AP Psychology Cognition, AP Psych Cognition
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
1
New cards
memory
the persistence of learning over time through the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information
2
New cards
recall
a measure of memory in which the person must retrieve information learned earlier, as on a fill-in-the-blank test
3
New cards
recognition
a measure of memory in which the person identifies items previously learned, as on a multiple-choice test
4
New cards
relearning
a measure of memory that assesses the amount of time saved when learning material again
5
New cards
encoding
the process of getting information into the memory system— for example, by extracting meaning
6
New cards
storage
the process of retaining encoded information over time
7
New cards
retrieval
the process of getting information out of memory storage
8
New cards
parallel processing
processing many aspects of a problem simultaneously; the brain's natural mode of information processing for many functions
9
New cards
sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
10
New cards
short-term memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly, such as digits of a phone number while calling, before the information is stored or forgotten
11
New cards
long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system. Includes knowledge, skills, and experiences
12
New cards
working memory
a newer understanding of short-term memory that adds conscious, active processing of incoming auditory and visual information, and of information retrieved from long-term memory
13
New cards
explicit memory
retention of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare."
14
New cards
effortful processing
encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
15
New cards
automatic processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time, and frequency, and of well-learned information, such as word meanings
16
New cards
implicit memory
retention of learned skills or classically conditioned associations independent of conscious recollection
17
New cards
iconic memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a picture-image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second
18
New cards
echoic memory
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli; if attention is elsewhere, sounds and words can still be recalled within 3 or 4 seconds
19
New cards
chunking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically
20
New cards
mnemonics
memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices
21
New cards
spacing effect
the tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice
22
New cards
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading, information
23
New cards
shallow processing
encoding on a basic level, based on the structure or appearance of words
24
New cards
deep processing
encoding semantically, based on the meaning of the words; tends to yield the best retention
25
New cards
semantic memory
explicit memory of facts and general knowledge; one of our two conscious memory systems
26
New cards
episodic memory
explicit memory of personally experienced events; one of our two conscious memory systems
27
New cards
hippocampus
a neural center located in the limbic system; helps process for storage explicit (conscious) memories of facts and events
28
New cards
memory consolidation
the neural storage of a long-term memory
29
New cards
flashbulb memory
a clear, sustained memory of an emotionally significant moment or event
30
New cards
long-term potentiation
an increase in a cell's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation; a neural basis for learning and memory
31
New cards
priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of certain associations, thus predisposing one's perception, memory, or response
32
New cards
encoding specificity principle
the idea that cues and contexts specific to a particular memory will be most effective in helping us recall it
33
New cards
mood-congruent memory
the tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one's current good or bad mood
34
New cards
serial position effect
our tendency to recall best the last (recency effect) and first (primacy effect) items in a list
35
New cards
anterograde amnesia
an inability to form new memories
36
New cards
retrograde amnesia
an inability to retrieve information from one's past
37
New cards
proactive interference
the forward-acting disruptive effect of older learning on the recall of new information
38
New cards
retroactive interference
the backward-acting disruptive effect of newer learning on the recall of old information
39
New cards
repression
in psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories
40
New cards
reconsolidation
a process in which previously stored memories, when retrieved, are potentially altered before being stored again
41
New cards
misinformation effect
occurs when misleading information has distorted one's memory of an event
42
New cards
source amnesia
faulty memory for how, when, or where information was learned or imagined
43
New cards
deja vu
that eerie sense that "I've experienced this before." Cues from the current situation may unconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier experience
44
New cards
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
45
New cards
concept
a mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
46
New cards
prototype
a mental image or best example of a category
47
New cards
creativity
the ability to produce new and valuable ideas
48
New cards
convergent thinking
narrowing the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution
49
New cards
divergent thinking
expanding the number of possible problem solutions; creative thinking that diverges in different directions
50
New cards
algorithm
a methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem
51
New cards
heuristic
a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently
52
New cards
insight
a sudden realization of a problem's solution; contrasts with strategy-based solutions
53
New cards
confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
54
New cards
fixation
(1) in cognition, the inability to see a problem from a new perspective; an obstacle to problem solving. (2) in personality theory, according to Freud, a lingering focus of pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier psychosexual stage, in which conflicts were unresolved
55
New cards
mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past
56
New cards
intuition
an effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought, as contrasted with explicit, conscious reasoning
57
New cards
representativeness heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes; may lead us to ignore other relevant information
58
New cards
availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind (perhaps because of their vividness), we presume such events are common
59
New cards
overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct—to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments
60
New cards
belief perseverance
clinging to one's initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited
61
New cards
framing
the way an issue is posed; how an issue is worded can significantly affect decisions and judgments
62
New cards
language
our spoken, written, or signed words and the ways we combine them to communicate meaning
63
New cards
phoneme
in a language, the smallest distinctive sound unit
64
New cards
morpheme
in a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning; may be a word or a part of a word
65
New cards
grammar
in a language, a system of rules that enables us to communicate with and understand others
66
New cards
babbling stage
beginning around 4 months, the stage of speech development in which an infant spontaneously utters various sounds at first unrelated to the household language
67
New cards
one-word stage
the stage in speech development, from about age 1 to 2, during which a child speaks mostly in single words
68
New cards
two-word stage
beginning about age 2, the stage in speech development during which a child speaks mostly in two-word statements
69
New cards
telegraphic speech
early speech stage in which a child speaks like a telegram—"go car"—using mostly nouns and verbs
70
New cards
aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage either to Broca's area or to Wernicke's area
71
New cards
Broca's area
helps control language expression—an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech
72
New cards
Wernicke's area
a brain area involved in language comprehension and expression; usually in the left temporal lobe
73
New cards
linguistic determinism
the strong form of Whorf's hypothesis—that language controls the way we think and interpret the world around us
74
New cards
linguistic influence
the idea that language affects thought
75
New cards
cognition
The mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating.

