Kaplan MCAT Orgo Review, CH 1 (Nomenclature)
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Will the MCAT ever ask you to name a compound?
No, Kaplan says no.
How might MCAT test orgo then?
give you IUPAC name of reactant
answers will show products
need to know rxn
IUPAC stands for
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
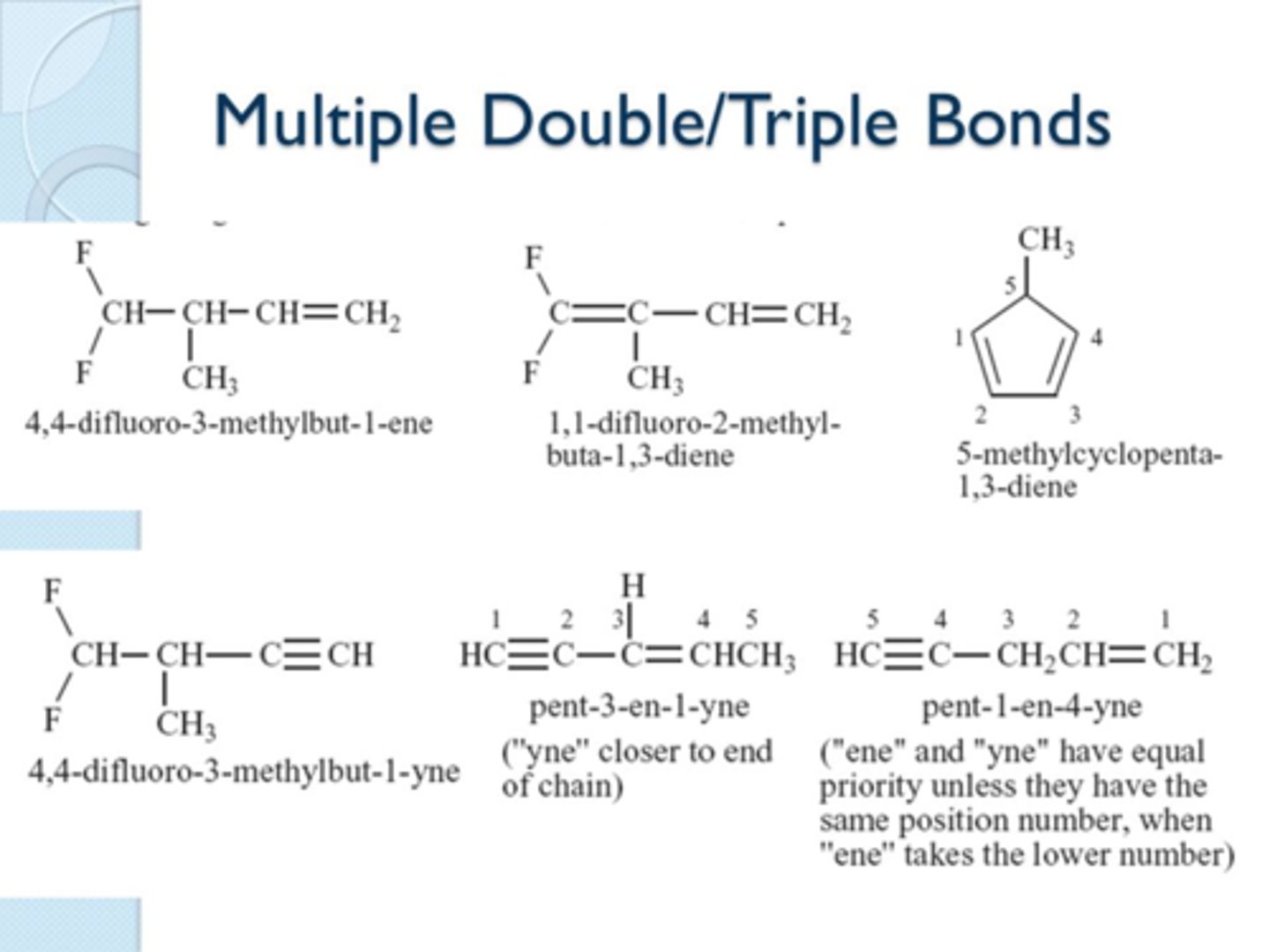
parent chain
longest chain find it
keep substitution and double and triple bonds in mind and fxnl group priorities
If no fxnl group priorities number parent chain so that
first substituent has lowest carbon number possible
the more oxidized a carbon is
the higher priority it has in the molecule
how does carbon oxidation state increase
with more bonds to heteroatoms
heteroatoms
atoms besides carbon and hydrogen
how does carbon oxidation state decrease
with more bonds to hydrogen
if there is a tie between double and triple bond location which takes priority>
double bond
this is only if they would have same number, if one is closer to start of parent chain you choose that one whether it is triple or double
substituents
fxnl groups that are not part of the parent chain
the highest priority fxnl group does what
determines the suffix for the compound and must be part of the parent chain
prefix n- means what
normal
a straight chain alkane substituent
you don't always have to say it
CH3- as a sub would be
methyl
CH3CH2- as sub would be
ethyl
CH3CH2CH2- as sub would be
propyl
or n-propyl (the other alkane subs mentioned could've been n- too)
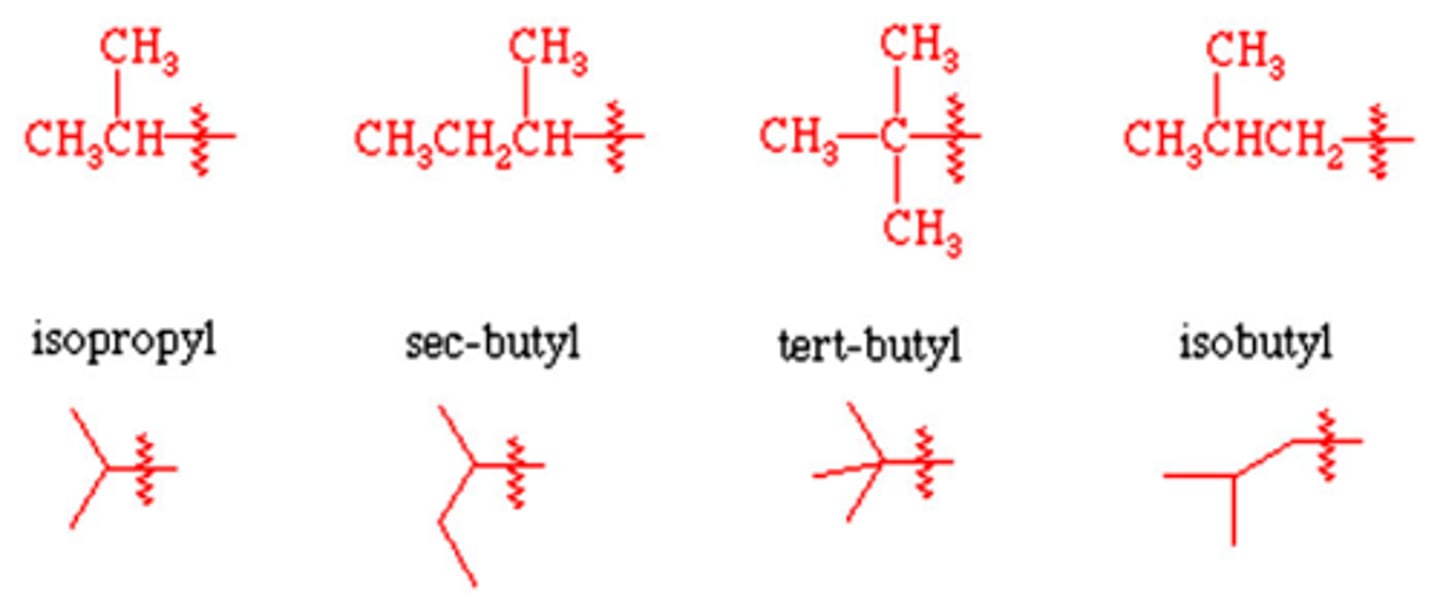
what do the following subs look like:
isopropyl
isobutyl
sec-butyl
tert-butyl
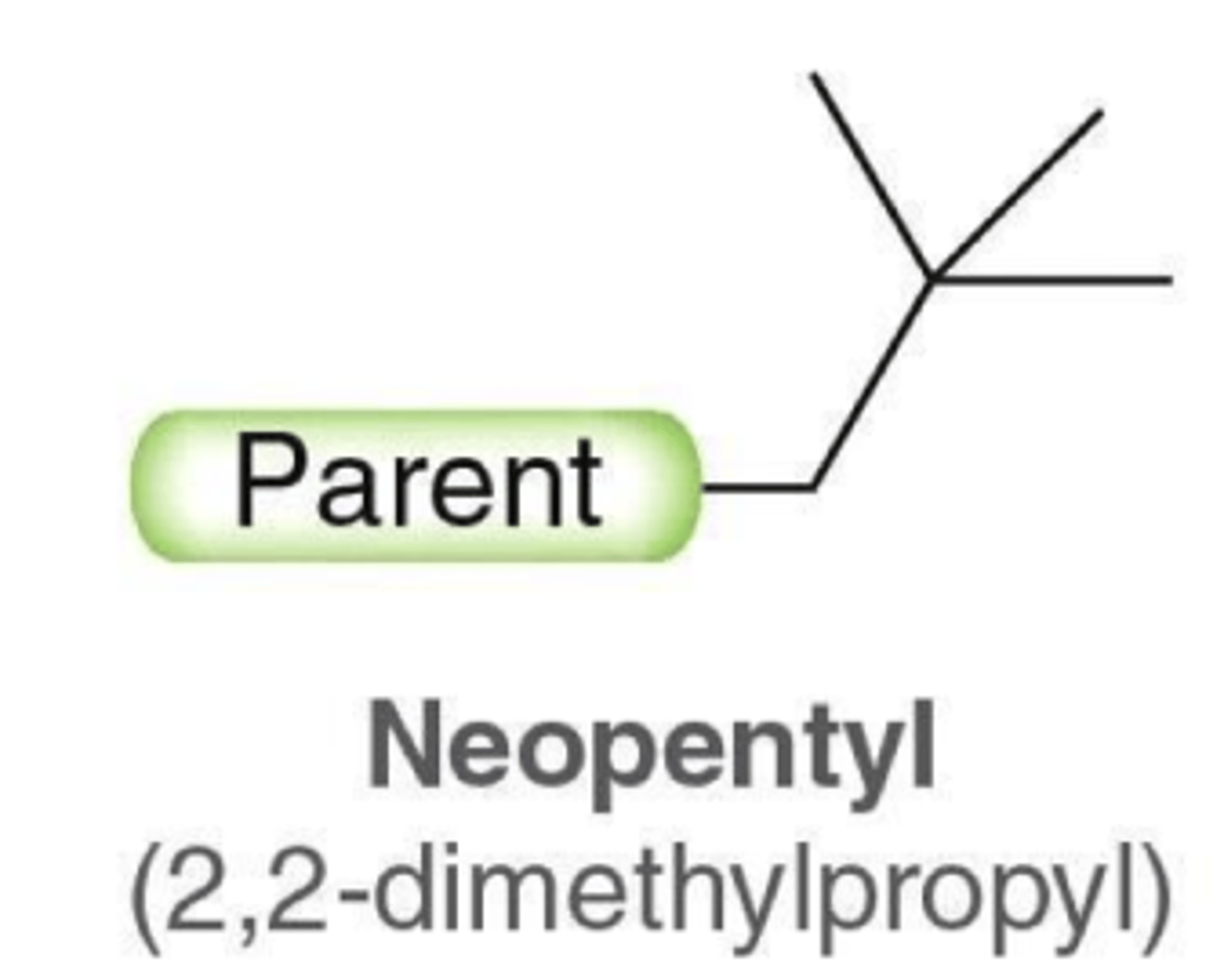
what does neopentyl look like
