UCI Bio 93 Midterm 2 (copy)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/177
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
178 Terms
1
New cards
What is a metabolic pathway?
A pathway that a molecule goes through, resulting in a specific product.
2
New cards
What is metabolism?
The totality of an organisms chemical reactions
3
New cards
Gibbs free energy
Portion of a system that can perform work when temp and pressure are uniform throughout the system.
4
New cards
What is a way to show change in free energy?
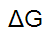
5
New cards
What does a negative Delta G mean?
A process that is spontaneous
6
New cards
What does spontaneous mean?
Means that a process will occur.
7
New cards
What happens to the energy in a exergonic reaction?
It is released
8
New cards
What happens to the energy in an endergonic reaction?
It is consumed in the reaction.
9
New cards
True or False
A cell must have endergonic and exergonic reactions
A cell must have endergonic and exergonic reactions
True
10
New cards
Is ATP Hydrolysis an exergonic or endergonic reaction?
Exergonic
11
New cards
Mechanical and Transport work are what kind of reactions?
Endergonic
12
New cards
Why does ATP hydrolysis release so much energy?
All 3 phosphate groups ate neg. charged, so there is mutual repulsion within all of them
13
New cards
What do enzymes do?
Lower energy barriers to drive chemical reactions
14
New cards
What does the suffix -ase usually mean?
An enzyme
15
New cards
How does an exergonic energy profile look like?
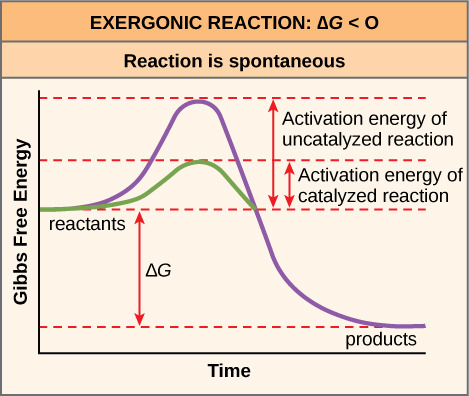
16
New cards
Enzymes are biological ___________
Catalysts
17
New cards
What is the site of cellular respiration in all eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondria
18
New cards
In Biology, what is another word for the addition of electrons to a substance?
Reduction
19
New cards
In Biology, what is another word for the loss of electrons to a substance?
Oxidation
20
New cards
What is cellular respiration?
Catabolic reactions used to generate ATP
21
New cards
Where does glycolysis happen?
In the cytosol
22
New cards
What is glycolysis?
The breaking down of glucose into 2 molecules of a compound of pyruvate.
23
New cards
What happens in the citric acid cycle?
The breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide is completed.
24
New cards
What is stage 1 of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis
25
New cards
What is stage 2 of cellular respiration?
Pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle
26
New cards
What is stage 3 of cellular respiration?
Oxidative Phosphorylation
27
New cards
What is the purpose of NADH?
Transfers electrons from food to electron transport chain.
28
New cards
Pyruvate is converted to what compound?
Acetyl CoA
29
New cards
Where does the citric acid cycle occur?
In the mitochondrial matrix
30
New cards
What happens in substrate-level phosphorylation?
A substrate gives a phosphate to ADP, making a product and ATP
31
New cards
Where does oxidative phosphorylation happen?
The inner mitochondrial membrane
32
New cards
About how many ATP/Glucose is made during cellular respiration?
30-32
33
New cards
What is ATP Synthase?
An enzyme that makes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphates.
34
New cards
What is chemiosmosis?
energy stored as a hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane is used to drive cellular work.
35
New cards
Establishing the H+ gradient is a major function of what?
The electron transport chain
36
New cards
What 2 processes can oxidize organic fuel and generate ATP without oxygen?
Fermentation and anaerobic respiration
37
New cards
What is the distinction between fermentation and anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration uses the electron transport chain
38
New cards
What is anaerobic respiration?
A process of harvesting chemical energy WITHOUT oxygen.
39
New cards
What, simply, happens in alcohol fermentation?
Pyruvate is converted into ethanol.
40
New cards
What happens in lactic acid fermentation?
Pyruvate is reduced by NADH to form lactate
41
New cards
What is lactate?
The ionized form of lactic acid
42
New cards
How much ATP does fermentation yield?
2
43
New cards
What are obligate anaerobes?
Organisms that only carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration.
44
New cards
What are catabolic pathways?
Chemical reactions that break down complex molecules into energy and smaller molecules
45
New cards
What are anabolic pathways?
When energy is used to make smaller molecules into a larger molecules
46
New cards
What type of metabolic reaction releases energy?
Catabolic
47
New cards
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
The energy in the universe is constant. Cannot be created or destroyed
48
New cards
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
Every energy transformation increases the entropy (disorder) of the universe.
