Biology: Cell Cycle
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Interphase
Growth and Preparation
What does interphase contain?
G0, G1, S, G2
G0
Resting/non-dividing phase
G1
Cell grows
S
DNA and centrosome replication
G2
Error check; prepares for mitosis, replication of organelles
Involves MPF (Mitosis Promoting Factor Protein)
DNA Replication: Prokaryotes
Binary fission for S
DNA Replication: Eukaryotes
S phase
M Phase: Cell Division
Includes Karyokinesis (nuclear division) and Cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division)
Microtubules
Made of tubulin; help move chromosomes
Centrosomes
Organize spindle; contain 2 centrioles (9 X 3 arrangement)
Polar Spindle
Connect centrosomes to opposite poles
Astral Spindle
Anchor centrosomes to cell membrane
Kinetochore Spindle
Attach to chromosomes and pull them apart
Cilia/Flagella
9 + 2 microtubule arrangement (for cell movement)
Cell Regulation
Surface-to-volume ratio: Low ratio = poor cellular exchange = cell death
Genome-to-volume ratio: Small nucleus can't support large cell = cell death
G1 Checkpoint
Checks cell size and DNA
G2 Checkpoint
Checks DNA replication accuracy
M Checkpoint
Ensures spindle fibers/microtubules are properly attached to chromosomes
Cyclin + CDK
Promote cell cycle progression
Anchorage dependence
Cells must be attached to divide (promote division)
Density dependence
Cells stop dividing when space is limited
Chromatin
Loose form of DNA
Chromosome
Condensed DNA made from chromatin
Genome
All genetic material (DNA) in a cell
Sister Chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome
Dyad
A pair of sister chromatids joined by X
Centromere
Region where sister chromatids are joined
Kinetochore
Protein site on centromere where spindle binds
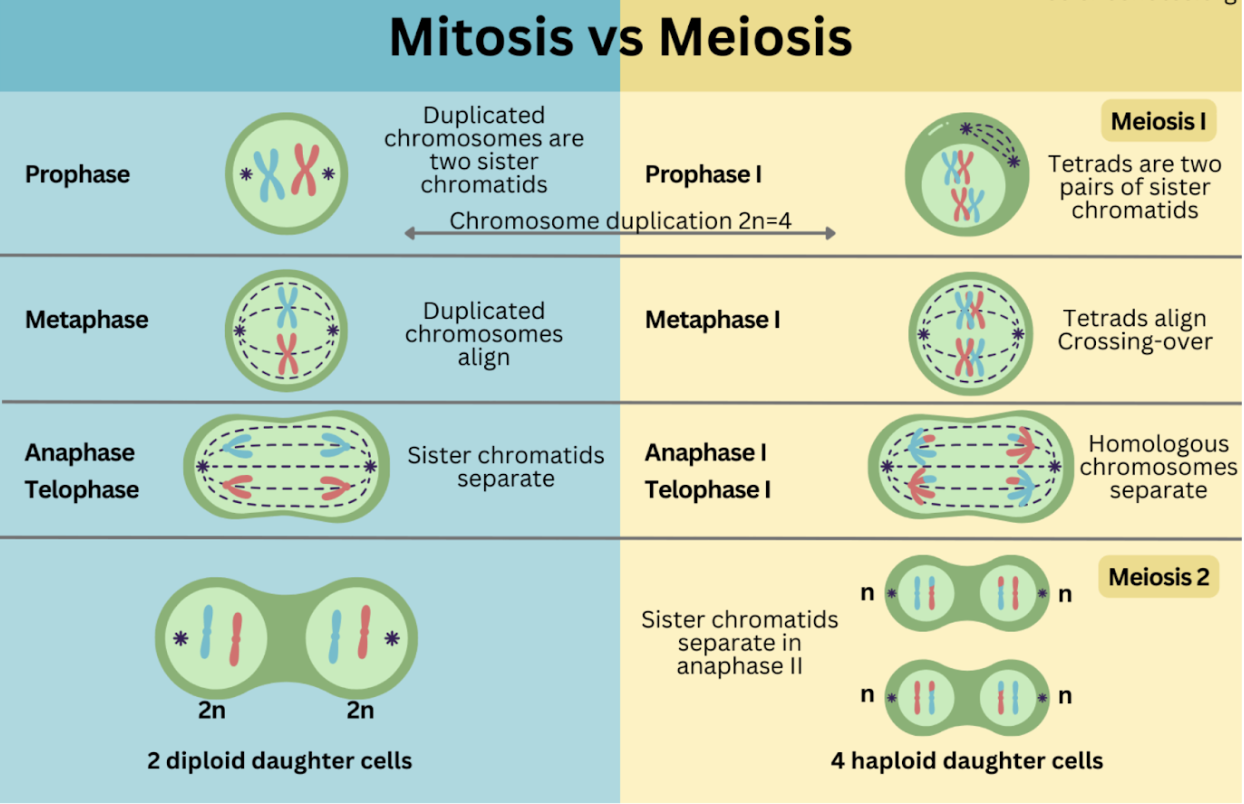
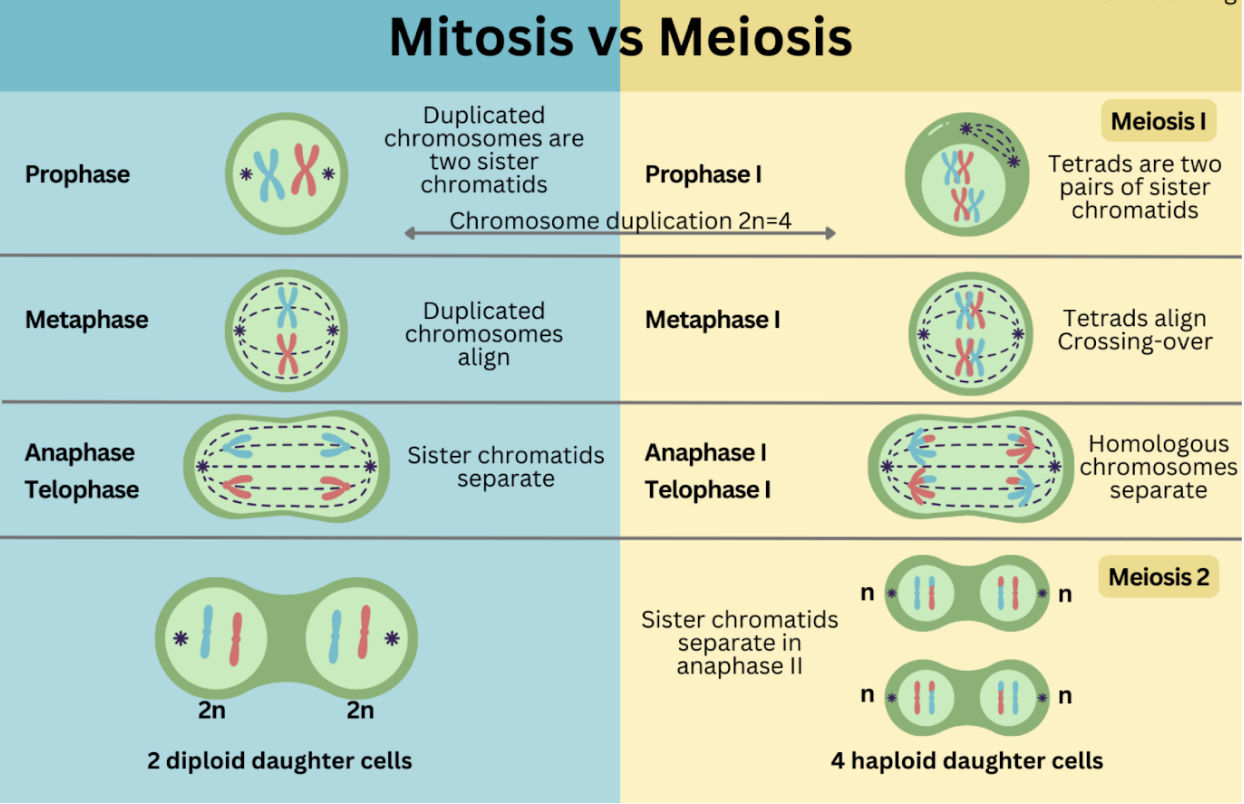
Mitosis
Prophase, Prometaphase, Metaphase, Anaphase (Cleavage furrow), Telophase (Cytokinesis)
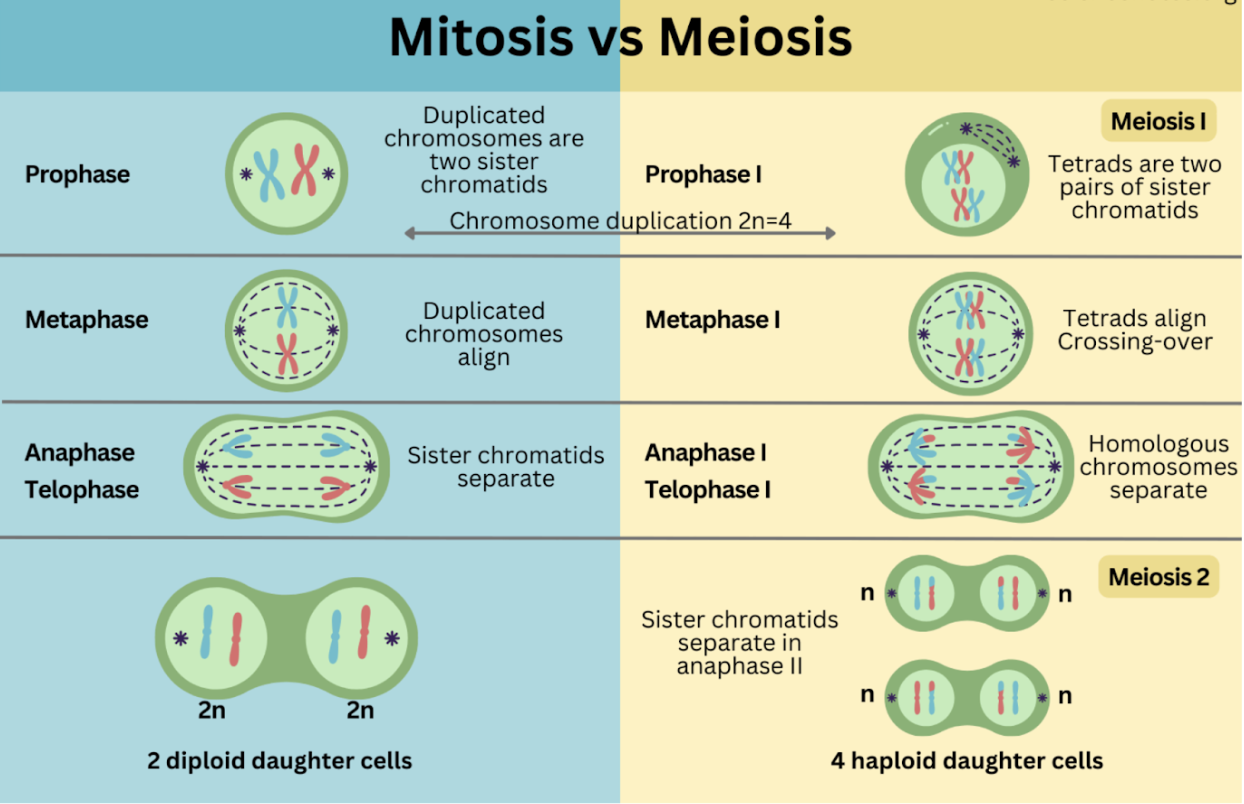
Prophase
Chromatin condenses, spindle forms, nuclear envelope breaks down
Prometaphase
Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores
Metaphase
Chromosomes align at the metaphase plate
Anaphase and Cleavage furrow
Sister chromatids pulled apart to opposite sides
Forms using actin and myosin (animal cells)
Telophase and Cytokinesis
Nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes return to chromatin (no spindle)