prefixes and ABC order rule
di, tri, tetra..., tert, n-, sec- (all IGNORED) ABC by part after prefix
non-hyphenated roots are part of ABC order: iso, neo, cyclo (ALL MUST BE CONSIDERED)
hydrocarbons
compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms
alcohols are denoted by the presence of
-OH, which lends additional reactivity to the molecule
alkanes
what
general formula
single bond alkanes
CnH(2n+2)
alkanes 1-12 carbon names
methane 1
ethane 2
propane 3
butane 4
pentane 5
hexane 6
heptane 7
octane 8
nonane 9
decane 10
undecane 11
dodecane 12
alkyl halides
compounds with halogen substituents
4 common halogen prefixes
fluoro-
chloro-
bromo-
iodo-
-ene means
alkene
double bond(s)
-yne means
alkyne
triple bond(s)
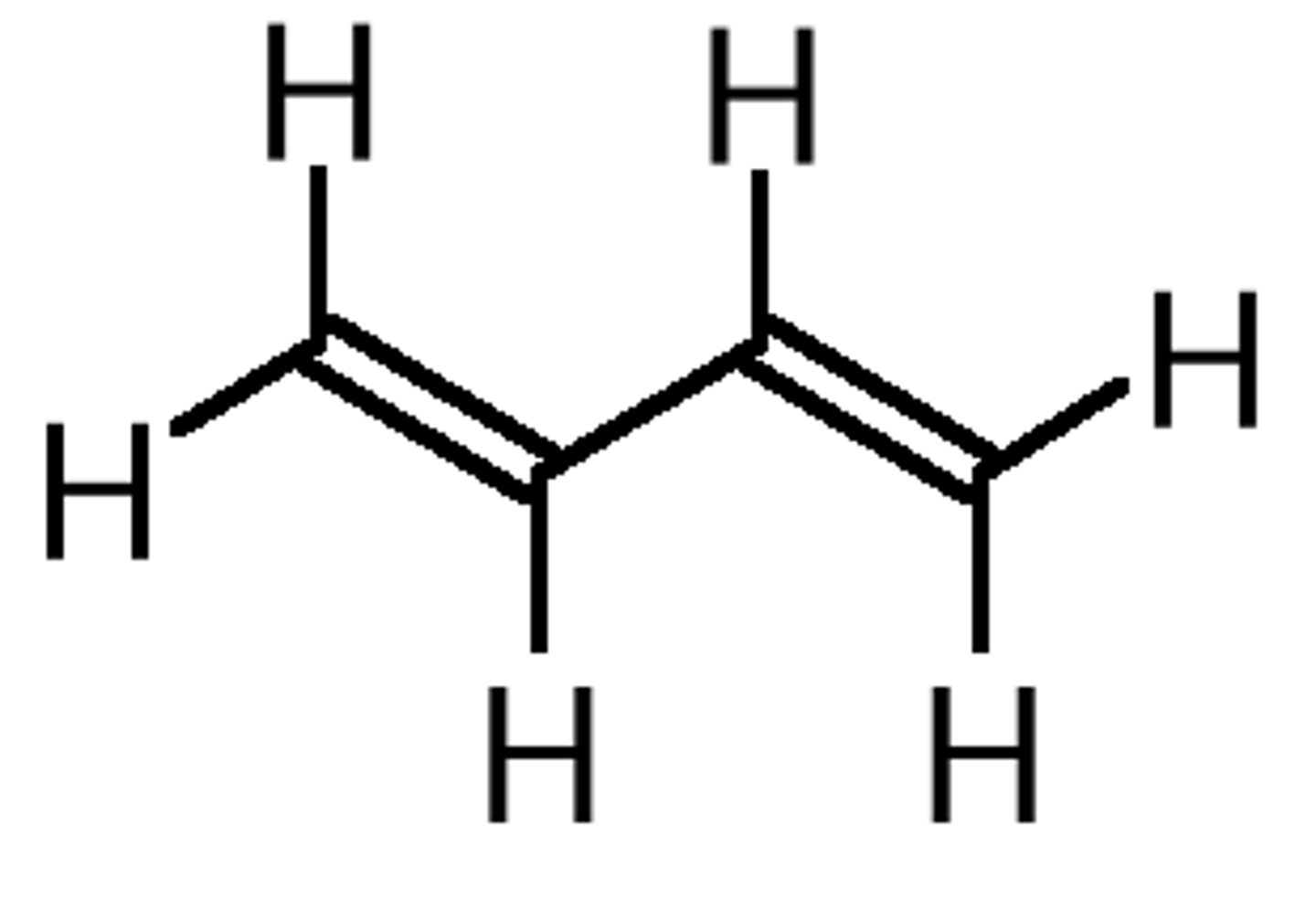
name compound in image
1,3-butadiene
how do you know there is an alcohol by name
it ends in -ol
how to number and name when there is an alcohol
the carbon attached to the hydroxyl group gets the lowest possible number
alcohol vs bonds for naming
alcohol takes priority over double and triple bonds
what does hydroxy- mean
it means there is an alcohol present and it is not the highest priority substituent
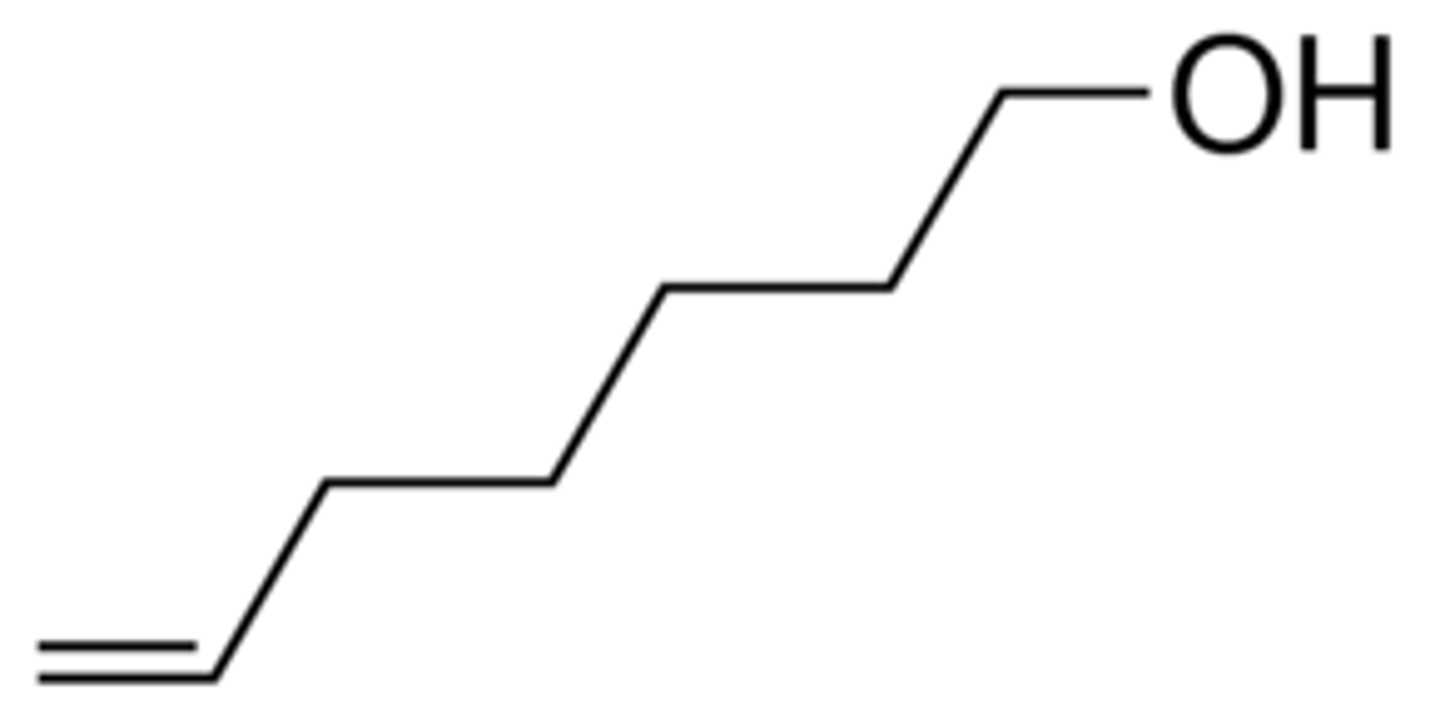
hept-6-en-1-ol image
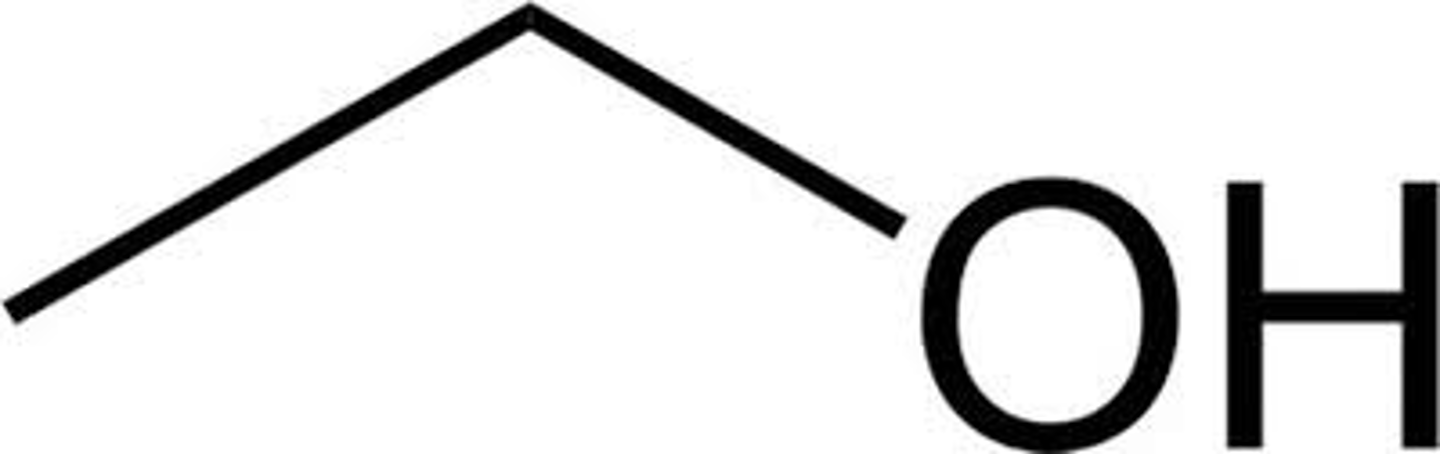
what does ethyl alcohol look like and other names
ethanol
drinking alcohol
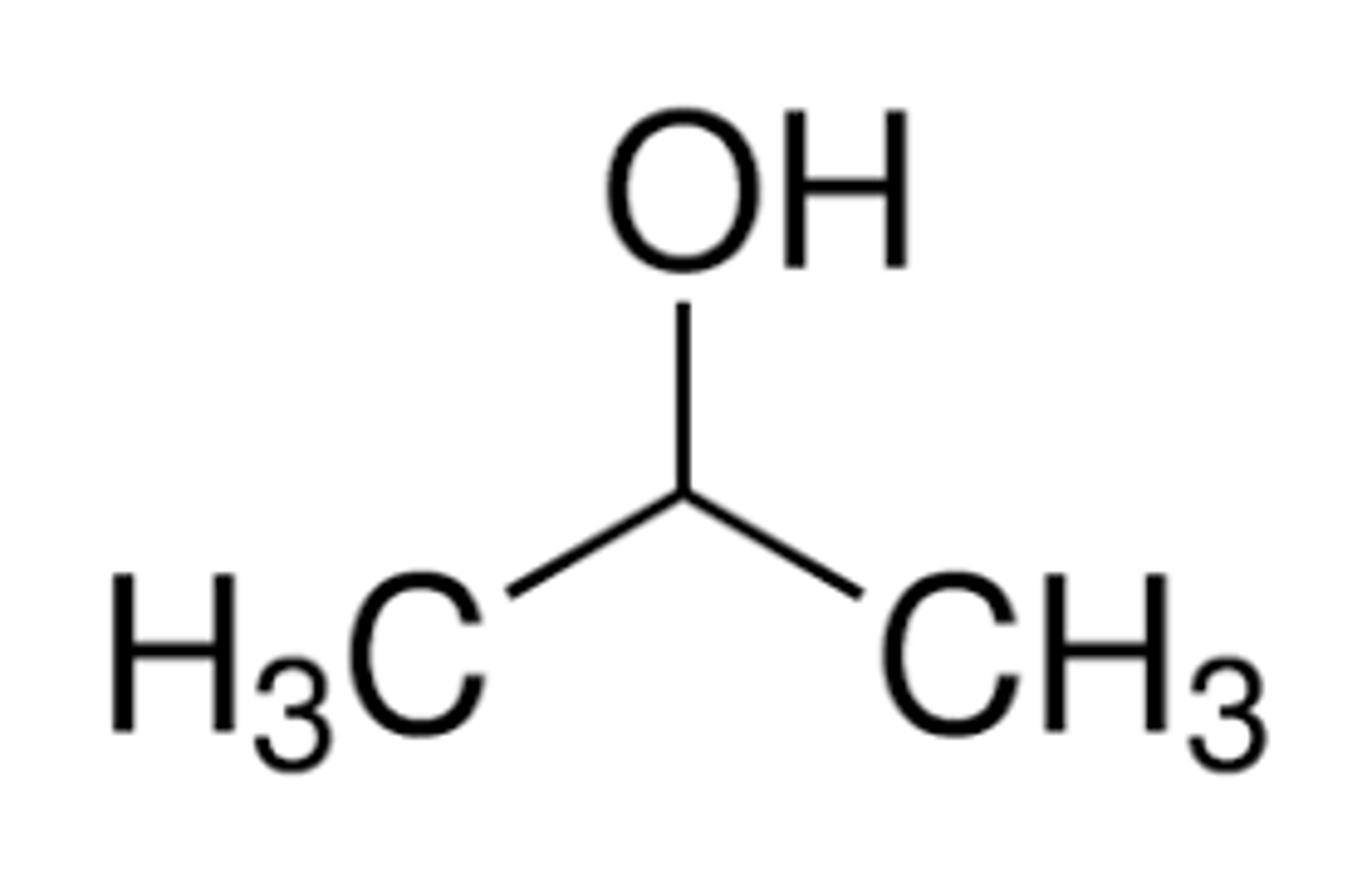
isopropyl alcohol
look like
other names
2-propanol
propan-2-ol
isopropanol
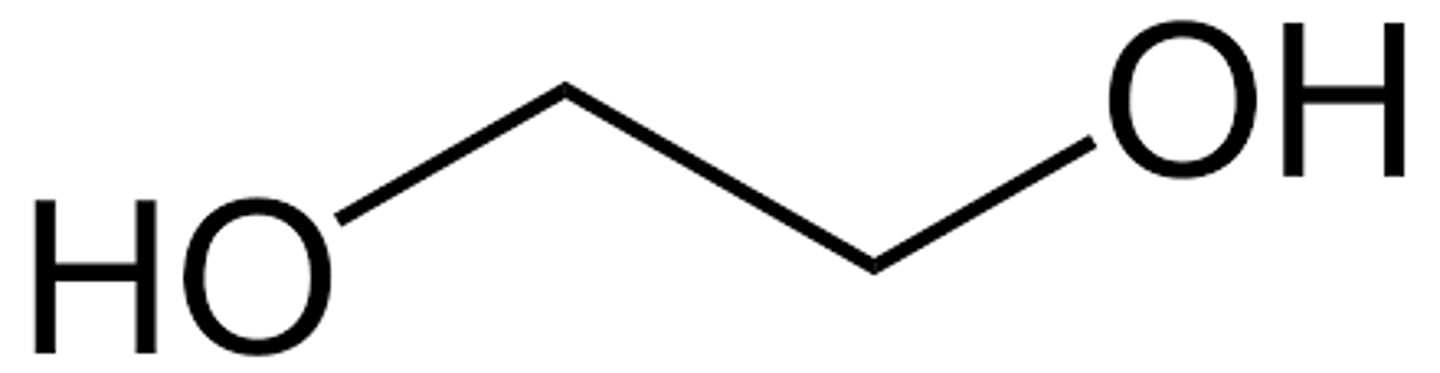
what is a diol
another name too
aka glycol
alcohols with 2 hydroxyl groups
how do you indicate a diol/glycol
the suffix -diol and the numbering of each alcohol
ex: ethane-1,2-diol
what is ethylene glycol
ethane-1,2-diol
NOT an alkene!
