Genetics Exam One (Final)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/29
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
1
New cards
If a plant of genotype A/a os selfed, and numerous offspring are scored, what proportion of the progeny is expected to have homozygous genotype?
50%
2
New cards
A pant is heterozygous at three loci. How many different phenotypes can it theoretically produce with respect to these three loci
8
3
New cards
A wildt-type strain of haploid yeast is crossed to a mutant strain with phenotype d. What phenotypic ratios will be observed in the progeny
50% wild type and 50% mutant (d)
4
New cards
Mice (*Mus musculus)* have 40 chromosomes per diploid cell (2n=40). How many double stranded DNA moleculres and how many chromsomes are there in a mouse cell that is G2 stage of the cell cycle?
80 DNA molecules and 40 Chromosomes
5
New cards
What is the mechanism that ensures Mendel’s First law of segregation?
Segregation of sister chromatids during meiosis 1
6
New cards
The diagram below shows a part of the biochemical pathway responsible for fruit color in peppers (*Caspicum annuum*). Enzyme 1 is responsible for catalyzing the reaction that turns the colorless precursor into yellow pigment, whereas Enzyme 2 catalyzes the step that turns the yellow pigment into red pigment. A breeder crosses a pure-breeding plant that makes yellow pepper to a pure-breeding plant that males red peppers. What portion of the offspring will makes red peppers?
\
Enzyme 1 Enzyme 2
Colorless------→Yellow Pigment----→ red pigment
\
Enzyme 1 Enzyme 2
Colorless------→Yellow Pigment----→ red pigment
All of the off spring
7
New cards
In pet rabbits, brown coat color is recessive to black coat color. A black female rabbit gives birth to four back-coated, and three-coated baby rabbits. What can be deduced about the genotype of the baby rabbits’ father
He could be heterozygous black/brown or homozygous brown
8
New cards
A very common type of red-green colorblindness in humans is caused by a mutation in a gene located on the X chromosome. Knowing that the mutation allele is recessive to the wild type, what is the probability that the son of a women whose father is colorblind is going to also be colorblind?
25%
9
New cards
You have three jars of gum-balls. The first jar has 100 white gum-balls and 25 green, the second jar has 50 white and 150 clue, the third jar contains 500 white and 10 red.
\
If you randomly draw one gum-ball from each jar what is the probability for all white gum-balls
\
If you randomly draw one gum-ball from each jar what is the probability for all white gum-balls
0\.196 or 19.6%
10
New cards
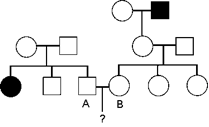
The following pedigree concerns the autosomal recessive disease Phenylketonuria (PKU). The couple marked A and B are contemplating having a baby but are concerned about the baby have PKU. What is the probability of the first child having PKU? unless you have evidence to the contrary, assume that the a person marrying into the pedigree is not a carrier. The filled-in individuals have PKU
1/12
11
New cards
Medal Crossed Y/Y;R/R (yellow wrinkled) peas with y/y;r/r(green smooth) peas and selfed the F1 to obtain an F2 . In the F2 what proportion of the yellow wrinkled individuals were pure-breeding?
1/16
12
New cards
A fish of genotype a/a;B/b is crossed to a fish whose genotype is A/a;B/s. What proportion of the progeny will be heterozygous for at least one of the genes (assume independent assortment)
6/8
13
New cards
Two pure-breeding mutant plants were crossed: One had small leaves (wild-type leaves are large), and the other made pink flowers (wild-type flowers are purple). All F1 individuals has small leaves and purple flowers. Assuming independent assortment, what proportion of the F2 individuals were expected to be phenotypically wild type?
3/16
14
New cards
In hogs, a dominant allele B results in a white belts around the body. At a separate locus, the dominant allele S causes fusion of the two parts of normally cloven hoof resulting in a condition known as syndactyly. A belted syndactylous sow was crossed to an unbelted colven-hoofed boar, and in the litter there were:
\
25% belted syndactylous
25% belted cloven
25% unbelted syndactylous
25% unbelted cloven
\
25% belted syndactylous
25% belted cloven
25% unbelted syndactylous
25% unbelted cloven
B/b;S/s X b/b;s/s
15
New cards
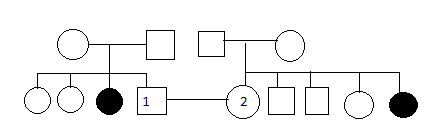
The following pedigree shows inheritance of a mild, but very rare condition in Siberian Husky dogs. If individuals 1 and 2 are crossed, what is the probability that they will produce an affected pup?
4/36
16
New cards
If a plant of genotype A/a;B/b;C/c;D/d is selfed and the genes assort independently, how many different genotypes will be found among the progeny?
