂CO₃</p><p></p><p>Then:</p><p></p><ul><li><p>[Ag⁺] = 2x</p></li><li><p>[CO₃²⁻] = x</p></li></ul><p></p><p><span data-name="abacus" data-type="emoji">🧮</span> Step 2: Write Ksp expression</p><p><strong>Ksp = [Ag⁺]² × [CO₃²⁻]</strong></p><p></p><p>Substitute:<br><strong>Ksp = (2x)² × (x) = 4x³</strong></p><p></p><p>We are told:<br><strong>Ksp = 8.2 × 10⁻¹²</strong></p><p></p><p>So:<br><strong>4x³ = 8.2 × 10⁻¹²</strong><br>→ <strong>x³ = (8.2 × 10⁻¹²) ÷ 4 = 2.05 × 10⁻¹²</strong></p><p></p><p>→ <strong>x = ∛(2.05 × 10⁻¹²) ≈ 1.27 × 10⁻⁴ mol/L</strong></p><p></p><p><span data-name="test_tube" data-type="emoji">🧪</span> Step 3: Find moles in 1.4 L</p><p><strong>mol = (1.27 × 10⁻⁴ mol/L) × (1.4 L) = 1.78 × 10⁻⁴ mol</strong></p><p></p><p><span data-name="scales" data-type="emoji">⚖</span> Step 4: Convert moles to grams</p><p><strong>Molar mass of Ag₂CO₃:</strong></p><p></p><ul><li><p>Ag = 107.87 × 2 = 215.74</p></li><li><p>C = 12.01</p></li><li><p>O = 16.00 × 3 = 48.00<br>→ <strong>Total = 215.74 + 12.01 + 48.00 = 275.75 g/mol</strong></p></li></ul><p></p><p><strong>Mass = mol × molar mass</strong><br>= (1.78 × 10⁻⁴ mol) × (275.75 g/mol)<br>≈ <strong>0.0491 g</strong><br>≈ <strong>4.9 × 10⁻² g</strong></p><p></p><p><span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span> Final Answer:</p><p><strong>Mass of Ag₂CO₃ = 4.9 × 10⁻² g</strong> <span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/96a0b4d1-7e20-475e-ba68-4fd70163371c.jpg)
52. What is the solubility, in mol/L, of AgC2H3O2 in a 0.45 mol/L solution of AgNO3 if the Ksp of AgC2H3O2 is 2.5 ◊ 10-3?
52.solubility = 5.6 x 10-3 mol/L
⚛ Step 1: Write the dissociation equation
AgC₂H₃O₂ (s) ⇌ Ag⁺ (aq) + C₂H₃O₂⁻ (aq)
Let the solubility of AgC₂H₃O₂ be x mol/L in the presence of 0.45 mol/L Ag⁺ from AgNO₃.
So:
[Ag⁺] = 0.45 + x ≈ 0.45 (apply the 100 rule because 0.45 is 100X bigger than the KSP)
[C₂H₃O₂⁻] = x
🧮 Step 2: Write the Ksp expression
Ksp = [Ag⁺][C₂H₃O₂⁻]
Substitute values:
2.5 × 10⁻³ = (0.45)(x)
Solve for x:
x = (2.5 × 10⁻³) ÷ 0.45 = 5.56 × 10⁻³ mol/L
✅ Final Answer:
Solubility of AgC₂H₃O₂ = 5.6 × 10⁻³ mol/L ✅
![<p><em>52</em>.solubility = 5.6 x 10<sup>-3</sup> mol/L</p><p><span data-name="atom" data-type="emoji">⚛</span> Step 1: Write the dissociation equation</p><p><strong>AgC₂H₃O₂ (s) ⇌ Ag⁺ (aq) + C₂H₃O₂⁻ (aq)</strong></p><p></p><p>Let the solubility of <strong>AgC₂H₃O₂</strong> be <strong>x mol/L</strong> in the presence of 0.45 mol/L <strong>Ag⁺</strong> from <strong>AgNO₃</strong>.</p><p></p><p>So:</p><p></p><ul><li><p>[Ag⁺] = <strong>0.45 + x</strong> ≈ <strong>0.45</strong> (apply the 100 rule because 0.45 is 100X bigger than the KSP)</p></li><li><p>[C₂H₃O₂⁻] = <strong>x</strong></p></li></ul><p></p><p><span data-name="abacus" data-type="emoji">🧮</span> Step 2: Write the Ksp expression</p><p><strong>Ksp = [Ag⁺][C₂H₃O₂⁻]</strong></p><p></p><p>Substitute values:</p><p></p><p><strong>2.5 × 10⁻³ = (0.45)(x)</strong></p><p></p><p>Solve for <strong>x</strong>:</p><p></p><p><strong>x = (2.5 × 10⁻³) ÷ 0.45 = 5.56 × 10⁻³ mol/L</strong></p><p></p><p><span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span> Final Answer:</p><p><strong>Solubility of AgC₂H₃O₂ = 5.6 × 10⁻³ mol/L</strong> <span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0fc89893-c038-460e-848a-c2f4332c8bd2.jpg)
If 45 mL of a 0.45 mol/L solution of AgNO3 was mixed with 85 mL of a 1.35 ◊ 10-2 mol/L solution of NaCl, would a precipitate form? Calculate the ion product for the potential precipitate. The Ksp of AgCl(s) is 1.8 ◊ 10-10.
53. AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO3(aq)
[Ag1+] = (0.45 mol/L)(0.045 L) / (0.045 L + 0.085) L [Cl1-] = (1.35 ◊ 10-2 mol/L)(0.085 L) / (0.045 L + 0.085) L
Qsp AgCl is [Ag1+][Cl1-] = 1.4 ◊ 10-3 > Ksp, yes a precipitate forms
⚛ Reaction:
AgNO₃ (aq) + NaCl (aq) → AgCl (s) + NaNO₃ (aq)
We are concerned with:
Ag⁺ (aq) + Cl⁻ (aq) ⇌ AgCl (s)
A precipitate forms if Q > Ksp.
🧮 Step 1: Calculate final concentrations after mixing
Total volume = 45 mL + 85 mL = 130 mL = 0.130 L
✅ [Ag⁺] after mixing:
From 45 mL of 0.45 mol/L AgNO₃:
mol Ag⁺ = 0.045 L × 0.45 mol/L = 0.02025 mol
[Ag⁺] = 0.02025 mol ÷ 0.130 L = 0.1558 mol/L
✅ [Cl⁻] after mixing:
From 85 mL of 1.35 × 10⁻² mol/L NaCl:
mol Cl⁻ = 0.085 L × 1.35 × 10⁻² mol/L = 0.0011475 mol
[Cl⁻] = 0.0011475 mol ÷ 0.130 L = 0.00883 mol/L
🧮 Step 2: Calculate the Ion Product (Q)
Q = [Ag⁺][Cl⁻]
= (0.1558) × (0.00883)
≈ 1.38 × 10⁻³
📌 Step 3: Compare Q to Ksp
Q = 1.38 × 10⁻³
Ksp (AgCl) = 1.8 × 10⁻¹⁰
Since Q > Ksp, a precipitate will form.
✅ Final Answer:
Yes, a precipitate will form.
Ion product Q = 1.38 × 10⁻³ > Ksp = 1.8 × 10⁻¹⁰ ✅
![<p><em>53</em>. AgNO<sub>3</sub>(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO<sub>3</sub>(aq) </p><p>[Ag<sup>1+</sup>] = (0.45 mol/L)(0.045 L) / (0.045 L + 0.085) L [Cl<sup>1-</sup>] = (1.35 ◊ 10<sup>-2</sup> mol/L)(0.085 L) / (0.045 L + 0.085) L</p><p>Qsp AgCl is [Ag<sup>1+</sup>][Cl<sup>1-</sup>] = 1.4 ◊ 10<sup>-3</sup> > Ksp, yes a precipitate forms<br><br><span data-name="atom" data-type="emoji">⚛</span> <strong>Reaction:</strong></p><p><strong>AgNO₃ (aq) + NaCl (aq) → AgCl (s) + NaNO₃ (aq)</strong><br>We are concerned with:<br><strong>Ag⁺ (aq) + Cl⁻ (aq) ⇌ AgCl (s)</strong></p><p></p><p>A <strong>precipitate forms if Q > Ksp</strong>.</p><p><span data-name="abacus" data-type="emoji">🧮</span> <strong>Step 1: Calculate final concentrations after mixing</strong></p><p><strong>Total volume</strong> = 45 mL + 85 mL = <strong>130 mL = 0.130 L</strong></p><p><span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span> [Ag⁺] after mixing:</p><p>From 45 mL of <strong>0.45 mol/L</strong> AgNO₃:</p><p></p><ul><li><p>mol Ag⁺ = 0.045 L × 0.45 mol/L = <strong>0.02025 mol</strong></p></li><li><p>[Ag⁺] = 0.02025 mol ÷ 0.130 L = <strong>0.1558 mol/L</strong></p></li></ul><p><span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span> [Cl⁻] after mixing:</p><p>From 85 mL of <strong>1.35 × 10⁻² mol/L</strong> NaCl:</p><p></p><ul><li><p>mol Cl⁻ = 0.085 L × 1.35 × 10⁻² mol/L = <strong>0.0011475 mol</strong></p></li><li><p>[Cl⁻] = 0.0011475 mol ÷ 0.130 L = <strong>0.00883 mol/L</strong></p></li></ul><p></p><p><span data-name="abacus" data-type="emoji">🧮</span> <strong>Step 2: Calculate the Ion Product (Q)</strong></p><p><strong>Q = [Ag⁺][Cl⁻]</strong><br>= (0.1558) × (0.00883)<br>≈ <strong>1.38 × 10⁻³</strong></p><p><span data-name="pushpin" data-type="emoji">📌</span> <strong>Step 3: Compare Q to Ksp</strong></p><ul><li><p><strong>Q = 1.38 × 10⁻³</strong></p></li><li><p><strong>Ksp (AgCl) = 1.8 × 10⁻¹⁰</strong></p></li></ul><p></p><p>Since <strong>Q > Ksp</strong>, a <strong>precipitate will form</strong>.</p><p></p><p><span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span> <strong>Final Answer:</strong></p><p><strong>Yes, a precipitate will form.</strong><br><strong>Ion product Q = 1.38 × 10⁻³ > Ksp = 1.8 × 10⁻¹⁰</strong> <span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span></p><p></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/84a350d9-72f3-440e-a7b4-9ee28bc7ec63.jpg)
54. If 78 mL of a 0.0026 mol/L solution of Zn(NO3)2 was mixed with 45 mL of a 7.13 ◊ 10-3 mol/L solution of K2CO3, would a precipitate form? Calculate the ion product for the potential precipitate. The Ksp of ZnCO3 is 1.0 ◊ 10-10.