what is a geminal diol
diols with hydroxyl groups on the same carbon
also called hydrates
not common
what is a vinicial diol
diols with hydroxyl groups on adjacent carbons
what are hydrates and are they common?
geminal diols
NOT common bc they spontaneously dehydrate (lose a water molecule) to produce carbonyl compounds with the functional group C=O
geminal vs vicinal mnemonic
geminal diols are like gemini, twins, on SAME carbon, like from same mom
vicinal diols sounds like vicinity which means adjacent carbons
what is a carbonyl group
a carbon double bonded to an oxygen
aldehydes
structures with a carbonyl group at one end (really it is C1 in the chain)
ketones
carbon double bonded to oxygen in the middle of a chain
naming aldehydes
generally the carbonyl carbon is C1
suffix becomes -al
when carbonyl is a position 1, which is usually, you do not need to include the numbered position of the carbonyl group
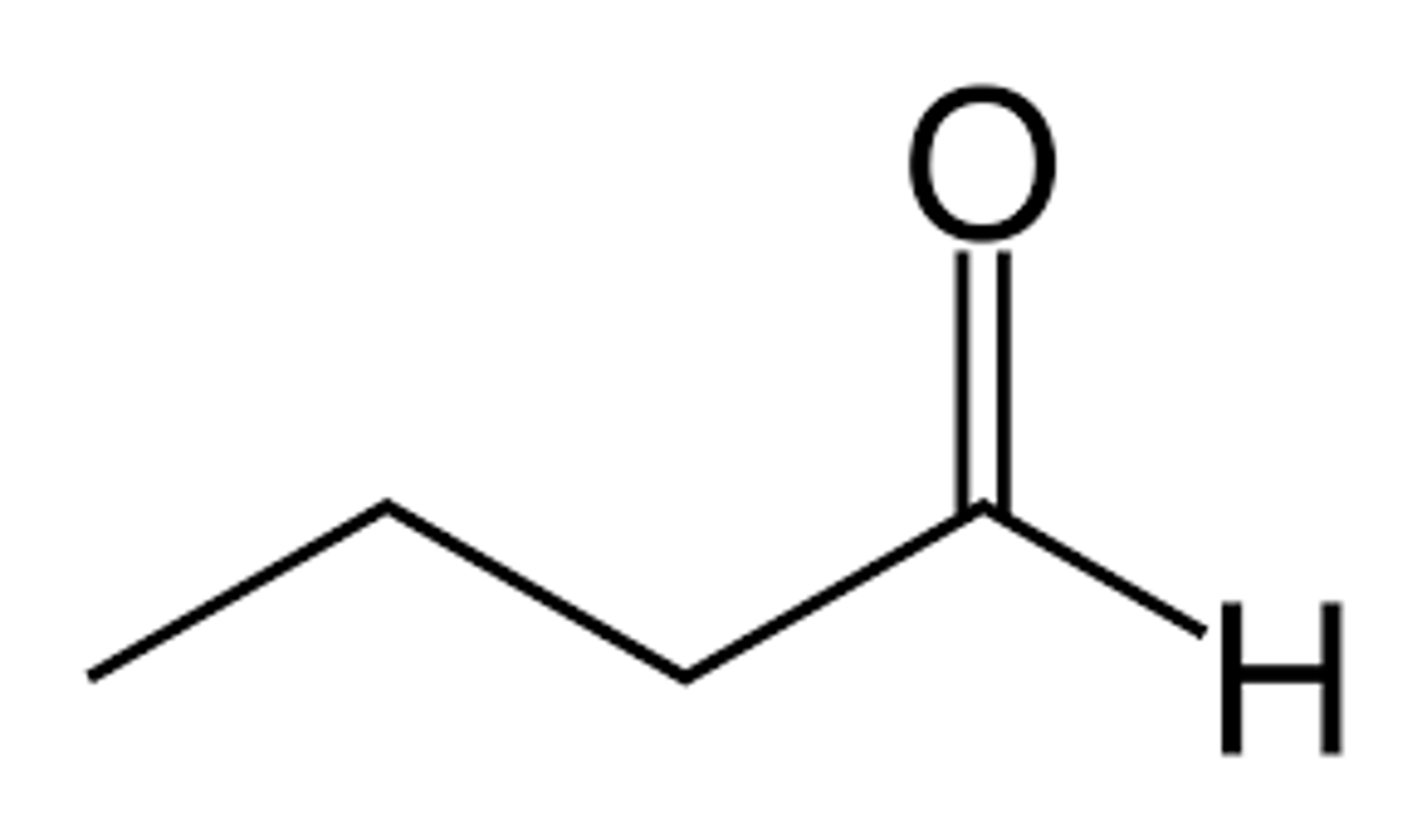
what does butanal look like?
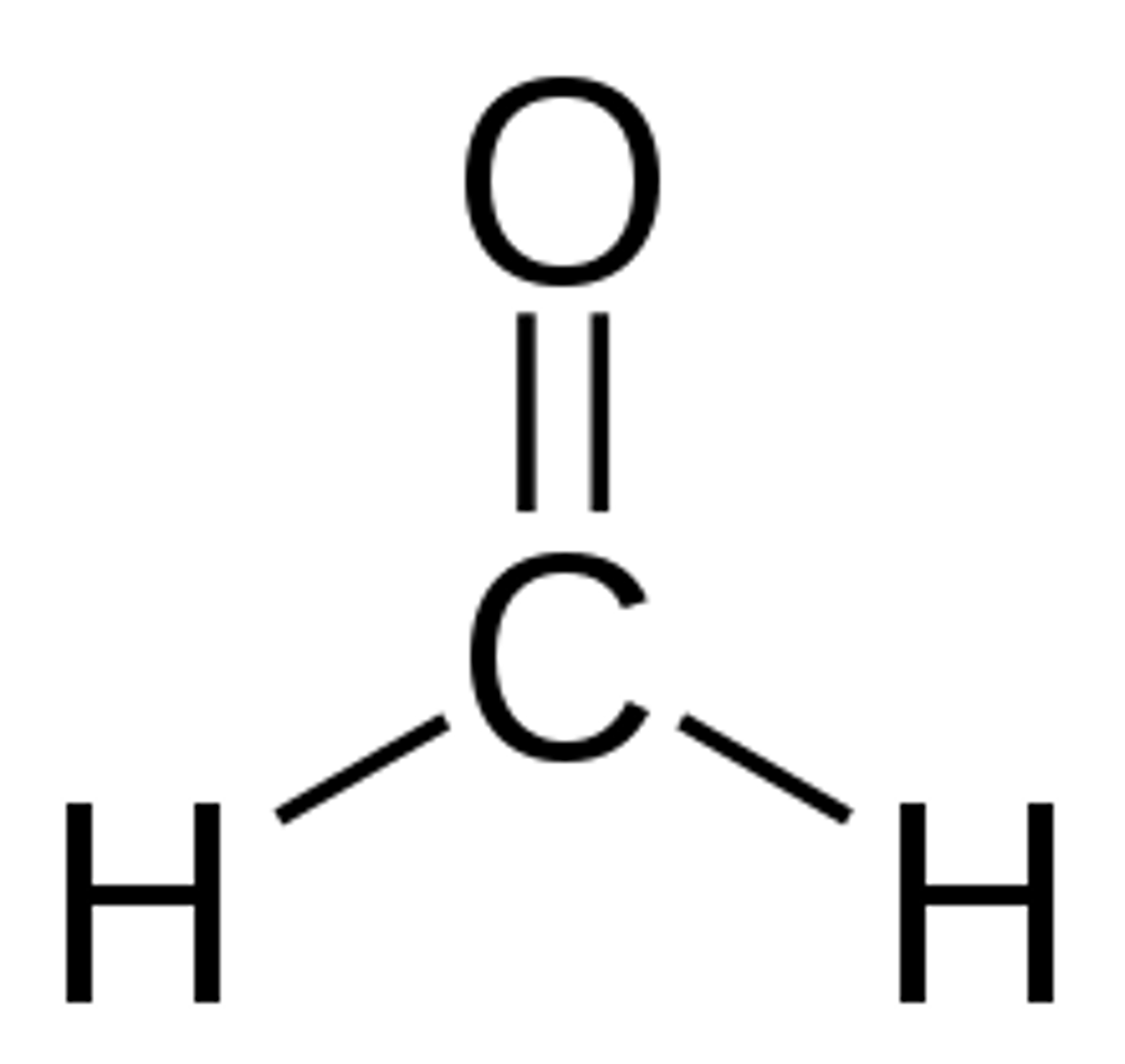
what is methanal's common name
formaldehyde