81
17
New cards
In drosophila cross, you mate a parental line displaying crossed eyes(recessive trait, autosomal) and corkscrew bristles (recessive trait, autosomal) by a wild-tyoe fly. The sites of the two genes are known to be unlinked. The F1 are wild type.
\
You self the F1 flies in the hope of regenerating the cross-eyes/corkscrewed phenotype.
\
How many individuals F2 flies would you need to analyze tp have 95% confidence of finding at least one cross-eyed/corkscrew fly?
\
You self the F1 flies in the hope of regenerating the cross-eyes/corkscrewed phenotype.
\
How many individuals F2 flies would you need to analyze tp have 95% confidence of finding at least one cross-eyed/corkscrew fly?
47 flies
18
New cards
Which of the following is/are TRUE with respect to haploid and diploid cells?
In diploid cells ,meiosis 1 results in the formation of two haploid cells
19
New cards
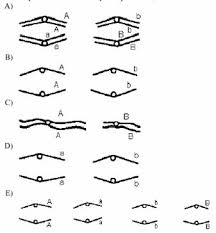
In a particular dihybrid, the two genes of interest, A and B are located on different chromosomes. Which of the following diagrams does NOT respect a stage of meiosis in this organism?
E
20
New cards
You generate a plant that is heterozygous for three qualitative trait loci (QTL). In the heterozygous states, each locus has one allele that contributes one does of trait (pigment) and another allele that does not contribute a does to a trait; genotype: R1/r1; R2/r2; R3/r3. Ig you testcross this plant by (r1/r1; r2/r2; r3/r3 all “0-does alleles) what distribution of pigment would be observed in the progeny?
1/8, three dose; 3/8 two does; 3/8 one does; 1/8 zero does
21
New cards
A plant of genotype C/C x d/d is crossed to c/c x D/D and the F1 is testcrossed. If the genes in question are linked, the percentage of double homozygous recessive individuals in the offspring of the testcross will be:
less thank 25%
22
New cards
A diploid plants is a trihybird for flowe color (gene “F”), leaf size (gene “L”) and seed weight (gene “S”); its phenotype includes red flowers, large leaves and heavy seeds. This plant is crossed to a tester plant (which has white flowers, small leaves and light seeds). the progeny is as follows
\
23 red, heavy,large
25 Red, Heavy, small
230Red, Light, large
235 Red, light, small
232 white, hevay,large
228 white,heavy,small
25 white, light,large
26 white,light,small
\
What Can be concluded about the linkage relationships of the three genes in question
\
23 red, heavy,large
25 Red, Heavy, small
230Red, Light, large
235 Red, light, small
232 white, hevay,large
228 white,heavy,small
25 white, light,large
26 white,light,small
\
What Can be concluded about the linkage relationships of the three genes in question
Genes F and S are linked while L assorts independently
23
New cards
In a diploid invertebrate, genes D and E are closely linked. Single crossovers between these two genes occurs only in 1 out of 40 meioses and multiple crossovers are never observed. If an individual has the genotype D e/d E, what percentage of its gametes are expected to be recombinant (either DE or de)?
1\.25%
24
New cards
Two genes, A and B are linked. An individual of genotype A b/A b is crossed to one that is a B/a B. The F1 is testcrossed. Which of the following ratios most likely represents the phenotypic ratio observed in the progeny of this testcross?
1:4:4:1
25
New cards
In *Drosophila*, two genes w and sn are X-linked and 25 map units apart. A female fly of genotype w+ sn+/ w sn is crossed to a male from a wildtype line. What percent of male progeny wi;; be w+ sn?
12\.5%
26
New cards
In maize, two plants that are both heterozygous for the recessive alleles a and b are crosses. What frequency of doubel-mutant progeny will appear if a and b are 7.2 map unites apart, and both parents carry a and b in replusion (trans)?
0\.001296
27
New cards
The F, G, and H loci are linked in the order written. There are 30 map units between F and G and 30 map units between G and H. If a plant F G H/ f g h. What proportions of progeny plants will be f g h/f g h if there is no interaction?
0\.245
28
New cards
Out of 800 progeny of a three-point testcross, there were 16 double crossover recombinants whereas 80 has been expected on the basis of no interference. The interference is
0\.80
29
New cards
In a linear tetrad analysis, the second divison segregation (Mn) frequency of the cyh locus is 16% The map distances from this locus to its centromere is:
8 m.u
30
New cards
A dihybord AaBb female drosophilia is testcrossed with an aabb male. The following offspring genotupes were obtained.
\
AaBb 99
Aabb 83
aaBb 86
aabb 92
\
A chi square was preformed to determine weather the data supported the original hypothesis that the genes are unlinked. How many degrees of freedom should be used in this analysis
\
AaBb 99
Aabb 83
aaBb 86
aabb 92
\
A chi square was preformed to determine weather the data supported the original hypothesis that the genes are unlinked. How many degrees of freedom should be used in this analysis
3