Grade 11 Biology Exam
1/142
Earn XP
Description and Tags
terror and destruction
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
Binomial Nomenclature
2 part system for naming species
1st word - Genus Name, first letter capital, and italic
2nd word - Species
Panthera tigris
Taxonomic Ranks
Dumb Kids Play Catch On Freeways, Get Squished
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Kingdoms
THIS WAS A TEST QUESTION
bacteria, archaea, protista, plantae, animalia, fungi
bacteria - 6 points
Staphylococcus, prokaryote, unicellular, cell wall - peptidoglycan, autotroph and heterotroph, asexual
Archaea - 5 points
prokaryote, unicellular, occasionally no cell wall (not pep), autotrophs and heterotrophs, asexual
Protista - 5 points
eukaryote, unicellular and multicellular, cellulose cell wall or no cell wall, autotroph and heterotroph, sexual and asexual
Plantae - 5 points
eukaryote, multicellular, cellulose, autotroph, sexual
Animalia - 5 points
eukaryote, multicellular, no cell wall, heterotrophs, sexual
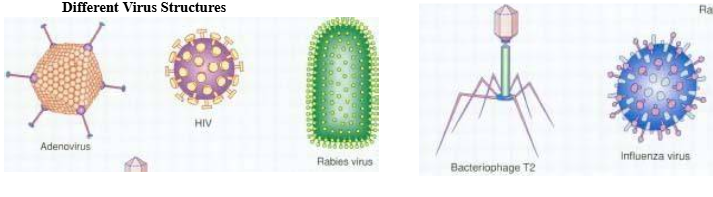
5 Different Virus Structures
adeno virus, HIV, rabies virus, bacteriophage T2, influenza virus
Lytic cycle
Attachment - proteins on surface of virus capsid bind to protein receptors on surface of host cell membrane
Entry - virus injects genetic material into host cell
Replication - host cell makes more viral dna or r na and proteins
Assembly - new viral particles are assembled
Lysis and release - host cell breaks open and releases new viral particles
Lysogenic Cycle
Attachment - proteins on surface of virus capsid bind to protein receptors on surface of host cell membrane
Entry - virus injects genetic material into host cell
Provirus formation - viral dna becomes part of host cells chromosome
Cell division - provirus replicates with hosts chromosomes
Provirus leaves hosts chromosomes
Replication - host cell makes more viral dna or r na and proteins
Assembly - new viral particles are assembled
Lysis and release - host cell breaks open and releases new viral particles
dichotomous key
extremophiles
archaea - live - extreme conditions
Thermophile - 5 points
heat lover - most heat tolerant - deep sea vents, hot springs - 120 deg celsius
Acidophile - 6 points
acid lover - pH of 0 - acidity of car battery acid - volcanic crater lakes, mine drainage lakes
Halophile
salt-lover - salt concentration of water exceeds 20% - live in concentrations as high as 37% - salt lakes, inland seas
8 characteristics used to classify animals
presence of a backbone
levels of organisms
number of body layers
symmetry of body plans
body cavities
segmentation
movement
reproduction
presence of a backbone
Invertebrates - no back bone
vertebrates - backbone
levels of organisms
classified by differences in structure, tissue, organ systems
number of body layers
ectoderm - outerlayer
mesoderm - middle layer
endoderm - inner layer
symmetry of body parts
radial symmetry, bilateral symmetry
radial symmetry and examples
body can be divided along any plane through central axis and roughly be identical halves
jellyfish, coral
bilateral symmetry and examples
can be divided along one plane through central axis and have identical halves
insects, vertebrates
body cavities
Coelom - fluid filled body cavity, provides space for development and suspension of organs and systems - coelomites, acoelomates
segmentation
division — multicellular bodies — series — repetitive segments
movement
active or sessile
reproduction
sexual, asexual
internal, external fertilization
non disjunction conditions and 2 types
errors in chromosome number
monosomy
trisomy
monosomy and example
one extra chromosome lost — non disjunction
