Nucleotides, Genetics/Pedigrees and Evolution/Biodiversity - Final Exam
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I am so sorry for how many flashcards this contains (answering with definition is recommended)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Transcription
the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. RNA Polymerase goes into the nucleus, finds the gene and transcribes the code from DNA to RNA language
Translation
involves decoding a messenger RNA (mRNA) to be translated into amino acids. Amino acids are linked together to build a polypeptide. takes place in three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. takes place in the ribosome
The Process of Gene Expression
Trigger of Gene Expression (hormones, nutrients, environment) arrives at cell/chromosome/gene
Transcription bubble forms
RNA Polymerase builds mRNA code
Get mRNA to raw materials and building machinery in cytoplasm
TRANSLATION: Construct POLYPEPTIDE (Amino Acid chain)
Finished!
What is each cell designed to detect?
Different stimuli or triggers of Gene Expression
What happens when the trigger for Gene Expression arrives?
A gene opens up its DNA sequence and protein synthesis begins
Codon
a DNA or RNA sequence of three nucleotides (a trinucleotide) that forms a unit of genomic information encoding a particular amino acid
Anti-codon
a trinucleotide sequence located at one end of a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule, which is complementary to a corresponding codon in a messenger RNA (mRNA) sequence
What happens to completed polypeptide sequences after there are no more amino acids to add onto the polypeptide chain?
This combination will be folded and shaped into the final protein, like an enzyme, antibody, structure or “portal”
What are the 3 triggers for Gene Expression?
Hormones (cortisol/progesterone etc.)
Nutrients (lactose/fructose etc.)
Environment (sun/light/temperature)
SnRNPs (Small Nuclear Ribonucleoproteins)
a large RNA-protein complex that cuts out unnecessary sections of the pre-mRNA
Spliceosomes
removes intronic sequences from primary transcripts to generate functional messenger and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA)
Regulate
control or maintain the speed or rate of a machine or process so that it operates properly
Denature
destroy the characteristic properties of a protein or other biological macromolecule by heat, acidity, or other effects that disrupt its molecular conformation
Lac Operon
a set of structural genes that code for proteins to metabolize (digest) lactose, which can be turned on or turned off
E. coli
a bacteria which is generally found in the intestines. they benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by harmful pathogenic bacteria
Mutation
a permanent change in a cell’s DNA; inheritable
Point mutation
substitution, insertion, or deletion of one or very few molecules
Substitution
a type of mutation in which one nucleotide is replaced by a different nucleotide. has a relatively minor effect overall
Insertion
a type of mutation that involves the addition of one or more nucleotides into a segment of DNA. usually results in a frameshift mutation
Deletion
occurs when part of a DNA molecule is not copied during DNA replication. usually results in frameshift mutation
Frameshift mutation
Insertion or deletion that results in a change to the reading frame of a gene
What feature of the genetic code helps protect a cell from the effects of nucleotide substitution?
The redundancy of genetic code (changes in a gene’s code may result in the same amino acid)
Mutagen
anything that causes a change (mutation) in a cell. increases the mutation rate in a cell
Carcinogen
a substance, organism or agent capable of causing cancer
Somatic Cell Mutation
a mutation that occurs in the body cells
Germ Line Mutation
a mutation that occurs in the reproductive cells
Silent point
a type of substitution, or point, mutation, wherein the change in the DNA sequence of the gene has no effect on the amino acid sequence
Mis-sense point
a DNA change that results in different amino acids being encoded at a particular position in the resulting protein
Nonsense point mutation
a change in DNA that causes a protein to terminate or end its translation earlier than expected
3 traits of a physical mutagen
Structure of DNA is altered
Replication is interfered with
Point mutations or chromosome loss
3 traits of a chemical mutagen
Induce mutations via DNA reacting to chemical reactions
Can cause incorrect nucleotides to be used during replication
Often associated with cancer
Ligase
an enzyme that joins together fragments of newly synthesized DNA to form a seamless strand
List in sequence the three stages of the replication process
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
Initiation
a sequence in protein synthesis that consists of the recruitment of a ribosome initiator tRNA complex to the initiation codon of a messenger RNA
Elongation
a key step of protein synthesis, during which the polypeptide chain extends by one amino acid residue during one elongation cycle
Termination
process in protein synthesis in which a stop codon becomes positioned in the ribosomal A-site and is decoded by a protein
Helicase
cuts the hydrogen bonds between nucleotides
Okazaki fragments
short segments of DNA built moving away from the replication fork toward the replication origin
What molecule replaces RNA primers during replication?
