Adv Plant Breeding - Exam 1
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
what are we doing???????!???
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Replications
how many times each genotype is planted in the field
Genotypes
amount of genotypes present in the field
Error
variation that is not attributable to any other listed sources of variation
Degrees of freedom
number of independent values that can vary in an analysis w/o breaking any constraints
used to calculate mean square estimate
sum of squares
dispersion of data points, how much dispersion, not the direction
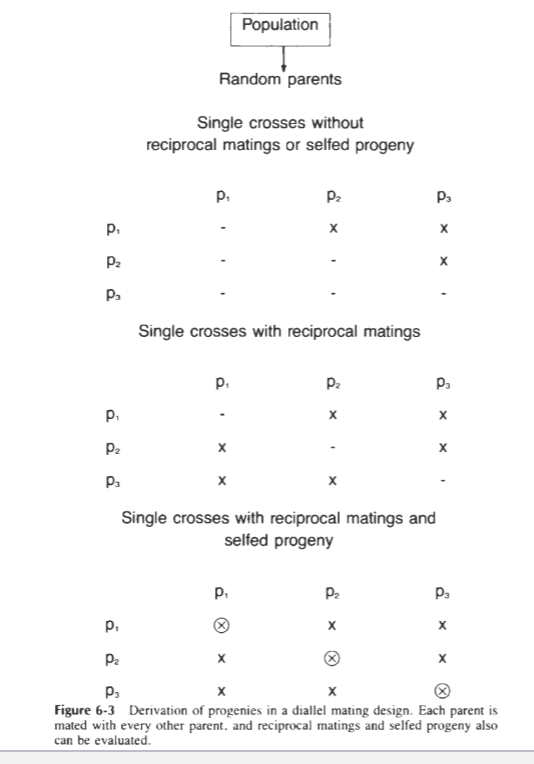
Diallel design
randomly select individuals in a population
cross selected individuals in all combinations
all parental crosses
reciprocal crosses
self parents
cross all possible combinations
estimate of general and specific combining ability
Half sibs = general combining ability
Full sibs = specific combining ability
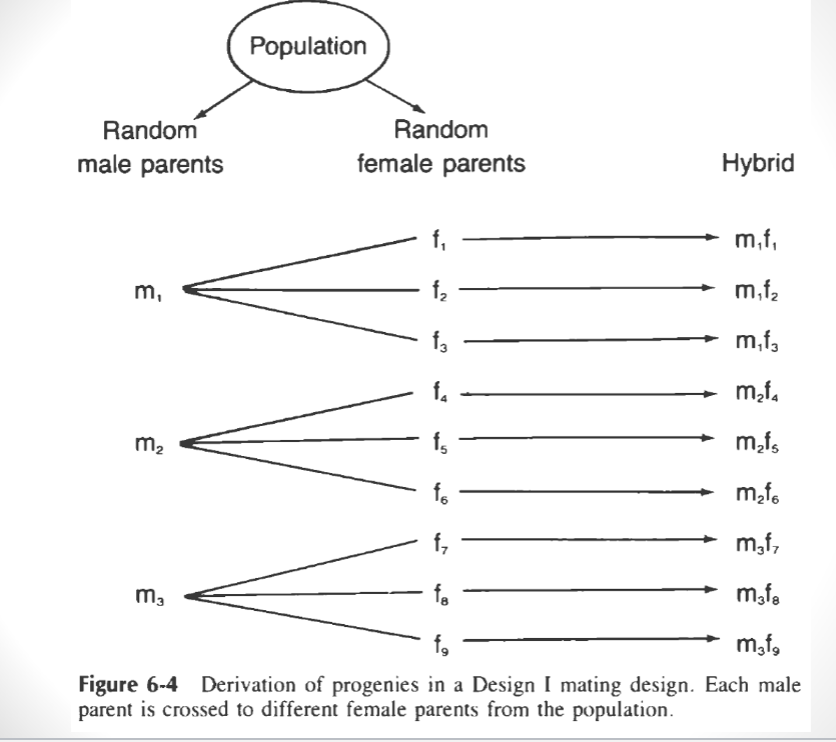
Design 1/Nested system
randomly select individuals in a population
designate male and female plants
each male is crossed to an equal number of females
a different group of females is used for each male
variation among single crosses is divided into variation among males and variation among females nested in males (???)
