Mark K Lectures
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
If the pH is low, what happens to everything else?
Everything else would also be low, except for potassium
If the pH is high, what happens to everything else?
Everything else would also be high, except for potassium
List some SE for a pt that has a pH of 7.50
tachycardia, tachypnea, HTN, seizures, irritability, spasticity, diarrhea, borborygmi, hyperreflexia (3+/4+), HYPOkalemia
List some SE for a pt who has a pH of 7.30
bradycardia, bradypnea, HOTN, constipation, absent BS, flaccid, obtunded, lethargy, coma, hyporeflexia (0,1+), HYPERkalemia
What is a nursing intervention for a pt in alkalosis?
Suctioning bc of seizures
What is a nursing intervention for a pt in acidosis?
ventilate pt with ambu bag bc of respiratory arrest
What is the significance of “MAC Kussmaul?”
Kussmaul resp is only seen in Metabolic ACidosis
If a pt is overventilating, are they in acidosis or alkalosis?
alkalosis
If a pt is underventilating, are they in acidosis or alkalosis?
acidosis
If a pt is on a PCA, what would their ABG interpretation be?
respiratory acidosis
If a pt has prolonged gastric vomiting, what would their ABG interpretation be?
metabolic alkalosis
What triggers high pressure alarms on a ventilator?
increased resistance to air flow
What is the appropriate order for addressing a high pressure alarm on a mech vent?
unkink the tubing
empty the water out of the tubing
turn the pt and ask them to cough or deep breathe
suction the tubing PRN
What are low pressure alarms on a vent triggered by?
decreased resistance to air flow caused by main tubing disconnection and O2 sensor disconnection
How do you respond to a low pressure alarm on a vent?
Reconnect all disconnected tubing
If the vent tubes are on the floor, what do you do?
bag the pt and call RT
If the vent setting is too high, is the pt in resp acid or resp alk?
resp alk bc they are overventilating/panting
If the vent setting is too low, is the pt in resp acid or resp alk?
resp acid bc they are underventiling/retaining CO2
The PCP wants to wean a pt off the vent in the morning. The ABG results say resp acid. What do you do next and why?
Notify PCP and let them know that the pt is not ready to be weaned off vent bc pt is underventilating.
The PCP wants to wean a pt off the vent in the morning. The ABG results say resp alk. What do you do next and why?
Notify PCP that the pt is ready to be weaned off bc pt is overventilating the vent
What is the #1 psychological problem?
Denial
How should a nurse respond to denial?
Confront the pt without aggression
A nurse tells the pt “Ok. You say you’re not an alcoholic but it’s 10 AM and you’ve have a 6 pack.” What did the nurse demonstrate?
Confrontation
What are the 5 stages of grief?
Denial
Anger
Bargaining
Depression
Acceptance
What is psychological problem #2?
Dependency or co-dependency
Define dependency.
This is when the abuser gets their SO to do things for them or make decisions for them, meaning the abuser is dependent on their SO
Define co-dependency.
This is when the SO obtains positive self-esteem from doing things for the abuser or making decisions for the abuser; SO is co-dependent since they feel food for “doing stuff” for abuser
How do you treat dependency/co-dependency?
Confront the abuser (dependent pt)
Tech co-dependent pts to set limits and enforce the, and work on self esteem
Teach SO to say no
What is the difference bw co-dependency and manipulation?
In co-dependency, the abuser tells SO to do things for them or make decisions for them, and the SO gets a self-esteem boost while manipulation is when the SO is not interested in doing what the abuser tells them to do bc it can be harmful for them
How do you treat manipulation?
Set limits and enforce them
Determine is the following scenario is a dependent/co-dependent issue or a manipulation issue: A 49-year-old alcoholic gets her 17-year-old son to go to the store and buy alcohol for her
Manipulation
Determine is the following scenario is a dependent/co-dependent issue or a manipulation issue: A 49-year-old alcoholic asks her 50 yo husband to go to the store and buy alcohol for her.