DNA Polymerase
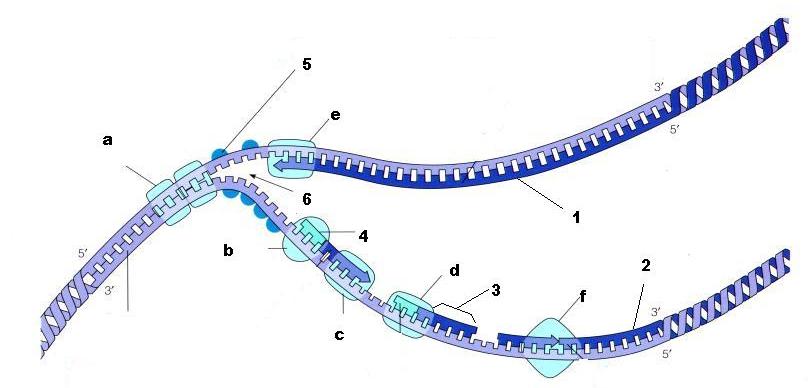
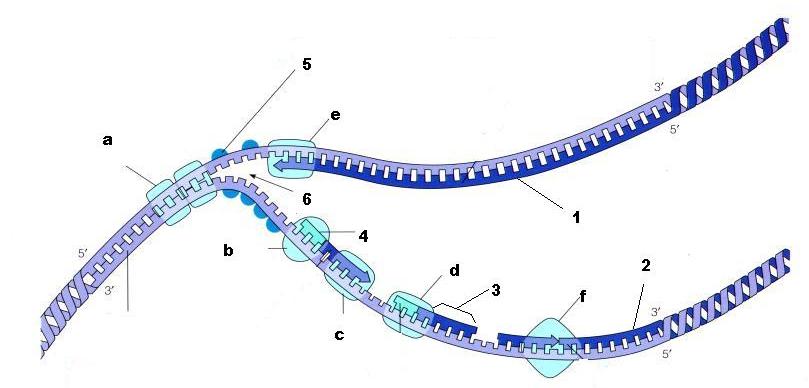
From the diagram above, what is structure 5?
SSBP - Single strand binding proteins
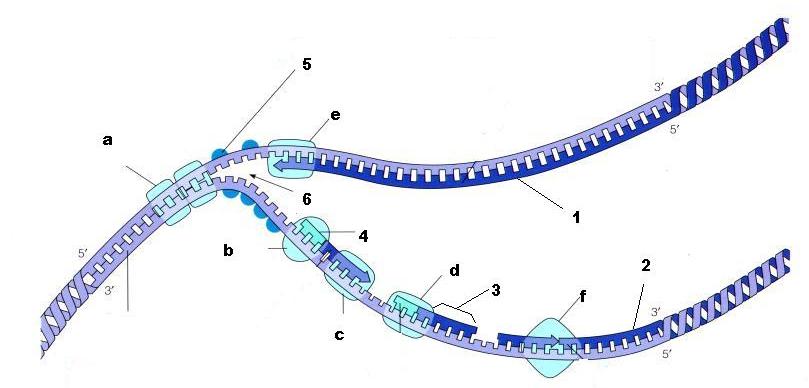
From the diagram above, is structure 1 the lagging strand or the leading strand?
Leading strand
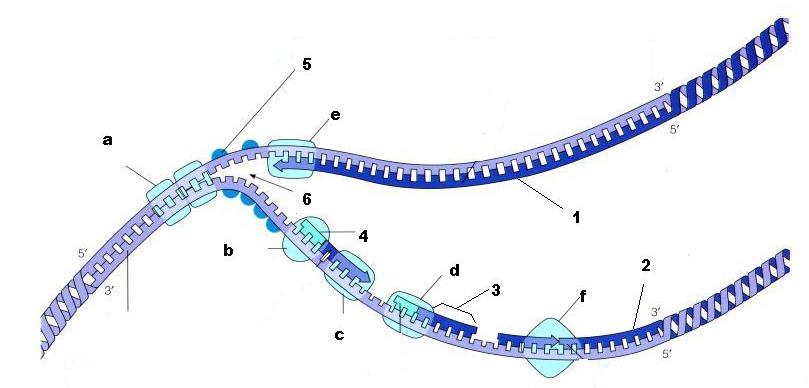
From the diagram above, is structure 2 the lagging strand or the leading strand?
