ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FINALS
5.0(3)Studied by 64 people
Card Sorting
1/371
Earn XP
Last updated 4:51 AM on 3/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
372 Terms
1
New cards
Hydrocarbons
Organic compounds that are made out of carbon and hydrogen only
2
New cards
Flammability
The property of hydrocarbons that allows them to be used mainly for fuel
3
New cards
Non-polar
The polarity of hydrocarbons
4
New cards
106
The number of the estimated potential combination for carbon chain/ring
5
New cards
Saturated hydrocarbons
Classification of hydrocarbons in which the carbons are bonded with single bonds
6
New cards
Alkanes
These are organic compounds that are bonded with single bonds
7
New cards
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
Classification of hydrocarbons in which the carbons are bonded with double or triple bonds
8
New cards
Alkenes
These are organic compounds that are bonded with double bonds
9
New cards
Alkynes
These are organic compounds that are bonded with triple bonds
10
New cards
Sigma bond
A strong type of bond
11
New cards
Pi bond
a weak type of bond
12
New cards
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
Which is more reactive, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbons?
13
New cards
Open-chain hydrocarbons
A classification of hydrocarbons in which the compounds are arranged in acyclic, linear, straight, or branched structures
14
New cards
closed-chain hydrocarbons
A classification of hydrocarbons in which the compounds are arranged in cyclic, ring, alipathic, or aromatic structures
15
New cards
Paraffins
Other name for alkanes
16
New cards
sp3
hybridization of alkanes
17
New cards
Olefins
Other name for alkenes
18
New cards
sp2
hybridization for alkenes
19
New cards
sp
hybridization for alkynes
20
New cards
Alkanes
Contains 1 sigma bond
21
New cards
Alkenes
Contains 1 sigma bond and 1 pi bond
22
New cards
Alkynes
Contains 1 sigma bond and 2 pi bonds
23
New cards
CnH2n+2
General formula for alkanes
24
New cards
CnH2n
general formula for alkenes
25
New cards
CnH2n-2
General formula for alkynes
26
New cards
IUPAC Nomenclature
The system used in naming chemical compounds
27
New cards
meth
suffix for 1
28
New cards
eth
suffix for 2
29
New cards
prop
suffix for 3
30
New cards
but
suffix for 4
31
New cards
pent
suffix for 5
32
New cards
hex
suffix for 6
33
New cards
hept
suffix for 7
34
New cards
oct
suffix for 8
35
New cards
non
suffix for 9
36
New cards
dec
suffix for 10
37
New cards