turner syndrome - one lost x chromosome
trisomy 3 types
extra chromosome
Trisomy 21 - Down Syndrome
Trisomy 18 - Edwards syndrome
Trisomy 13 - Patau Syndrome
Diploid vs haploid
Diploid # - total count of chromosomes in somatic cells - 2n - 2 complete sets - one from each parent - 23 x 2 - 46 chromosomes
Haploid # - number of chromosomes in a single set in gamete cells - 23
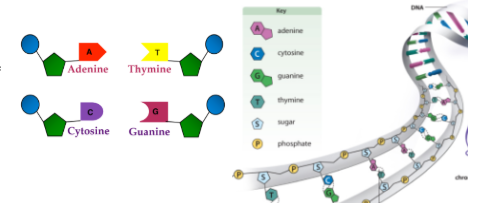
DNA sequence
2 Invasive prenatal tests
amniocentesis
chronic villus sampling (CVS)
amniocentesis
Sample of amniotic fluid containing fetal cells is taken after the 14th week of pregnancy
chronic villus sampling (CVS)
Sample of cells from chorion (part of placenta) is taken after 9th week of pregnancy
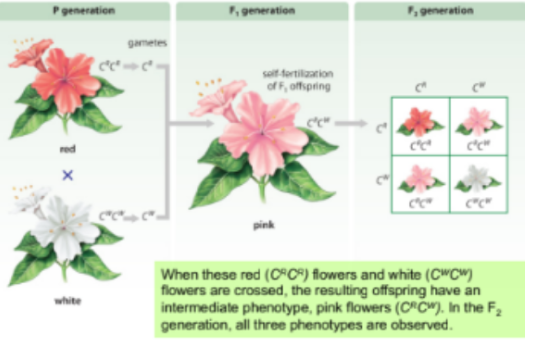
incomplete dominance
Neither of two alleles for the same gene can completely conceal the eachothers presence
Codominance
Both alleles for a trait are equally expressed in a heterozygote
Autosomal Dominant pedigree
Affected child must have at least one affected parent to be affected
Unaffected child born of two affected parents
Autosomal Recessive pedigree
Two unaffected parents can have an affected child
Can skip generations
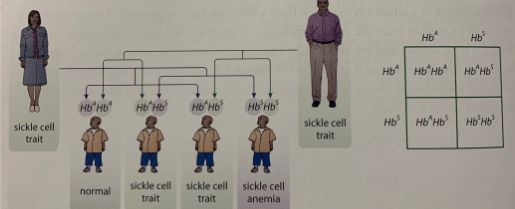
Sickle cell anemia
Sickle cell anemia
Hb^A - Normal red blood cell
Hb^S - Sickle cell
Type a blood type
IA IA homozygotes or IAi heterozygotes
Type b blood type
IB IB homozygotes or IBi heterozygotes
Type AB blood type
IAIB heterozygotes
Type O blood type
ii homozygotes, no antigen
Incomplete dominance punnet square examples
CRCR - R is color red, CWCW - w - white, CRCW - incomplete dominance
Mitosis
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telphase
prophase - 3 points
DNA coils up and becomes visible as chromosomes
nuclear membrane breaks down
spindle fibres form.
metaphase
Spindle fibres guide chromosomes to cell equator
anaphase
The centromere splits, and sister chromatids are pulled apart.
telophase
Chromosomes uncoil and become less visible. A new nuclear membrane forms around each set.
meiosis I + before and after interphase and after meiosis I chart
prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I
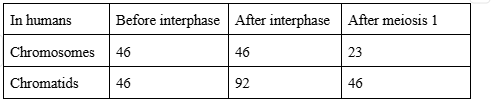
prophase I
each pair of homologous chromosomes lines up side by side (synapsis), while they are lined up segments of the chromosomes may be exchanged (crossing over)
metaphase I
homologous chromosomes line up side by side in the middle of the cell
anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends. The cell goes from diploid to haploid.
fossils - 2 points
Remains or traces of organisms found in sedimentary rock
Reveals kinds of organisms that lived in the past
3 pieces of evidence of fossil record
Fossils found in young layers of rock are from recent geological periods vice versa
Fossils appear in chronological order
Not all organisms appear in the fossil record at the same time
types of fossils
Transitional fossils, vestigial fossils
transitional fossils - 2 points
fossils that show intermediary links between groups of organisms
shares characteristics to two now separate groups
vestigial fossils
reduced version of a structure that was functional in the organisms ancestors
sympatric speciation + example
When populations within the same geographical areas diverge, become reproductively isolated
Polyploid plant
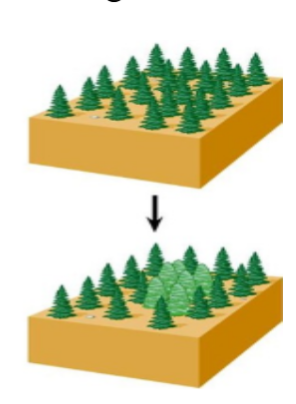
Gradualism + example
Geological changes are not catastrophic but are instead slow and gradual
Floods in the past had no greater power than floods now
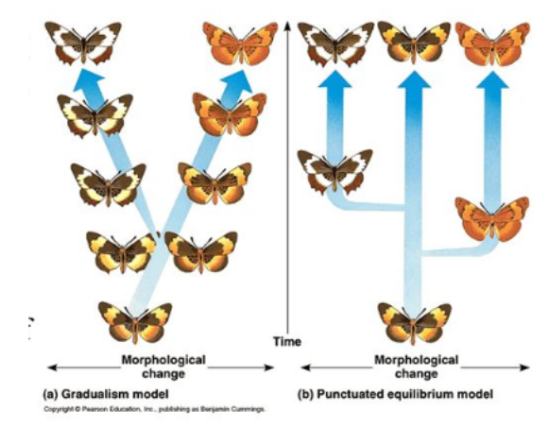
adaptive radiation
One original species splits into many different species, each adapted to different environments or ways of life.