54.Zn(NO3)2(aq) + K2CO3(aq) → ZnCO3(s) + 2KNO3(aq)
[Zn2+] = (0.0026 mol/L)(0.078 L) / (0.078 L + 0.045) L
[CO32-] = (7.13 ◊ 10-3 mol/L)(0.045 L) / (0.078 L + 0.045) L
Qsp ZnCO3 is [Zn2+][CO32-] = 4.3 ◊ 10-6 > Ksp of ZnCO3, yes a precipitate occurs
![<p><em>54</em>.Zn(NO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>(aq) + K<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub>(aq) → ZnCO<sub>3</sub>(s) + 2KNO<sub>3</sub>(aq)</p><p>[Zn<sup>2+</sup>] = (0.0026 mol/L)(0.078 L) / (0.078 L + 0.045) L </p><p>[CO<sub>3</sub><sup>2-</sup>] = (7.13 ◊ 10<sup>-3</sup> mol/L)(0.045 L) / (0.078 L + 0.045) L</p><p>Qsp ZnCO<sub>3</sub> is [Zn<sup>2+</sup>][CO<sub>3</sub><sup>2-</sup>] = 4.3 ◊ 10<sup>-6</sup> > Ksp of ZnCO<sub>3</sub>, yes a precipitate occurs</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/92a02941-d0b4-4615-a541-6df2451c47ff.jpg)
55. AgCl(s)↔Ag+(aq)+ Cl-(aq). Apply the common ion effect and arrange the following solutions such that AgCl has a decreasing solubility in them. (3 marks)
i)1M Na2S ii)2M AgNO3 iii)1M AgNO3 iv)1M Pb(NO3)2 v)2M KNO3
55. -decreasing solubility would mean that the rate of crystallization increased
iv. 1M Pb(NO3)2 > i. 1M Na2S > v. 2M KNO3 > iii. 1M AgNO3 > ii. 2M AgNO3
1M Pb(NO3)2 increases the solubility because the Pb2+ ion ppt out 2 Cl- ions
1M Na2S increase the solubility because the S2- ion ppt out the Ag+ ion
2M KNO3 has no effect
1M AgNO3 decrease the solubility by adding common ion which drives rxn to crystallization
2M AgNO3 decrease the solubility by adding common ion which drives rxn to crystallization
*1. Explain what is happening in a dynamic equilibrium and explain how it can be demonstrated experimentally using different isotopes of iodine in saturated solutions. (5 marks)
In a dynamic equilibrium, the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, so the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time. Although it appears static macroscopically, the system is still active at the molecular level, with particles continuously reacting in both directions.
This can be shown using radioactive isotopes of iodine, such as I-131. In a saturated solution of iodine in water, the undissolved solid iodine is in equilibrium with dissolved iodine (I₂ (s) ⇌ I₂ (aq)). If radioactive iodine is added to the solid phase, over time radioactivity appears in the aqueous phase, even though the total amount of dissolved iodine doesn’t increase. This shows that iodine particles are continuously dissolving and precipitating, proving the system is in dynamic equilibrium.
Define or explain the following (or explain how it is used)
a. Reaction Quotient (Q):
b. Saturated Solution:
c) Common Ion Effect
a. Reaction Quotient (Q):
The reaction quotient, Q, is a number that shows the ratio of the concentrations (or partial pressures) of the products to the reactants at any given point in a reaction (not necessarily at equilibrium). It’s calculated the same way as the equilibrium constant (K), but it's used to determine whether a system is at equilibrium or which direction it will shift to reach equilibrium.
If Q < K, the reaction will shift right (toward products).
If Q > K, the reaction will shift left (toward reactants).