Aromatic hydrocarbons
These are cyclic hydrocarbons with delocalized pi electrons between carbon atoms of ring or alternating double bonds
38
New cards
Aromacity
The term that describes the natural characteristics of aromatic hydrocarbons
39
New cards
* Must be cyclic in structure
* must be flat or planar in configuration
* must have conjugated double bonds
* must follow huckel’s rule of aromacity
* must be flat or planar in configuration
* must have conjugated double bonds
* must follow huckel’s rule of aromacity
Criteria for aromacity
40
New cards
Huckel’s Molecular Orbital Theory
“A compound is particularly stable if all its bonding molecular orbitals are filled with paired electrons”
41
New cards
Benzene
The most common example of an aromatic compound
42
New cards
Benzene
\
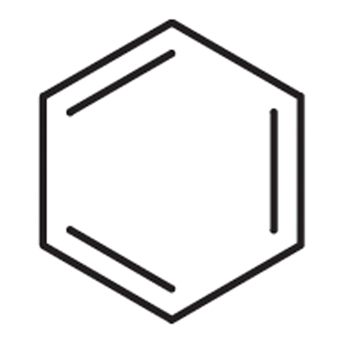
43
New cards
Acetanilide
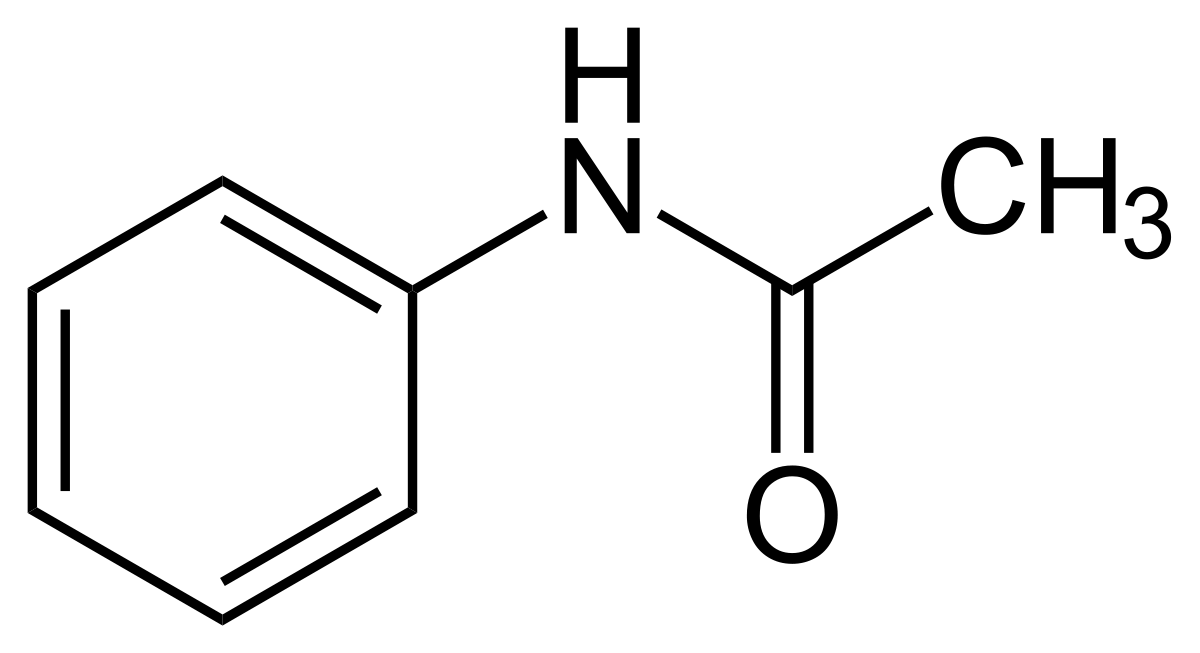
44
New cards
Cyclohexane
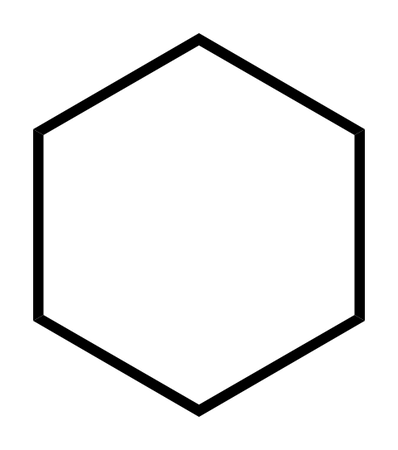
45
New cards
n-hexane
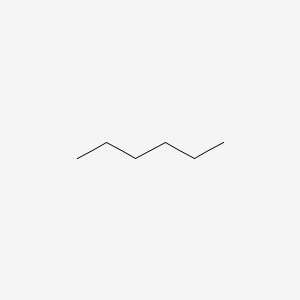
46
New cards
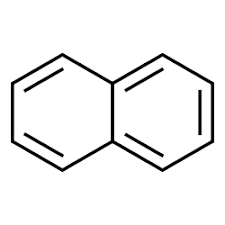
Naphthalene
47
New cards
Hydrocarbons - structures and chemical properties
Title of experiment 12
48
New cards
Experiment 12
What experiment uses benzene, n-hexane, cyclohexane, acetanilide, gasoline and naphthalene as samples?
49
New cards
gasoline
the only sample in experiment 12 that produced non-luminous flame and had no soot
50
New cards
Luminous flame
burns bright yellow flame due to not enough oxygen
51
New cards
Non-luminous flame
burns an almost invisible blue flame due to enough oxygen
52
New cards
1 drop
How many drops of samples did the experiment 12 - ignition test require?
53
New cards
Combustion reaction
A reaction in which hydrocarbons react with oxygen to produce CO2, H2O, and heat
54
New cards
Incomplete combustion
Yellow flame, has soot, not much energy and heat produced
55
New cards
Complete combustion
Blue flame, no soot, burns efficiently and produces hotter flame
56
New cards
Benzene, n-hexane, cyclohexane
The samples that produced soot and luminous flame in the experiment 12 - ignition test
57
New cards
Baeyer’s test for unsaturation
A test used to determine the presence of double and triple bonds
58
New cards
Adolf von Baeyer
The scientist named after the test to determine the presence of double and triple bonds
59
New cards
Sodium hydroxide
A compound used to make the potassium permanganate alkaline in Baayer’s test
60
New cards
10 drops
How many drops of samples did the Baeyer’s test for unsaturation require?