Dependency/co-dependency
What is Wernicke and Korsakoff induced by?
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) deficiency
What are the primary s/sx of Wernicke and Korsakoff syndrome?
Amnesia (memory loss) and confabulation (making up stories)
If a pt with Wernicke and Korsakoff is confabulating about going to a meeting with Barack Obama this morning, what would you do?
Redirect the pt into doing something they can do
What are the characteristics of Wernicke and Korsakoff syndrome?
Preventable… Take B1
Arrestable (stop it from getting worse)… Take B1
Irreversible (70%)… Will kill brain cells
What does disulfiram do?
Helps someone stop drinking alcohol
What does Naltrexone do?
Acts as an antidote for alcoholism
What is Aversion Therapy?
a type of behavior therapy that makes a pt give up an undesirable habit by causing them to associate it with an unpleasant effect
What is the onset and duration of effectiveness for disulfiram and naltrexone?
2 weeks
Why should pts avoid all forms of alcohol while taking disulfiram or naltrexone?
It can cause N/V or death
List some not-so-obvious items that contain alcohol.
mouthwash
cologne/perfume
aftershave
elixir
most OTC liquid meds
insect repellant
hand sanitizer
vanilla extract
Does Red Wine vinaigrettes have alcohol in them?
No
List the “Upper” drugs.
Caffeine
Cocaine
PCP/LSD
Methamphetamines
Adderall
What are the s/sx of upper drugs?
Euphoria, seizures, restlessness, irritability, hyperreflexia, (3+/4+), tachycardia, borborygmi, diarrhea
What are the s/sx of downer drugs?
Lethargy, respiratory depression/arrest, constipated, etc.
What is the highest priority to anticipate for those on an upper drug?
suctioning d/t seizures
What is the highest priority to anticipate for those on a downer drug?
intubation/ventilation d/t resp arrest
If your pt is high on cocaine, is having a RR of 12 important? If not, then what should be assessed instead?
No; assess for reflexes (3+/4+), irritability, borborygmi, or inc temp
What s/sx are expected if a pt has overdosed on cocaine?
Irritability, 4+ reflexes, borborygmi, inc temp, etc.
What s/sx are expected if a pt is withdrawing from cocaine?
RR < 12, difficult to arouse
What drug should be given if a pt was withdrawing from cocaine?
Naloxone
When should you assume a newborn is intoxicated?
If the newborn is less than 24 hours old after birth
When should you assume a newborn is in withdrawal?
If the newborn is 24 hours old or more
If an infant is born to a Quaalude addicted mother 24 hours after birth, what s/sx are expected to be seen in the newborn?
difficulty to console, seizure risk, shrill, high-pitched cry, exaggerated startle reflex
When do pts go through AWS and is it life-threatening??
Approx. 24 hours after pt stops drinking; it’s not life-threating
When do pts go through DT and is it life-threatening?
Approx 72 hours after pt stops drinking; it’s life-threatening
What is included in the nursing care plan for AWS?
Regular diet
Semiprivate room, anywhere on the unit
Pt is up ad lib (free to move around)
No restraints
What is included in the nursing care plan for DT?
NPO (seizures) or clear liquid diet
Private room, near nursing station
Restricted bedrest (pt not free to move around and can’t use bathroom)
Restraints (vest or 2-point lock letters)
What meds can you give for both AWS and DT?
Anti-HTN meds
tranquilizers
Multivitamin with Vitamin B1
In what two situations would resp arrest be a priority?
overdose on a downer
withdrawal of an upper
In what two situations would seizure be a priority?
overdose of an upper
withdrawal of a downer
What do aminoglycosides treat?
Serious, resistant, life-threatening, gram negative infx.
Ex: TB, septic peritonitis, fulminating pyelonephritis, septic shock, infx from 3rd degree wound covering >80% of body
What do aminoglycoside drug names have in common?
End in “-mycin” BUT NOT “-thromycin”
What are the top two toxic effects of aminoglycosides?