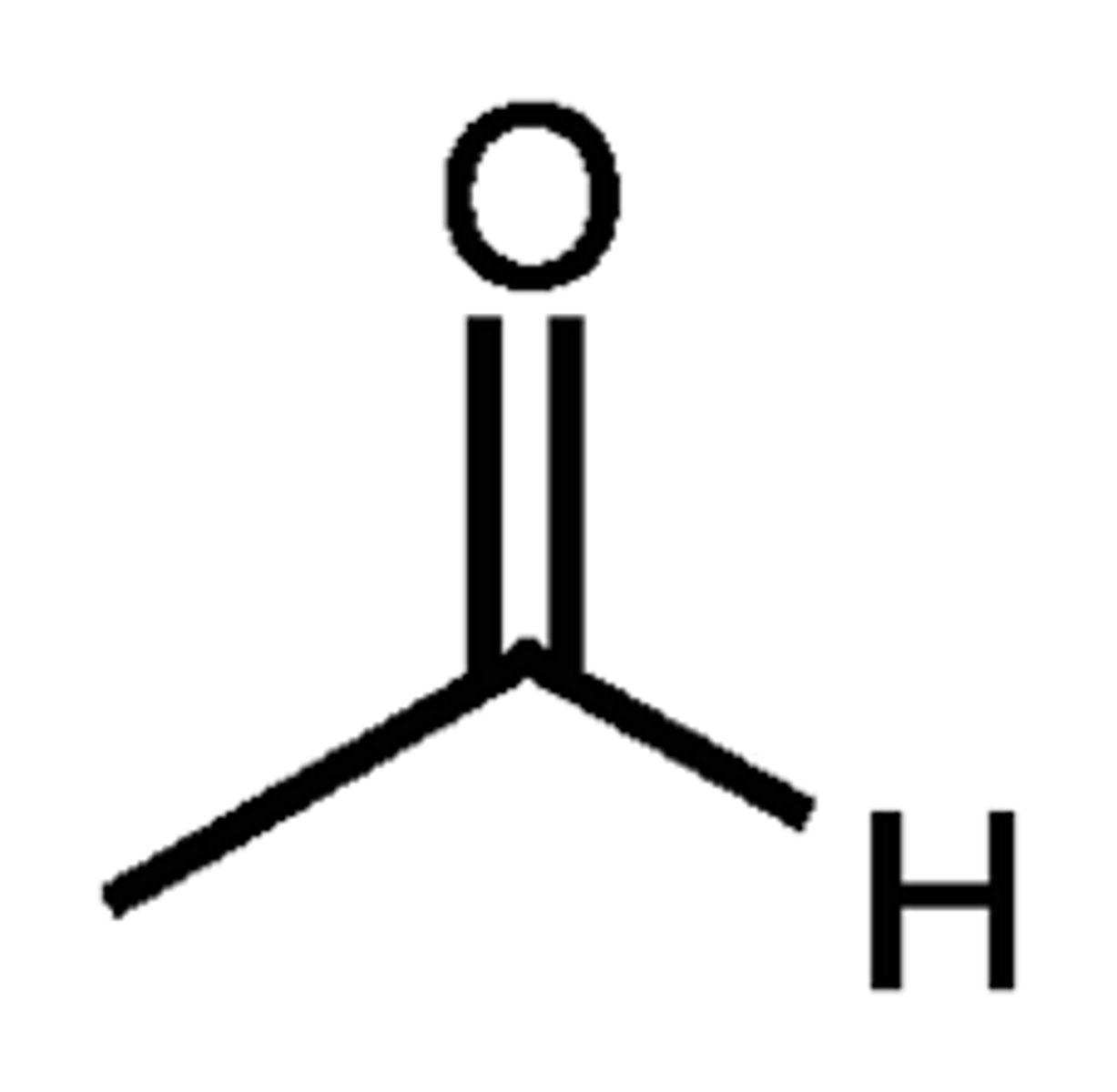
what is ethanal's common name
acetaldehyde
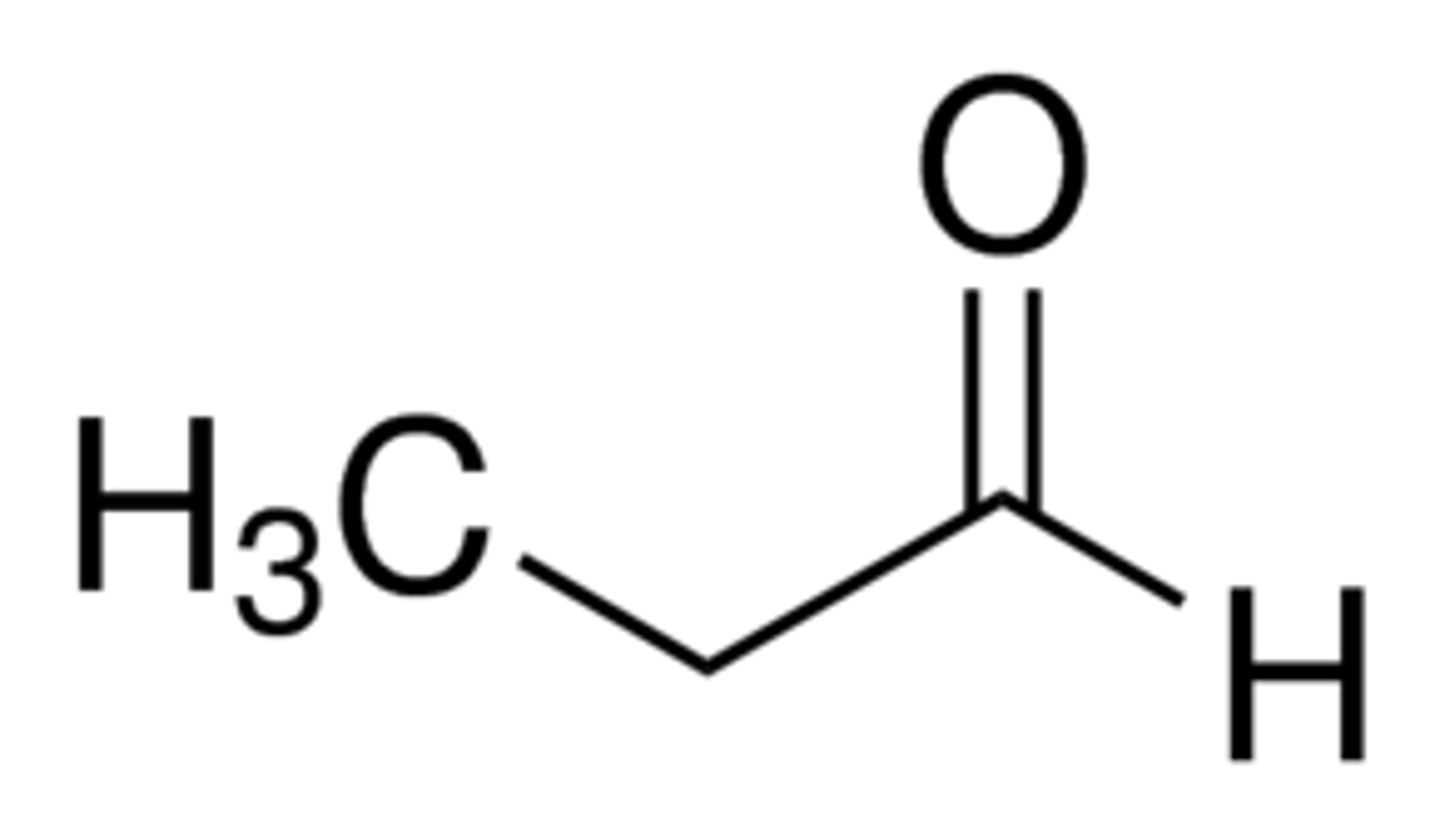
what is propanal's common name
propionaldehyde
naming ketones
you almost always have to assign a number to the keton bc it is in the middle somewhere (except for propanone where it is assumed at C2 by default)
suffix will be -one
give ketone carbonyl highest priority unless it is trumped by another fxnl group
how may an ketone be names in none IUPAC
by listing the alkyl groups in ABC order then writing ketone
ex: ethylmethylketone
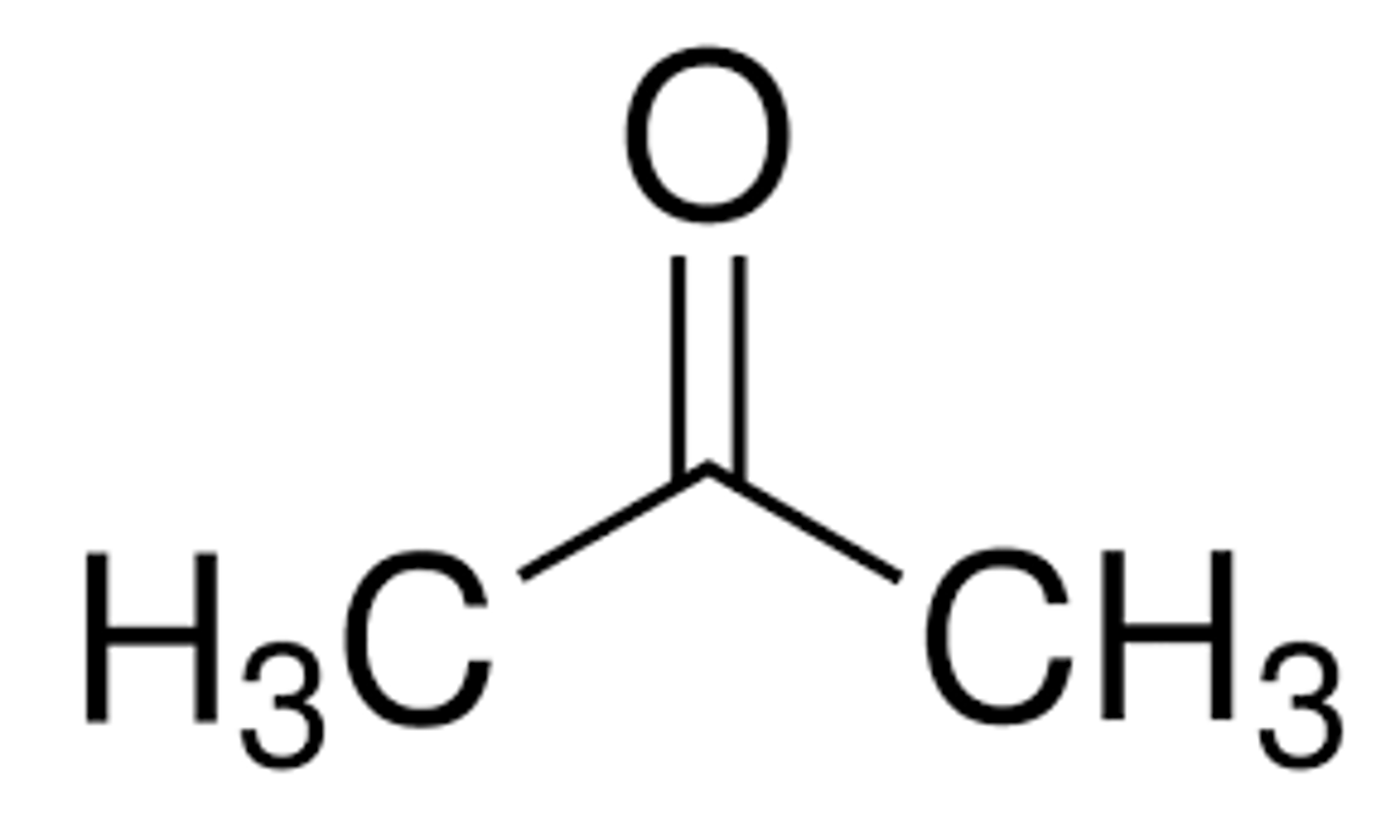
what does acetone look like and why is it special
it is the smallest ketone possible and it is weird bc "act-" usually refers to two carbons but here it is a 3 carbon compound
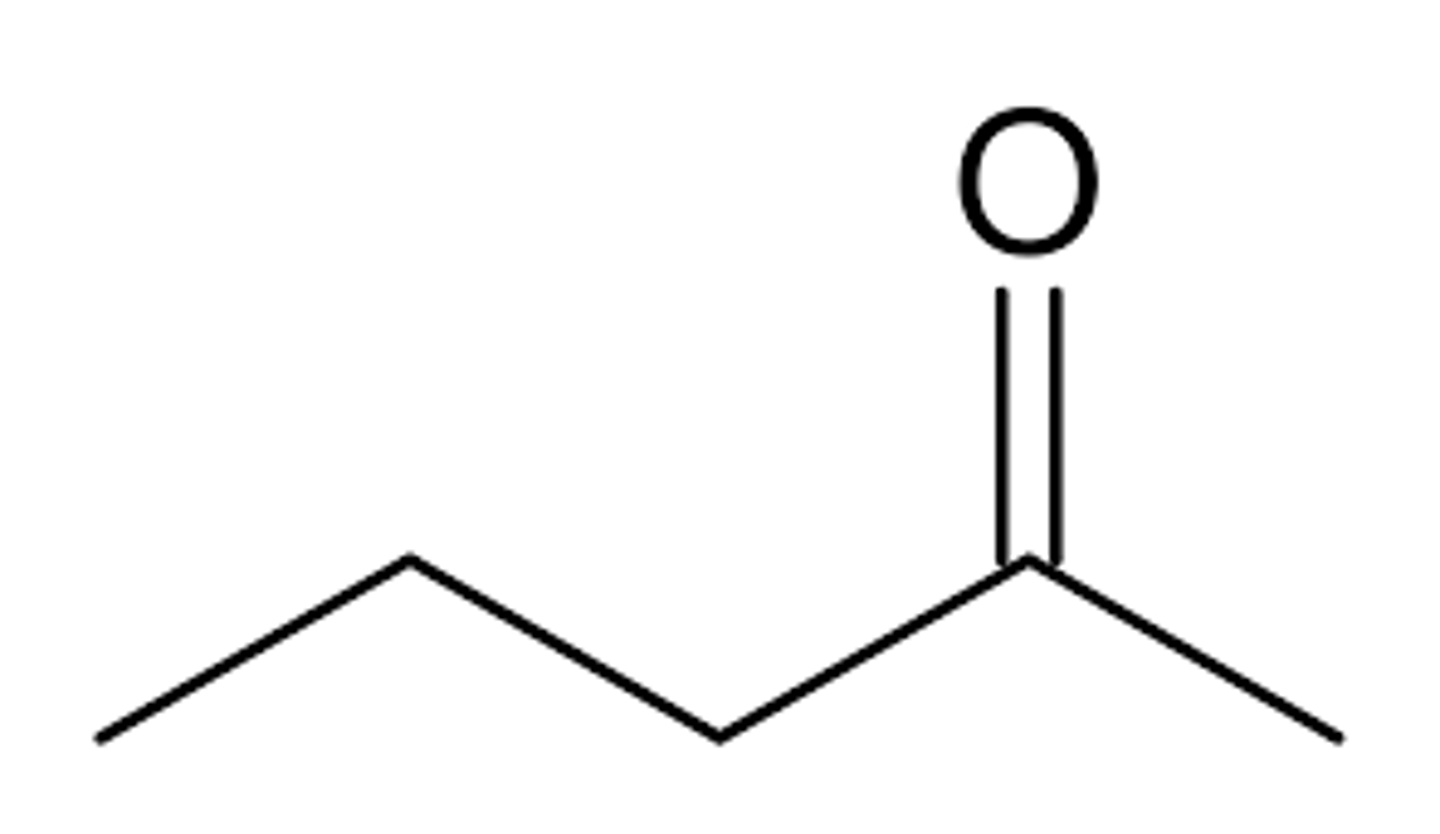
what does 2-pentanone look like
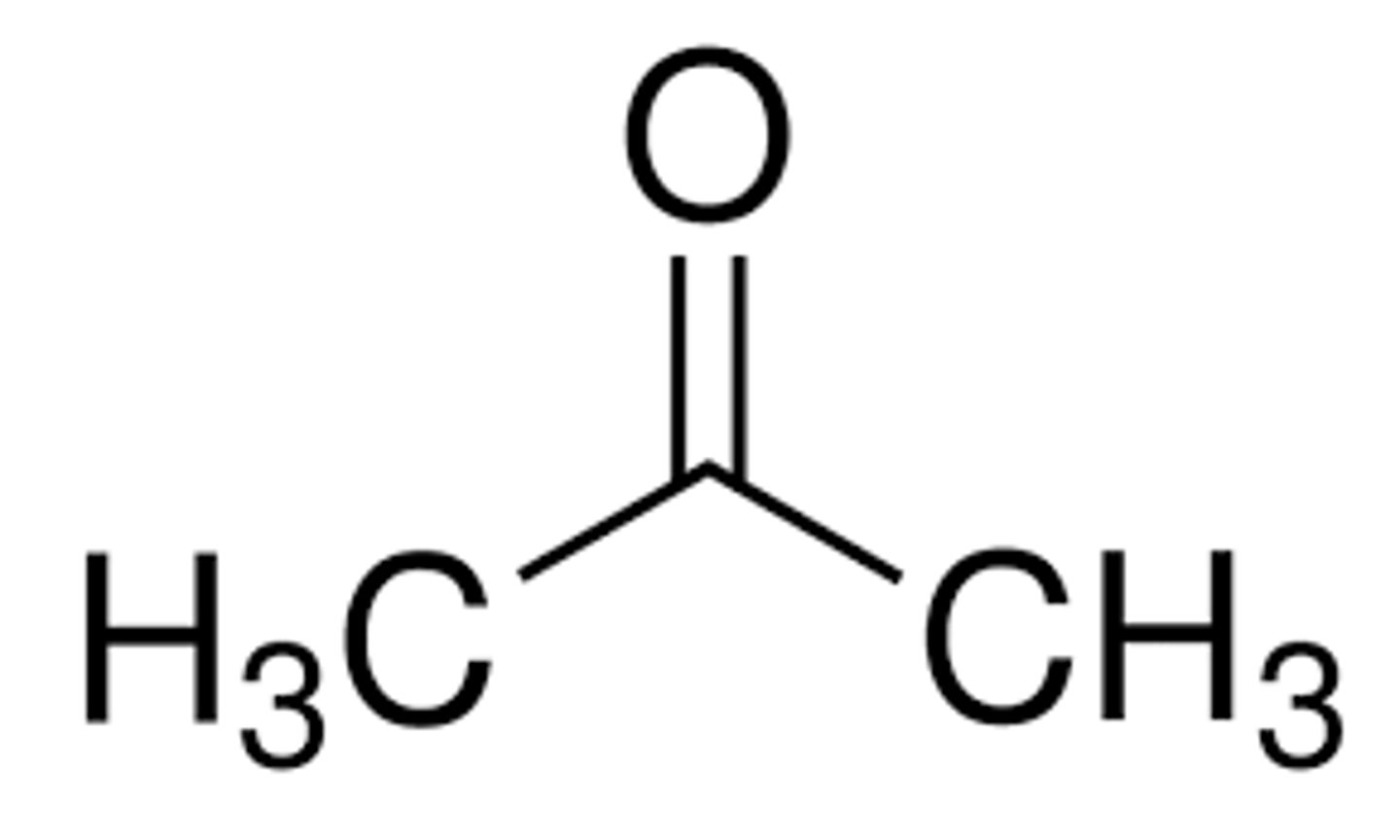
what does propanone look like and what are 3 other names for it
2-propanone
acetone
dimethylketone
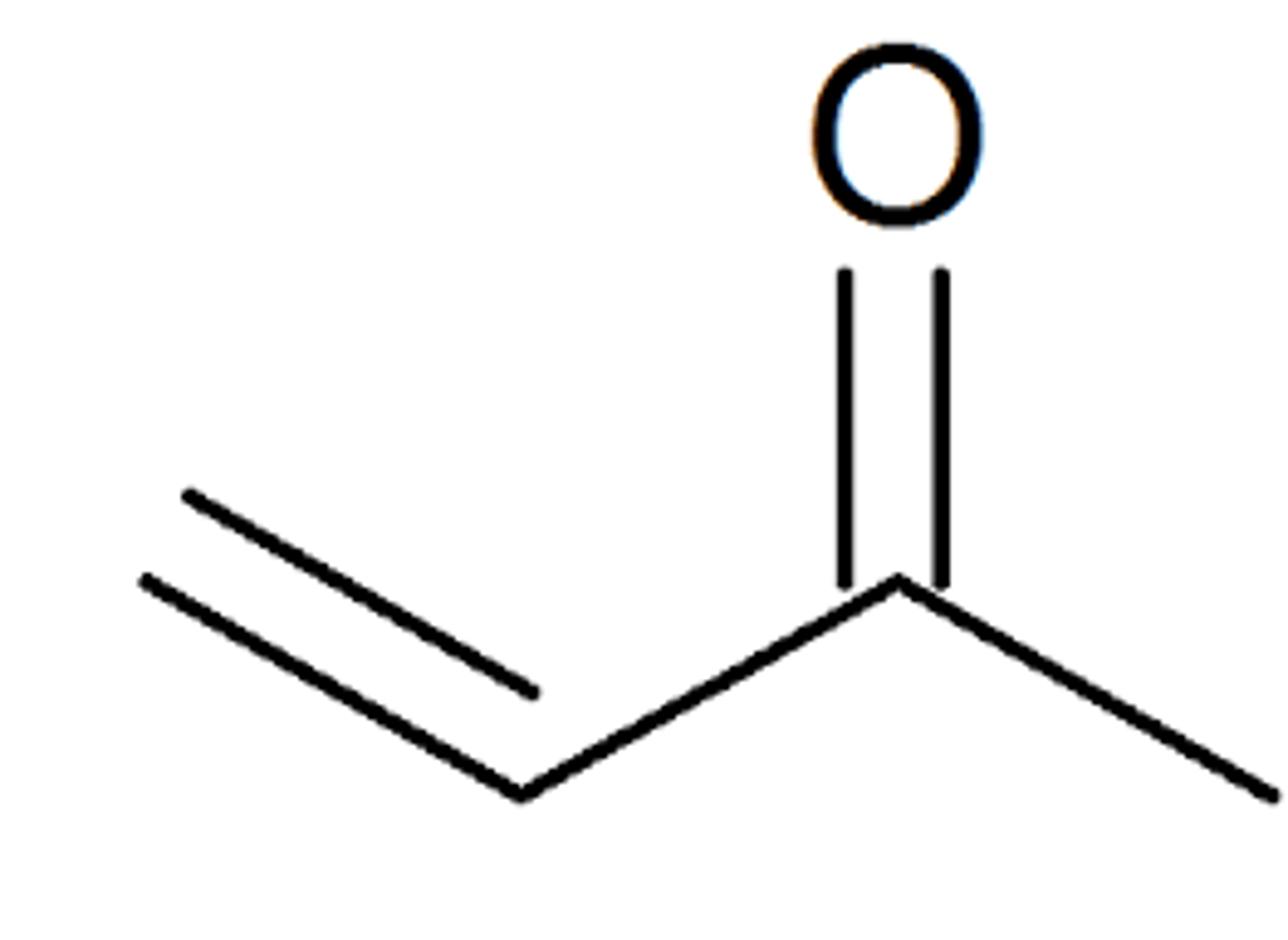
what does 3-butene-2-one look like and what is its common name