If Q = K, the reaction is at equilibrium.
b. Saturated Solution:
A saturated solution contains the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a solvent at a given temperature and pressure. If any more solute is added, it will not dissolve and will remain as a solid precipitate. At this point, the solution is in dynamic equilibrium between the dissolved ions and the undissolved solid.
c. Common Ion Effect:
The common ion effect occurs when a solution contains an ion that is also part of the solute being added. This added ion suppresses the solubility of a salt due to Le Chatelier’s Principle. For example, if you add NaCl to a solution that already contains Cl⁻ ions (like from HCl), less NaCl will dissolve because the system shifts to reduce the increase in Cl⁻ concentration.
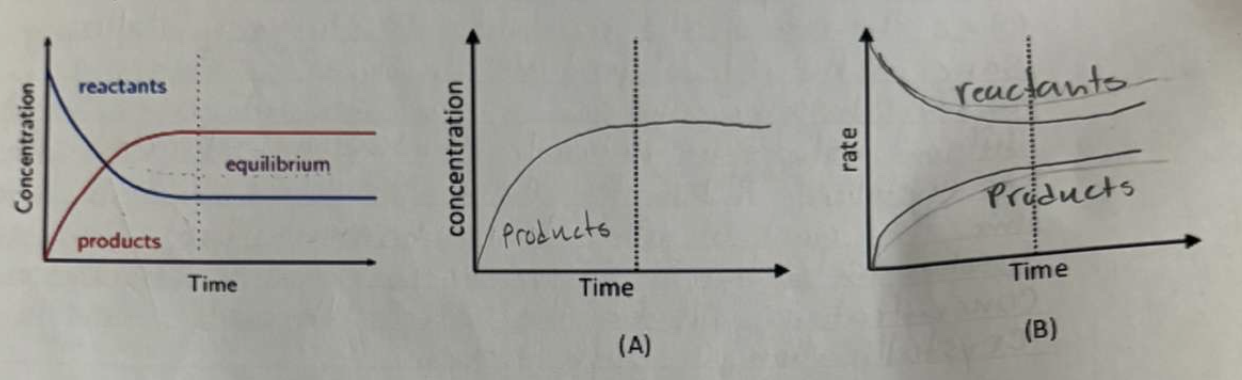
Consider a reaction such as A + B ↔ C
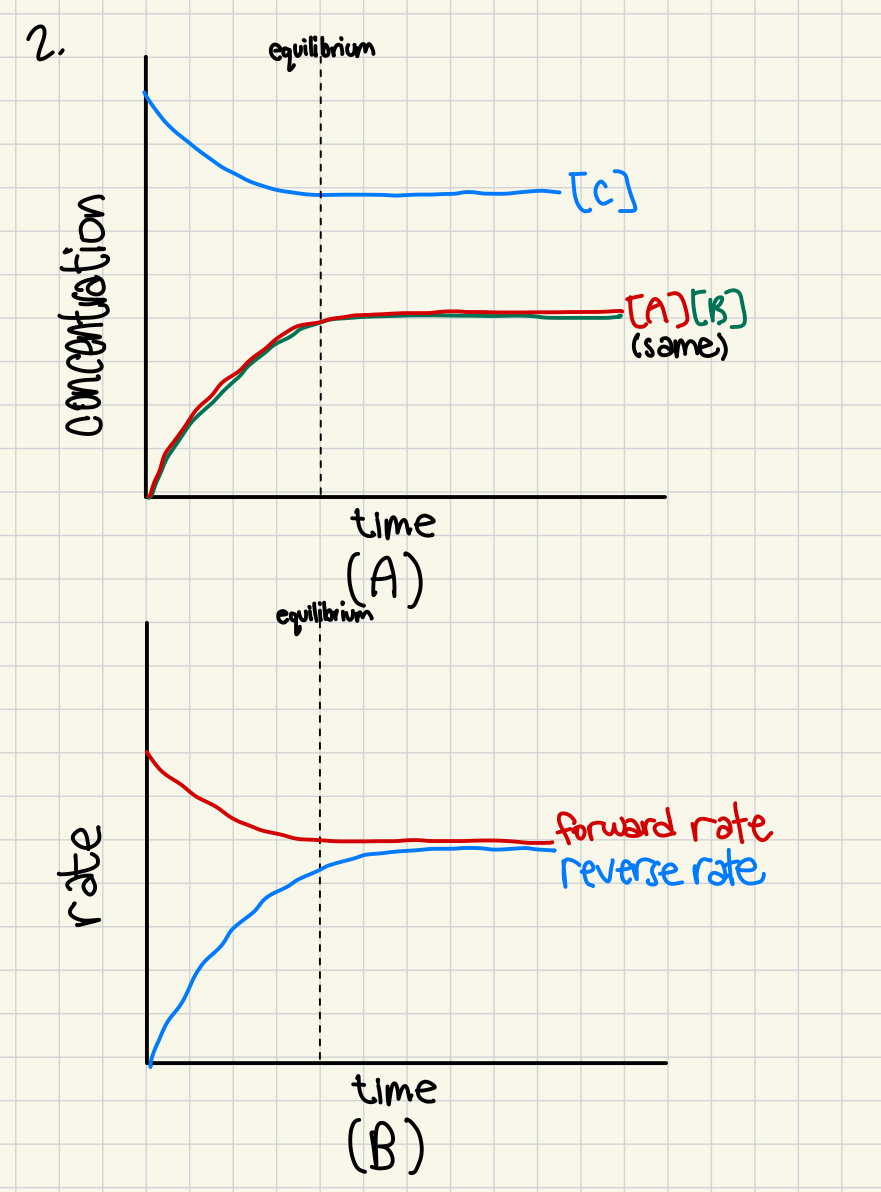
In an initial experiment, reactants are placed into a container and allowed to come to equilibrium, as shown in the completed sketch graph below.
