2025 term three hpe bone types and structure
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
long bones (description, purpose, example)
longer than they are wide
have long shaft + two heads
all bones of the limbs are long bones
act as a lever and helps support the weight of the body
eg. humerus, radius, ulna, metacarpals (in fingers and toes), femur
short bones (description, purpose, example)
small + compact
somewhat cube-shaped
found in confined spaces
absorb force
designed for strength and stability
these bones support the wrist + ankle to keep the region stable + compact
eg. carpals, tarsals
flat bones (description, purpose, example)
thin and flat
often slightly curved
protect underlying organs
provide broad dense surfaces for muscle attachment
eg. cranium, ribs, scapula, pelvis
irregular bones (description, purpose, example)
have unique shapes that cannot be classified as long, short or flat
have varied shapes, many surfaces for attachment of muscles
eg. vertebrae
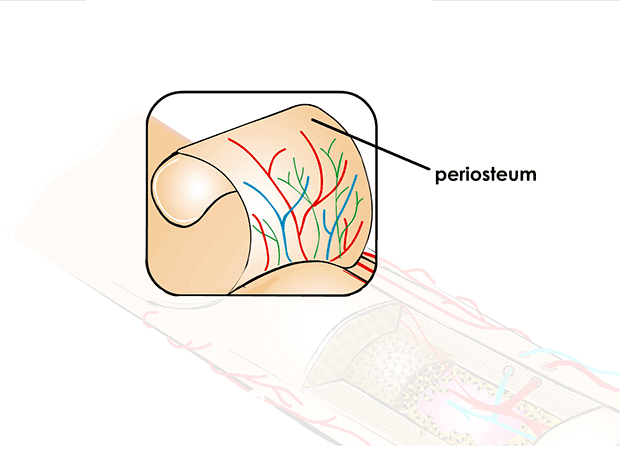
