Lecture #2 | Tree of Life
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Common descent
Darwin hypothesis that all life, living or extinct has descended without interruptions from one or a few original forms
key goal is to construct “tree of life”
Age of single-celled ancestor
Lived around 3-4 billion years ago
all extant lineages are the same age
Sources of data for phylogenies
Fossils
Issue: habitat vary, complicating fossilization. Some organisms fossilize worse than others
Living organisms
Where most evolutionary past has arose from. We deduce the past from the present
Ancestors and ancestral traits are implicit to phylogenies
Uses for phylogenies
Infer evolutionary relationships
Reconstruct evolutionary origins and divergence of key traits
Trace human origins and migrations
Forensics and criminology
Deduce the sources and carriers of diseases
What does this tree show?
HIV 1 and 2 arose from SIV that infected sooty mangabeys and chimpanzees
jumped twice to humans
Phylogenetic trees
Branching diagram that represents a hypothesis about the evolutionary history of a group of organisms
Root
Point that represents ancestral lineage
Branch tips
Represents the most recent descendants of that ancestor
Node
Represents a common ancestor and the divergence of two evolutionary lineages from that common ancestor (speciation)
Common ancestor
An ancestral organism that gave rise to two or more descendent lineages
MRCA
Most recent common ancestor
Clade/monophyletic group
Common ancestor and all descendants
Paraphyletic
Ancestor and some (but not all descendants)
Polyphyletic
Distantly related species but not most recent common ancestor
Sister taxa
Groups that share a common ancestor that is no shared by an other group
Taxon
A systematic unit or group to which organisms are assigned
ex: species
Characters
The variable features of an organism: multiple character states are used to infer phylogenies
can be phenotypes or genotypes
Phenotypes
Morphological, physiological, behavioral, biochemical
Genotypes
Specific set of genes/DNA sequences possessed by an individual
Constructing a phylogenetic tree
Group species according to character states, can be used to infer common descent
Calculate similarity by number of shared character states
Useful traits in a phylogeny
Traits shared by some, but not all lineages and are derived from a common ancestor
phylogenies reconstruct evolutionary history, not similarity
Certainty of phylogenies
Every tree built is a hypothesis, proposing a particular evolutionary sequence of events
we can usually not know with 100% certainty what the true history is
can use different methods to find the tree that fits the data the best
Maximum Parsimony
The best phylogenetic hypothesis is the one that postulates the fewest evolutionary changes
used in the absence of other evidence
fewest steps
5 General patterns of morphological evolution
Most features of organisms have been modified from preexisting features
Different traits/characters evolve at different rates
Evolution is often gradual
Homoplasy is common
Many lineages contain adaptive radiations
Homologous characters
Similar physical features in different organisms that share a common ancestor, but the features serve different functions
related organisms have these characters
most complex structures do not evolve de novo (from nothings), but are modified from ancestral traits
Tetrapod forelimb
An ancient, lobe fin that is a homologous structures that has been modified for many new uses including swimming, flying, running, digging, and manual manipulation
Mosaic evolution
Species dont evolve as a whole
individual traits can evolve in a piecemeal fashion and at different rates
Conserved characters
Traits or structures that change little over evolutionary time
Evolution is often graudual
Evolutionary gradations are often observed
pattern of incremental differenced between species are often observed

Homoplasy
Similarity in a specific trait/character without any shared ancestry
ex: while birds and pterosaurs both have wings, they independently evolved in each species
is the result of convergent evolution
Convergence
Superficially similar features that have indecently evolved in separate lineages
ex: vertebrate vs. invertebrate eyes
both have lens and retina, but are otherwise profoundly different
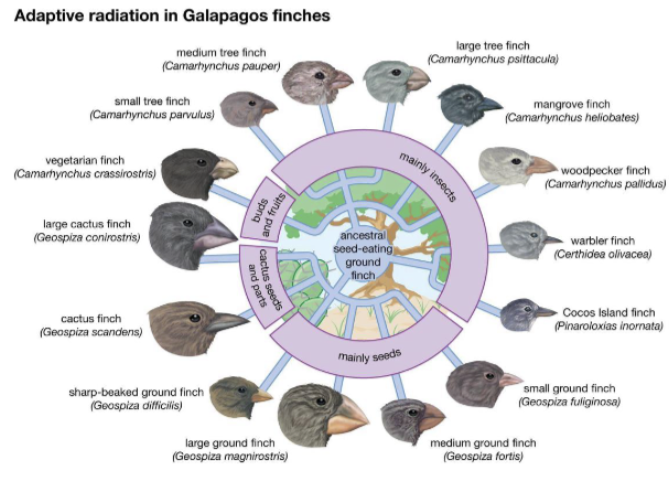
Adaptive radiation
Periods of rapid formation of new species whose adaptations allow them to fill different ecological roles
radiations often occur when a species invades open and diverse habitats (islands)
ex: Galapagos finches