a) complete the sketch graph (A) if the same container is used and the experiment is repeated, but instead, products are put into the container (no reactants) and allowed to come to equilibrium (2 marks)
b) Use the initial experiments and complete sketch graph (B), which shows rates (2 marks)
(pic has wrong answers so dont use those )
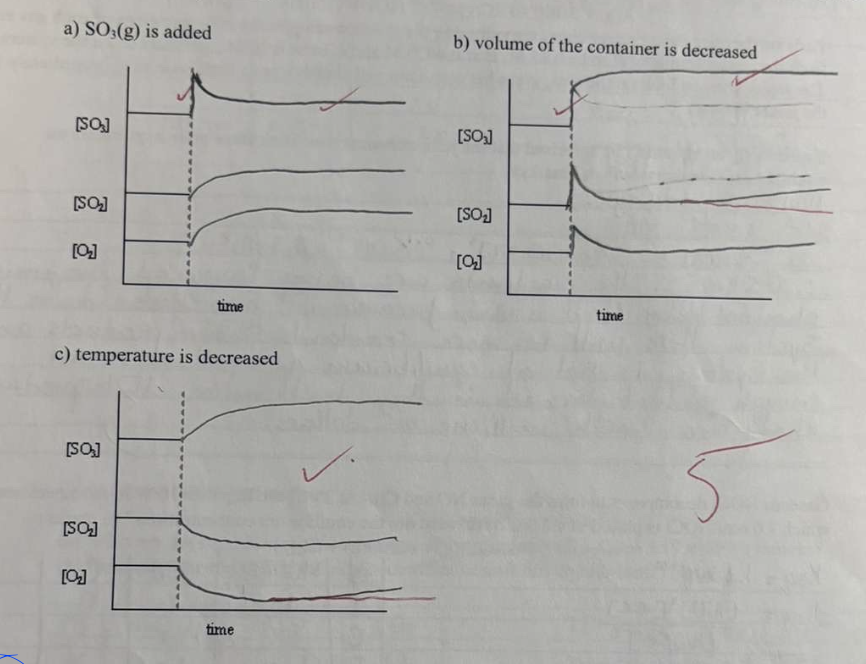
For the following reaction: 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) <-> 2 SO3(g) + 197kJ
Show graphically how the equilibrium system will respond to the following changese at the time indicated by the dashed line: (5 marks)
a) SO3 is added
b) volume of the container is decrasd
c) temperature is decreased
the answers are already on the front card
AgCl(s) <-> Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq). Arrange the following solutions such that AgCl has a decreasing solubility in them. EXPLAIN your reasoning (4 marks)
i. 1M HCl
ii. 2M AgNO3
iii. 1 M NH4NO3
iv. 1 M PbNO3
v. 1 M (NH4)3PO4
a. _____ > b. _____ > c. _____ > d. _____ > e. _____
Final Ranking (from highest to lowest solubility):
a. v. (NH₄)₃PO₄ > b. iv. Pb(NO₃)₂ > c. iii. NH₄NO₃ > d. i. HCl > e. ii. AgNO₃
(NH₄)₃PO₄ increases AgCl solubility the most by removing Ag⁺ (forms Ag₃PO₄).
Pb(NO₃)₂ slightly increases solubility by removing Cl⁻ (forms some PbCl₂).
NH₄NO₃ has no effect — no common ions or reactions.
HCl decreases solubility by adding Cl⁻ (common ion effect).
AgNO₃ decreases it the most by adding a high [Ag⁺] (strong common ion effect).
6. A hypothetical reaction takes two or three days to complete. The product of the hypothetical reaction is worth millions of dollars per gram but the reaction is incredibly difficult to maintain. Miraculously, they manage to get the reaction going.
A(g) + 3B(g) ⇌ 2C(g) (at 450°C, the K_eq = 1.5 × 10⁸)
Early on the third day, a junior chemist monitoring the reaction samples the concentrations of each gas and finds the concentration of A to be 0.15 M, B at 0.0020 M and C to be 0.10 M. He shuts down the system.
The senior chemist looks at the data, grabs his calculator and shortly goes a little pale, then immediately fires the junior chemist.