Lagging strand
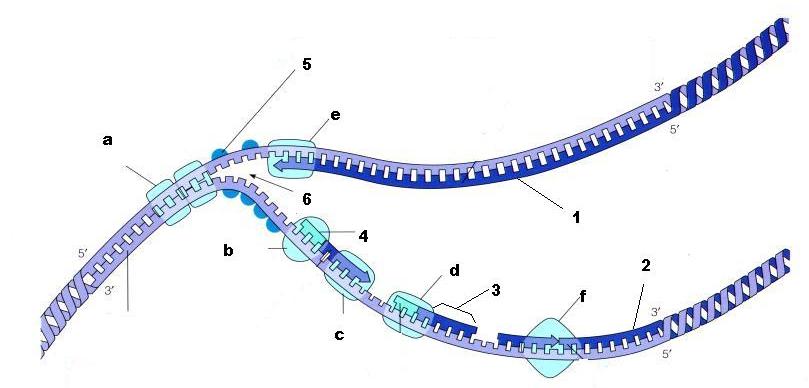
What is enzyme E?
DNA Polymerase
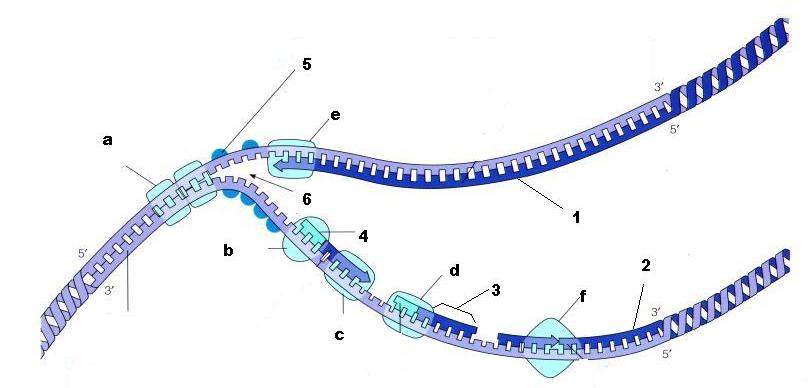
What is structure 4 being built by enzyme B?
Primer
What is structure 3 called?
Okazaki fragment
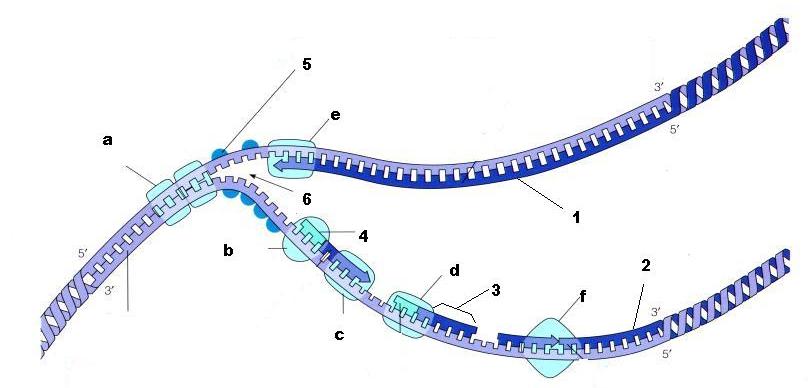
What is the name of enzyme F?
Ligase
Gyrase
an enzyme that reduces/stops the super-coiling effects of DNA during replication
Chargoff’s Rule
The amount of Cytosine is equal to the amount of Guanine in a DNA molecule, and the amount of Adenine is equal to that of Thymine in a DNA molecule (A=T, C=G)
Describe DNA’s structure
Double helix (2 strands twisted)
Complementary base pairing (purine to a pyrimidine)
Antiparallel (strands run in opposite directions same distance apart)
Gene vs Genome
Both refer to the genetic makeup of an organism/DNA
Gene = 1 DNA instruction along 1 part of a chromosome
Genome = the collection of all the DNA instructions on all the chromosomes of an organism
The building machinery of a replication fork can only function by…
Reading template nucleotides that read in a 3 to 5 direction
Adding new nucleotides to the new DNA in a 5 to 3 direction
(Meaning there are some delays in the building process)
Poly A tail
the section of the mature mRNA added to the 3’ end of the mature mRNA
Cap
the section of the mature mRNA that is added to the 5’ end of the mRNA
Chromosomal mutation
changes in the number or structure of chromosomes
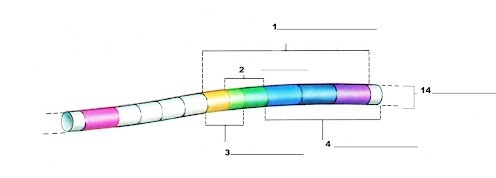
What is label number 1?