76
New cards
concept
A mental grouping of similar objects, events, idea, or people.

77
New cards
prototype
a mental image or best example of a category. Matching new items to a prototype provides a quick and easy method for sorting items into categories (as when comparing feathered creatures to a prototypical bird, such as a robin).

78
New cards
algorithm
a methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem. Contrasts with the usually speedier—but also more error-prone—use of heuristics.

79
New cards
heuristic
a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; usually speedier but also more error prone than an algorithm.
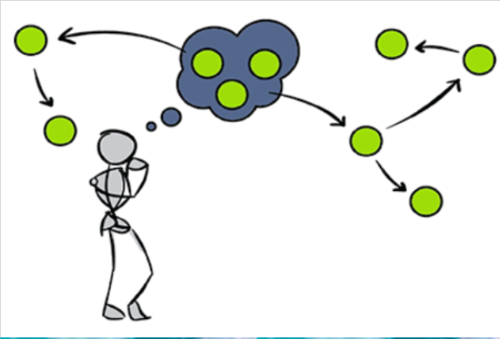
80
New cards
insight
a sudden realization of a problem's solution; contrasts with strategy-based solutions.

81
New cards
creativity
the ability to produce new and valuable ideas.

82
New cards
convergent thinking
narrowing the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution.
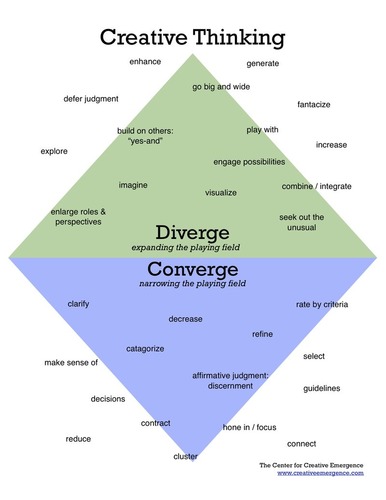
83
New cards
divergent thinking
expanding the number of possible problem solutions; creative thinking that diverges in different directions.
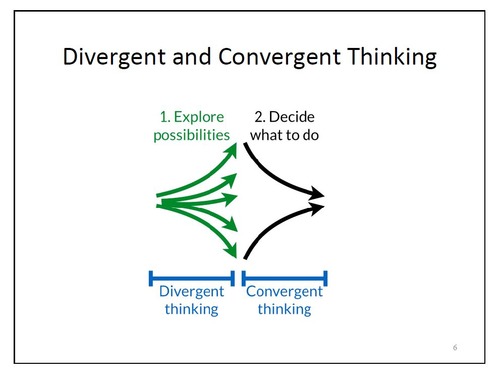
84
New cards
confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence.

85
New cards
fixation
in cognition, the inability to see a problem from a new perspective; an obstacle to problem solving.
86
New cards
mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past.

87
New cards
intuition
an effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought, as contrasted with explicit, conscious reasoning.

88
New cards
functional fixedness
The tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions.
89
New cards
representativeness heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes; may lead us to ignore other relevant information.

90
New cards
availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind (perhaps because of their vividness), we presume such events are common.

91
New cards
overconfidence
the tendency to be more confident than correct—to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.

92
New cards
belief perseverance
clinging to one's initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited.

93
New cards
framing
the way an issue is posed; how an issue is worded can significantly affect decisions and judgments.

94
New cards
language
Our spoken, written, or signed words and the ways we combine them to communicate meaning.

95
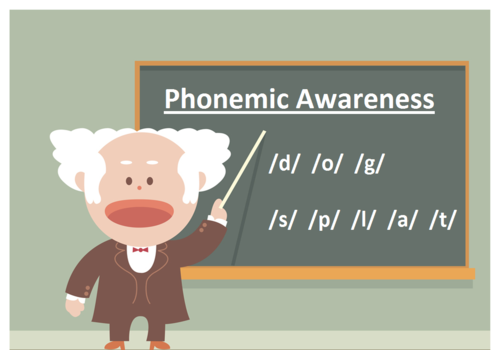
New cards
phoneme
In language, the smallest distinctive sound unit.
96
New cards
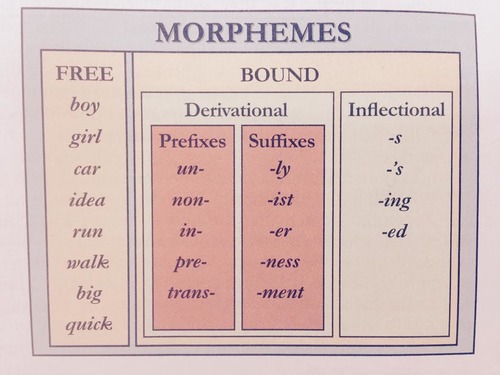
morpheme
In a language, the smallest unit that carries meaning; may be a word or part of a word.
97
New cards
grammar
in a language, a system of rules that enables us to communicate with and understand others. Semantics is the language's set of rules for deriving meaning from sounds, and syntax is its set of rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences.

98
New cards
semantics
The set of rules by which we derive meaning from morphed, words, and sentences in a given language; the study of meaning.

99
New cards
syntax
The rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences in a given language.

100
New cards
babbling stage
Beginning at about 4 months, the stage of Speech development in which the infant spontaneously utters various sounds at first unrelated to the household language.