49
New cards
A spontaneous reaction is a type of reaction that leads to ___________
An increase in entropy
50
New cards
What is a type of reaction that decreases the entropy of the universe?
A non spontaneous reaction
51
New cards
What is enthalpy?
The total energy of a biological system
52
New cards
What is free energy?
The usable energy that is able to perform work
53
New cards
What is the equation to find change in free energy?
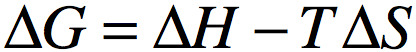
54
New cards
If Delta G
Exergonic
55
New cards
If Delta G>1, then it is a __________ reaction
Endergonic
56
New cards
What are autotrophs?
Organisms that can sustain themselves without eating other organisms.
57
New cards
Plants are what kind of autotroph?
Photoautotrophs
58
New cards
What are heterotrophic organisms?
Organisms that eat other organisms
59
New cards
What is the mesophyll?
The tissue in the interior of the leaf
60
New cards
What are stomata?
Microscopic pores on the leaf
61
New cards
What is the dense fluid in a chloroplast?
Stroma
62
New cards
What are the small sacs within the Stroma?
Thylakoids
63
New cards
What is a stack of thylakoids called?
A grana (granum)
64
New cards
What is the green pigment that gives plants their color?
Chlorophyll
65
New cards
What are the 2 stages of photosynthesis?
Light reactions and the Calvin Cycle
66
New cards
What is the process called when a light reaction makes ATP, using chemiosmosis to add a phosphate to ADP?
Photophosphorylation
67
New cards
What happens during the light reactions in photosynthesis?
Solar energy is converted into chemical energy
68
New cards
What are the names of the 2 types of photosystems in light reactions?
Photosystem I and Photosystem II
69
New cards
What is a photosystem composed of?
A reaction-center complex and light harvesting complexes.
70
New cards
Chloroplast and Mitochondria both use what process to generate ATP?
Chemiosmosis
71
New cards
What is the name of the sugar that is produced by the Calvin Cycle?
G3P
72
New cards
What are the 3 stages of the Calvin Cycle?
1. Carbon Fixation
2. Reduction
3.Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor
2. Reduction
3.Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor
73
New cards
What happens during carbon fixation?
A CO2 molecule is attached to an RuBP sugar and then splits in half to make 2 molecules of 3-Phosphoglycerate
74
New cards
What is the name of the enzyme that catalyzes carbon fixation?
Rubisco
75
New cards
Where are chlorophyll molecules found?
Thylakoid membrane
76
New cards
What is fluorescence?
Emission of a photon of light.
77
New cards
What is transformation in DNA genetics?
A change in the genotype and phenotype
78
New cards
What is the name of a virus that infects bacteria?
Bacteriophages
79
New cards
What is a shorter name for Bacteriophages?
Phages
80
New cards
What is the name of the 4 nucleotides of DNA?
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine
81
New cards
What is Chargaff's rule?
The percentages of A and T, and G and C are roughly equal.
82
New cards
What is the name of the process that Rosalind Franklin used to make a picture of DNA?
X-Ray Crystallography
83
New cards
What are the 3 models of DNA Replication?
Conservative, Semi- Conservative, and Dispersive
84
New cards
What happens at the origin of replication?
The 2 DNA Strands are separated, making a replication bubble.
85
New cards
What kind of structure does DNA make?
A double helix
86
New cards
In base pairing, what 2 structures have to be paired together?
1 purine and 1 pyrimidine
87
New cards
DNA replication follows what model?
Semi-Conservative
88
New cards
Where does the replication of chromosomes start?
Origins of replication
89
New cards
What are helicases?
Enzymes that untwist the double helix
90
New cards
What are the 3 steps of glycolysis?
Energy Investment, Energy Payoff, and net output phase
91
New cards
How many net ATP does glycolysis make?
2
92
New cards
Why is pyruvate important?
It assists in making Acetyl coA
93
New cards
Is Glycolysis anaerobic or anaerobic?
Both
94
New cards
What is the ratio when 1 pyruvate is broken down.
1:1:1
95
New cards
What is 1 pyruvate broken down into?
1 CO2
1 NADH
1 Acetyl CoA
1 NADH
1 Acetyl CoA
96
New cards
In Glycolysis, in what step does substrate-level phosphorylation occur?
The energy payoff phase
97
New cards
What is the ratio when 1 Acetyl CoA is broken down?
2:3:1:1
98
New cards
What is 1 Acetyl CoA broken down into?
2 CO2
3 NADH
1 FADH
1 ATP
3 NADH
1 FADH
1 ATP
99
New cards
How many pyruvate does 1 Glucose make?
2
100
New cards
What are NADH and FADH?
Electron Carriers