mutation
introduces new alleles into a population, change that
randomly occurs in the dna of an individual
selective advantage
Genetic advantage that improves an organisms chance of survival usually in a changing environment
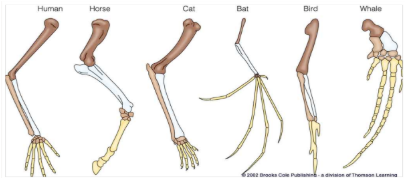
homologous structure
similar structural elements, different function
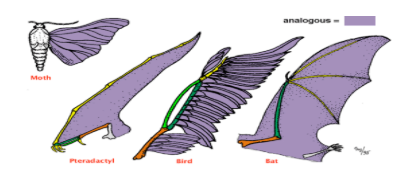
analogous structures
Structures of organisms that don't have a common evolutionary origin but perform similar functions
what are post zygotic isolating mechanisms for
Prevents hybrids from developing viable fertile individuals
hybrid inviability
Genetic incompatibility of interbred species may stop development of hybrid zygote during early stages
hybrid sterility + example
Hybrid offspring is sterile, representing reproductive barrier (mule)
hybrid breakdown
First gen hybrids of crossed species are viable and fertile offspring. Mating hybrids produce weak sterile offspring
peppered moth and natural selection
Peppered moths rest in trees, they are bird prey
Flecked moths in Manchester were camouflaged on white trees but the black moths were easily seen and eaten by birds so white flecked moths were more typical
50 years later the industrial revolution took place and soot covered Manchester's trees. Now the black peppered moths could camouflage better so they grew more popular
5 factors that change allele frequency
mutations, gene flow, non random mating, genetic drift, natural selection
Mutations
introduces new alleles into a population, change that randomly occurs in the dna of an individual
gene flow
flow of alleles into and out of a population, exchange of genes with another population, due mainly to migrations
non random mating
Preferred Phenotype, Inbreeding
preferred phenotypes
Selecting a mate based on physical and behavioral traits, prevents individuals with particular phenotypes from breeding
inbreeding
When closely related individuals breed together,
share similar genotypes — frequency — homozygous genotype increases
genetic drift
change in frequencies of alleles due to chance events in breeding populations
founder effect
by chance, a small number of dispersed individuals establish a new population. It carries on few alleles of the original population, diversity of population is limited. Increased inherited health conditions
inbreeding
When closely related individuals breed together, and share similar genotypes so the frequency of the homozygous genotype increases
bottleneck effect
By chance alone a severe environmental stress nearly wipes out an entire population. Some alleles may be lost forever because only a small number of individuals reproduce in the next generation. Low genetic diversity.
natural selection
nature selects, the ones that survive are the ones that can adapt to the environment and reproduce
3 types of natural selection
stabilizing selection, directional selection, disruptive selection
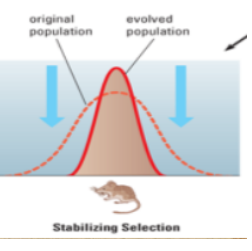
stabilizing selection
intermediate phenotypes of a trait, operates against extreme forms
directional selection
directional shift in the environment results in a shift in one extreme aspect of a trait. Phenotypes at one extreme.

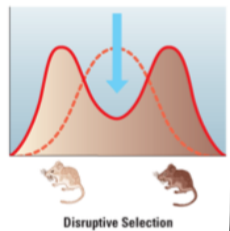
disruptive selection
favors extreme phenotypes of a trait, not the intermediate
two types of speciation
sympatric speciation, allopatric speciation
sympatric speciation
When populations within the same geographical areas diverge and become reproductively isolated, polyploid plant
allopatric speciation
When a population is split into two or more isolated groups by a geographical barrier
5 sources of evidence for evolution
fossils, biogeography, anatomy, embryology, dna
biogeography
Study of where species live now and where they lived in the past.
anatomy
evidence — studying body structure, function
homologous and analogous structures
embryology
Study of early development before birth; similar embryos in different species show they come from a common ancestor.
DNA
similar patterns in dna sequences indicates that two species must have shared a common ancestor
how macromolecules in food are broken down
hydrolysis, enzymes
hydrolysis
chemical reaction - water breaks apart macromolecules - smaller molecules
enzymes
Protein molecule - speeds up important chemical reactions in body without being used up
inhalation
Warm, moist, clean air → from nasal passages → to pharynx → behind the tongue at base of pharynx is trachea → air enters trachea through glottis → passes through larynx → air passes through vocal cords (vibrate → sound) → moves down trachea → splits into bronchi → each bronchus enters a lung → bronchus divides into bronchioles → end in grape-like clusters called alveoli → surrounded by capillaries → gas exchange occurs
hemoglobin
helps transfer oxygen
av node - 3 points
When atria contract, signal is sent to the AV node
Transmits electrical signal that is transmitted through specialized fibres - bundle of His
Initiates simultaneous contraction of right and left ventricles