methylvinylketone
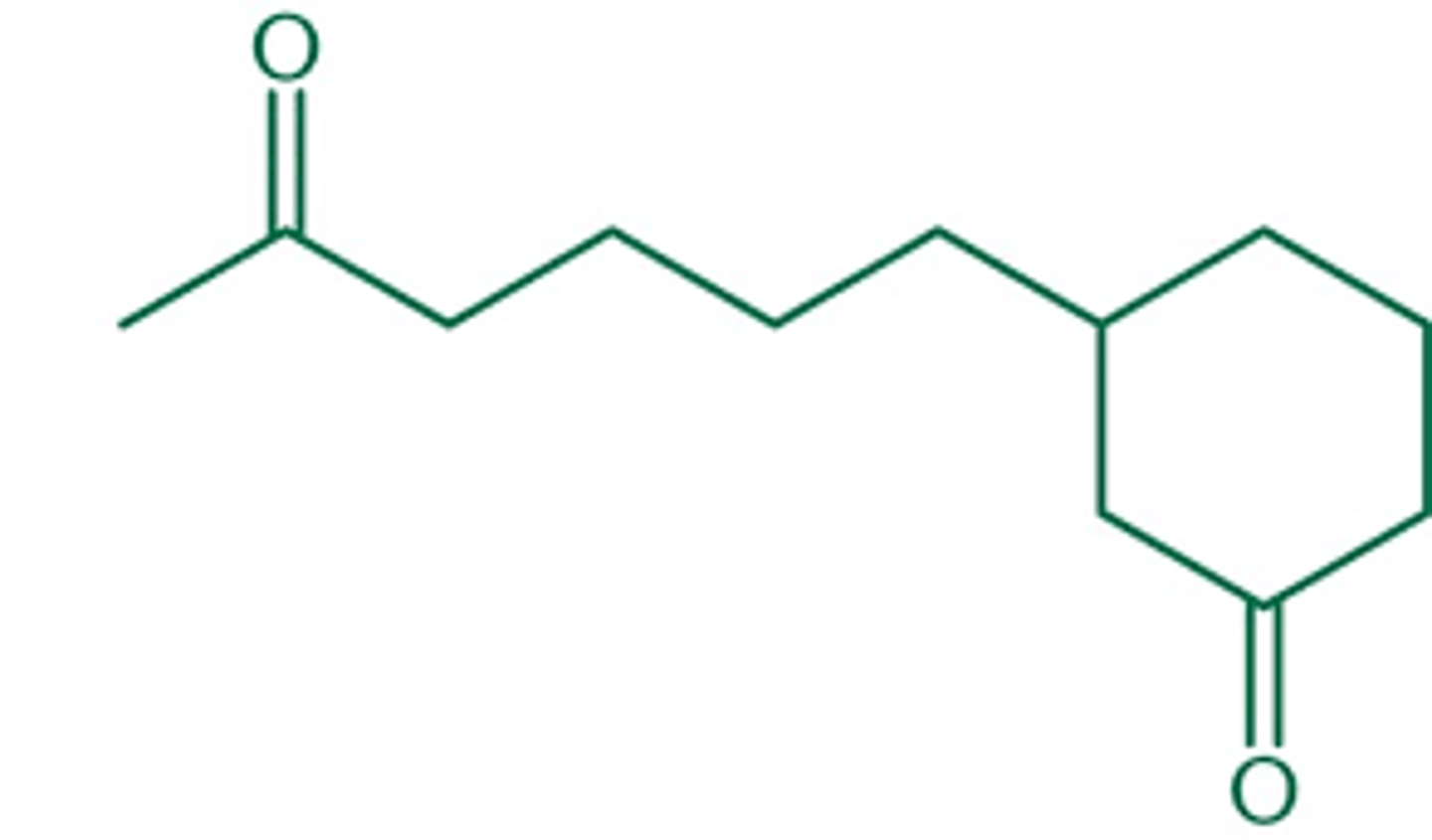
what does 3-(5-oxohexyl)cyclohexanone look like
what does oxo- mean
there is either a ketone or an aldehyde in the structure that does not take the highest priority
what does keto- mean
there is a ketone that does not take highest priority (does not apply suffix -one) so you can use this or oxo-
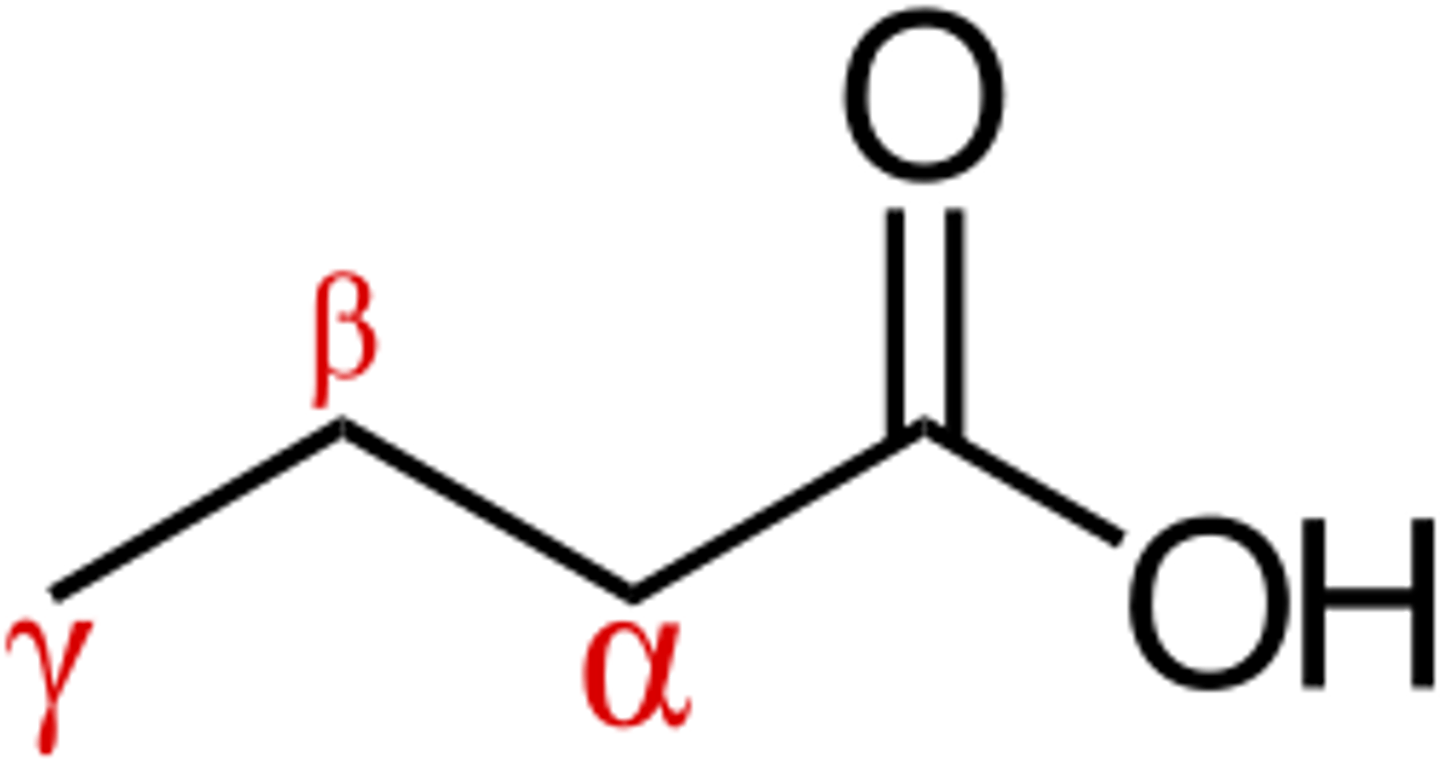
alpha vs beta vs gamma carbon on diagram in reference to a carbonyl carbon
ex: the carbons on both sides of a ketone group are alpha carbons
ketones and aldehydes vs alcohols and double bonds for numbering
ketones and aldehydes take preference over both alcohols and double bonds
carboxylic acids
contain both a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) on a terminal carbon
numbering carboxylic acids
C1 since it is the most oxidized functional group that will appear on the MCAT
you do not say the number for the carboxylic acid in the name bc position is assumed
what is the only scenario where a carbon is more oxidized than in a carboxylic acid situation