Explain why we shouldn’t be surprised that the junior chemist was fired. Base your arguments on equilibrium chemistry only. (3 marks)
We shouldn’t be surprised the junior chemist was fired because the system had not yet reached equilibrium when it was shut down. Using the equilibrium expression:
Q = [C]² / ([A] × [B]³)
Substituting values:
Q = (0.10)² / (0.15 × (0.0020)³) = 0.01 / (1.2 × 10⁻⁹) = 8.33 × 10⁶
Since Q (8.33 × 10⁶) is much less than K (1.5 × 10⁸), the reaction was still shifting forward, meaning more product (C) could still be formed. By stopping the reaction early, the chemist prevented further formation of the valuable product, making a serious mistake of losing millions of dollars
7. Gaseous NOCl decomposes to form the gases NO and Cl₂. At 35°C, the Keq = 1.6 × 10⁻⁵.
In an experiment in which 1.0 mol NOCl is placed in a 2.0 L flask, what are the equilibrium concentrations? (6 marks)
2NOCl(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) + Cl₂(g)
Given:
Reaction: 2NOCl(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) + Cl₂(g)
Initial moles NOCl = 1.0 mol
Volume = 2.0 L → so [NOCl]₀ = 1.0 mol / 2.0 L = 0.50 M
K_eq = 1.6 × 10⁻⁵
Step 1: ICE Table
Species | Initial (M) | Change (M) | Equilibrium (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
NOCl | 0.50 | –2x | 0.50 – 2x |
NO | 0 | +2x | 2x |
Cl₂ | 0 | +x | x |
Step 2: Write the expression for K_eq
K_eq = [NO]² × [Cl₂] / [NOCl]²
Substitute in terms of x:
1.6 × 10⁻⁵ = (2x)² × x / (0.50 – 2x)²
1.6 × 10⁻⁵ = 4x³ / (0.50 – 2x)²
Step 3: Assume x is small (to simplify)
Since K is very small, assume 2x << 0.50, so:
(0.50 – 2x) ≈ 0.50
Now:
1.6 × 10⁻⁵ ≈ 4x³ / (0.50)² = 4x³ / 0.25
Multiply both sides:
1.6 × 10⁻⁵ × 0.25 = 4x³
4.0 × 10⁻⁶ = 4x³
x³ = 1.0 × 10⁻⁶
x = (1.0 × 10⁻⁶)^(1/3) ≈ 0.010
Step 4: Solve for Equilibrium Concentrations
[NOCl] = 0.50 – 2x ≈ 0.50 – 0.020 = 0.48 M
[NO] = 2x = 2(0.010) = 0.020 M
[Cl₂] = x = 0.010 M
✅ Final Answer (3 sig. figs):
[NOCl] ≈ 0.480 M
[NO] ≈ 0.0200 M
[Cl₂] ≈ 0.0100 M
![<p><strong>Given:</strong></p><ul><li><p>Reaction: <strong>2NOCl(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) + Cl₂(g)</strong></p></li><li><p>Initial moles NOCl = 1.0 mol</p></li><li><p>Volume = 2.0 L → so <strong>[NOCl]₀ = 1.0 mol / 2.0 L = 0.50 M</strong></p></li><li><p><strong>K_eq = 1.6 × 10⁻⁵</strong></p></li></ul><p></p><div data-type="horizontalRule"><hr></div><p><strong>Step 1: ICE Table</strong></p><table style="min-width: 100px"><colgroup><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"><col style="min-width: 25px"></colgroup><tbody><tr><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Species</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Initial (M)</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Change (M)</p></th><th colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Equilibrium (M)</p></th></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>NOCl</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0.50</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>–2x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0.50 – 2x</p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>NO</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>+2x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>2x</p></td></tr><tr><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>Cl₂</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>0</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>+x</p></td><td colspan="1" rowspan="1"><p>x</p></td></tr></tbody></table><p><strong>Step 2: Write the expression for K_eq</strong></p><p><strong>K_eq = [NO]² × [Cl₂] / [NOCl]²</strong></p><p></p><p>Substitute in terms of x:</p><p></p><p><strong>1.6 × 10⁻⁵ = (2x)² × x / (0.50 – 2x)²</strong><br><strong>1.6 × 10⁻⁵ = 4x³ / (0.50 – 2x)²</strong></p><p></p><p><strong>Step 3: Assume x is small (to simplify)</strong></p><p>Since K is very small, assume <strong>2x << 0.50</strong>, so:</p><p></p><p><strong>(0.50 – 2x) ≈ 0.50</strong></p><p></p><p>Now:</p><p></p><p><strong>1.6 × 10⁻⁵ ≈ 4x³ / (0.50)² = 4x³ / 0.25</strong></p><p></p><p>Multiply both sides:</p><p></p><p><strong>1.6 × 10⁻⁵ × 0.25 = 4x³</strong><br><strong>4.0 × 10⁻⁶ = 4x³</strong><br><strong>x³ = 1.0 × 10⁻⁶</strong><br><strong>x = (1.0 × 10⁻⁶)^(1/3) ≈ 0.010</strong></p><p></p><p><strong>Step 4: Solve for Equilibrium Concentrations</strong></p><ul><li><p><strong>[NOCl] = 0.50 – 2x ≈ 0.50 – 0.020 = 0.48 M</strong></p></li><li><p><strong>[NO] = 2x = 2(0.010) = 0.020 M</strong></p></li><li><p><strong>[Cl₂] = x = 0.010 M</strong></p></li></ul><p></p><p><span data-name="check_mark_button" data-type="emoji">✅</span> Final Answer (3 sig. figs):</p><ul><li><p><strong>[NOCl] ≈ 0.480 M</strong></p></li><li><p><strong>[NO] ≈ 0.0200 M</strong></p></li><li><p><strong>[Cl₂] ≈ 0.0100 M</strong></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/01305776-e1ad-4b04-8825-94aab25bdd50.jpg)
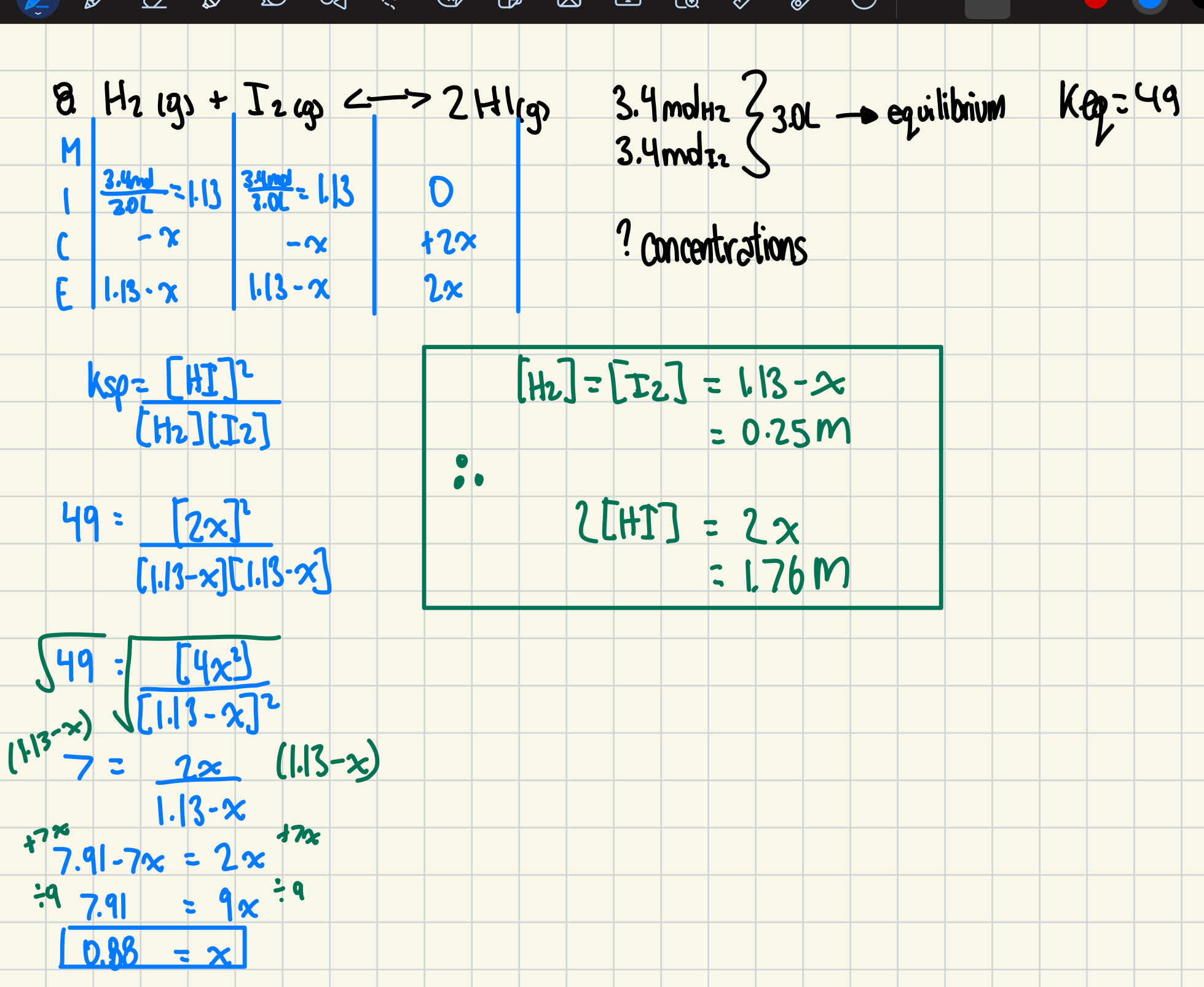
8. Consider the equilibrium:
H₂(g) + I₂(g) ⇌ 2HI(g) K_eq = 49
If 3.4 mol of both H₂ and I₂ are placed in a 3.0 L container and allowed to reach equilibrium, what would the equilibrium concentrations be for H₂(g), I₂(g), and HI(g)? (6 marks)
9. Consider the following reaction:
AgIO₃(s) ⇌ Ag⁺(aq) + IO₃⁻(aq)
(a) What are the equilibrium concentrations of the reaction with a Ksp of 3.17 × 10⁻⁸? (3 marks)
(b) How would precipitating the silver out affect or shift this equilibrium? (1 mark)
b) Removing Ag⁺ from solution reduces its concentration.