Lac Operon
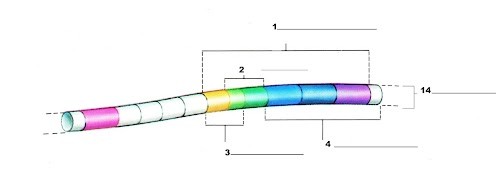
What is label 2?
The operator region
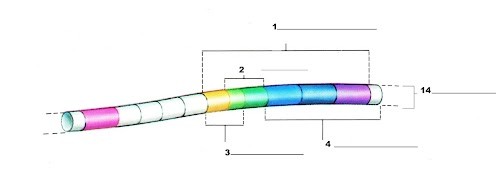
What is label 3?
The promoter region
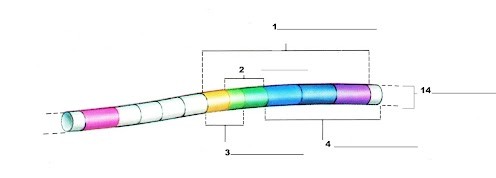
What is label 4?
The structural genes
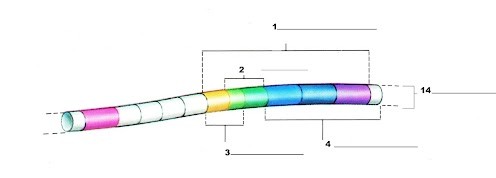
What is label 14?
The chromosome
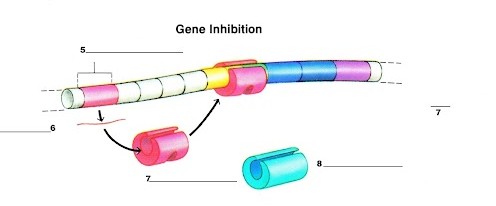
What is label 5?
The regulator gene
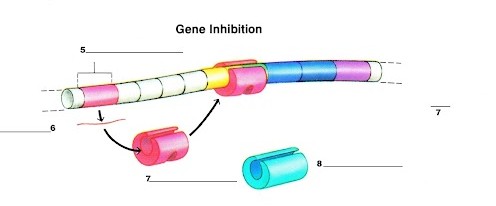
What is label 6?
The mRNA
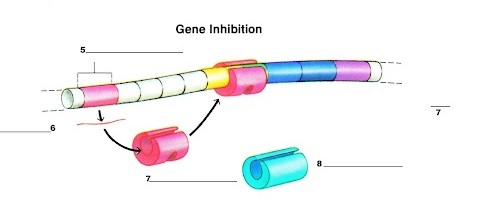
What is label 7? (ignore the one off to the right)
The repressor protein
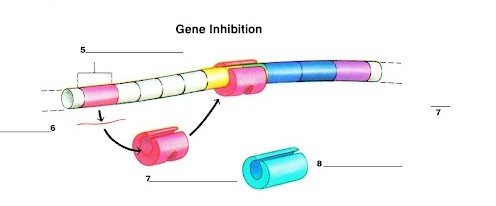
What is label 8?
RNA Polymerase
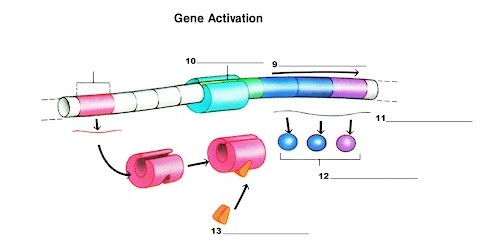
What is label 10?
RNA Polymerase
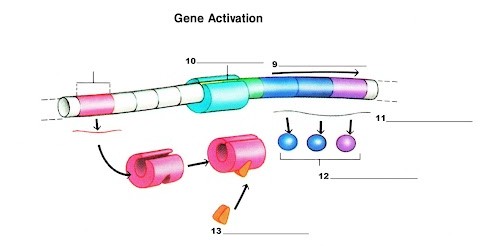
What is label 9?
Transcription
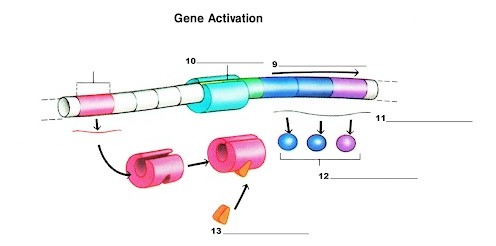
What is label 11?
mRNA
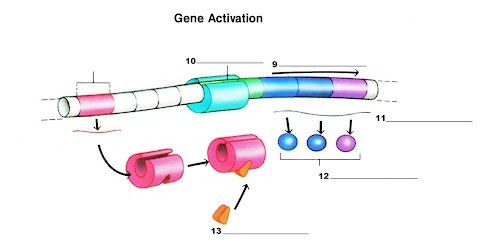
What is label 12?