each cross creates a specific hybrid
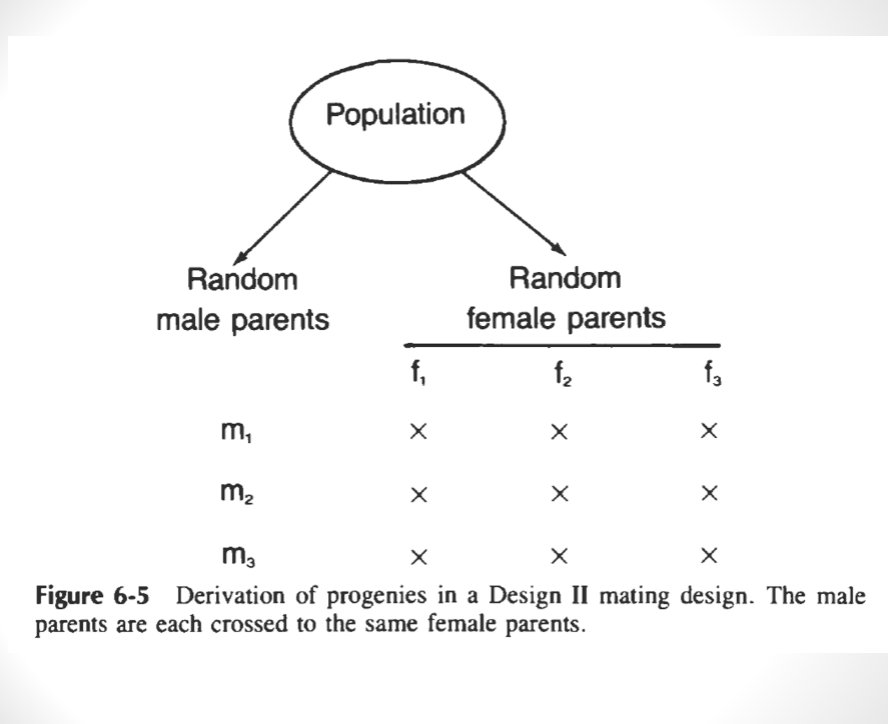
Design 2/Factorial Design
randomly select individuals in a population
designate male and female parents
male parents are not crossed to each other and female parents are not crossed to each other
variation among crosses is divided into variation among males, variation among females, and the interaction of male and female parents
covariance
average variance between two variables
variance components
all of your sources of variance inputted into the left side of the anova table
sort of like independent variables, kinda
ex- replication, genotypes, year, etc.
hardy Weinberg equilibrium
when gene and genotypic frequencies do not change from one generation to the next
Reciprocal
making a cross between f and m plant, then making the inverse
so if plant 1 f x plant 2 m, then you cross plant 2 f and plant 1 m to see both
Additive gene effects
Each gene added enhances the expression of the trait
Dominance Gene Effects
Heterozygote is more like one parent than the other
Epistatic Gene Effects
Genes have no affect individually but do when combined
Overdominance Gene Effects
Each allele has an effect when separate and a greater effect when combined
Broad Sense heritability
Total genetic variance/phenotypic variance
more meaningful when all types of genetic variance can be exploited, as in selection among clones of an asexually propagated species or selection among single crosses between inbreds
Inbred/hybrid cultivars
Narrow sense heritability
Additive variance/phenotypic variance
determines the amount of progress that can be made from selecting and recombining the best individuals in a population
pure line cultivars
Coupling Linkage
dominant alleles at 2 loci are on one chromosome and the recessive alleles are on another
offspring more like parents
repulsion linkage
dominant allele at one locus is on the same chromosome as a recessive allele at another locus
heterozygous
HW assumptions
random mating
no artificial selection
change by mutation should affect both alleles equally
no loss or addition of alleles from outside sources
population size is large enough that alleles are not excluded from genetic by genetic drift.
when is it more efficient to make your selection and why?
before pollination because in an open populated area you can choose both male and female plants but after pollination you can only choose the female
general combining ability
average contribution of an inbred line to the performance of its hybrid
avg contribution/performance of an inbred in a series of hybrid combinations
specific combining ability
cross with a specific inbred line to others, not comparing one inbred line to others with another inbred line
the performance of a combination of a specific inbred in a particular cross
Steps to estimating phenotypic and genetic variances
one or more types of progeny are developed
progeny are evaluated in a set of environments
variance components are estimated from the mean squares in the anova
variance components are interpreted in terms of the covariance between relatives
Genetic Gain
the improvement in the mean performance of a population that is realized with each cycle of selection
1 cycle of selection
avg 4-5yrs
develop a segregating population with genotypes for evaluation
evaluate genotypes
select superior genotypes
use superior genotypes as parents
Pedigree method
select single plants to create plant families
select individual plants within plant families
Heritability
the proportion of the total phenotypic variation expressed among genotypes that can be attributed to genetic differences among them
h²
heritability
D
selection differential
σph
phenotypic variance
Parental control (C)
the relationship between the plant or seed used for identifying superior genotype and the plant or seed used for recombination
the selection unit is the same as the recombination unit and only the female parent is selected
C = ½
when the selection unit is the same as the recombination unit and both parents are selected
C = 1
when the selection unit and the recombination unit are not the same
C = 2
Steps to predicting genetic gain
list alternatives for the species being considered
basically, the type of cultivar you are releasing, hybrids, inbreds, clonally propagated, etc.
define the resources available
obtain estimates for the variables in the prediction equation from doing field trials and an analysis of variance table (anova)
compute predicted genetic gain for variance alternatives
summarize computed values
speed breeding
adjusting the lighting of the growing season by reducing the light so you have a shorter season
1 season per yr
yield evaluation and all breeding operations can be conducted in one year
referred to as one season
two similar seasons
two seasons per yr can be used for yield evaluation and breeding operations
usually occurs in tropical areas
two nonsimilar seasons
two seasons per yr, one of which can be used for yield evaluation and all other breeding operations and the second of which can be used for all breeding operations, except yield evaluation
usually occurs when one season can be grown in a temperate climate, and a second season is grown in a greenhouse or tropics winter nursery
three seasons
three seasons per yr in which the first can be used for yield and all other breeding operations and the second and third can be used for all other breeding operations except yield
occurs when greenhouse/winter nurseries are used
o²
plot to plot variance
o²w
variance among plants within a plot
o²u
environmental variance
gxe expected mean sq formula
o²e + Ro²ge
(error variance + R(gxe))
g expected mean sq formula
o²e+Ro²ge+REo²g
(error variance + R(gxe variance) +R(E)(g variance)