carbon dioxide (4 bonds from C to heteroatoms, the oxygen atoms, whereas only 3 in carboxylic acid)
naming carboxylic acids
always as a suffix since always highest priority
-oic acid
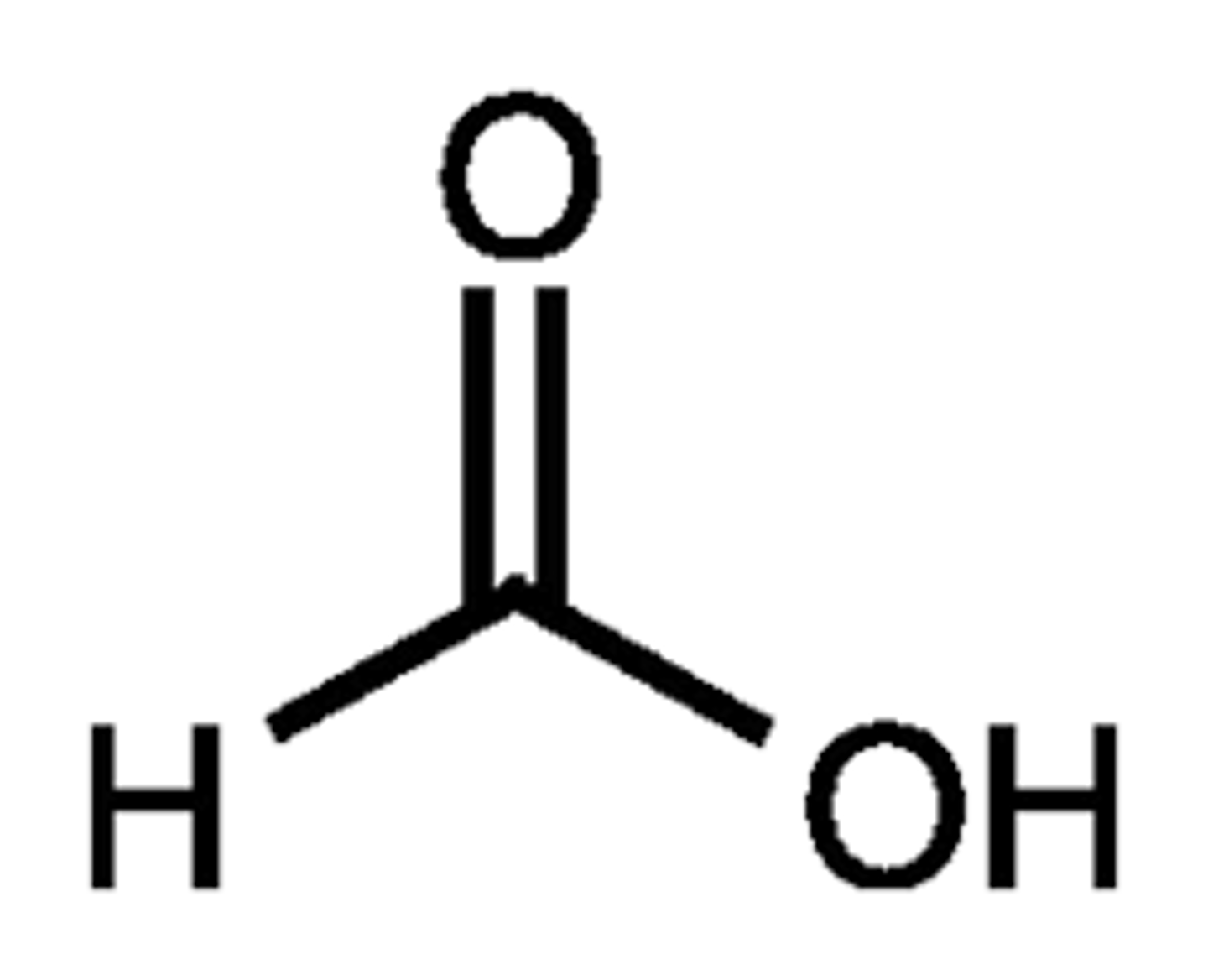
methanoic acid
appearance and common name
formic acid
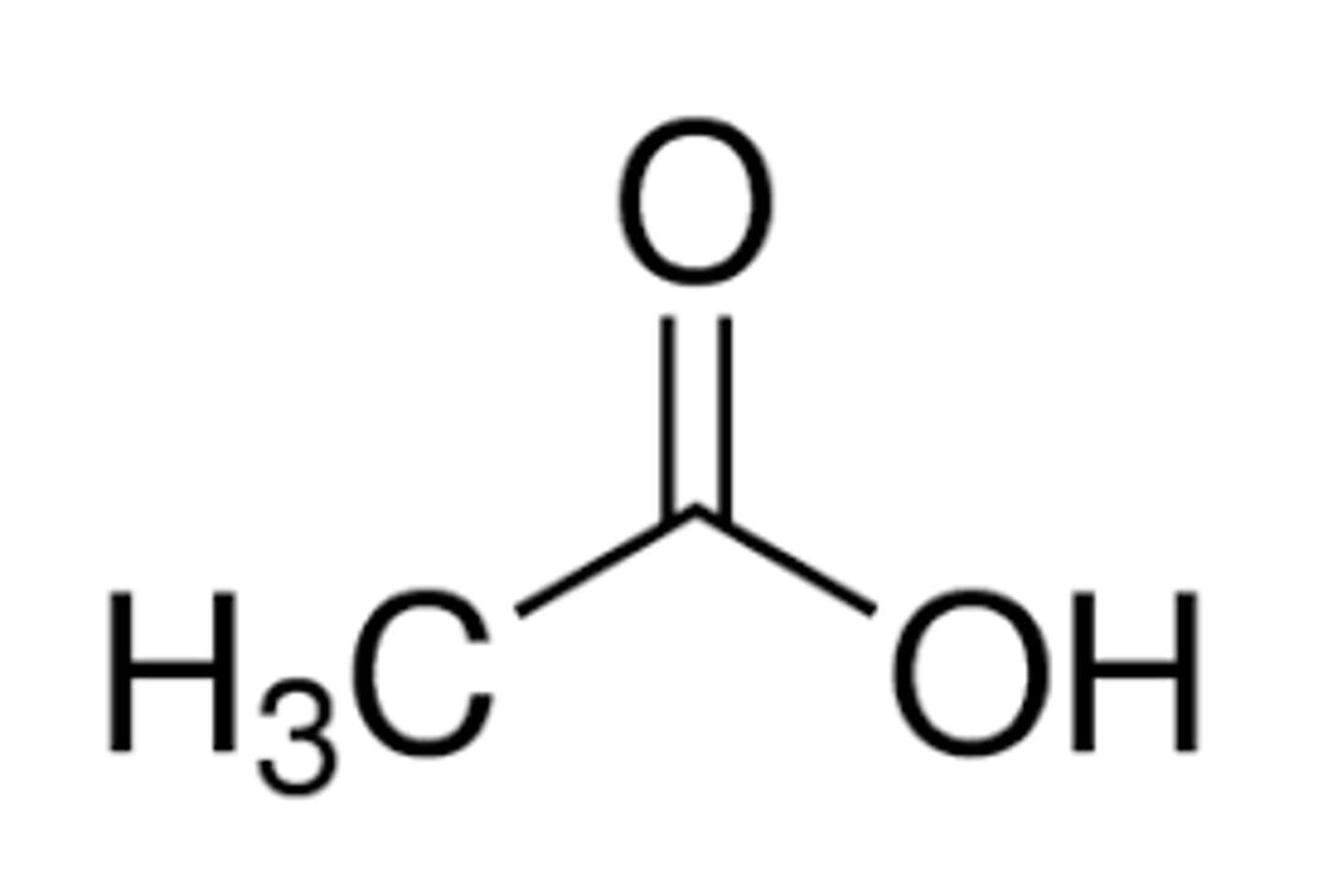
ethanoic acid
appearance and common name
acetic acid
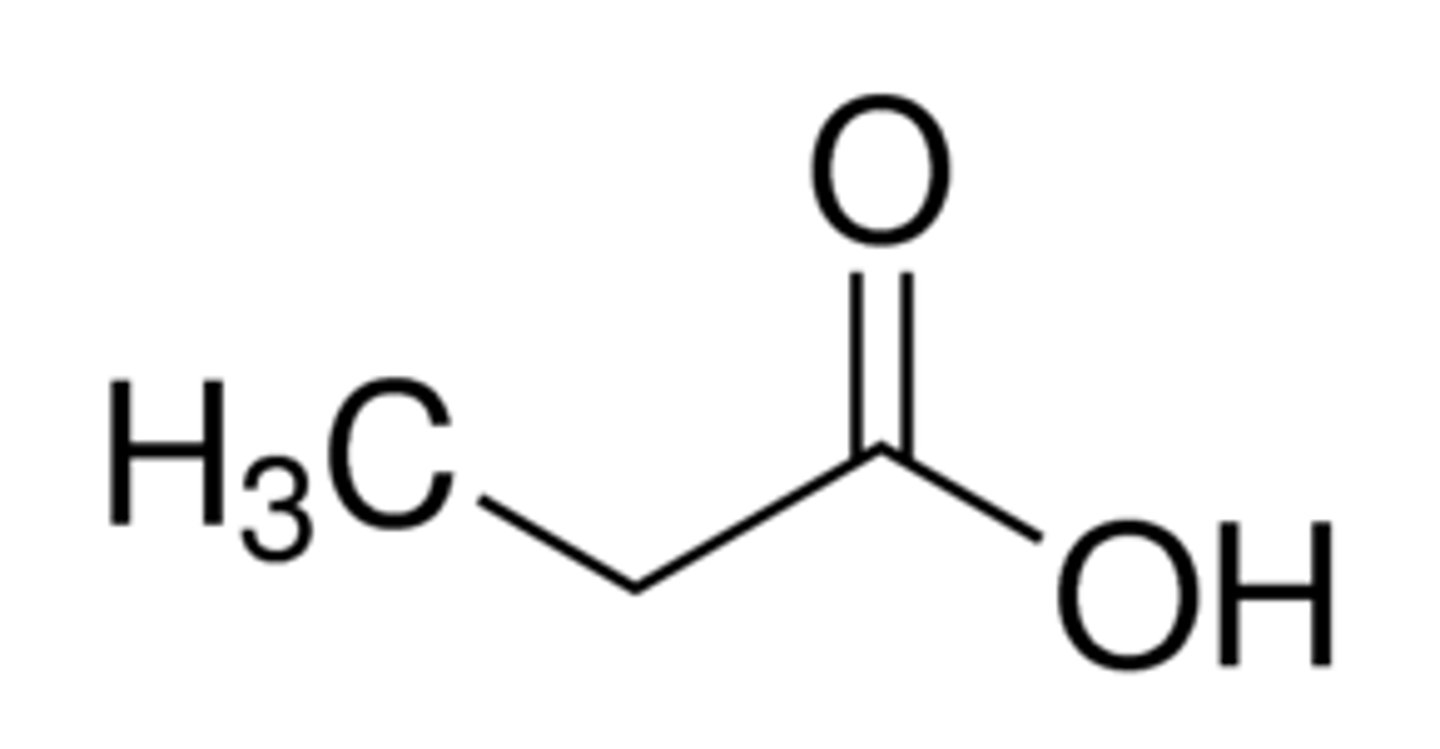
propanoic acid
appearance and common name
propionic acid
3 types of carboxylic acid derivatives
esters
amines
anhydrides
esters
carboxylic acid derivative
the hydroxyl group (-OH) of the carboxylic acid is replaced with an alkoxy group (-OR) where R is any hydrocarbon chain
alkoxy group
-OR
where R is any hydrocarbon chain
how to name an ester
the first part is the alkyl group of the -OR
the second part is the parent acid with the suffix -oate (count the carbonyl carbon as part of the parent chain)
ex: butyl methanoate
ex: ethyl propanoate
what would form if you exposed formic acid to butanol under the right conditions
butyl methanoate
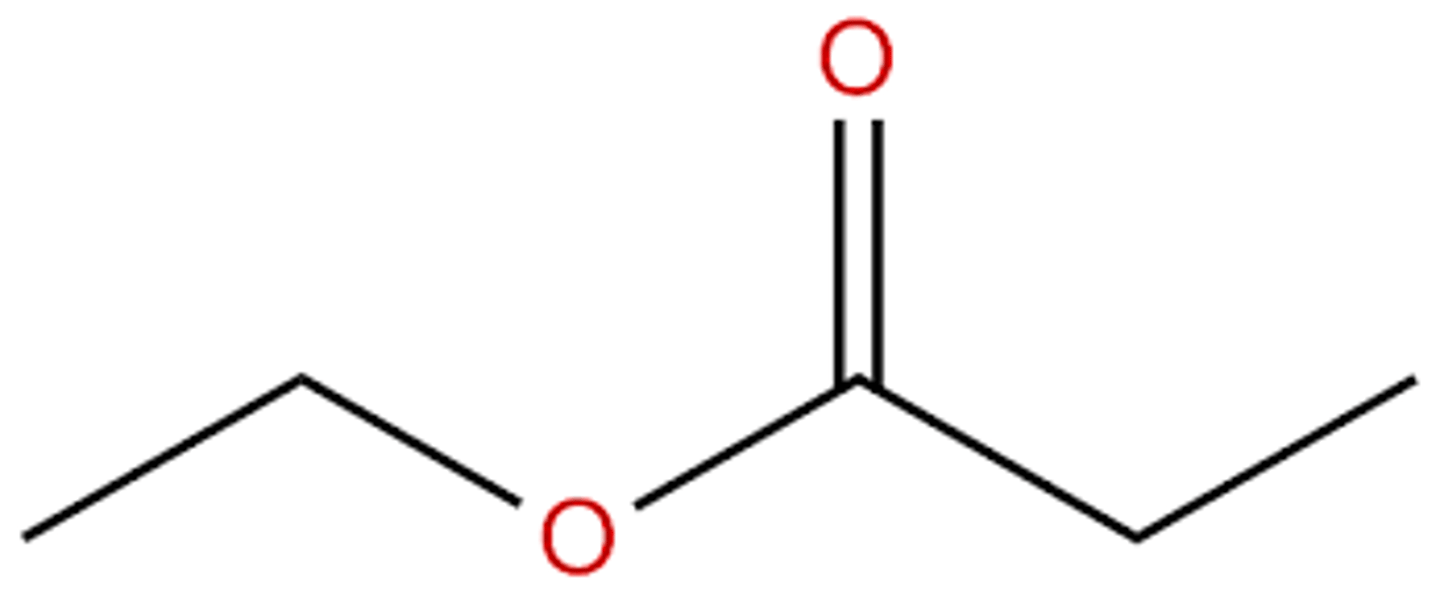
what would ethyl propanoate look like
amides
carboxylic acid derivative
the hydroxyl group of the carboxylic acid is replaced by an amino group (a nitrogen containing group)
naming amides
suffix is -amide
substituents attached to the nitrogen are labeled N- (no numbers)
then named similarly to esters
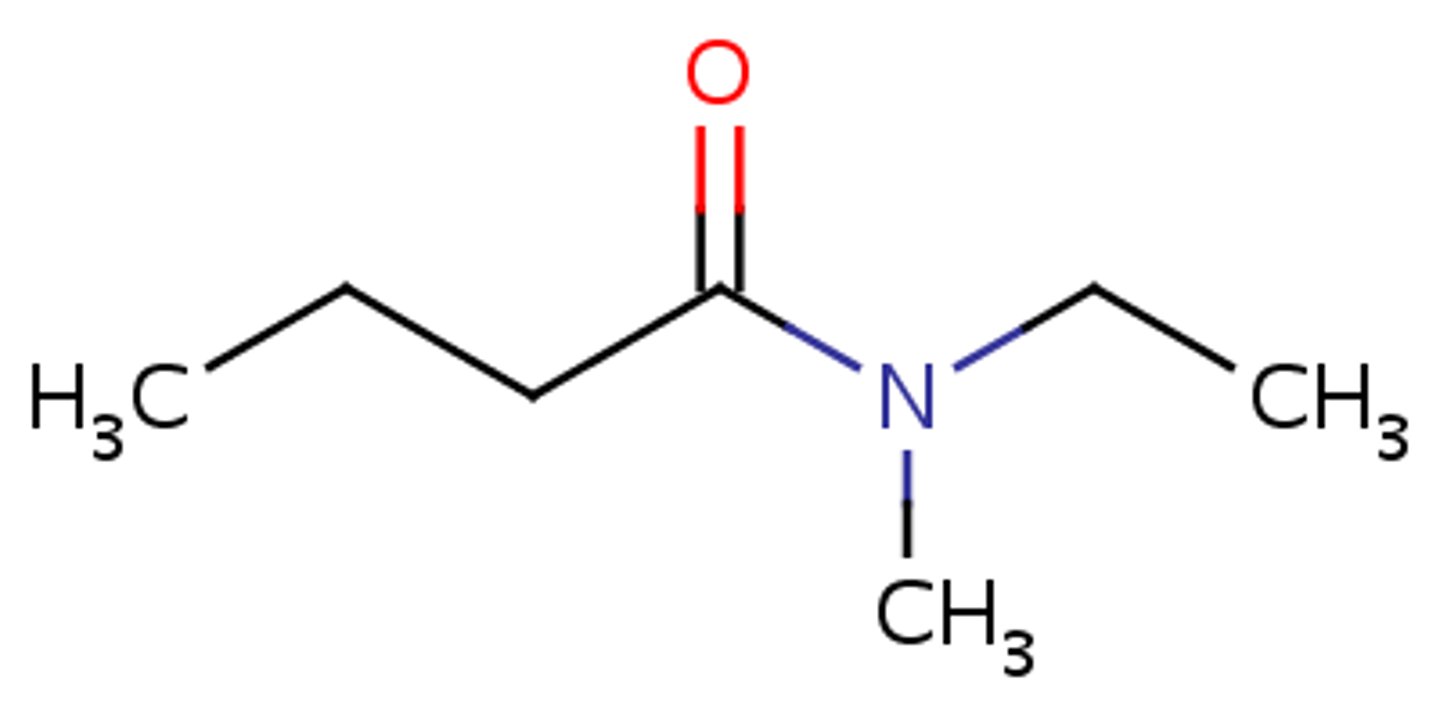
what does N-ethyl-N-methylbutanamide look like
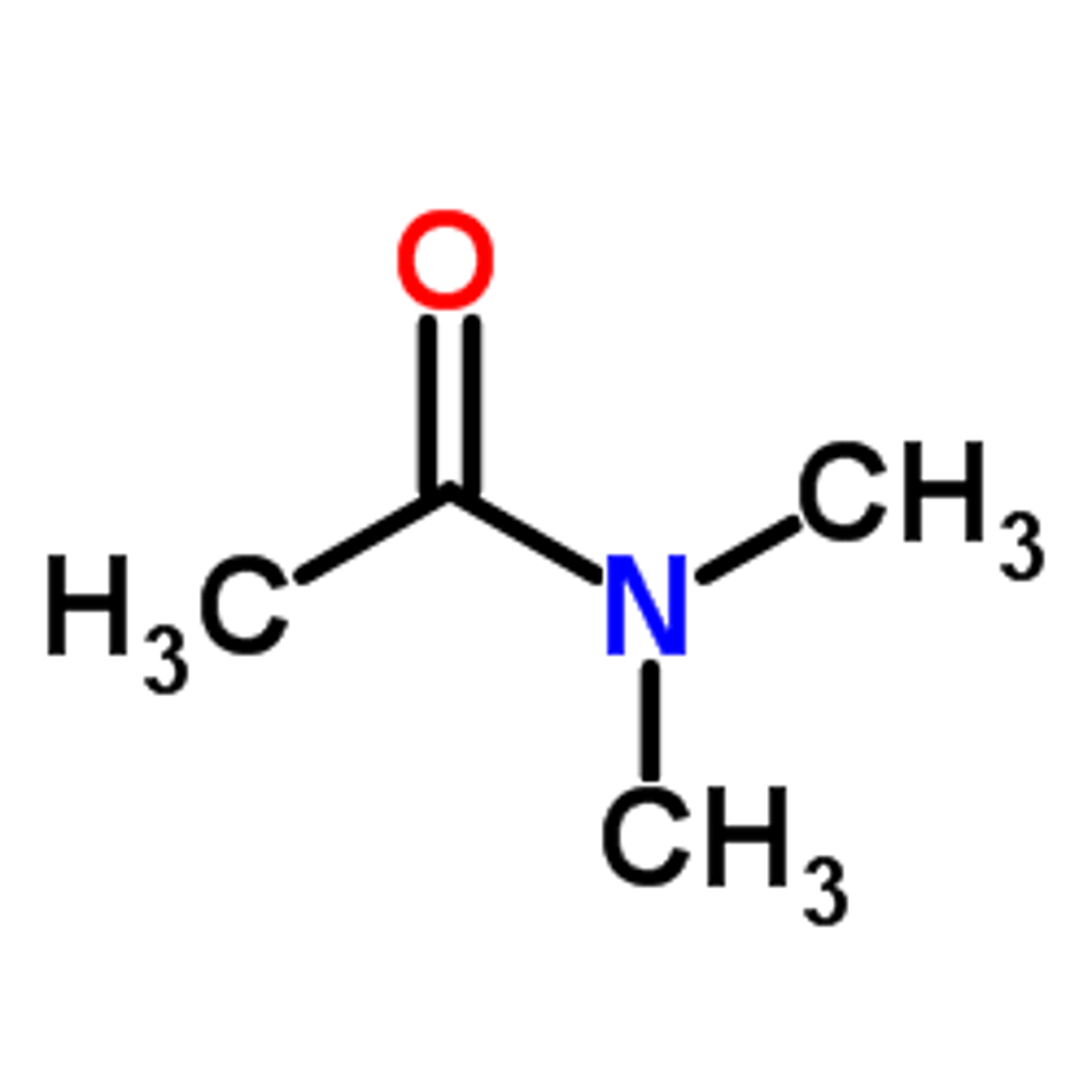
how to name amide that has two of the same groups hanging off the N
N,N-dimethylethanamide
how to name amide that has only H hanging off the N
propanamide (or change based on parent chain) this is just example for this one
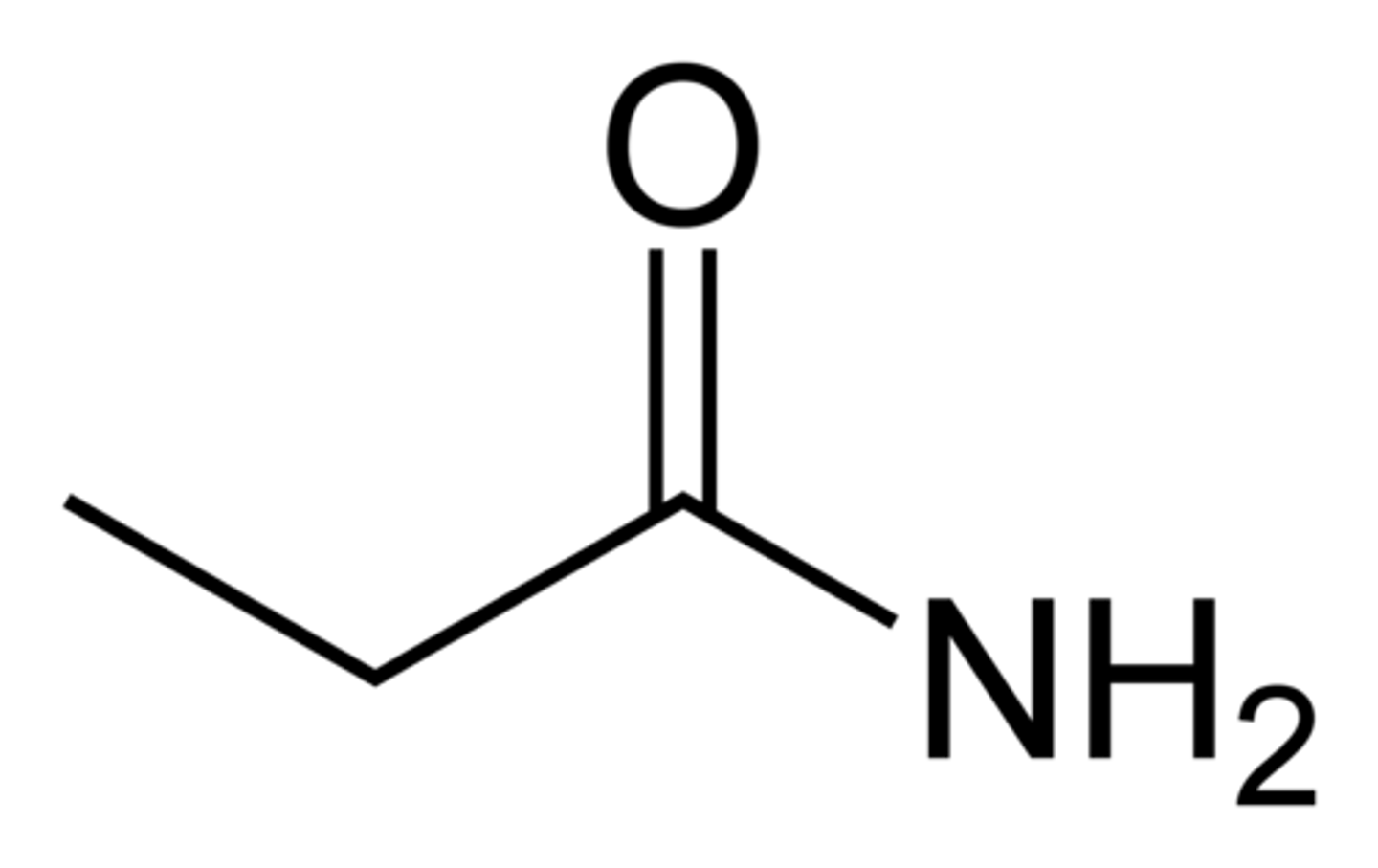
anhydrides
carboxylic acid derivative
forms when two carboxylic acid molecules combine and one water molecule is removed
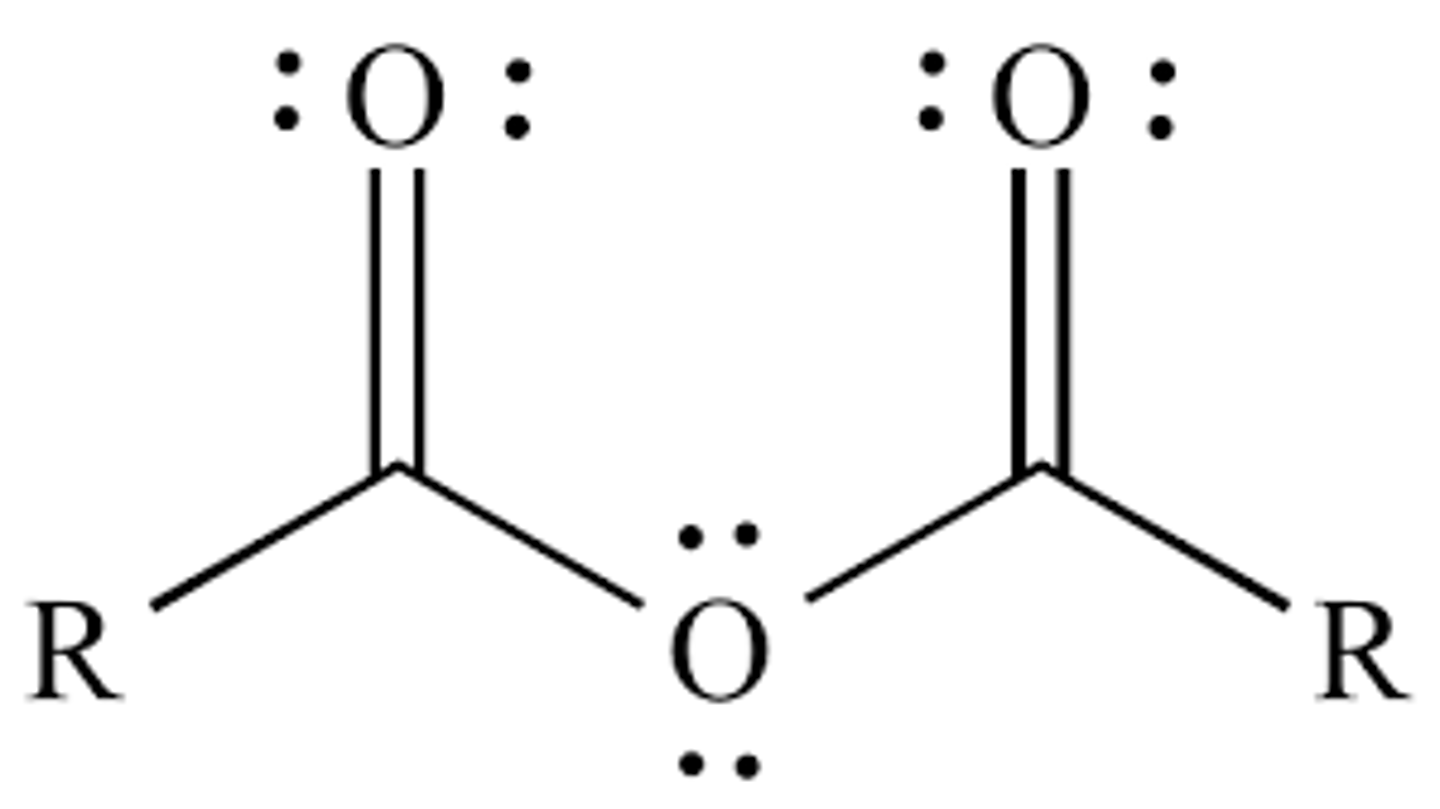
many anhydrides are ________, which may result from
cyclic
which may result from the intramolecular dehydration of dicarboxylic acid
how to name anhydrides
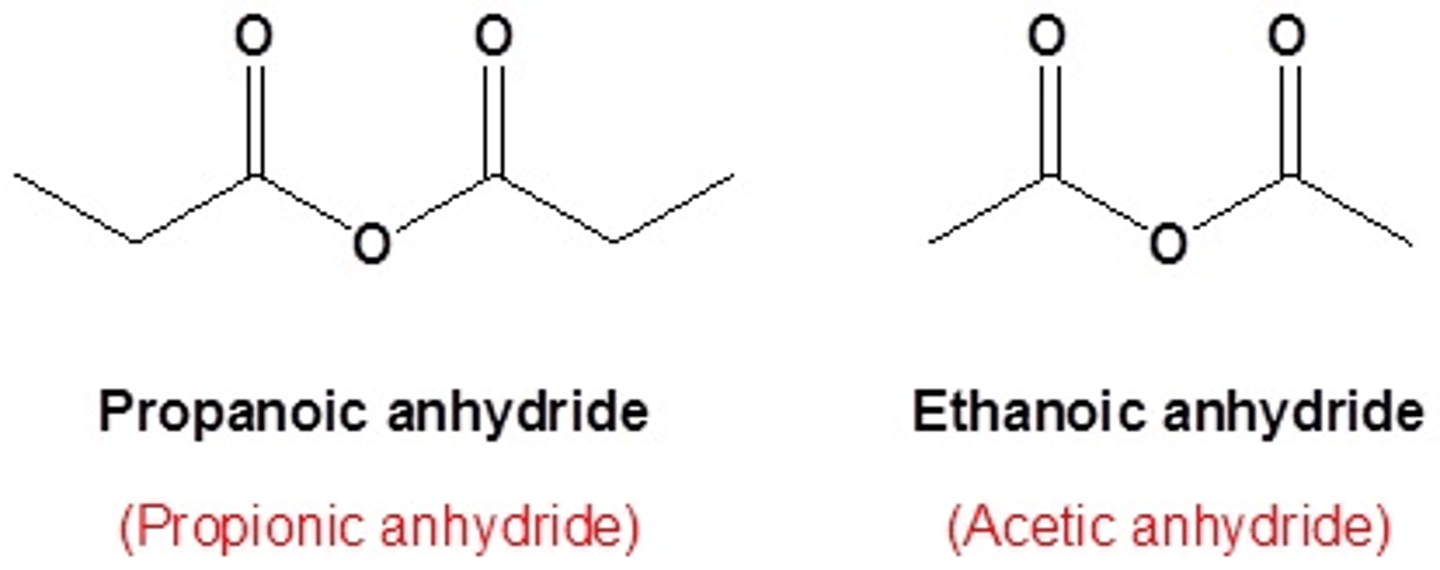
- if the anhydride is formed from only one TYPE of carboxylic acid, then take the carboxylic acid name (-oic acid) and drop acid, it is now -oic anhydride
ex: ethanoic anhydride
-if the anhydride is formed from two types of carboxylic acids (aka NOT symmetrical) both carboxylic acids are named (without the suffix acid) before anhydride is added to the name
ex: ethanoic propanoic anhydride
name this anhydride on other side
an- as a prefix generally means
not
so anhydride means without water, this is how you should remember that a water is removed during anhydride formation
in nomenclature,
use the suffix if
use the prefix if
suffix for the sub that is highest priority
prefix for all other subs
substituent priority list for only the fxnl groups on the MCAT
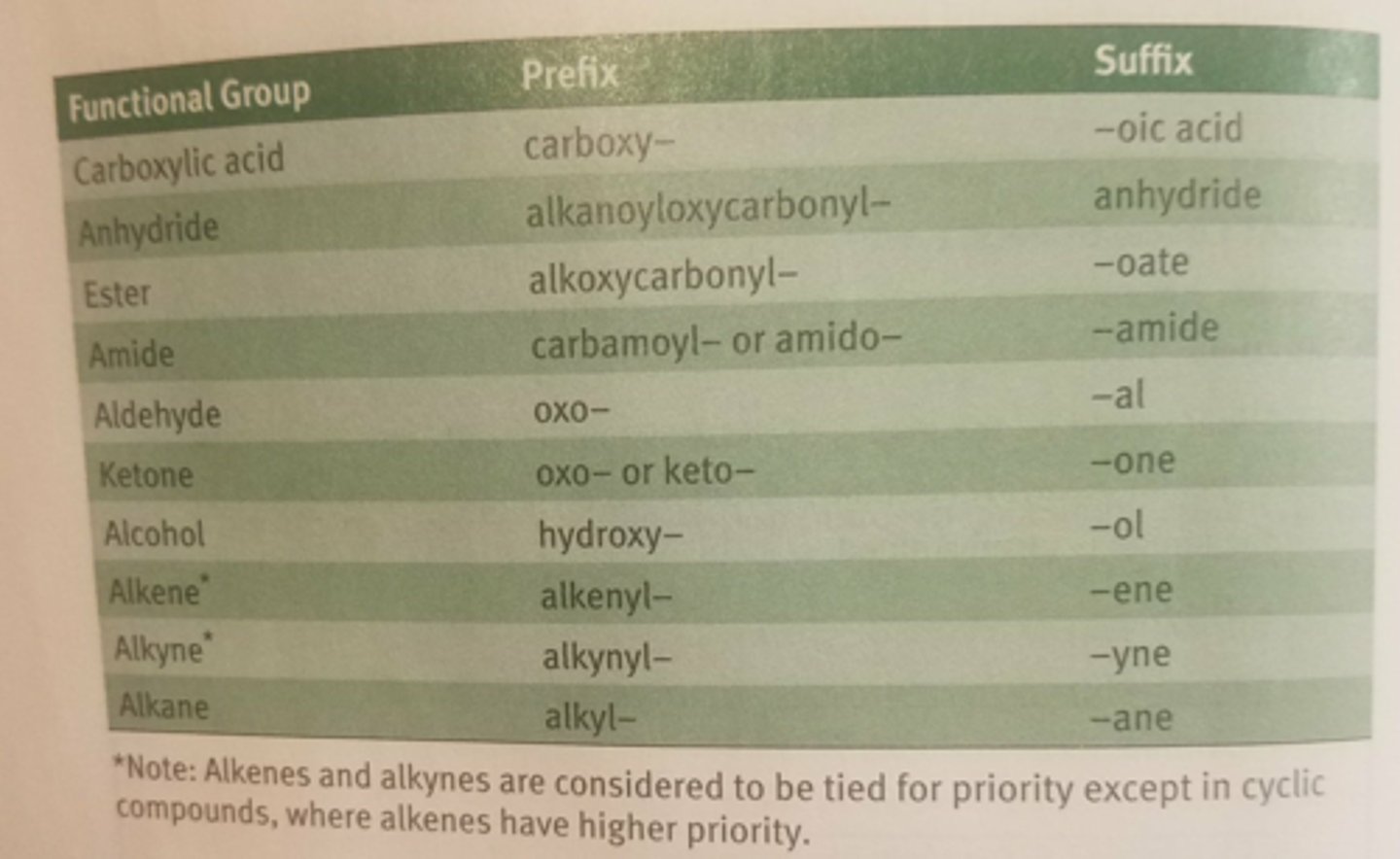
never miss easy points by quickly answering the wrong abc order
never do it
acetic anhydride is a common name for
ethanoic anhydride
methyl formate is a common name for
methyl methanoate
what common name prefix suggests aldehydes and carboxylic acids with only one carbon
form-