AP Psych Units 0-5
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All the vocab from units 0 to 5 in the newest edition of the Meyer's Psychology textbook (4th edition)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
The scientific approach
using observation and experimentation to test ideas / theories
“Scientific Attitude” (3 components)
Curiosity: does it work?
skepticism: what do you mean?
humility: “that was unexpected", lets explore further”
curiosity (1/3 scientific attitude)
does it work?
skepticism (2/3 scientific attitude)
what do you mean?
humility (3/3 scientific attitude)
that was unexpected, lets explore further
hindsight bias
the tendency to believe the event was predictable after it has occurred.
overconfidence
an excessive belief in one's abilities or knowledge, often leading to errors in judgment.
perceiving order in random events
eagerness to find “pattern” in random events
3 road blocks to critical thinking
hindsight bias
overconfidence
perceiving order in random events
critical thinking
not immediately agreeing w''/arguments and conclusions.
The objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgment. It involves thinking reflectively and reasoning systematically.
The scientific method
self correcting process for evaluating ideas with observation - analysis `
peer reviewers evaluate:
theory
originality
accuracy
theory
explanation of the world using set of principles, with organized observations and evidence.
hypothesis
testable prediction
operational definition
carefdully worded statements of the exact procedure
to eliminate bias
allow for easy replication
case study
the examination of one person or group
naturalistic observation
observing and recording behaviors without any manipulation of events
describes behaviors, does not explain it
survey
questioning a random sample of a group to obtain self-reported behaviors
social desirability bias
participants answer in a way they believe they think is desired by the administrator
self-report bias
participants do not accurately report their own behaviors
sampling bias
flawed sampling that produces unrepresentative results
random sample
everyone has an equal chance of being surveyed to ensure representative results.
convenience sampling
collecting samples form areadily/easily available group
population
all those in a group being studied, from whhich random samples are drawn
illusory correlation
perceiving a relationship where none exists
regression towards the mean
the tendency for extreme/unusual scenes scores or events to fall back towrad the average after
experimenter bias
researchers unintentionally influencing results to confirm their own beliefs
random assignment
assigning participants to a treatment group randomly
expiremental group
experiences treatment
control group
does not experience treatment, has ‘placebo’ typically
single blind procedure
either participant or staff are ignorant ab treatment
double b lind procedure
both the staff and participants are ignorant about treatments
placebo effect
results caused by expectations alone
independent variable
factor being manipulated
dependent variables
the outcome measured
confounding variable
factor other than studied-factor that might influence results (uncontrollable)
validity
extent to which the test/experiment measures or predicts what it is supposed to.
predicting everyday behavior
experiment where lab environment is a simplified reality
to test theoretical principles
confederates
pretend ‘fellow participants’ that participate in experiments to minimize social desirability bias
Todays ethics codes
obtain participants informed consent
protect from greater-than-usual harm and discomfort
keep individuals information confidential
fully debrief patients
informed consent
gives potential particpants enoigh information about a study to enable them to chose if they want to participate
deberiefing
post-experimental explanation of a study, including its purpose and any deceptions to participants
descriptive stats
numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups
includes masures of central tendency
measure of variation
inferential statistics
taking received information about a population and making an inference on the larger population
meta analysis
statistics procedure for analyzing the results of multiple studies to reach an overall conclusion
mode
most frequent number
mean
total/n
median
center score of a distribution
percentile rank
% of scores lower than given score1
skewed distribution
scores missing symmetry around its average value
always note measure of central tendency: if theres a mean, is there an outlier?
range
max - min
standard deviation
average distance of each score from the mean
normal curve
bell shaped curve
most scores fall near the mean
68 - 95 - 99.7% rule
mean, median, and mode all the same number
natural selection
nature selects traits that best enable survival + reproduction
eugenics
racist evolution-theory
humans selectively breed to promote certain characteristics
behavior genetics
the study of relative power/limits of genetics=environments influences on behavior
Evolutionary psychology
what makes us so alike?