Lactose-digesting proteins
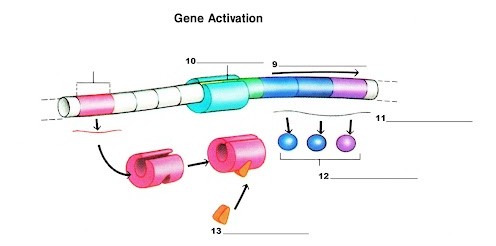
What is label 13?
Lactose
Methionine
the starter amino acid of a codon sequence. encoded as AUG
DNA vs. RNA
Both carry genetic information/are essential for genetic processing
DNA encodes genetic information, forms a double helix, and is typically housed in a cell’s nucleus
RNA decodes genetic information, is single stranded, and different types of RNA can be found in multiple locations (mRNA: nucleus, tRNA: cytoplasm, rRNA: ribosomes)
What does RNA and DNA stand for?
RNA: Ribonucleic Acid
DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid
What is the literal translation of Semi-Conservative replication?
Semi → half or partial
Conservative → saving/reserving something
Replication → Copy + paste, duplication
True or False: the leading strand of DNA is built toward the replication fork
True
True or False: the lagging strand of new DNA is built in one continuous piece
False
True or False: the lagging strand of DNA is made of Okazaki fragments
True
True or False: primase is the only enzyme that makes RNA primers
True
True or False: An RNA primer is made of nucleotides that use Ribose sugars and have bases like A, C, G, and T
False
True or False: when A bonds to C, two hydrogen bonds are formed
False
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
A method invented by biochemist Kary Mullis for rapidly producing (amplifying) millions to billions of copies of a specific segment of DNA. The steps of PCR are as follows: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands by applying extreme heat; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers. This process is repeated 35-40 times
Taq Polymerase
a thermostable DNA polymerase often used in PCR because of it’s resistance to unwinding in extreme heat
Genetics
a branch of biology that attempts to predict the outcome of sexual reproduction through understanding gene-to-gene actions and meiosis
Evolution
change in inheritable traits (genes) in living things, over time
Macro-evolution
big changes over longer periods of time
Micro-evolution
small changes over a short period of time
Early Philosophies
Plato and Aristotle believed life was unchanging
This belief carried on to western culture
“All life was created independently of one another and has remained unchanged ever since”
Buffon
Challenged the idea species never changed
Wrote Histoire Naturelle, a book detailing his understandings of the world
Noted ape and human similarities
Suggested Earth was older than 6000 years
Essentially kick-started evolution theories
Cuvier
Largely credited for developing paleontology
Each rock layer contains unique fossil species; the farther down you go the older they get
Proposed Earth experienced “revolutions,” destructive natural disasters that caused mass extinctions
Rejected the evolution theory
Lyell
Rejected the “revolution” theory
Geological processes operated at the same rate in the past as they do today
Slow, continuous processes means Earth is older than 6000 years
These slow processes result in big changes
Lamarck
Wrote Philosophie Zoologique, detailing the changes of animals over time
Line of descent (series of fossils leads to modern species)
Inheritance of acquired characteristics (traits, or an animal’s adaptation to the environment, are passed down to offspring)
His theory was ultimately rejected as biologists learned about cells, genes and heredity
Darwin and Wallace
The Beagle Expedition/Galapagos Islands
The study of many species and the comparison of similarities between them on different landmasses
Made records and took notes of species all over the world
Developed natural selection theory
On the Origin of Species (book about evolution theory)
Darwin’s Two Main Ideas (On the Origin of Species)
Present life forms have arisen by descent and modification from an ancestral species
The mechanism for moderation is natural selection working for long periods of time
Artificial selection
selective breeding to obtain varieties of plants or animals with desired traits
Fossil record
remains or traces of a past life preserved in sedimentary rock, which reveal the history of life on Earth
Index fossils
fossils that are known to be common during a particular time, and so indicate the age of the rock they are found in
Radiometric dating
method of dating rocks and minerals that uses measurements of certain radioactive isotopes to calculate the absolute age in years
Transitional fossils
fossils that show intermediary links between groups of organisms
Biogeography
the study of past and present geological distribution of species
Analogous structures
physical features that evolved separately but perform similar functions in different types of organisms
Homologous structures
physical features with the same evolutionary origin and underlying structural elements, but that may have different functions
Convergent evolution
tendency among species that are not closely related to develop similar body plans when living under the same conditions