Animals: Via cleavage furrow
Plants: Via cell plate and middle lamella
Meiosis
Ploidy Transitions: Diploid (2n) → Haploid (n) → Haploid (n)
Somatic cells
Body cells (undergo mitosis only)
Gametocytes
Germ cells (can undergo meiosis or mitosis)
Gametes
Sex cells (sperm and egg) = 2 autosomal
Meiosis I (Reductional Division)
Prophase I: Synapsis (pair chromosomes) forms tetrads/bivalents via synaptonemal complex; crossing over at chiasmata
Metaphase I: Homologous pairs line up; independent assortment adds genetic diversity
Anaphase I: Homologous chromosomes are pulled apart
Telophase I: Results in two haploid cells
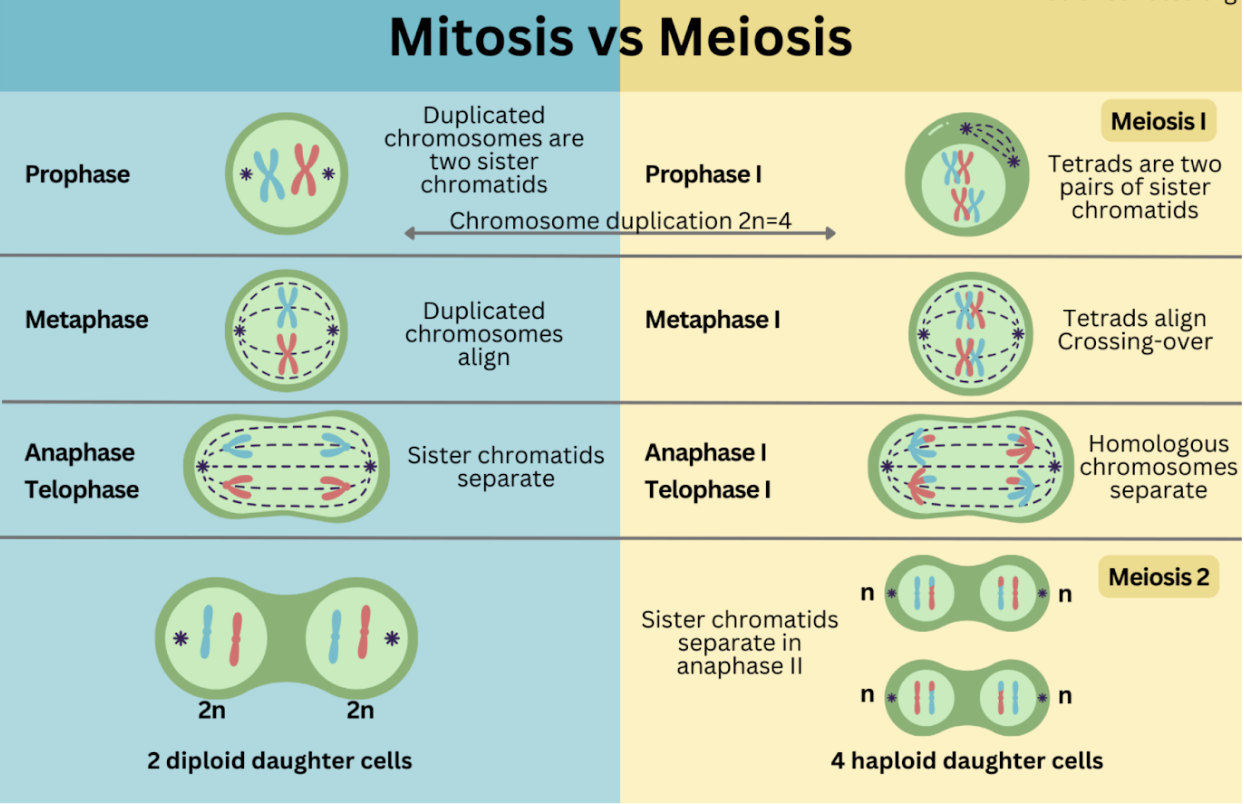
Meiosis II (Similar to Mitosis)
Anaphase II: Sister chromatids separate
Telophase II: Produces four genetically unique haploid gametes