darwinism - survival of the fittest
mutation
random errors in gene replication
fitness
ability to surve and reproduce
behavior genetics
predicting individual differences
humans share: biological heritage + social behaviors
environment
every non-genetic influence
heredity
the genetic transfer of characteristics
heritability
how much of the variance seen in a population can be attributed to genetic variation instead of the environment
monozygotic twins
identical twins
1/3 do not share placenta
same genes but not the same # of copies
why one is more succeptibel to cancer
dizygotic twins
fraternal twins
biologically siblings
adaptability
genes and experience interact
interaction
interplay that occurs when effect of one factor depnds on another
epigenetics
triggers that swtich gees on and off
environment can influence genetic expression
epigenetic marks
self-regulating system for genes
attached to part of dna
can instruct cell to ignore any gene in dna
will be ‘turned off’
CNS (Central nervous System)
brain and spinal cor
PNS (Peripheral Nervous System)
nerves, pathway for CNS decisions
afferent neurons
SENSORY neurons
carry info INTO body from tissue/sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord (CNS)
efferent neurons
MOTOR neurons
carry info OUT from brain and CNS to the muscles and glands
Interneurons
within the brain and spincla cord (CNS)
process info between the afferent and efferent neurons
Somatic Nervous system
PNS (1/2)
controls the bodys skeletal muscles
sensory input
motor output
autonomic system
PNS (1/2)
controls glands and muscles
has sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
adrenaline boost
“fight or flight”
parasympathetic nervous system
calms you down
rest and digest
reflexes
automatic response to a sensory stimulus
simple
ex: knee-jerk
spinal pathway
dendrites
neurons that receive the message
axon
passes messages to toher neurons
myelin sheath
encases axon
speed
glial cells
support, nourish, and protect neurons
resting potential
fluid otuside the axon membrane is mostly +,
fluid inside the axon membrane is mostly -`
action potential
depolarization: when neuron fires, starting a chain reaction
excitatory neurons
pushing accelerator on neurons
inhibitory neurons
pushing the brake on neuron
treshold
level of stimulation requried to trigger a neural impulse
refractory period
a pause (rest) that occurs after a neuron fires
All-or-none response
neuron either fires or does not
intensity is demonstrated by NUMBER of neurons that fire
synapse
how neurons communicate
gap between axon tip and dendrites
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that pass synaptic gap to send messages
reuptake
neurotransmitter reabsorption by the sending neuron
some antidepressants are made to block the re-uptake of mood enhancing neurotransmitters
neurotransmitters (CHART)
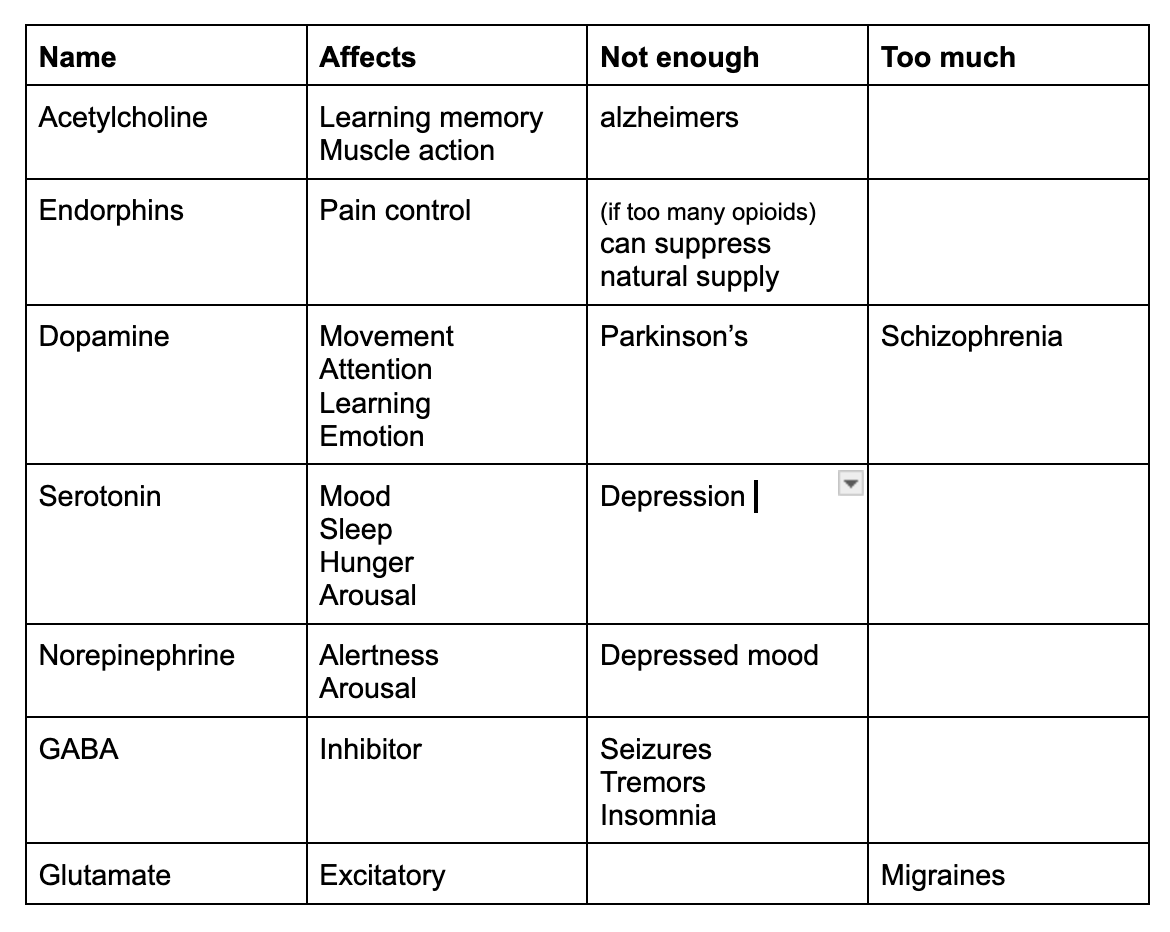
endorphins
bodys natural opioids
agonist
drugs
molecule that increases neurotransmitters action
antagonist
drug
drug molecule that inhibits/blocks neurotransmitters actions
hormones
chemical messengers manufacturedbby endocrine glands
pituitary gland
in core of brain, controlled by hypothalamus
oxytocin
enabels orgasm, labor contractions, milk growth, social support