Ch.4 Functional Anatomy of Bacteria
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Spherical “berries”
Coccus
Rod-shaped; “little staffs”
Bacillus
What are the 4 types of basic shapes of prokaryotes?
Coccus, bacillus, coccobacillus, spiral
What are the 3 types of spiral prokaryotic shapes?
Vibrio, Spirillum, Spirochete
Spiral; curved rods
Vibrio
Spiral; rigid corkscrew
Spirillum
Spiral; flexible corkscrew
Spirochete
What does prokaryotic cell arrangements depend on?
Plane of division
With bacilli, how many planes of division are possible?
1
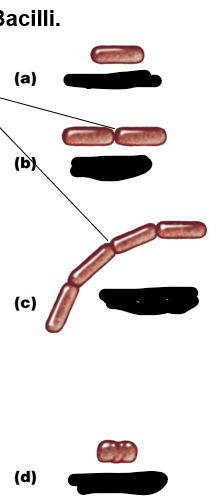
From A to D
Bacillus, diplobacilli, streptobacilli, coccobacillus
With cocci, how many planes of division are possible?
Multiple
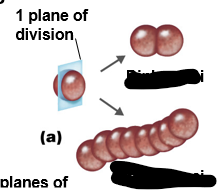
Diplococci; streptococci
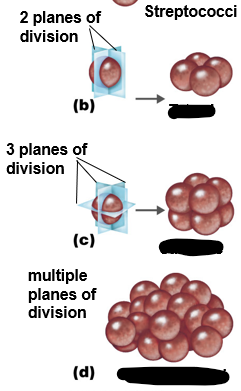
B to D
Tetrad; sarcinae; staphylococci
“Sugar coat” outside of cell wall; thick, sticky polymer made of polysaccharides
Glycocalyx
Two main roles of capsules
Prevent phagocytosis, formation of biofilm
Neatly organized and firmly attached glycocalyx
Capsule
Unorganized and loosely attached glycocalyx
Slime layer
Long filaments, propel bacteria. Not membrane bound. Made of flagellin. Made of a basal body, hook, and filament
Flagella
Can allow us to distinguish between serovars (variations within a species) of gram-negative bacteria
H antigen (flagellar protein)
The name for cells with no flagella
atrichous
The name for when flagella all over cell; “Perimeter”
Peritrichous
When flagella at one or both ends of the cell
Polar
A polar cell with a single flagellum at one pole
Monotrichous
A polar cell when a tuft of flagella is at one pole
Lophotrichous
A polar cell when flagella at both poles
Amphitrichous
How does the flagella move?
Rotation of basal body; runs and tumbles
What are the two types of stimulus for flagella motility?
Chemotaxis and phototaxis
Endoflagella; in spirochetes; made of flagellin; bundles of fibrils that spiral around the cell
Axial filaments
Made up of pilin, allow attachment to other bacteria (biofilm formation)
Fimbriae
Made of pilin, twitching motility (grappling hook model); conjugation from one bacteria (F+) connects to receptors on another bacteria (F-)
Pili (conjugation pili)
What are the two disaccharides peptidoglycan is a polymer of?
NAG & NAM
Alternating NAM and NAG molecules are linked in _____ to form carbohydrate backbone
Rows
Adjacent rows of NAM/NAG are linked by polypeptides form what?
Tetrapeptide and cross-bridge amino acids
Gram+ cell wall contain what? Negatively charged molecules
Teichoic acids (alcohol + phosphate)
Strong negative charge, protection from host defenses, susceptible to breakage, contains porins, outer leaflet contains lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Gram negative outer membrane
What does the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) consist of?
Lipid A, Core polysaccharide, O polysaccharide
Endotoxin released when the cell bursts
Lipid A
Structural stability part of LPS
core polysaccharide
part of LPS; Antigen to distinguish species/strains
O polysaccharide
Very small bacteria, no cell walls. Their plasma membrane has sterols
Mycoplasma (only plasma membrane)
Mycolic (waxy) acid bound to peptidoglycan
Acid-fast bacteria cell walls (mycobacteria)
How does lysozyme affect gram positive cells?
Digests outer cell wall
How does lysozyme affect gram negative cells?
add chemical to disrupt outer membrane then lysozyme can digest cell wall
After lysozyme does its job, what could happen to both types of cells?
Osmotic lysis (burst in water)
What inhibits peptide cross bridges in peptidoglycan?
penicillin
The 3 types of movement of material that does not require energy/goes down/with a [ ] gradient?
simple diffusion (O2, CO2), facilitated diffusion (glucose), osmosis
the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of lower water concentration
Osmosis
Movement of material that goes against [ ] gradient/requires energy?
Active transport, group translocation
Substrate is chemically altered during transport across the membrane, can’t return across the membrane
Group translocation
What is the size of the prokaryotic ribosome?
70S (50S + 30S subunits)
Reserve substances; used as energy reserves
Inclusions
inclusions of iron oxide- act like magnets (may help bacteria orient themselves
Magnetosomes
Dormant, highly durable dehydrated cells; only in bacillus and clostridium species
Endospores
Endospore formation induced by scarcity of key nutrient (starvation)
Sporulation
Return to vegeatative state; triggered by damage to endospore coat
Germination
In eukaryotes, flagella and cilia are made of…
microtubules
in eukaryotes, flagella and cilia are anchored to cell by _________ _________
Basal body
in eukaryotes, flagella and cilia movement is controlled by ________ ___________
motor proteins
Eukaryotic flagella move in what kind of motion
Wave-like manner
How does eukaryotic cilia move?
Power & recovery stroke
Generates forceful movement of water
Power stroke
Return cilia to original position
Recovery stroke
some epithelial cells (respiratory tract, uterine tubes) → move fluids and mucus through tubes (remove microbes)
Motile cilia
Eukaryotic cell wall made of what?
cellulose and chitin
“(cell eating”) pseudopods extend and engulf particles
Phagocytosis
(“cell drinking”) membrane folds inward, bringing in fluid and dissolved substances
Pinocytosis
Movement of cytoplasm throughout cells
Cytoplasmic streaming
eukaryotic ribosome size
80s