RESEARCH METHODS
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1 AOS 3, SAC 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is the aim?
An outline of the investigation that is one concise sentence.
What is a hypothesis?
A testable prediction, of two or more variables.
Prediction between events or characteristics.
How is a hypothesis reviewed?
Either rejected or supported, never proved!
What is a controlled variable
An experimental investigation to test the relationship between an independent variable and a dependant varinalem whilst controlling all other variables.
What is a variable?
Something that can change (‘vary’) in amount or type and is measurable
What is a controlled variable?
Variables other than the I.V which are kept constant to ensure the D.V changes solely from the I.V.
independent variable (IV) is
The variable that has it’s quantities manipulated in order to effect D.V
dependent variable (DV) is
The variable the researcher measures
Operationalising variables
Refers to specifying exactly how the variables will be manipulated or measured in a particular controlled experiment.
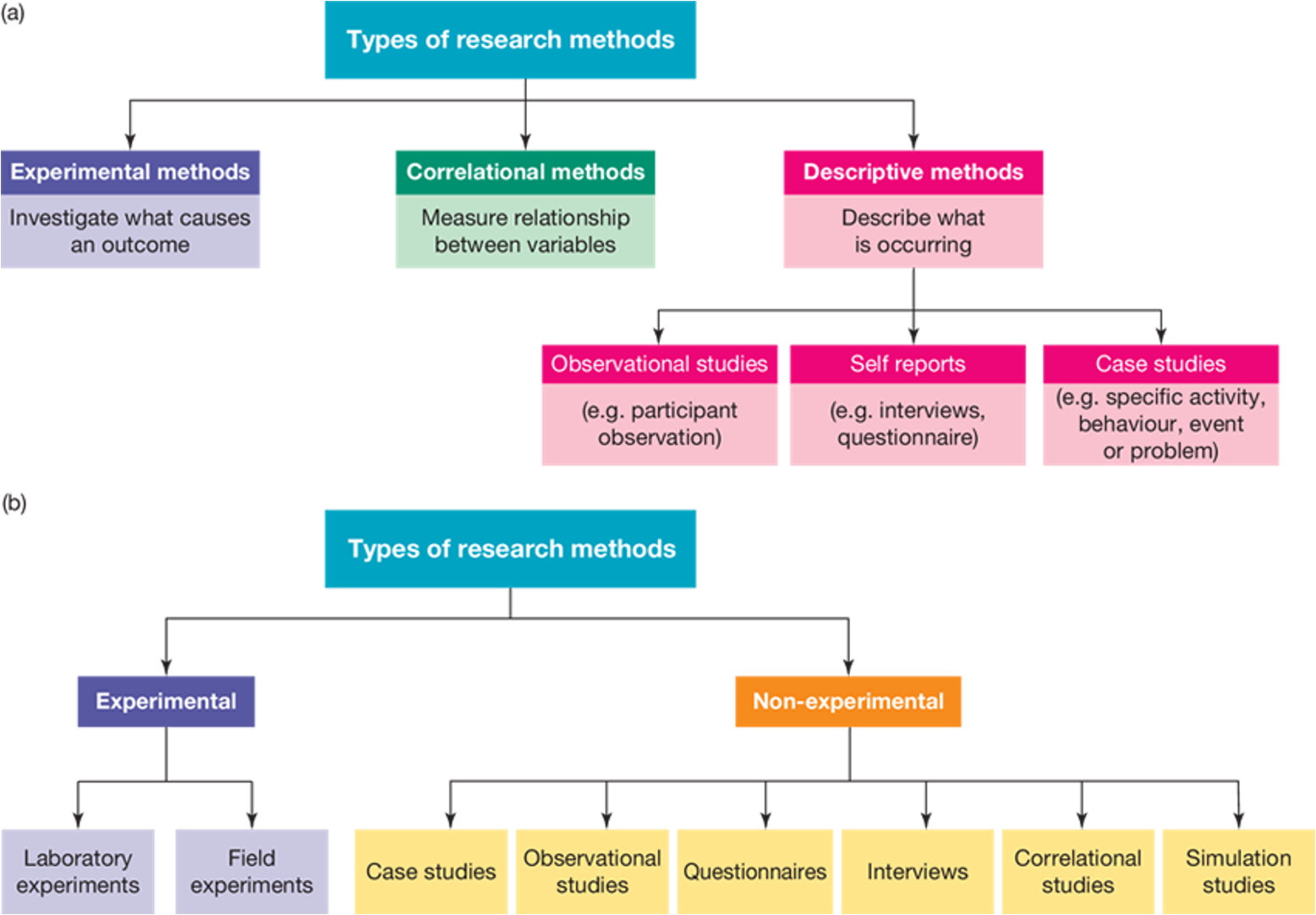
Lists the types of research methods
Experimental Methods
Correlational Methods
Descriptive Methods: observational studies, self reports, case studies
Experimental: laboratory experiments, field experiments
Non-experimental: case studies, observational studies, questionnaires, interviews, correlational studies, simulation studies
What is a correlational study?
Measures the relationship between variables with no manipulation from the researcher which includes controlling the setting.
List the types of descriptive methods
Observational studies
Self reports
Case studies
List the types of experimental methods
Laboratory experiments, Field experiments
List the types of non-experimental research methods
case studies, observational studies, questionaires, interviews, correlational studies, simulation studies.
What is a self-report?
A participant’s answers to questions presented by the researcher
What is an oberservational study?
Involves collection of data by carefully watching and recording behaviour as it occurs without any intervention or manipulation of the behaviour being observed.
What is a case study.
Is an intensive, in-depth investigation of some behaviour, activity, event or problem of interest in a single individual, group, organisation or situation. In psychology, the ‘case’ that is the subject of ‘study’ is usually a person.
What is cross-sectional method
A type of observational research method used to analyse data from a population at a specific point of time.
Variables are not manipulated the study,
What is a longitudinal study?
A research method that involves repeated observations of the same individuals over a long period of time
What is the population?
Refers to the entire group of research interest from which a sample is drawn.
What is the point of the population?
Researcher can aim to generalise (apply) results of investigation to the population.
What is the sample?
The subset or part of the population that is selected for research purposes
What is sampling
The process of selecting a part of the population.
What is random sampling?
Sampling technique that ensure every member of the population of research interest has equal chance of being selected as part of the sample.
What is stratified sampling?
Process of selecting a sample form the population comprised of variou subgroups so that each subgroup is represented,
what is convenience sampling?
Involves selecting a sample of individuals who are readily available.
Advantages of convenience sampling
Advantages: most time-effective and can be cost-effective
Disadvantages: The most likely to create an unrepresentative sample, therefore making it harder for researchers to generalise results to the population.
Stratified sampling advantages/disadvantage
Advantages:
Most likely to produce a representative sample.
Disadvantage:
Can be time consuming & expensive
be demanding for researcher to select most appropriate sample
Random sampling advantages/disadvantages
Advantages:
Sample generated can be more representative than convenience sampling.
Reduces experimenter bias in selecting participants.
Can make a fairly representative sample if the sample is large.
Disadvantage:
May be time consuming - to ensure every member of population has equal chance of being selected
May not create representative sample when sample is small.