Ototoxicity
Nephrotoxicity
Is 24 hour Cr clearance better than serum Cr?
Yes
What admin route are aminoglycosides given through?
IM or IV
When are aminoglycosides given PO?
hepatic encephalopathy (high ammonia levels)
Pre-op bowel surgery (to sterilize bowel b4 surgery)
Which drugs can sterilize bowel?
Neomycin and Kanamycin
What is “TAP” and what is the purpose?
Trough
Administer
Peak
Trough and peak are drawn bc of a drug’s Narrow Therapeutic Index, which means there is a small difference in what works and what kills
What drugs should you draw troughs and peaks for?
Furosemide, Digoxin, and Aminoglycosides
When do you draw a trough?
30 min before next dose of a med
When do you draw the peak?
Depends on the route:
SubL: 5-10 min after drug dissolved
IV: 15-30 min after drug is done (bag empty)
IM: 30-60 min
SubQ: depends on insulin
PO: not necessary, not tested
You give 100 mL of a drug at 200 mL/hr (drug takes 30 min to run). If you hang it at 1030, when will the drug peak?
1100
What is the purpose of CCB?
Relax and slow down the heart by having negative chronotropic, inotropic, and dromotropic properties
When do you want to relax and slow down the heart?
To treat: A, AA, AAA
Antihypertensive
Anti Anginal drugs (dec O2 demand)
Anti Atrial Arrythmia
What are some common SE of CCB?
HA and HoTN
Name some CCB.
“-dipine”
Diltiazem
Verapamil
When should CCB be held and not given?
If SBP < 100
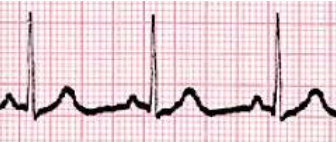
Which cardiac rhythm is shown?
NSR
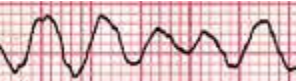
Which cardiac rhythm is shown?
V-Fib
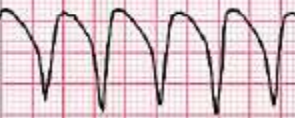
Which cardiac rhythm is shown?
V-tach
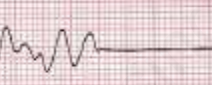
Which cardiac rhythm is shown?
Asystole
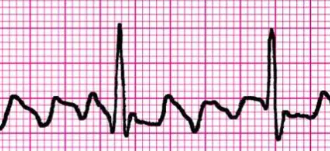
Which cardiac rhythm is shown?
Atrial Flutter
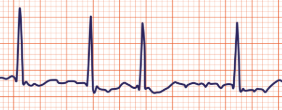
Which cardiac rhythm is shown?
A-fib
What does a P wave represent?
Atrial depolarization
What does a QRS complex represent?
Ventricular depolarization
Are PVCs a low or high priority and why?
Low priority bc it is common to see PVCs after an MI
When do you elevate PVCs to moderate priority?
More than 6 PVCs in a min
More than 6 PVCs in a row
R on T phenomenon (a PVC falls on a T wave)
Which arrythmias are high priority and why?
Asystole and A-fib bc they both produce low or no CO, which means no brain perfusion so confusion and death may occur
Which arrythmia can be potentially lethal?
V-tach bc even tho it has CO
How do you treat PVCs and V-tach?
Lidocaine or Amiodarone
How do you treat supraventricular arrythmias?
Adenosine (SVT)
Beta-Blockers (-olol)
CCBs (-dipine + diltiazem, verapamil)
Digoxin, Lanoxin
Does Beta blockers have positive or negative tropic effects on the heart?
negative
How do you treat V-fib?
Defib/shock them
How do you treat asystole?
Epinephrine and Atropine
What is the purpose of chest tubes?
To reestablish negative pressure in the pleural space
Define pleural space
space bw the lung (visceral pleura) and chest wall (parietal pleura)
In a pneumothorax, what does the chest tube remove?
Air
In a hemothorax, what does the chest tube remove?
Blood