61
New cards
15 drops
How many drops of the alkaline potassium permanganate did the Baeyer’s test for unsaturation require?
62
New cards
Benzene, cyclohexane, n-hexane
The samples that. produced a purple-colored solution in the exp 12, baeyer’s test
63
New cards
Gasoline
the sample that produced a dark brown precipitate in the exp 12, baeyer’s test
64
New cards
Brown
The color of precipitate that indicates a positive result in Baeyer’s test for unsaturation
65
New cards
Oxidation reaction
A reaction that produces an alkane with 4 hydroxyl groups, a manganese dioxide, and a permanganate ion
66
New cards
resist addition
aromatic compounds ___ to the pi bonds in which the ring system would be destroyed
67
New cards
preserved
aromatic compounds readily undergo substitution in which the ring system is ___.
68
New cards
0\.67 grams
how many grams of acetanilide and naphthalene did the exp 12 - electrophilic aromatic substitution require?
69
New cards
Glacial acetic acid
The reagent (2.5ml) that the acetanilide and naphthalene were dissolved into in the electrophilic aromatic substitution
70
New cards
15 drops
how many drops of bromine in acetic acid solution did the electrophilic aromatic substitution require?
71
New cards
Distilled water
What reagent was added to the solution solution in the electrophilic aromatic substitution until it turned cloudy?
72
New cards
Alcohols
What is the title of experiment 13?
73
New cards
Alcohols
organic compounds composed of an alipathic carbon atom with a hydroxyl functional group
74
New cards
Hydroxyl group
the functional group of all alcohols
75
New cards
ROH
the general formula for the hydroxyl group
76
New cards
Length
Some properties of alcohols depend on the __ of alkyl chain attached to the hydroxyl group
77
New cards
Primary alcohol
Classification of alcohol wherein a carbon with the OH group is attached to one other carbon atom
78
New cards
Secondary alcohol
Classification of alcohol wherein a carbon with the OH group is attached to two other carbon atoms
79
New cards
Tertiary alcohol
Classification of alcohol wherein a carbon with the OH group is attached to three other carbon atoms
80
New cards
RCH2OH
General formula for primary alcohols
81
New cards
R2CHOH
General formula for secondary alcohols
82
New cards
R3COH
General formula for tertiary alcohols
83
New cards
higher
Alcohols have ___ boiling points compared to hydrocarbons
84
New cards
hydrogen bonding
The intermolecular force found between the OH that is responsible for the high boiling points and solubility of alcohols
85
New cards
Increases
the boiling point of alcohols ___ as the number of carbon in alipathic chain increases
86
New cards
decreases
the boiling point of alcohols ____ as the branching in alipathic carbon chain increases
87
New cards
longer
The ___ the alkyl chain is, the lesser the alcohol becomes soluble in water
88
New cards
Polar
Polarity of alcohols
89
New cards
acidic
alcohols are ___ in nature because of their ability to react with active metals, forming corresponding alkoxide
90
New cards
Primary alcohols
Of all the classifications of alcohols, which are more acidic?
91
New cards
decreases
the acidity of alcohols ___ when an electron donating group is attached to the hydroxyl group as the electron density increases on the oxygen atom
92
New cards
Jones test
The other name for the chromic acid test
93
New cards
n-butyl, sec-butyl, tert-butyl
The samples used in the chromic acid test
94
New cards
20 drops
How many drops of samples did the chromic acid test require?
95
New cards
potassium dichromate
Along with the sulfuric acid, what reagent did the chromic acid test used?
96
New cards
Chromic acid test
A test used to distinguish primary and secondary alcohols from tertiary alcohols
97
New cards
Blue-green
the color of the solution that depicts a positive result in the jones test
98
New cards
Jones reagent
A reagent that is made out of chromium oxide in sulfuric acid
99
New cards
Lucas reagent
A reagent that is made our of zinc chloride in concentrated hydrochloric acid
100
New cards
Ewart Jones
The scientist that the chromic acid test was named after