According to Le Châtelier’s Principle, the equilibrium will shift right to replace the missing Ag⁺ ions, so more AgIO₃ will dissolve.

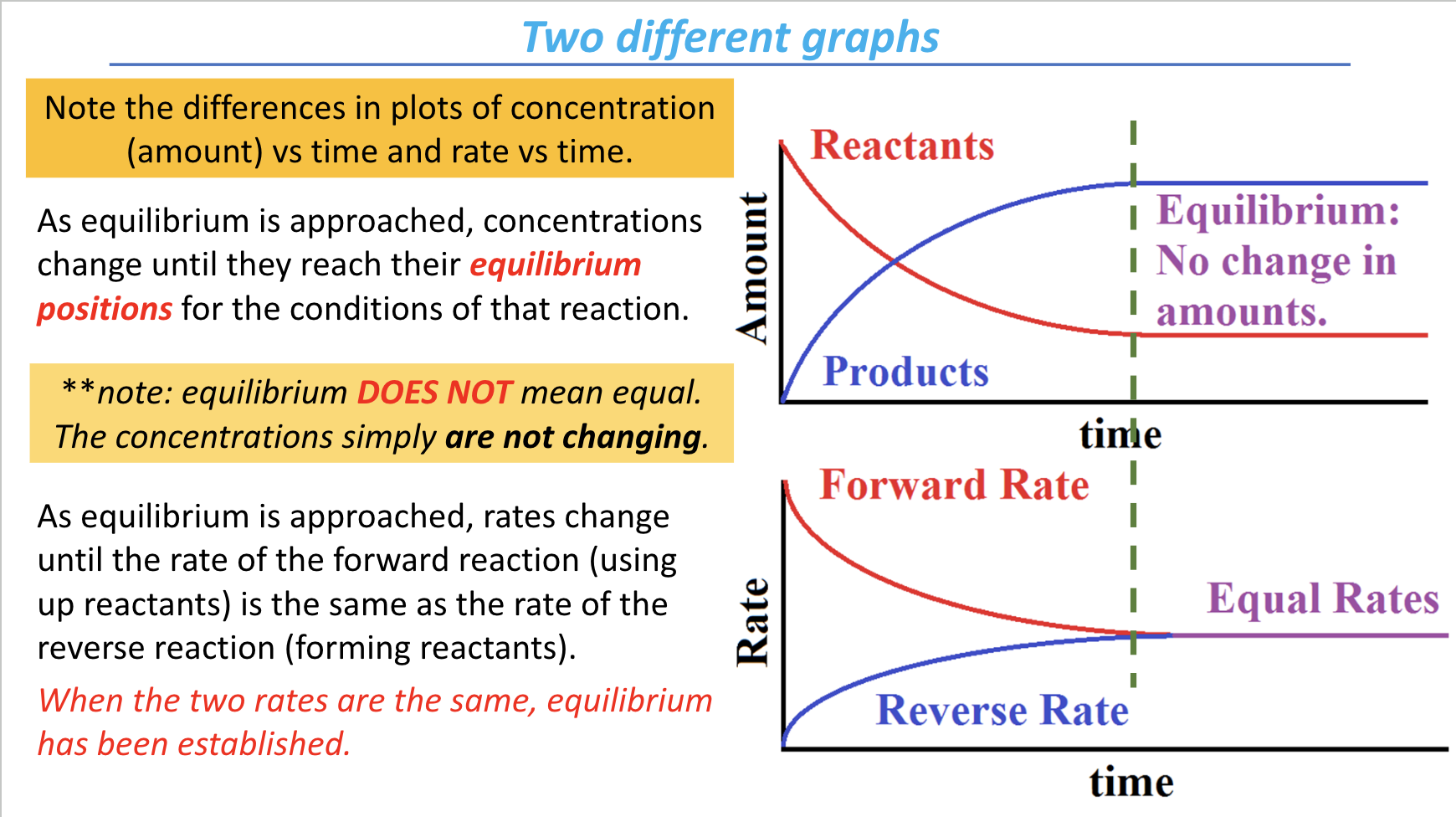
be able to establish/differentiate between rate and concentration graphs
explain iodine experiment and its counter exp.