periosteum
thin, dense membrane on the surface of the bone contains nerves and blood vessels that help nourish bone tissue
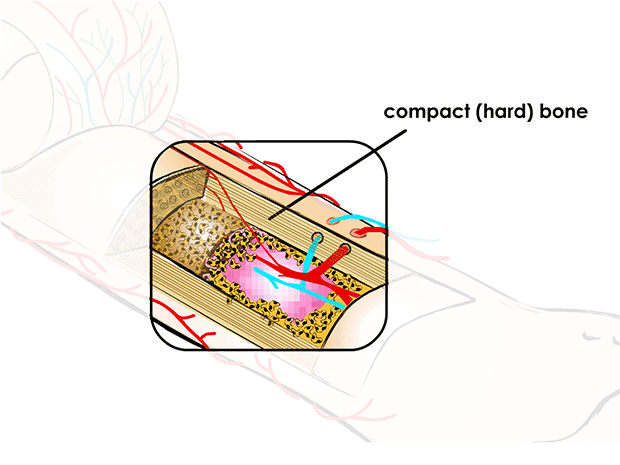
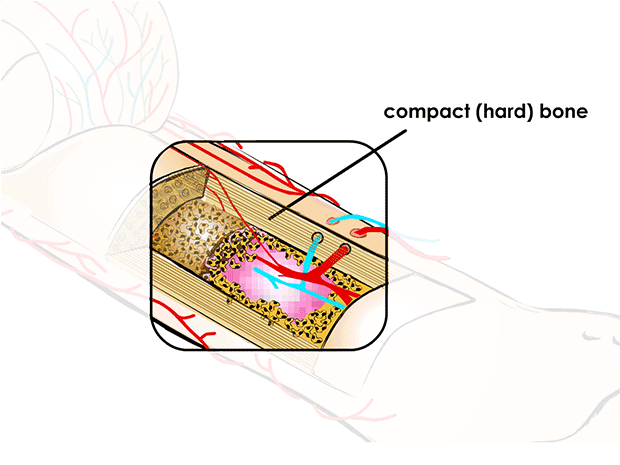
compact (hard) bone
solid, hard outside part that looks like ivory and is extremely strong
holes and channels run through it, carrying blood vessels and nerves
compact bone provides strength, protection, structure and mineral storage, while supporting movement
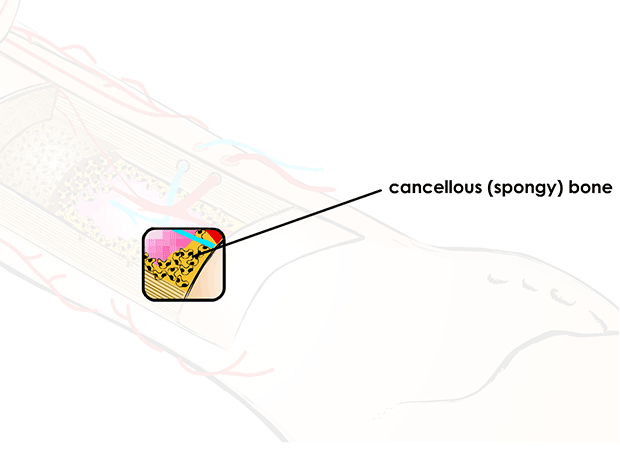
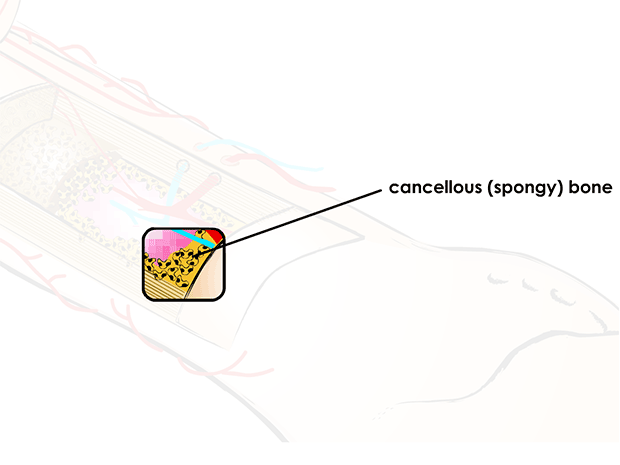
cancellous (spongy) bone
which looks like a sponge, is inside compact bone
made up of a mesh-like network of tiny pieces of bone called trabeculae
where bone marrow is found
lightweight support, shock absorption, and blood cell production
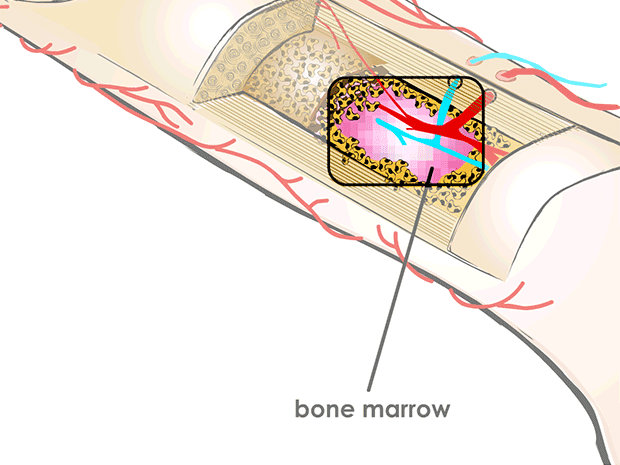
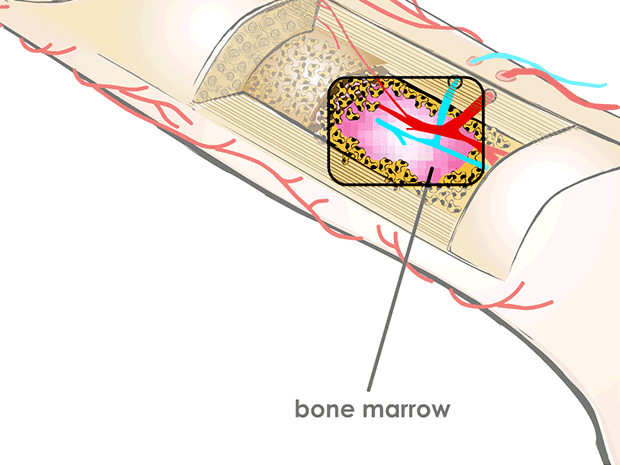
bone marrow
soft bone marrow, which is found inside many bones, makes most of the body's red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets